exam 3 (final)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
1
New cards
functions of the respiratory system
\-maintain a constant O₂ & CO₂ in blood
\-acid-base balance
\-provides a means of gas exchange b/n the environment & the body
\-acid-base balance
\-provides a means of gas exchange b/n the environment & the body
2
New cards
ventilation
process of moving air in & out of lungs
3
New cards
respiration
ventilation & exchange of gases in lungs
4
New cards
internal respiration
at the cell
5
New cards
external respiration
at the lung
6
New cards
conducting zone
\-10% of total lung volume
\-air passed to the alveoli
\-anatomical dead space
\-nose, trachea, carina
\-air passed to the alveoli
\-anatomical dead space
\-nose, trachea, carina
7
New cards
respiratory zone
\-90% of total lung volume
\-where gas exchange (O₂ & CO₂) occurs
\-alveolar ducts & capillaries
\-where gas exchange (O₂ & CO₂) occurs
\-alveolar ducts & capillaries
8
New cards
nose
\-warms, humidifies & filters air (air conditioning)
\-100% humidified (47 mmHg at body temp)
\-100% humidified (47 mmHg at body temp)
9
New cards
trachea
\-surrounded by cartilage
\-high resistance to airflow, slows done air
\-high resistance to airflow, slows done air
10
New cards
carina
\-at base of trachea
\-primary coughing reflex
\-primary coughing reflex
11
New cards
type 1 alveoli
1 layer of epithelial cells
12
New cards
type 2 alveoli
surfactant secreting
13
New cards
surfactant
\-lines surface of alveoli
\-liquid containg lipoproteins
\-↓ surface tension of alveolar membranes
\-gives lungs good compliance
\-liquid containg lipoproteins
\-↓ surface tension of alveolar membranes
\-gives lungs good compliance
14
New cards
compliance
\-change in volume for a change in pressure
\-reason why we can inflate & deflate our lungs easily
\-reason why we can inflate & deflate our lungs easily
15
New cards
O₂ cost of breathing
at rest= 6 mLO₂/min
16
New cards
inspiration at rest
diaphragm pulls down, lungs are expanded (active)
17
New cards
expiration at rest
diaphragm relaxes, lungs passively recoil
18
New cards
muscles of inspiration (exercise)
\-pulls ribs up: scalenes & sternoclridomastoid
\-pulls ribs out: external intercostal
\-diaphragm
\-pulls ribs out: external intercostal
\-diaphragm
19
New cards
muscles of expiration (exercise)
\-pulls ribs down & in: internal intercostal
\-external oblique, rectus abdominis, internal oblique, transverse abdominis (abdominals push diaphragm up)
\-external oblique, rectus abdominis, internal oblique, transverse abdominis (abdominals push diaphragm up)
20
New cards
gas diffusion
moves from areas of high to low pressure
21
New cards
sites of gas diffusion in the body
\-alveoli-capillary interface
\-tissue-capillary interface
\-tissue-capillary interface
22
New cards
factors that affect gas exchange
↑ gas solubility, ↑ pressure gradient, ↑ diffusion space, ↑ surface area
23
New cards
Fick

24
New cards
Hartog Hamburger

25
New cards
gas solubility
\-positively related
\-how easily gas can dissolve into environment
\-how easily gas can dissolve into environment
26
New cards
pressure gradient
\-positiviely related
\-biggest driver of oxygen, high to low pressure
\-biggest driver of oxygen, high to low pressure
27
New cards
diffusion space
\-inversly related
\-tissue thickness
\-connection with cells of capillaries & alveoli, want it to be very thin
\-tissue thickness
\-connection with cells of capillaries & alveoli, want it to be very thin
28
New cards
surface area
positively related
29
New cards
ficks law of diffusion
\-R= rate pf gas exchange
\-D= solubility constant
\-A= surface area
\-∆p= difference in pressure gradient between capillaries & alveoli
\-d= diffusion space/tissue thickness
\-D= solubility constant
\-A= surface area
\-∆p= difference in pressure gradient between capillaries & alveoli
\-d= diffusion space/tissue thickness
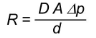
30
New cards
atmospheric gas fractions at sea-level
\-O₂= 0.2093
\-CO₂= 0.0003
\-N₂= 0.7904
\-CO₂= 0.0003
\-N₂= 0.7904
31
New cards
change in atmospheric pressure
\-↑ altitude= ↓ pressure
\-due to gravity which causes gas molecules to be close to the ground
\-due to gravity which causes gas molecules to be close to the ground
32
New cards
alveolar partial pressure of gases
\-O₂= 0.146
\-CO₂= 0.056
\-CO₂= 0.056
33
New cards
O₂ transport in blood
1)dissolved in blood
\-3 mLO₂/L blood dissolved
\-low dissolvability of O₂
\-1.5%
2)bound to hemoglobin
\-binds & carries O₂
\-1.34 mLO₂/ gm Hb (when fully saturated)
\-98.5 %
\-3 mLO₂/L blood dissolved
\-low dissolvability of O₂
\-1.5%
2)bound to hemoglobin
\-binds & carries O₂
\-1.34 mLO₂/ gm Hb (when fully saturated)
\-98.5 %
34
New cards
hemoglobin
\-250 million Hb or 1 RBC
\-binds 4 O₂ molecules
\-men= 150 g Hb/L blood
\-women= 130 g Hb/L blood
\-1 g Hb can combine w/ 1.34 mLO₂
\-binds 4 O₂ molecules
\-men= 150 g Hb/L blood
\-women= 130 g Hb/L blood
\-1 g Hb can combine w/ 1.34 mLO₂
35
New cards
arterial-venous O₂ difference
\-(a-v)O₂
\-diffencene b/n CaO₂ & CvO₂
\-amount of O₂ extracted by tissue
\-diffencene b/n CaO₂ & CvO₂
\-amount of O₂ extracted by tissue
36
New cards
Fick equation VO₂
\-(HR×SV)×(a-v)O₂ diffencene
\-illustrated the factors determining VO₂
\-illustrated the factors determining VO₂
37
New cards
CO₂ transport
1)dissolved in plasma (10%)
2)bound to Hb (20%)
3)formed as HCO₃ on RBC (70%)
2)bound to Hb (20%)
3)formed as HCO₃ on RBC (70%)
38
New cards
bicarbonate-CO₂ transport system
\-CO₂ + H₂O→H₂CO₃→H⁺ + HCO₃⁻
\-Cl⁻ shift/ Hamberger shift
\-Cl⁻ shift/ Hamberger shift
39
New cards
rest-to-work transitions
1)rapid ↑ in ventilation
\-proportional to intensity
2)rapid ↑ in pulmonary blood flow
3)airway dilation & ↓ resistance to air flow
\-bronchioles
\-proportional to intensity
2)rapid ↑ in pulmonary blood flow
3)airway dilation & ↓ resistance to air flow
\-bronchioles
40
New cards
ventilatroy control during submax exercise
\-higher brain center (primary drive to increase ventilation during exercise)
\-chemoreceptors (↑ pCO₂ & ↓ pH) & mechanoreceptors (muscular movement)
\-respiratory muscles (↑ ventilation)
\-peripheral chemoreceptors carotid/aortic (↓ pO₂, ↑ pCO₂ & ↓ pH)
\-↑ temp & catecholamines
\-chemoreceptors (↑ pCO₂ & ↓ pH) & mechanoreceptors (muscular movement)
\-respiratory muscles (↑ ventilation)
\-peripheral chemoreceptors carotid/aortic (↓ pO₂, ↑ pCO₂ & ↓ pH)
\-↑ temp & catecholamines
41
New cards
ventrilation: incremental exercise
\-sharp rise in Vε
\-motor recruitment pattern
\-propriceptive input
\-↑ acidosis
\-↑ body temp
\-↑ epi/ne
\-motor recruitment pattern
\-propriceptive input
\-↑ acidosis
\-↑ body temp
\-↑ epi/ne
42
New cards
anterior pituitary hormones
\-thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
\-adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH)
\-LH & FSH (act on ovaries, regulate menstration)
\-growth hormone
\-prolactin (milk production when pregnant)
\-adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH)
\-LH & FSH (act on ovaries, regulate menstration)
\-growth hormone
\-prolactin (milk production when pregnant)
43
New cards
growth hormone (GH)
\-signal for release: exercise & hypoglycemia
\-acts on muscle, adipose, & liver
\-releases from anterior pituitary
\-essential for normal growth
\-stimulated protein synthesis & bone growth
\-decreases glucose uptake into muscle
\-increases lipolysis
\-stimulates gluconeogenesis in liver
\-acts on muscle, adipose, & liver
\-releases from anterior pituitary
\-essential for normal growth
\-stimulated protein synthesis & bone growth
\-decreases glucose uptake into muscle
\-increases lipolysis
\-stimulates gluconeogenesis in liver
44
New cards
anti-diuretic hormone
\-released from posterior pituitary
\-signal for release: sweating or dehydration & ↑ plasma osmolality
\-acts on kidney (collecting duct)
\-↑ H₂O reabsorption
\-maintain plasma volume
\-signal for release: sweating or dehydration & ↑ plasma osmolality
\-acts on kidney (collecting duct)
\-↑ H₂O reabsorption
\-maintain plasma volume
45
New cards
osmolality
\-decreased water in plasma
\-concentration of solutes
\-concentration of solutes
46
New cards
adrenal medulla
\-part of the SNS
\-secretes catecholamines (epi/ne)
\-secretes catecholamines (epi/ne)
47
New cards
adrenal cortex
\-secretes steroid hormones
\~mineralocorticoids: aldosterone, corticosterone, deoxycorticosterone
\~glucocorticoids: cortisol
\~androgens
\~mineralocorticoids: aldosterone, corticosterone, deoxycorticosterone
\~glucocorticoids: cortisol
\~androgens
48
New cards
aldosterone
\-releases from adrenal cortex
\-signal for release:
\~decreased blood volume/pressure
\~decreased plasma sodium
\~angiotensin II: potent vasoconstricter
\-acts on kidney (distal convoluted tubule)
\-actions:
\~maintain plasma Na⁺ & volume
\~↑ H₂O reabsorption
\~BP regulation
\~stimulate thirst
\-signal for release:
\~decreased blood volume/pressure
\~decreased plasma sodium
\~angiotensin II: potent vasoconstricter
\-acts on kidney (distal convoluted tubule)
\-actions:
\~maintain plasma Na⁺ & volume
\~↑ H₂O reabsorption
\~BP regulation
\~stimulate thirst
49
New cards
erythropoietin (EPO)
\-released from the kidney
\-signal for release: hypoxia, anemia, & blood loss
\-ergogenic aid alert
\-action: stimulates RBC production
\-signal for release: hypoxia, anemia, & blood loss
\-ergogenic aid alert
\-action: stimulates RBC production
50
New cards
insulin
\-released from pancreas (β cells)
\-signal for release: ↑ BG & AA’s in blood
\-acts on muscle & adipose
\-actions:
\~untake of FFA’s, AA, & glucose
\~inhibits gluconeogenesis, lypolysis, & protein breakdown
\-signal for release: ↑ BG & AA’s in blood
\-acts on muscle & adipose
\-actions:
\~untake of FFA’s, AA, & glucose
\~inhibits gluconeogenesis, lypolysis, & protein breakdown
51
New cards
glucagon
\-released from the pancreas (α cells)
\-signal for release: ↓ BG/AA’s in blood & prolonged exercise
\-acts on liver
\-actions:
\~↑ gluconeogenesis & glycogen breakdown
\~↑ lypolysis & protein breakdown
\~inhibits TG & glycogen synthesis
\-signal for release: ↓ BG/AA’s in blood & prolonged exercise
\-acts on liver
\-actions:
\~↑ gluconeogenesis & glycogen breakdown
\~↑ lypolysis & protein breakdown
\~inhibits TG & glycogen synthesis
52
New cards
epi/norepi
\-released by adrenal medulla
\-↑ linearly with exercise
\-acts on liver, muscle, & adipose
\-actions: ↑ lipolysis, gluconeogenesis in liver, & glycogenolysis in muscle
\-↑ linearly with exercise
\-acts on liver, muscle, & adipose
\-actions: ↑ lipolysis, gluconeogenesis in liver, & glycogenolysis in muscle
53
New cards
athletic amenorrhea
\-FSH & LH have altered release from pituitary
\-↓ estrogen
\-causes female athletes to lose period
\-↓ estrogen
\-causes female athletes to lose period
54
New cards
temperature homeostasis
to maintain a constant core temp, heat lost must match heat gain
55
New cards
heat gain
\-PA
\-TEF: thermic effect of food
\-hormonal responses
\-warm environment
\-TEF: thermic effect of food
\-hormonal responses
\-warm environment
56
New cards
heat loss
\-radiation
\-conduction
\-convection
\-evaporation
\-conduction
\-convection
\-evaporation
57
New cards
conduction
transfer of heat via direct contact with another surface (cold bleacher)
58
New cards
convection
transfer of heat via movement of molecules within fluids or gases (air)
59
New cards
evaporation
\-transfer of heat when liquids change physical state becoming gas
\-80% heat loss during exercise
\-20% heat loss at rest
\-80% heat loss during exercise
\-20% heat loss at rest
60
New cards
radiation
\-transfer of electromagnetic heat waves
\-60% heat loss at rest
\-5% heat loss during exercise
\-60% heat loss at rest
\-5% heat loss during exercise
61
New cards
evaporative cooling rate depends on
\-temp & relative humidity
\-convective current around the body
\-amount of skin surface exposed
\-convective current around the body
\-amount of skin surface exposed
62
New cards
factors related to heat injury
\-aclimatization
\-hydration
\-wind
\-temp
\-humidity
\-clothing
\-fitness
\-exercise intensity
\-hydration
\-wind
\-temp
\-humidity
\-clothing
\-fitness
\-exercise intensity
63
New cards
acclimatization
\-earlier onsent of sweating
\-↑ sweat rate, ↓ body temp
\-9-14 days, > 1 hr exercise
\-↑ sweat rate, ↓ body temp
\-9-14 days, > 1 hr exercise
64
New cards
hydration
↑ sweat rate, ↓ body temp
65
New cards
wind
\-↑ heat loss by convection
\-↑ rate of evaporation
\-↑ rate of evaporation
66
New cards
temp
\-↑ temp=heat gain
\-evaporative cooling
\-evaporative cooling
67
New cards
humidity
\-↑ humidity=heat gain
\-lose evaporative cooling
\-lose evaporative cooling
68
New cards
clothing
need skin exposure
69
New cards
fitness
↑ fitness=↓ risk of injury
70
New cards
exercise intensity
\-↑ intensity=↑ risk of injury
\-monitor intensity closely
\-monitor intensity closely
71
New cards
sweat rate
2-3 L/hr
72
New cards
dehydration: CV function
\-↓ skin BF, SV, & Q
\-↑ HR & (a-v)O₂, maintain O₂ supply to muscle
\-↑ HR & (a-v)O₂, maintain O₂ supply to muscle
73
New cards
hyperthermia: CNS
\-motivation & motor control
\-hypothalamus can be damaged
\-hypothalamus can be damaged
74
New cards
hyperthermia: neuromuscular
↓ neural activation of muscle (MU recruitment)
75
New cards
signs of heat acclimatization
\-↑ plasma volume & VR
\-early onset of sweating during exercise
\-more dilute sweat (less Na⁺ lost)
\-↑ SV & ↓ HR, Q is maintained
\-↑ capacity for sustained sweat response
\-↓ core temp for given workload
\-↓ glycogenolysis
\-early onset of sweating during exercise
\-more dilute sweat (less Na⁺ lost)
\-↑ SV & ↓ HR, Q is maintained
\-↑ capacity for sustained sweat response
\-↓ core temp for given workload
\-↓ glycogenolysis
76
New cards
dehydration
\-1%: rapid ↑ in temp
\-2%: ↓ performance
\-3%: ↓ coordination
\-4%: headache/nausea
\-5%: failure of thermoreg
\-6%: serious risk for collapse, permanent injury, & organ failure
\-2%: ↓ performance
\-3%: ↓ coordination
\-4%: headache/nausea
\-5%: failure of thermoreg
\-6%: serious risk for collapse, permanent injury, & organ failure
77
New cards
dehydration calculation
\[(pre-exercise kg−post-exercise kg)÷pre-exercise kg\]×100
78
New cards
gastric emptying rates affected by
\-temp
\-pH (acidity)
\-volume of fluid
\-CHO (6%), ↓ fat, ↓ protein, ↓ fructose
\-pH (acidity)
\-volume of fluid
\-CHO (6%), ↓ fat, ↓ protein, ↓ fructose
79
New cards
max gastric emptying rate
1\.2 L/hr
80
New cards
water replacement before exercise
\-300-500 mL H₂O, 2 hrs prior (based on hydration status)
\-more H₂O w/ glycerol (“hyperhydration”)
\-1.2 g glycerol/kg w/ 26 mL water/kg for 2 hrs prior
\-more H₂O w/ glycerol (“hyperhydration”)
\-1.2 g glycerol/kg w/ 26 mL water/kg for 2 hrs prior
81
New cards
water replacement during exercise
\-< 1 hr: H₂O only
\->1 hr: H₂O & CHO
\-> 2 hrs: add Na⁺ (40 mmol/L)
\->1 hr: H₂O & CHO
\-> 2 hrs: add Na⁺ (40 mmol/L)
82
New cards
rehydration is improved by
\-volume ingested > 1.5 times body weight loss
\-CHO-electrolyte solution is ingested
\-glycerol is added to drink
\-CHO-electrolyte solution is ingested
\-glycerol is added to drink
83
New cards
severe hypohydration
\-> 4% body weight loss
\-can require >24 hrs for complete rehydration
\-can require >24 hrs for complete rehydration