AQA GCSE Physics - Magnetism and Electromagnetism
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is a permanent magnet?
A magnet that produces its own magnetic field
What is an induced magnet?
A material that becomes a magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field
What type of force do induced magnets always cause?
Force of attraction
What happens to an induced magnet when removed from the magnetic field?
It loses most/all of its magnetism
What is a magnetic field?
The region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet/magnetic material
What is the strength of a magnet dependent on?
The distance from the magnet. The field is strongest at the poles
How do you plot the magnetic field pattern of a magnet, using a compass?
Place the compass near the North Pole of the compass, and draw a cross there
Move the South Pole of the compass onto the cross
Draw another cross at the North Pole of the compass
Continue until you have plotted a complete field line!
What direction do magnetic field lines go?
North to south
How does a compass prove the Earth has a magnetic field?
The needle of a compass always points in the north-south direction
How can we prove that a wire with current flow produces a magnetic field?
Placing the compass near the wire will deflect the needle so north and south no longer line up with the Earth’s magnetic field
How can you determine the direction of the magnetic field?
Using the right hand grip rule (eg if the direction of current is away from you, it will be clockwise)
What is a solenoid
A wire coiled into a spiral shape
How can you increase the magnetic field strength around a wire with current flowing?
Increase size of current
Increase number of turns of coil
Adding an iron core
What is an electromagnet?
A solenoid containing an iron core
How does a relay (an electromagnetic device) work?
A relay consists of a low voltage circuit (contains an electromagnet) & high voltage circuit
When a current flows through the electromagnet , it generates a magnetic field which pulls the iron armature (small metal bar)
As the armature moves, it pushes the switch contacts together, completing a separate high-voltage circuit.
When the current in the coil stops, the magnetic field disappears, and a spring returns the armature to its original position, breaking the circuit.
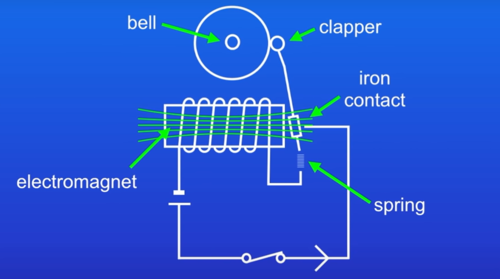
How does a doorbell (electromagnetic device) work?
When the doorbell button is pressed, a switch is closed and current flows through the electromagnet, creating a magnetic field.
The magnetic field attracts an iron contact and pulls it towards a metal bell.
The striker hits the chime or bell, producing a sound, and breaks the circuit
The current stops, magnetic field disappears, and contact returns to its original position.
What is the motor effect?
The force exerted by a current-carrying wire interacting/being in another magnetic field at an right angle
What is magnetic flux density?
A measure of the strength of a magnetic field (measured in Tesla)
What factors affect the size of the force on a the wire?
The magnetic flux density
Size of current
Length of wire
Explain the Fleming’s left hand rule
Used to determine the direction of the force on a wire
Position your thumb, index and middle fingers at right angles to each other
Index finger = direction of magnetic field (N to S)
Middle finger = direction of conventional current (+ to -)
Thumb = direction of force