Anatomy- Chapter 1: Intro to Human Anatomy and Phisiology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:32 AM on 9/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
What is Anatomy?
The structure of the body and it's parts
What are things called?
What are things called?
2
New cards
What is Physiology?
The function of body parts
How do they work?
How do they work?
3
New cards
How are anatomy and physiology correlated?
FORM = FUNCTION
The functional role of a body part depends on how it is constructed
The functional role of a body part depends on how it is constructed
4
New cards
What is the focus of anatomists?
Dissections and observation
5
New cards
What is the focus of physiologists?
Experimentation
6
New cards
What is homeostasis?
Maintaining a stable internal environment
Homeostasis is regulated through control systems which have receptors
Homeostasis is regulated through control systems which have receptors
7
New cards
What are examples of homeostasis?
Body Temperature
Sugar, Blood Sugar Level
Sugar, Blood Sugar Level
8
New cards
What does every individual use homeostatic mechanisms for?
to keep body levels within normal range (normal range varies with the person)
9
New cards
Levels of organization of the body (order)
atom -> molecule-> macromolecule-> ORGANELLE-> CELL-> TISSUE-> organ -> organ system-> organism (human)
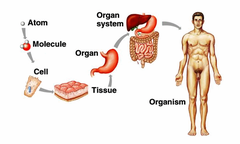
10
New cards
Levels of organization
1.) atoms are the simplest level
2.) 2+ atoms make a molecule
3.) Macromolecules are large (MACRO)
- Biologically important molecules inside cells
4.) organelles -> aggregates (total/accumulate/gather tg) of macromolecules
- used to carry out specific functions in the cell
5.) Cells -> basic living unit
6.) tissues - GROUPS OF CELLS FUNCTIONING TG
7.) groups of tissues form organs
8/) groups of organs functioning together form organ systems
organ systems functioning tg make up an organism
2.) 2+ atoms make a molecule
3.) Macromolecules are large (MACRO)
- Biologically important molecules inside cells
4.) organelles -> aggregates (total/accumulate/gather tg) of macromolecules
- used to carry out specific functions in the cell
5.) Cells -> basic living unit
6.) tissues - GROUPS OF CELLS FUNCTIONING TG
7.) groups of tissues form organs
8/) groups of organs functioning together form organ systems
organ systems functioning tg make up an organism
11
New cards
What are the major features of the human body?
CAVITIES, MEMEBRANES, AND ORGAN SYSTEMS
12
New cards
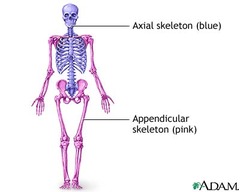
What is appendicular portion?
upper and lower limbs
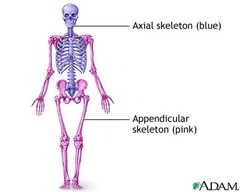
13
New cards
What is the axial portion of the body?
head, neck, trunk
14
New cards
What is viscera?
organs within the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
15
New cards
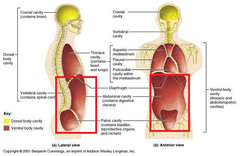
What is the dorsal cavity?
cranial cavity and spinal cavity
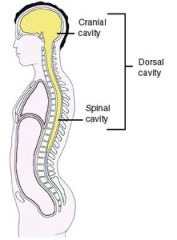
16
New cards
What is the ventral cavity?
thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity
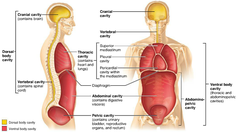
17
New cards
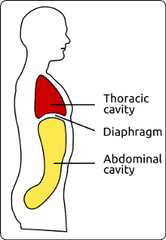
What is the thoracic cavity?
lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea, bronchial tubes, thymus gland, aorta (large artery)
18
New cards
What is the abdominopelvic cavity?
abdominal and pelvic cavities
19
New cards
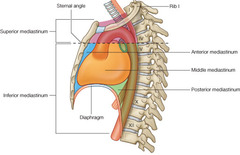
What is the mediastinum?
structure separating the right and left thoracic cavities
space between the lungs
space between the lungs
20
New cards
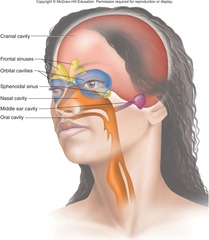
What are the smaller cavities within the head?
oral
nasal
orbital
MIDDLE EAR
nasal
orbital
MIDDLE EAR
21
New cards
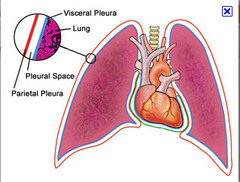
Thoracic(cavity)
chest cavity
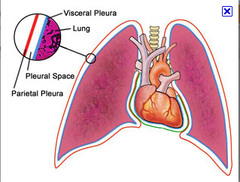
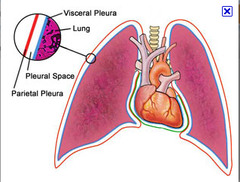
The thoracic cavity is lined with pleura
Parietal pleura lines the cavity while the visceral pleura covers the lungs
- thin layers of serous fluid separates the 2 layers
The thoracic cavity is lined with pleura
Parietal pleura lines the cavity while the visceral pleura covers the lungs
- thin layers of serous fluid separates the 2 layers

22
New cards
pleura
membrane surrounding the lungs and lining the walls of the pleural cavities
23
New cards
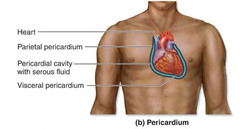
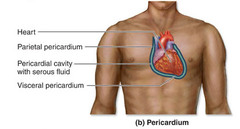
What is the heart surrounded by?
the pericardium
The visceral pericardium covers the heart and the parietal pericardium makes up an outer sac
- serous fluids separate the 2 layers
The visceral pericardium covers the heart and the parietal pericardium makes up an outer sac
- serous fluids separate the 2 layers
24
New cards
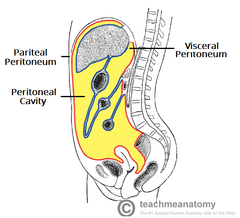
What lines the abdominopelvic cavity?
peritoneum (serous membrane)
The parietal peritoneum lines the wall while the visceral peritoneum covers the organs
The parietal peritoneum lines the wall while the visceral peritoneum covers the organs
25
New cards
What is a visceral membrane?
Membrane that covers the organs in the cavities
on the surface
on the surface
26
New cards
What is a parietal membrane?
A membrane that is farther away from the organ, but lines the cavity.
27
New cards
What is a cavity?
any fluid-filled space within the body
Space between membranes with serous fluid
Space between membranes with serous fluid
28
New cards
What is serous fluid?
It is a fluid within the pleural space that acts as a lubricant to reduce friction during the breathing process.
A watery lubricative fluid
A watery lubricative fluid
29
New cards
What is the pleural?
lungs
30
New cards
What is the pericardial?
heart
31
New cards
What is the peritoneal?
Abdominal organs
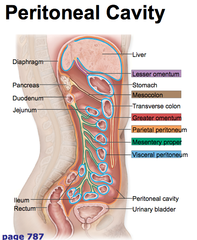
32
New cards
What is the visceral pleural membrane?
The membrane on the surface of the lung
33
New cards
What is the parietal pleural membrane?
Membrane on the OUTSIDE of the lung
34
New cards
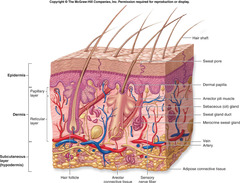
What is the integumentary system composed of?
skin, sweat glands, oil glands, hair, and nails
35
New cards
What does the integumentary system do?
protects the body as a whole from the external environment
covers the body, senses changes outside of the body, and helps the body to regulate temperature
covers the body, senses changes outside of the body, and helps the body to regulate temperature
36
New cards
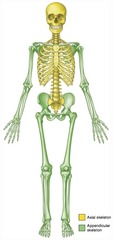
What is the skeletal system composed of?
bones, cartilages, joints, ligaments
37
New cards
What does the skeletal system do?
supports and protects tissues, stores calcium and minerals, forms blood cells
38
New cards
What is the muscular system composed of?
muscles and tendons
39
New cards
What does the muscular system do?
Allows manipulation of the environment, locomotion, and facial expression. Maintains posture, and produces heat.
40
New cards
What does the nervous system consist of?
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors
41
New cards
What does the nervous system do?
controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli
42
New cards
What does the endocrine system consist of?
glands that secrete hormones
43
New cards
What does the endocrine system do?
Assists the nervous system in homeostasis and plays important roles in growth and sexual maturation
Helps to integrate metabolic functions
Helps to integrate metabolic functions
44
New cards
What is the cardiovascular system composed of?
heart, blood vessels, blood
45
New cards
What does the cardiovascular system do?
via the blood, distributes oxygen and nutrients to all body cells and delivers wastes and carbon dioxide to deposal organs
46
New cards
What does the lymphatic system consist of?
lymph nodes, lymph vessels that carry lymph a clear fluid rich in antibodies), the spleen, the thymus, and the tonsils.
47
New cards
What does the lymphatic system do?
1. removes excess fluids and waste products from the body's tissues
2. helps the immune system fight infection
2. helps the immune system fight infection
48
New cards
What does the digestive system consist of?
mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines, and accessory organs
49
New cards
What does the digestive system do?
takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and eliminates unabsorbed matter (feces)
50
New cards
What does the respiratory system consist of?
lungs and air passages
51
New cards
What does the respiratory system do?
Supplies the body with oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide waste
52
New cards
What does the urinary system consist of?
kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
53
New cards
What does the urinary system do?
It eliminates metabolic waste from the body, maintains appropriate levels of water; regulates the acid base balance (pH), blood pressure, and red blood cell production
54
New cards
What does the reproductive system do?
produces offspring/new organisms
55
New cards
What does the male reproductive system consist of?
testes, accessory organs, and vessels that conduct sperm to the penis
56
New cards
What does the female reproductive system consist of?
Ovaries, uterine tube, uterus, vagina, and external genetalia
also houses developing offspring
also houses developing offspring