BSC226: Seeded Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
1/97
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
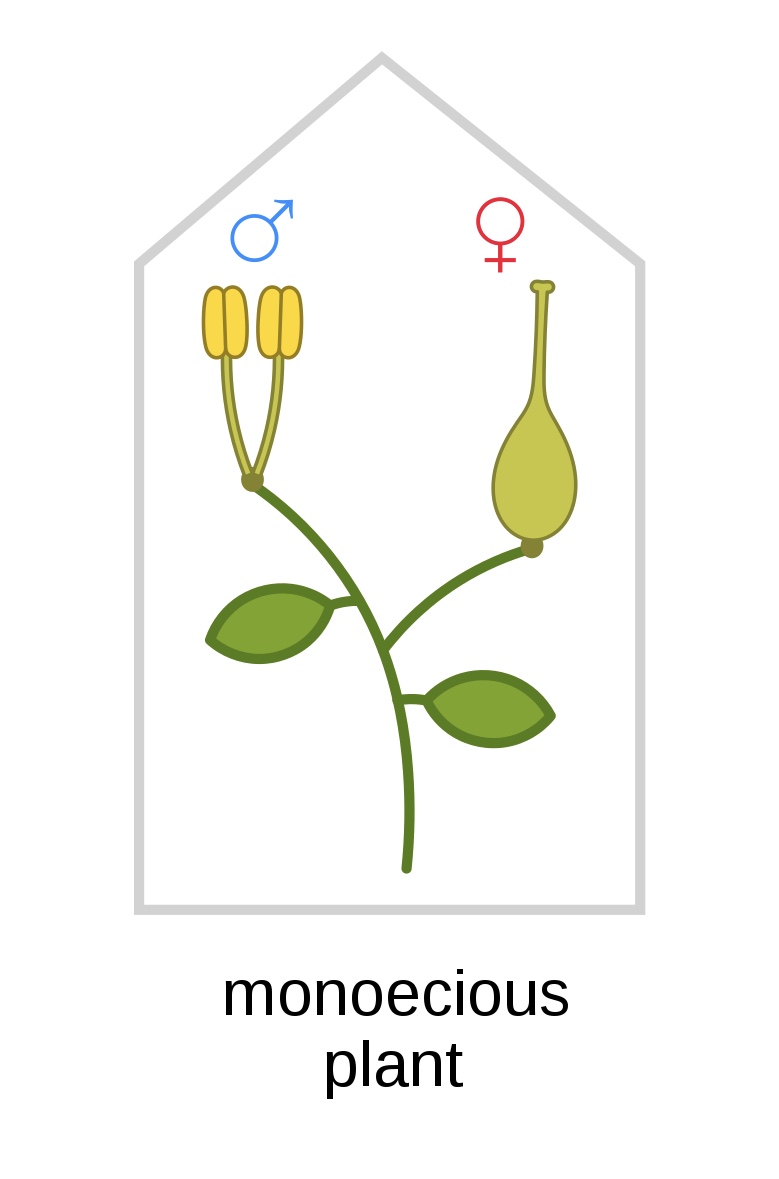
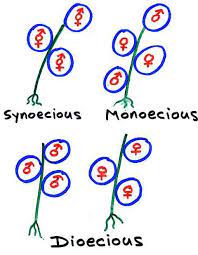
Monoecious
Having female and male reproductive structures on the same plant.
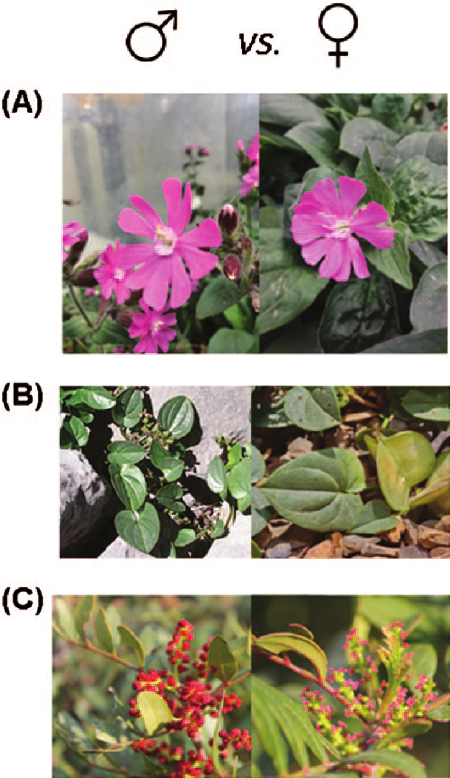

Dioecious
Having female and male reproductive structures on separate plants.
Synoecious
Having male and female organs in the same flower or receptacle.
Zygomorphic
Bilaterally symmetric. Flower can be divided into 2 equal halved along only 1 plane

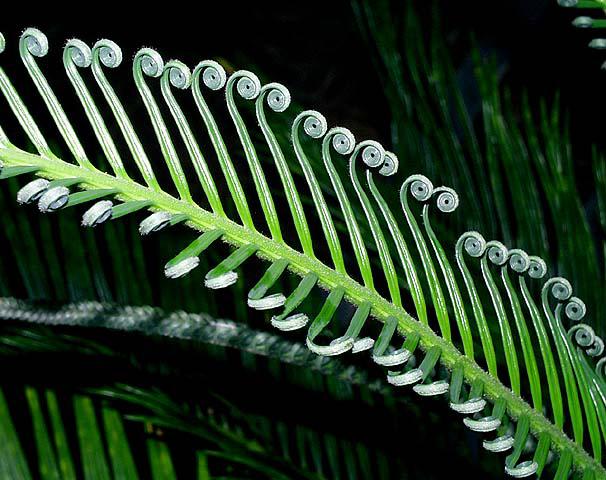
Circinate vernation
The unrolling of leaves as plants mature, found in ferns and cycads.

Cotyledon
Seed leaves.
Dichotomous venation
Veins fork by twos extending from a common point forming a "y" pattern fanning out in leaves.
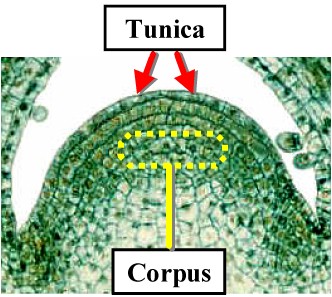
Tunica
The organization of the shoot apex consisting of one or more peripheral layers of cells and interior.
Reticulate venation
Veins form a network-like pattern in leaves.
Gymnosperms
Seed plants with naked seeds, about 1079 species.
Angiosperms
Seed plants with seeds inside additional structures, retention of the megaspore, and all seed plants are heterosporous.
Seed
A fertilized reproductive structure consisting of three parts of a plant life cycle:mother sporophyte covering/integument (2n), nutritive megagametophyte (n), and zygote (2n).
Ovule
The non-fertilized unit of a seed, consisting of an integument and a micropyle.
Micropyle
A small opening in the integument to the megasporangium.
Cycadophyta
A phylum of gymnosperms with 337 species, pinnately divided leaves with circinate vernation, and vascular tissue located in eustele.
→ reproduction located In cones
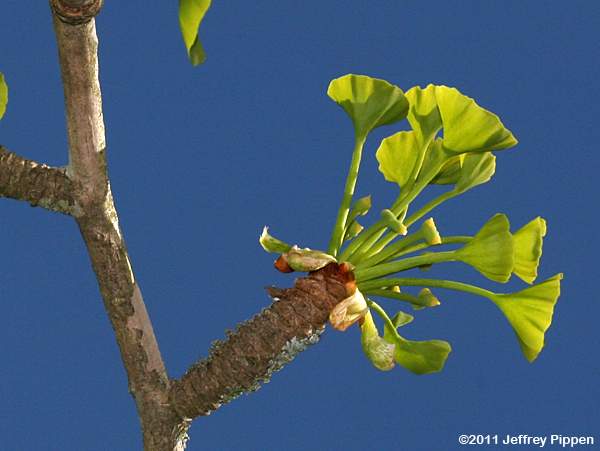
Ginkgophyta
A phylum of gymnosperms with a single extant species (Ginkgo biloba), dioecious, and leaves with dichotomous venation.
contain long and short shoots
ovules/seeds In stalked pairs
sperm is flagellated

Gnetophyta
A phylum of gymnosperms with male and female cones associated with one another, vessel present in wood, and mostly dioecious.
mostly dioecious
Ephedra
A genus in the phylum Gnetophyta, a source of ephedrine, pseudoephedrine, and other stimulants, and leaves are opposite or whorls.
→ mostly dioecious
→ bracts under micro and megasporangia
→ pollen germinates directly onto megagametophyte
Gnetum
A genus in the phylum Gnetophyta with leaves opposite, cone/strobilus divided into conspicuous nodes and internodes, and morphologically similar to angiosperms.
Welwitschia
A genus in the phylum Gnetophyta with one species in the Namib Desert of Angola and Namibia, producing two leaves that grow indefinitely, and dioecious.
→ cones on branched stalks
Anthophyte Hypothesis
A hypothesis proposing that gnetophytes are the sister group of angiosperms, based on morphological evidence such as the presence of vessels in xylem and similarities in shoot apical meristems and double fertilization.
Coniferophyta
A phylum of gymnosperms dominant in the largest forests of the world, with woody plants, needle-like leaves, and mostly monoecious’
→male gametes lack flagella
→megaspore division to form gametophyte occurs within the sporgangia
Angiosperms
Flowering plants with flowers, fruits, vessels, embryo sac, and double fertilization.
Monocots
A group of angiosperms with flowering parts in threes, one cotyledon, parallel venation, scattered vascular bundles, and herbaceous.
Eudicots
A group of angiosperms with two cotyledons, flower parts in fours or fives, reticulate venation, and tricolpate pollen.
Magnoliids
A group of angiosperms with flower parts in spirals or threes, two cotyledons, reticulate venation, and ethereal oils.
Stamen
The male reproductive structure of a flower, consisting of an anther and filament.
Pistil/Fruit
The female reproductive structure of a flower, consisting of a stigma, style, and ovary.
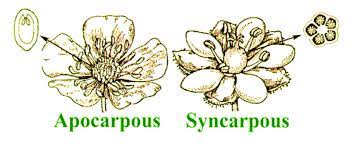
Apocarpous
Multiple free pistils in a flower.

Syncarpous
Pistils fused together to form a single pistil.
Megasporangium
The ovule-oriented structure within the pistil that contains the megasporangia.
Ovary Superior
An ovary attached to the receptacle above the attachment of other floral parts.
Flower Hypogynous
Sepals, petals, and stamens attached to the receptacle below the ovary.
Flower Perigynous
Sepals, petals, and stamens attached to the margin of a cup-shaped extension of the receptacle (hypanthium).
Ovary Inferior
An ovary that sits below the point of attachment for the other parts of the flower.
Flower Epigynous
Sepals, petals, and stamens grow from the top of the ovary.
Hypanthium
The floral cup of a flower.
Generative cell
One of the two cells formed by the division of the generative cell of a pollen grain upon germination on the stigma. It will further divide to form two sperm nuclei.
Vegetative cell
One of the two cells formed by the division of the generative cell of a pollen grain upon germination on the stigma. It does not participate in fertilization.
Alternation of Generations
The life cycle of an angiosperm where there is a alternation between a diploid sporophyte generation and a haploid gametophyte generation.
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma in angiosperms.
Abiotic pollination
Pollination that occurs through the use of wind, water, or gravity.
Biotic pollination
Pollination that occurs through the transfer of pollen by animals such as bees, wasps, butterflies, and beetles.
Nectar
A sweet liquid produced by flowers that serves as a food source for pollinators.
Pollination Syndromes
Patterns that exist between specific floral traits and the types of pollinators they attract.
Bees and Wasps
Pollinators attracted to flowers that are yellow and blue, often with UV lines.
Flies and Beetles
Pollinators attracted to flowers with bad smells, such as rotting or dead scents.
Butterflies
Pollinators attracted to bright flowers, especially those that are red, yellow, or white, with a landing platform.
Moths
Pollinators attracted to dusk or night-blooming flowers with a heavy sweet scent.
Bats
Pollinators attracted to broad flowers with lots of stamen, typically dusk or night-blooming.
Birds
Pollinators attracted to red, tubular flowers with lots of nectar and little to no odor.
Water pollination
Pollination that occurs in aquatic plants, where pollen floats to the top of the water and is carried to other flowers.
Fruit/Seed Dispersal
The process by which fruits or seeds are spread away from the parent plant.
Orchidaceae
A family of flowering plants characterized by having monocot flowers with an inferior ovary and zygomorphic (bilaterally symmetric) flowers. They often rely on specific pollinators for successful reproduction.
Asteraceae
The sunflower family, the largest flowering family, characterized by having eudicot flowers with an inferior ovary. The flowers are partially radially symmetric and partly bilateral, and are often clustered into heads or landing pads.
inetgument
prtotective convering of the seed
ovule
a nonfertilized female reproductive unit is called
heterosporous
are seed plants heterosporous or homosporous
Eustele
vascular tissue in Cycadophyta is locted in sepeparete bundles around the edge of the stem, called the
Vessels in wood
each megasporangium is surronded by two parts
shoot apical meristems
double fertilization
no archegonia
Similarites of gymnosperms and angiosperms
Phylum Coniferophyta
cedars, yews. Douglas firs, cypress, firs, junipers, and pines
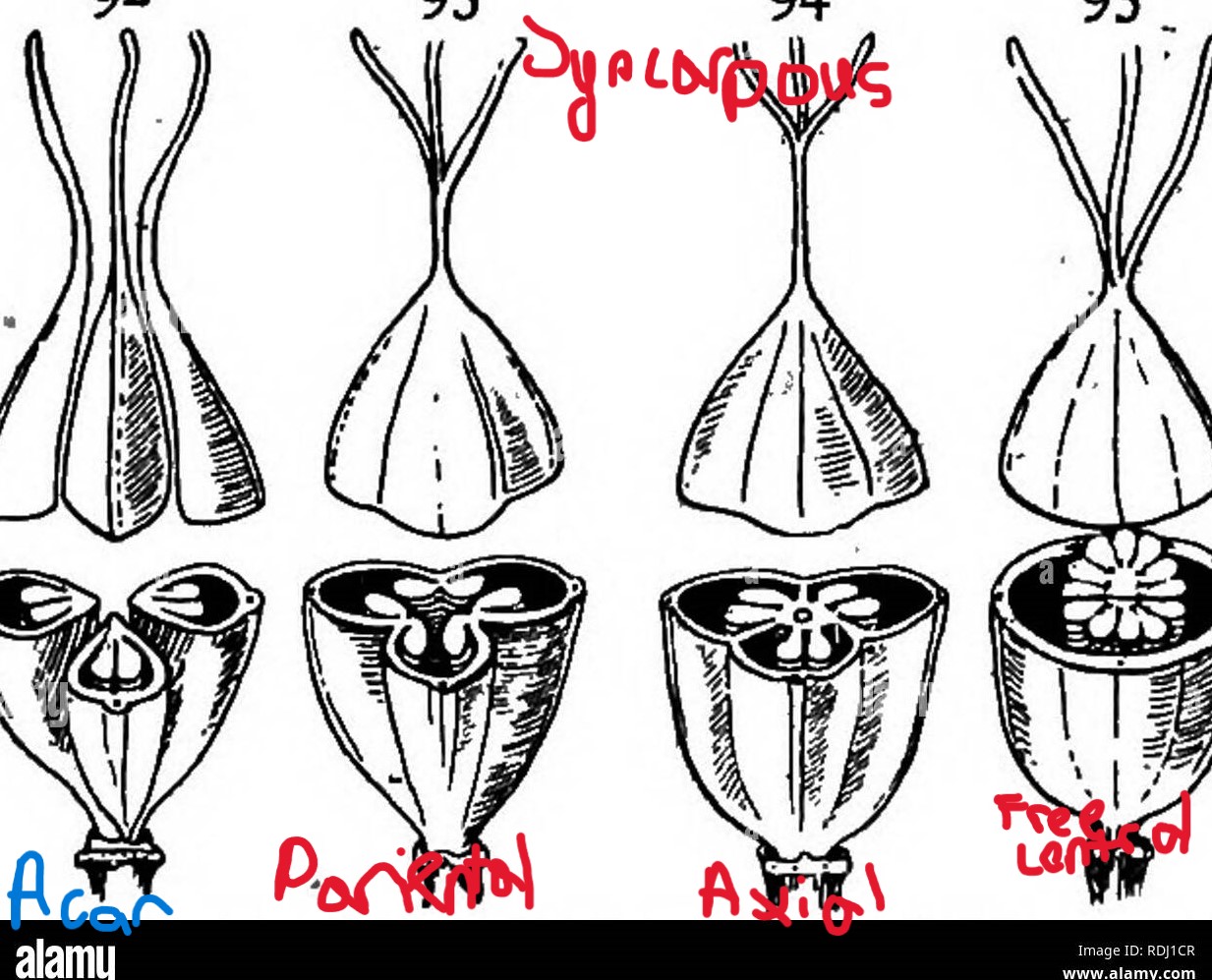
pariental
type of syncarpous flower where pistils are found in the side of the wall
ex: pumpkin
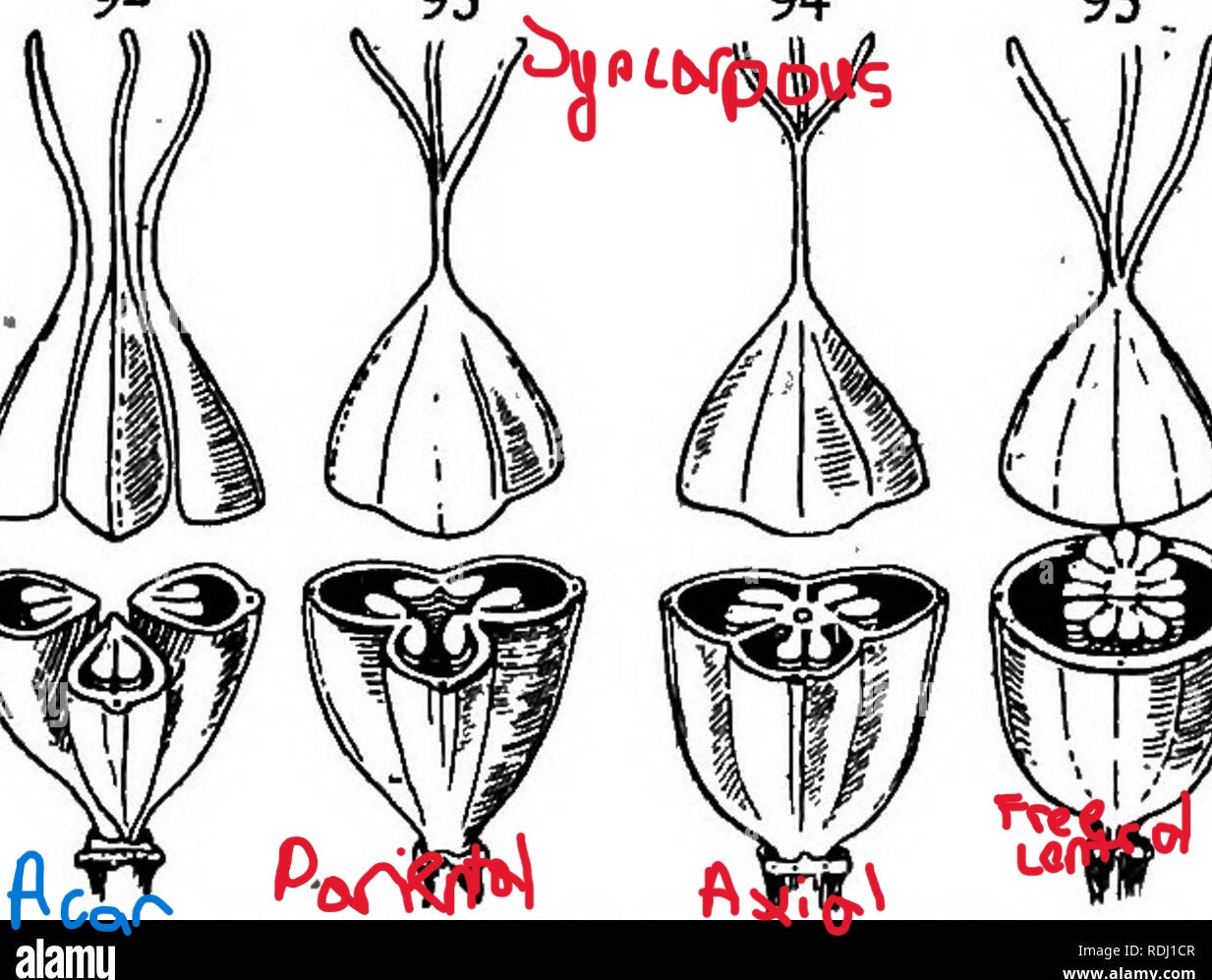
Axile
type of syncarpous flower, where carpels are on central walls
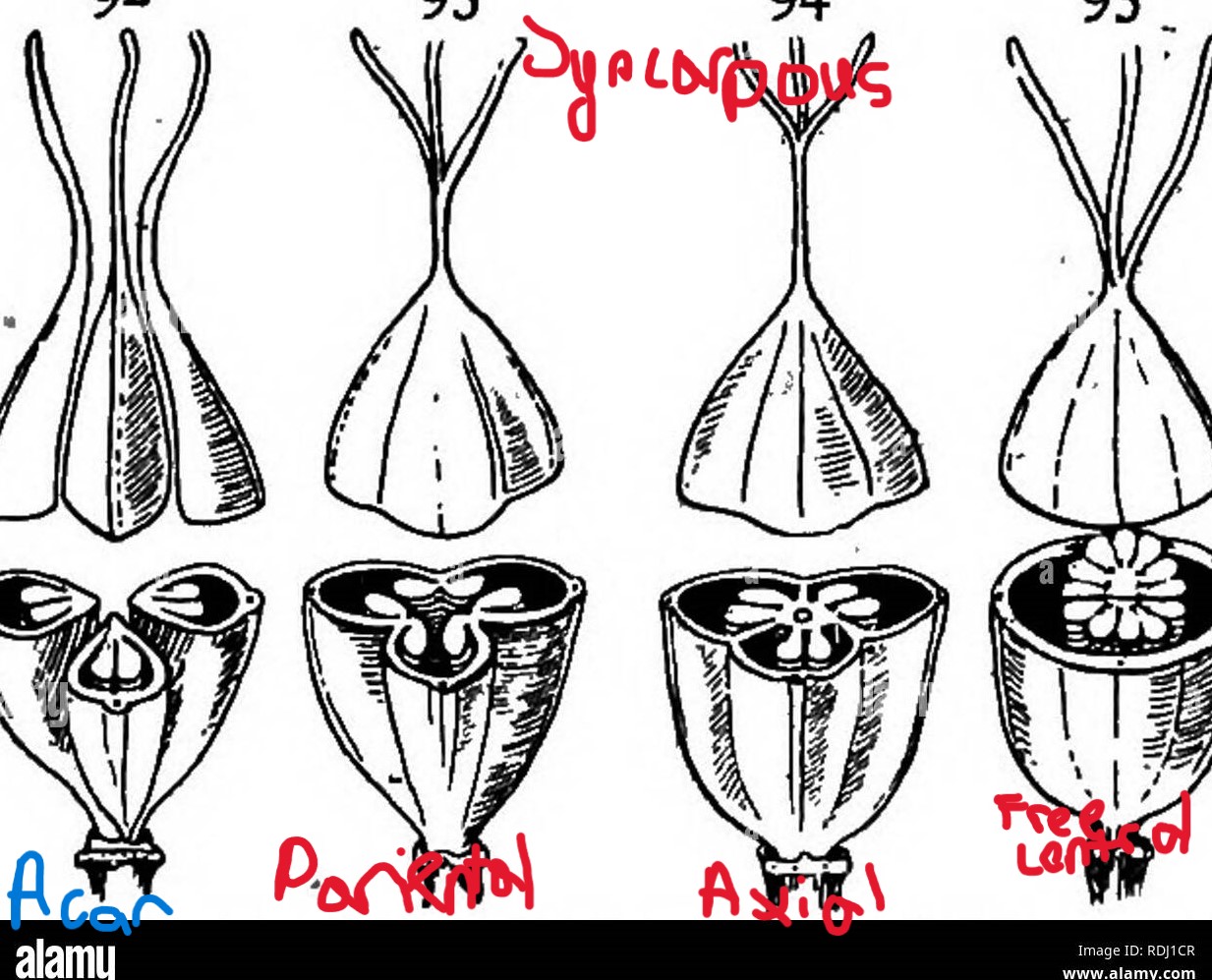
free central
type of syncarpous flower where carpls are attached to a flagpole inside the flower
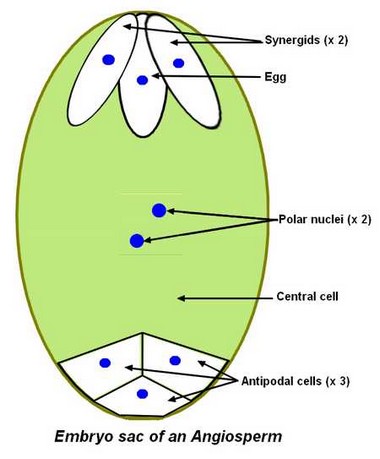
Embryo Sac
in angiosperms, the reduction of the female gametophyte to 7 cells and 8 nuclei bodies
Monocolplate
pollen morph where grains have a single germinal furrow
→ pollen tube only coems out of this segment, meaning the pollen has to land exaclty so to pollinate
found in Magnoliids and Monocots
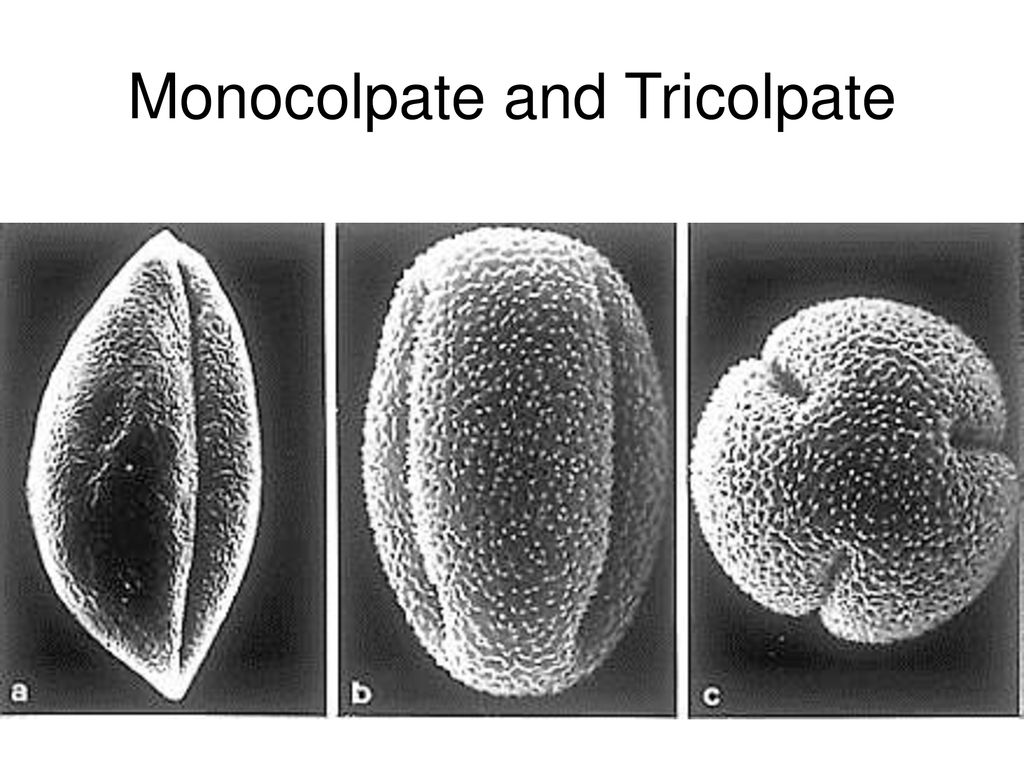
tricolplate
pollen with three aperatures, equally spaced and parallel to the polar axis
eusteles
vascular bundles of phloem and xylem strands with parenchyma cells between bundles
→ found in dicots and some gynmnosperms
Monocots
which classification of angisperms have vascular tissue scattered through the stem
Pinus longaeva
oldest individual
Sequoia sempervirens
tallest individual
Sequiadendron giganteum
most voluminous individual
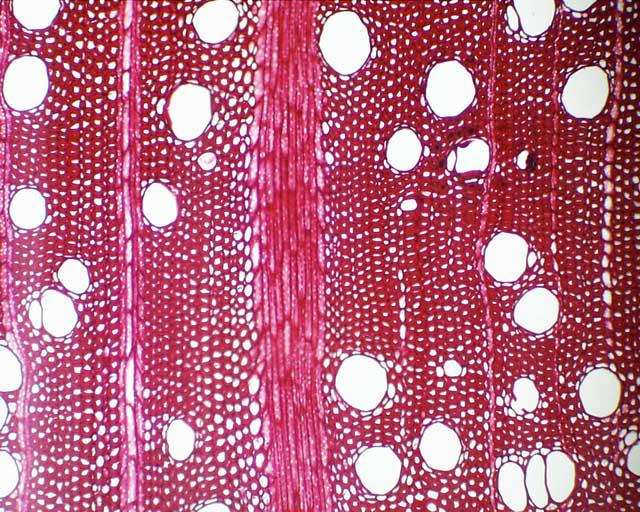
vessels
big water transport pipes present in gnetophytes and angiosperms
take less energy to absorb and transport water
Lamina
in angiosperms, male sporgania are held ona a petal like strucute instead of a filament
→ found in Magnoliids
Middle East
the grasses of wheat, barely rye and oats found and cultivated in this area
Middle East
these legumes: lentils, english peas (green pea, snow pea) and chickpea are from
Middle East
these fruits: dates palms, figs, grapes are found from this area
Middle East
Mints such as basil, thyme, rosemary, spearmind, sage, oregano are found in this area
sub-saharan africa
coffee and kola are typically found in this region
subsaharan africa
the grasses millets, sorghum, tef are typically found in this area
southeast asia
rice is a grass that orginates from
soybean oil
source of oil from the southeast asian region is
Americas
grasses such as corn and maize orignate from what area
Nix v. Henden
Suoreme Court case that ruled that tomatoes shoulod be treated as vegetables not fruits, thus keeping the high tax on tomatoes
legume/beans
plants that is a rich source of proteins
vegetable
any part that comes from a plant is considered
dog
what animal was domesitcated before plants
carbohydrates
grains, tuberous plants, sugar fruits that are high energy and easily digestible are considered
oil
seeds (olives, sunflowes, plams, canola, cottenseed) that provide high energy
vitamins and minerals
leafy, colofrul vegetables. and herbs are sources of
grasses and starchy tubers
80% of caolories consumed by humans comes from
starchy tubers
potatoes
sweet potatoes
manihot/yuca
disadvantges to biotechnology
allergic reactions
good qualities may escape into weeds *superweeds
unaticipated side effects (other insects, Ecologically)
ignorance on disruption too genome
transgenic
genetically engineered organisms w/ genes from different species
insect resistance
resistance to glyphosphate
addition of genes to make nutrients
GMO uses
Self pollinating
plant breeding techqniue used in wheat, rice, pears
easy to generate homozygous, pure lines due to inbreeding
cross=pollinating
type of plant breeding in corn, cucumbers, squash, anf fruit trees
typically yield heterozygous
Norman Borlaug
father of the Green Revolution
New strains of wheat in Mexico , and exported to India
Won the 1970 Nobel Peace Prize