Chapter 6: Correlational Analysis: Pearson's r
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Last updated 1:08 AM on 1/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
1
New cards
Francis Galton
________ invented correlation but Karl Pearson developed it, discovering spurious correlations (a statistical relationship only-- not due to a real relationship between the two variables)
2
New cards
correlation coefficient
The strength or magnitude of the relationship between the two variables-- the test statistic, called the ________, varies form 0 (no relationship between the variables) to 1 (perfect relationship between the variables)
3
New cards
correlational relationship
A(n) ________ can not automatically be regarded as implying causation.
4
New cards
REMEMBER
________: Statistical significance does not necessarily equal psychological significance.
5
New cards
correlational analysis
The purpose of performing a(n) ________ is to discover whether there is a meaningful relationship between variables, which is unlikely to have occurred by sampling error (assuming the null hypothesis to be true), and unlikely to be spurious.
6
New cards
Bivariate Correlation
________: when we are considering the relationship between two variables.
7
New cards
Correlation Coefficient
________ (r): a ratio between the covariance (variance shared by the 2 variables) and a measure of the separate variances.
8
New cards
correlation coefficient
The ________ tells you how well the variables are related, and the probability value is the probability of that value occurring by sampling error.
9
New cards
Bivariate Correlation
when we are considering the relationship between two variables
10
New cards
Francis Galton invented correlation but Karl Pearson developed it, discovering spurious correlations (a statistical relationship only
- not due to a real relationship between the two variables)
11
New cards
the direction of the relationship
- whether it is positive, negative, or zero
12
New cards
the strength or magnitude of the relationship between the two variables
- the test statistic, called the correlation coefficient, varies form 0 (no relationship between the variables) to 1 (perfect relationship between the variables)
13
New cards
Perfect Positive Relationship
where all the points on the scattergram would fall on a straight line
14
New cards
Example
relationship between arousal and performance
15
New cards
full name
Pearsons product moment correlation
16
New cards
Correlation Coefficient (r)
a ratio between the covariance (variance shared by the 2 variables) and a measure of the separate variances
17
New cards
REMEMBER
Statistical significance does not necessarily equal psychological significance
18
New cards
Multiply 1/√(n
3) by 1.96
19
New cards
Zero-Order Correlation
correlation between two variables without taking any other variables into account
20
New cards
Partial Correlation
can be explained by lookin at overlapping circles of variance; a correlation between two variables, with one partialled out
21
New cards
If you look carefully, you can see that the variables that share most variance with each other have to do with quality of life
satisfaction with relationships and life
22
New cards
weak moderate
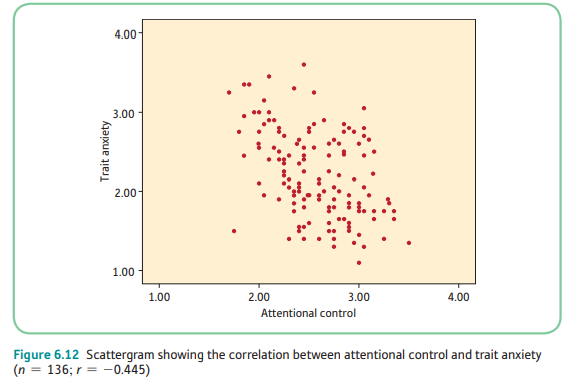
What kind of correlation is this? (choices: zero, weak, weak moderate, moderate, moderate strong, strong, perfect)
23
New cards
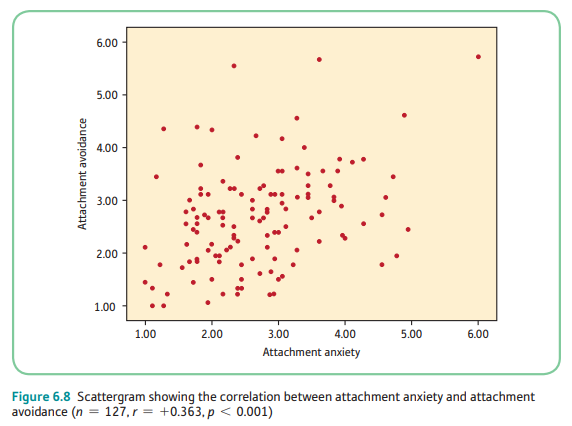
moderate negative
What kind of correlation is this? (choices: zero, weak positive, weak negative, weak moderate positive, weak moderate negative, moderate positive, moderate negative, moderate strong positive, moderate strong negative, strong positive, strong negative, perfect positive, perfect negative)
24
New cards
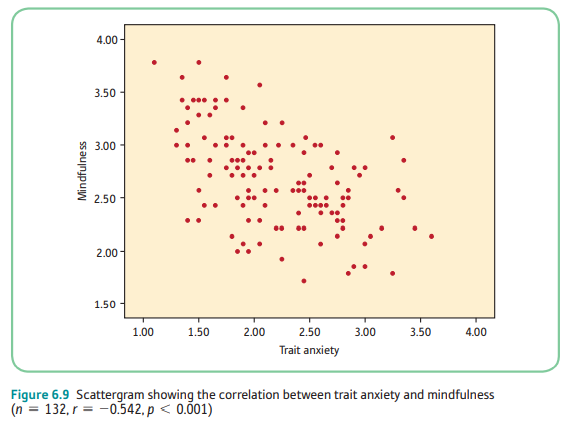
zero
What kind of correlation is this? (choices: zero, weak positive, weak negative, weak moderate positive, weak moderate negative, moderate positive, moderate negative, moderate strong positive, moderate strong negative, strong positive, strong negative, perfect positive, perfect negative)
25
New cards
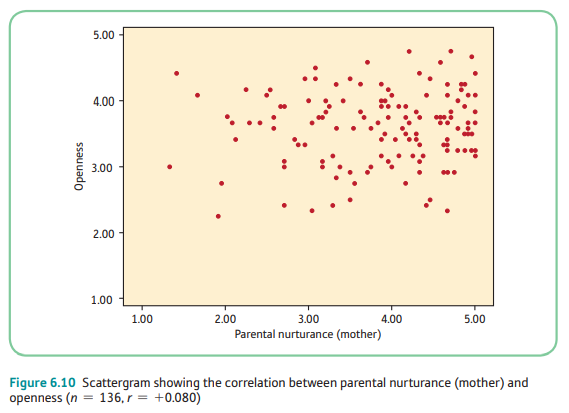
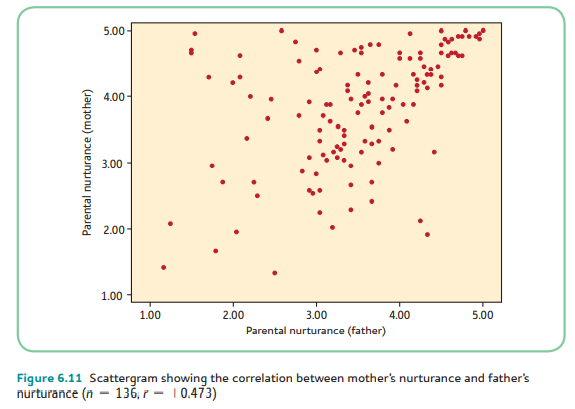
moderate strong positive
What kind of correlation is this? (choices: zero, weak positive, weak negative, weak moderate positive, weak moderate negative, moderate positive, moderate negative, moderate strong positive, moderate strong negative, strong positive, strong negative, perfect positive, perfect negative)
26
New cards
moderate negative
What kind of correlation is this? (choices: zero, weak positive, weak negative, weak moderate positive, weak moderate negative, moderate positive, moderate negative, moderate strong positive, moderate strong negative, strong positive, strong negative, perfect positive, perfect negative)