SA abdomen, gastroinestinal tract, perineum
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
1
New cards
what is the most important layer of the stomach wall
submucosa
* is the layer of strength
* holding layer
* if you dont open it up you dont need to suture it
* if you open you have to suture it together
* is the layer of strength
* holding layer
* if you dont open it up you dont need to suture it
* if you open you have to suture it together
2
New cards
what influences the gastric axis
liver size
3
New cards
what happens if the liver is small
the stomach goes to the left
4
New cards
what happens if the liver is too big
the stomach shifts to the right
5
New cards
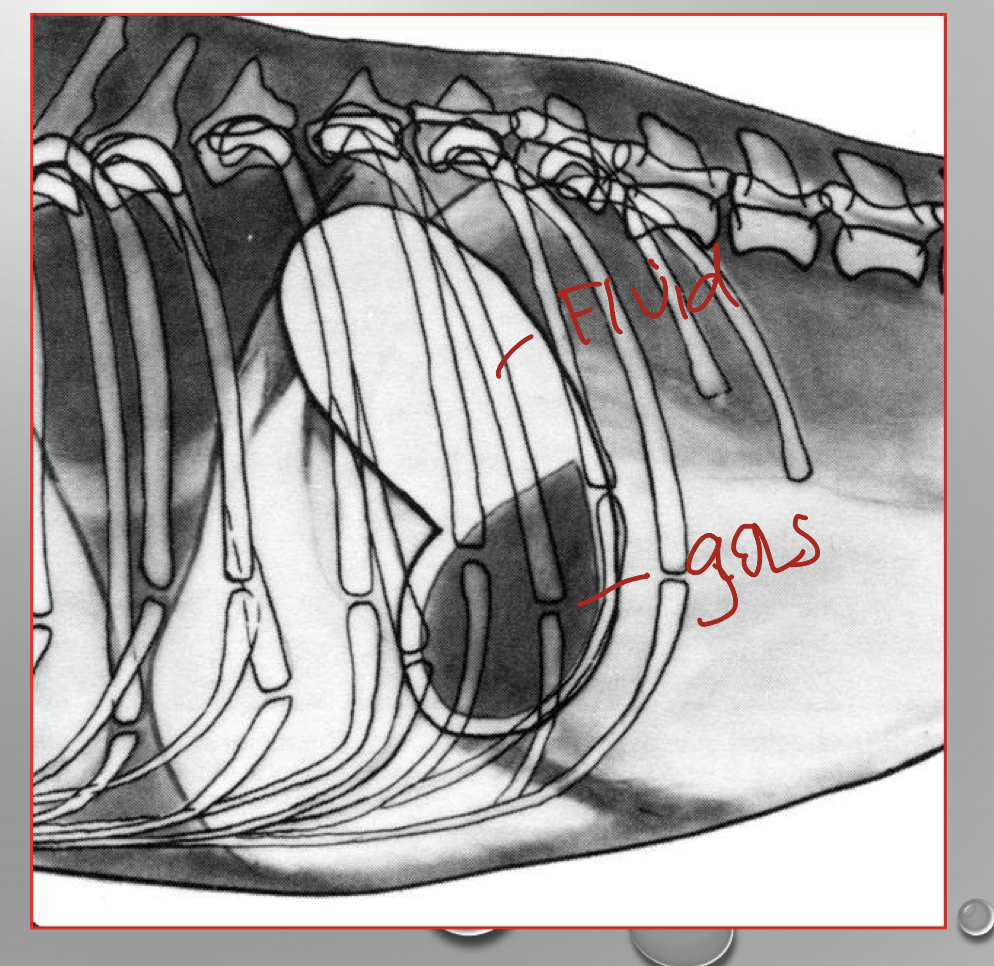
what view are we looking at
left lateral view
* dog is laying on their left side so the right side will be higher
* fluid in fundus
* gas in pylorus (higher up because its on the right side)
* dog is laying on their left side so the right side will be higher
* fluid in fundus
* gas in pylorus (higher up because its on the right side)
6
New cards
what side is the spleen on
left side
7
New cards
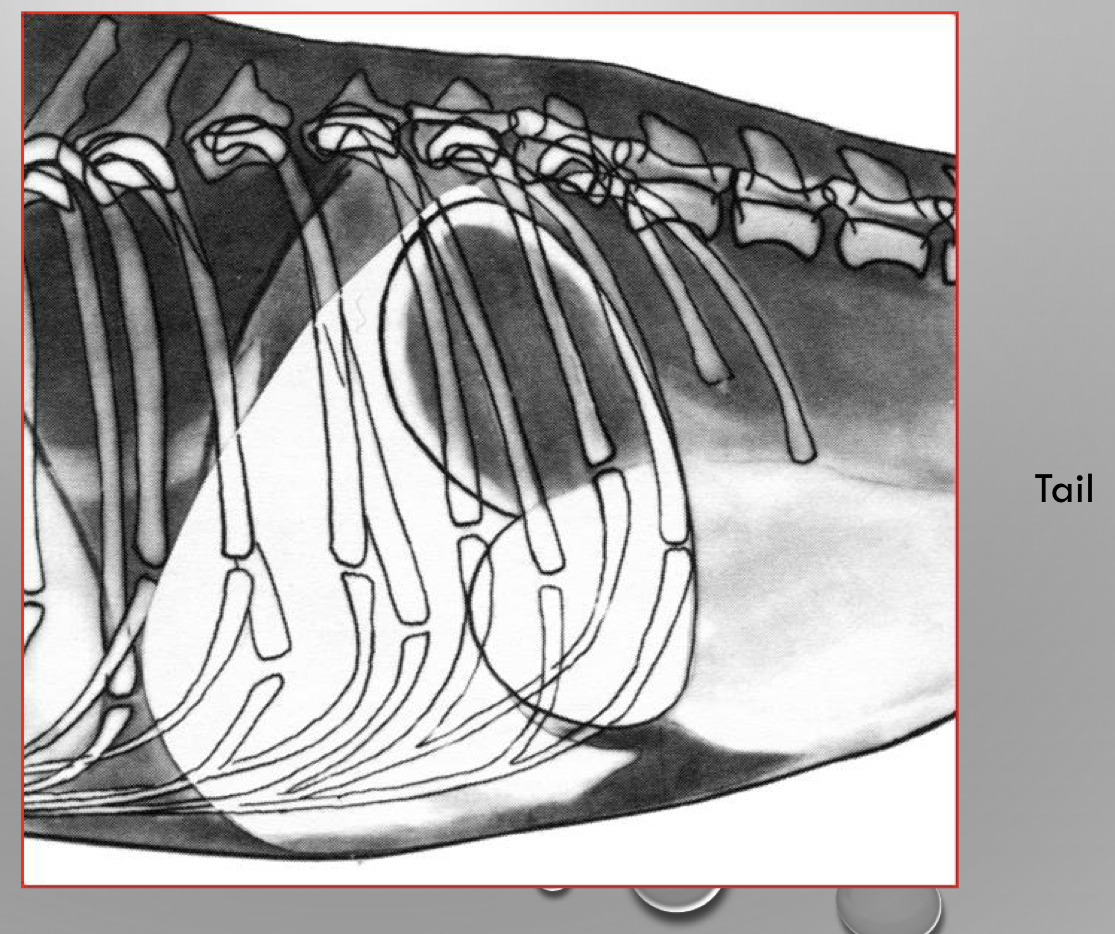
is this left or right lateral view
right lateral view
* laying on their right side
* gas in fundus (higher up because its on the left side)
* fluid in pylorus
* laying on their right side
* gas in fundus (higher up because its on the left side)
* fluid in pylorus
8
New cards
when does gas rise
it rises to the highest point
9
New cards
CASE
* 7yr old FS Great dane
* retching in the back yard
* weak and collapsed
* bloated abdomen
* poor pulses in rear limbs
* shocky
* 7yr old FS Great dane
* retching in the back yard
* weak and collapsed
* bloated abdomen
* poor pulses in rear limbs
* shocky
GDV
gastric dilation-volvulus
gastric dilation-volvulus
10
New cards
what does retching mean
* trying to vomit but it cant
11
New cards
describe GDV gastric dilatation volvulus
* always does a clockwise rotation
* pyloris starts to move left dorsal
* the stomach tissue starts to die from severe bloating and gas can not escape
* pyloris starts to move left dorsal
* the stomach tissue starts to die from severe bloating and gas can not escape
12
New cards
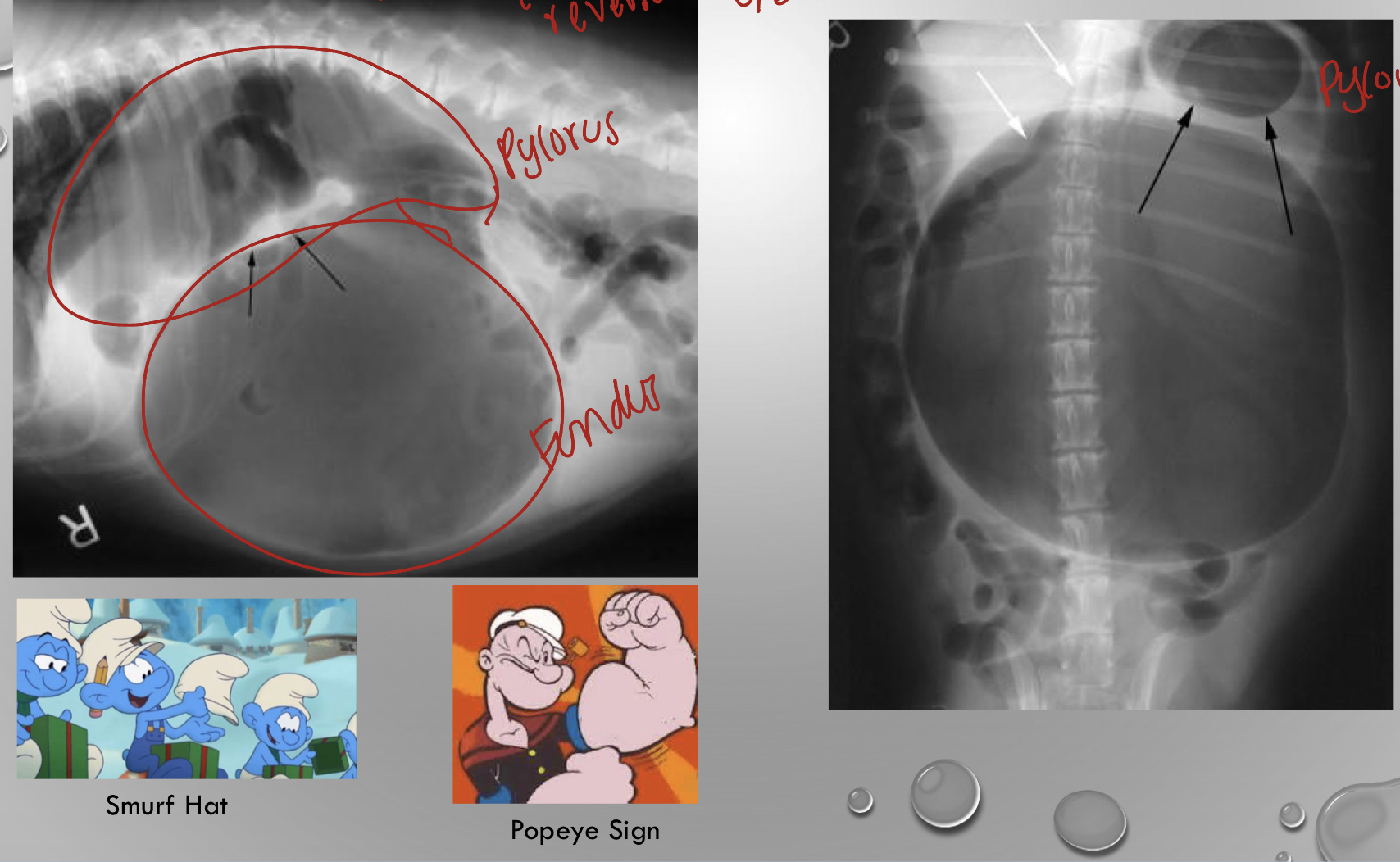
what is going on in the xray
gdv
13
New cards
what does the greater omentum do
its an organ
its the policemen of the abdomen
if there is a problem greater omentum will go to the spot
can drain certain areas
finds problems like tumors and sticks to it
its the policemen of the abdomen
if there is a problem greater omentum will go to the spot
can drain certain areas
finds problems like tumors and sticks to it
14
New cards
what happens to the gastric vessels when theres a GDV
* gastrosplenic ligament causes stomach to drag the spleen as it twists
* short gastric vessels can rupture and bleed
* blood supply to spleen and greater curvature of the stomach can become compromised
* short gastric vessels can rupture and bleed
* blood supply to spleen and greater curvature of the stomach can become compromised
15
New cards
describe gastroplexy
suture the serosa and muscularis of the pyloric antrum to the right side of the body wall
* submucosa and mucosa are not incised
* submucosa and mucosa are not incised
16
New cards
describe the anatomy of the liver
* 6 lobes
* 3 divisions
* left
* central
* right
* 3 divisions
* left
* central
* right
17
New cards
what divides the liver between right medial and quadrate lobes
gallbladder
18
New cards
which is the biggest liver lobe
left lateral lobe
19
New cards
responsibilites of the celiac-hepatic artery
* 20% of blood flow
* 80% of the oxygenated blood supply
* 80% of the oxygenated blood supply
20
New cards
responsibilites for the portal vein
* 80% of blood flow
* 20% of the oxygenated blood supply
* 20% of the oxygenated blood supply
21
New cards
what drains into the portal system
* pancreas
* spleen
* gi tract
* spleen
* gi tract
22
New cards
what does the liver do
* metabolize
* detoxify
* detoxify
23
New cards
are there branches to the vena cava in front of the kidneys
no
24
New cards
what is part of the extrahepatic biliary system
* gallbladder
* stores bile
* cystic duct
* hepatic duct
* comes from the liver and biles go through
* common bile duct
* duodenal papilla
* also called sphincter of oddi
* terminal portion of the common bile duct
* stores bile
* cystic duct
* hepatic duct
* comes from the liver and biles go through
* common bile duct
* duodenal papilla
* also called sphincter of oddi
* terminal portion of the common bile duct
25
New cards
CASE
* 1yr F Yorkie
* runt of the litter
* becomes lethargic
* stares at walls after eating
* had a seizure a week ago
* acts drunk
* eats and falls over
* 1yr F Yorkie
* runt of the litter
* becomes lethargic
* stares at walls after eating
* had a seizure a week ago
* acts drunk
* eats and falls over
portosystemic shunt
* liver isn’t used to the amount of blood flow and go into shock and die if too fast
* you have to slowly shunt it down
* common in toy breed dogs
* yorkies
* maltese
* min schnauzers
* low protein diet
* liver isn’t used to the amount of blood flow and go into shock and die if too fast
* you have to slowly shunt it down
* common in toy breed dogs
* yorkies
* maltese
* min schnauzers
* low protein diet
26
New cards
what are the different shunts in a portosystemic shunt
* an extra vessel
* blood doesn’t pass through the portal system
* portal to caval shunt
* toxic materials into systemic materials
* blood doesn’t pass through the portal system
* portal to caval shunt
* toxic materials into systemic materials
27
New cards
whats important about the duodenocolic ligament
* makes it a consistent shape
* holds the descending duodemun to the dorsal body wall right side
* easy to resect and mobilize the duodenum
* holds the descending duodemun to the dorsal body wall right side
* easy to resect and mobilize the duodenum
28
New cards
describe the blood supply of the duodenum
* tied to the pancreas
* not forgiving
* segmental blood supply
* cranial and caudal pancreaticoduodenal
* difficult to resect duodenum
* not forgiving
* segmental blood supply
* cranial and caudal pancreaticoduodenal
* difficult to resect duodenum
29
New cards
is the jejunum held down by anything
no
it is very loose
has mesentery that has several blood supply that is forgiving archietict
it is very loose
has mesentery that has several blood supply that is forgiving archietict
30
New cards
how can you tell the difference between ileum and jejunum
ileum is very shorts and it has a antimesentric vessel that sits on the top
it also terminates at the ileocecocolic junction
it also terminates at the ileocecocolic junction
31
New cards
describe the colon
* it has segmental blood supply compared to the small intestine
* not very forgiving
* if you resect you have to take from small branches not the big ones
* not very forgiving
* if you resect you have to take from small branches not the big ones
32
New cards
where are the anal sacs located
in between internal and external anal sphincter
33
New cards
CASE
* 6yr MN yorkie
* scooting frequently
* odor around rectum
* enlarged anal sacs
* 6yr MN yorkie
* scooting frequently
* odor around rectum
* enlarged anal sacs
anal gland abscess
* if its happens often you can take out the anal glands
* if its happens often you can take out the anal glands
34
New cards
CASE
* 5 yr old male boxer
* straining to defecate
* produces ribbon like stools
* bilateral perineal hernia
* 5 yr old male boxer
* straining to defecate
* produces ribbon like stools
* bilateral perineal hernia
* perineal hernia
* pelvic muscles have weakened and ruptured
* his abdominal structures are moving to the back
* pelvic diaphragm reduces pressure to defecate
* pelvic muscles have weakened and ruptured
* his abdominal structures are moving to the back
* pelvic diaphragm reduces pressure to defecate
35
New cards
what are the three muscles that hold the pelvic diaphragm in place and form a pelvic wall
\
external anal spincter
levator ani
coccygeus muscle
\
external anal spincter
levator ani
coccygeus muscle
\
36
New cards
what are the arteries and innervation in the perineal
* caudal rectal nerve and artery
* pudendal nerve and internal pudendal artery
* pudendal nerve and internal pudendal artery
37
New cards
what are some major concerns with herniation
* urinary bladder retroflexion
* small intestinal loop strangulation
* loose pelvic diaphragm
* happens with presence of androgen weakens these muscles
* small intestinal loop strangulation
* loose pelvic diaphragm
* happens with presence of androgen weakens these muscles
38
New cards
how to fix herinas
* internal obturator muscle transposition
* restructer the pelvic diaphragm
* neuter them
* females not so common but it will be if they have given birth multiple times
* restructer the pelvic diaphragm
* neuter them
* females not so common but it will be if they have given birth multiple times
39
New cards
describe what forms the inguinal canal
* external abdominal oblique- external ring cranial border
* internal abdominal oblique- internal ring cranial border
* rectus abdominus- medially
* connective tissue
* vaginal process- spermatic cord in males
* external pudenal artery and vein
* genitofemoral nerve
* cremaster muscle (males)
* round ligament (females)
* inguinal ligament- laterally
\
* internal abdominal oblique- internal ring cranial border
* rectus abdominus- medially
* connective tissue
* vaginal process- spermatic cord in males
* external pudenal artery and vein
* genitofemoral nerve
* cremaster muscle (males)
* round ligament (females)
* inguinal ligament- laterally
\
40
New cards
what hernia doesnt have a hernia sac
traumatic hernias
41
New cards
describe umbilical hernia
* cogenital/ typically inherited
* failure of fusion of the rectus abdominis muscle at the umbilicus
* usually falciform fat herniates through
* if large enough intestine can herniate
* failure of fusion of the rectus abdominis muscle at the umbilicus
* usually falciform fat herniates through
* if large enough intestine can herniate
42
New cards
what is inside the inguinal canal
* connective tissue
* vaginal process- spermatic cord in males
* external pudenal artery and vein
* genitofemoral nerve
* cremaster muscle (males)
* round ligament (females)
* vaginal process- spermatic cord in males
* external pudenal artery and vein
* genitofemoral nerve
* cremaster muscle (males)
* round ligament (females)