CH 10 - Deep time
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what is uniformitarianism?
hutton’s idea that geological forces are at work in the present day are the same as those that operated in the past
relative age vs. numerical age
relative age - age of a feature with respect to another in a sequence
numerical age - age given in years
ways to determine relative ages
uniformitarianism
original horizontality
superposition
lateral continuity
cross-cutting relations
baked contacts
inclusions
index fossils
original horizontality
layers of sediment, when first deposited, are fairly horizontal. with this, it can be concluded that folding, tilting, and faulting of sedimentary beds occur after the beds were deposited
superposition
in a sequence of sedimentary rock layers, each layer must be younger than the one below.
lateral continuity
sediments generally accumulate in continuous sheets within a region.
cross-cutting relations
if one geologic feature cuts across another, the feature that has been cut through must be older.
baked contacts
an igneous intrusion “bakes” surrounding rocks, so the rock that has been baked must be older than the intrusion
inclusions
a rock containing an inclusion must be younger than the inclusion.
a conglomerate containing basalt, is younger than the basalt fragments
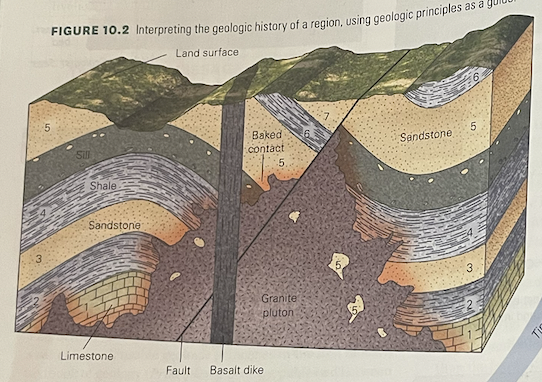
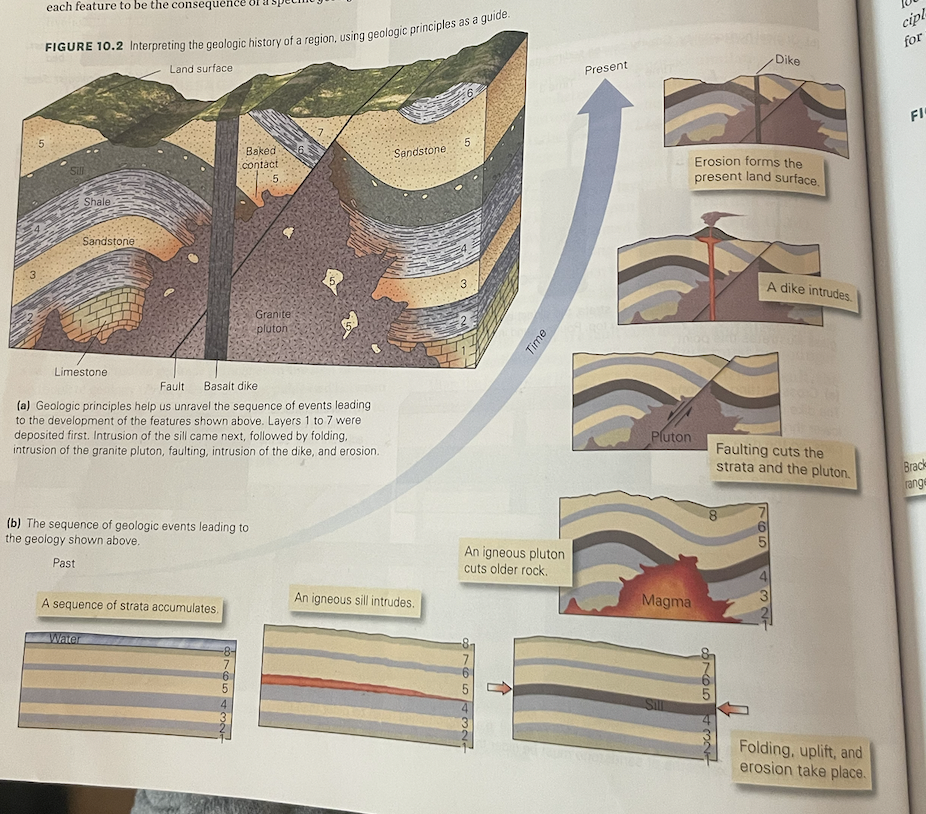
describe the sequence of events
index fossils
widespread fossils, but survived only for a short interval of geologic time. they can be used by geologists to associate strata with a specific time interval
what is an unconformity?
surface between two units that represents erosion - missing rock!
types of unconformities
angular unconformity
nonconformity
disconformity
angular unconformity
rocks below an angular unconformity were tilted or folded before the unconformity developed. the orientation of layers below an unconformity differs from those above
nonconformity
sedimentary rocks overlie much older igneous rocks or metamorphic rocks. these igneous or metamorphic rocks underwent cooling, uplift and erosion prior to becoming the basement rock on which sediments accumulated
disconformity
beds above and below the disconformity are parallel, but the contact between them represents an interruption in deposition (a hiatus)
EX: sequence of sedimentary rocks has been deposited beneath a shallow sea. sea level drops, exposing the units. during this time, NO new sediment accumulates and some of the old sediment gets eroded away. later, sea level rises and a new sequence of sediment accumulates over the old.
what occurrence represents the archean eon? the late proterozoic? the precambrian-cambrian boundary? paleozoic? triassic?
archean - simple bacteria
late proterozoic - complex invertebrates starting
precambrian-cambrian boundary - invertebrates with shells
paleozoic - more complex organisms
triassic - dinosaurs
what is the “cambrian explosion”?
diversification of organisms
what is an isotope
various versions of an element, which differ from one another because they have different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus, and therefore, different masses
unstable isotopes undergo radioactive decay which releases energy stored in nuclear bonds in the nucleus. some types of radioactive decay result in the explosion of fragments from the nucleus of an atom, which changes the atomic number and therefore element
what is half-life
how long it takes for a group of parent atoms to decay
parent atoms is an atom of a radioactive isotope that hasn’t decayed
isotopic dating technique
collect unweathered rocks for dating, since the chemical reactions that happen during weathering may lead to the loss of daughter atoms (the product of radioactive decay from a parent atom)
crush rocks to separate the appropriate minerals from the debris
extract parent and daughter atoms from minerals
once you have a sample of appropriate atoms, you pass them through a mass spectrometer, which counts the number atoms of specific isotopes separately
define the ratio of parent to daughter atoms in a minerals, and from this ratio, calculate the age of the mineral
this only works when the crystal is cool enough for atoms to be locked into the lattice, so the parent-daughter ratio can be measured = closure temperature
does isotopic dating work for sedimentary rocks?
no. we can only determine when these minerals first crystallized as part of an igneous or metamorphic rock, not when they were deposited as sediment or when the sediment lithified to form a sedimentary rock
what rocks does isotopic dating work for?
igneous and metamorphic
how to date sedimentary rocks
cross-cutting relationships between sedimentary rocks and datable igneous or metamorphic rocks
you can date what it cross-cuts and constrain the age because we know it’s younger
how old is the earth?
4.56 billion years old
know this from isotopic dating
represents the time when the planet internally differentiated into a core and mantle
a rock record of the first half billion years of Earth history doesn’t exist, the oldest dated whole rock is 4 billion years
what is geologic time, as a whole, based on?
time since the earth’s formation