Unit 9: Coastlines- Beaches and Estuaries
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Anoxic
a condition where the water environment is depleted of dissolved oxygen
Where do anoxic conditions often occur?
Anoxic conditions often occur in deep waters, coastal areas with high organic matter (like algae), etc.
Anaerobic
processes, organisms, or environments that exist or function without the presence of oxygen
Anthropogenic
any process, activity, or effect in the ocean that is caused by or influenced by human activities (eg. introduction of non-native species)
Bar-Built Estuary
a type of estuary formed when sandbars or barrier islands built up by ocean currents and waves create a barrier between the ocean and a river or stream mouth, partially enclosing the water behind them
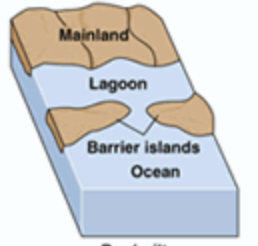
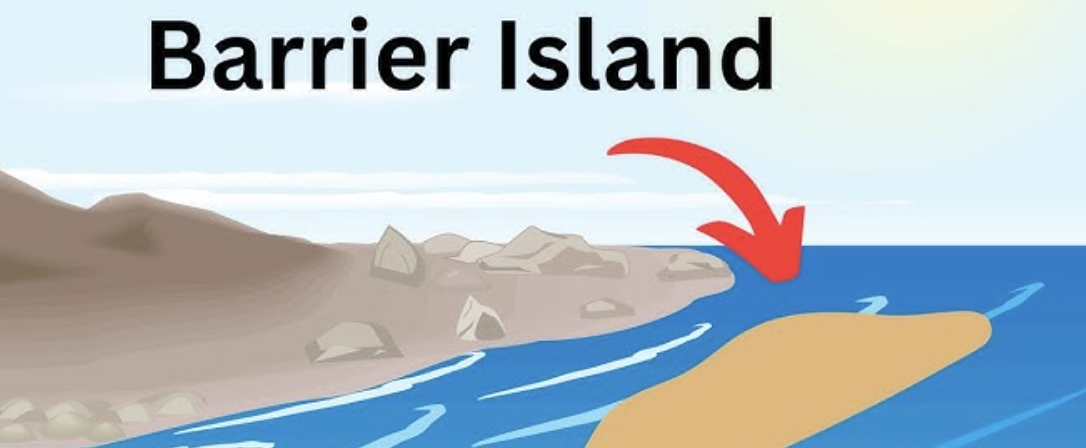
Barrier Beach
a long, narrow, sand or shingle ridge parallel to the shoreline, separated from the mainland by a lagoon or estuary
Biomagnification
the process where the concentration of a substance, like a pollutant, increases as it moves up the food chain (eg. predatory fish, like sharks, accumulate higher concentrations of pollutants than smaller fish)
Brackish
water that contains a higher concentration of salt than freshwater but not as much as saltwater (usually where rivers and oceans meet, like estuaries)
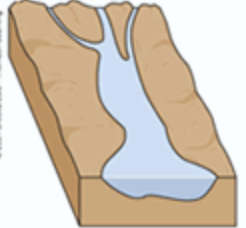
Coastal Plain Estuary
an estuary formed when rising sea levels flood existing river valleys
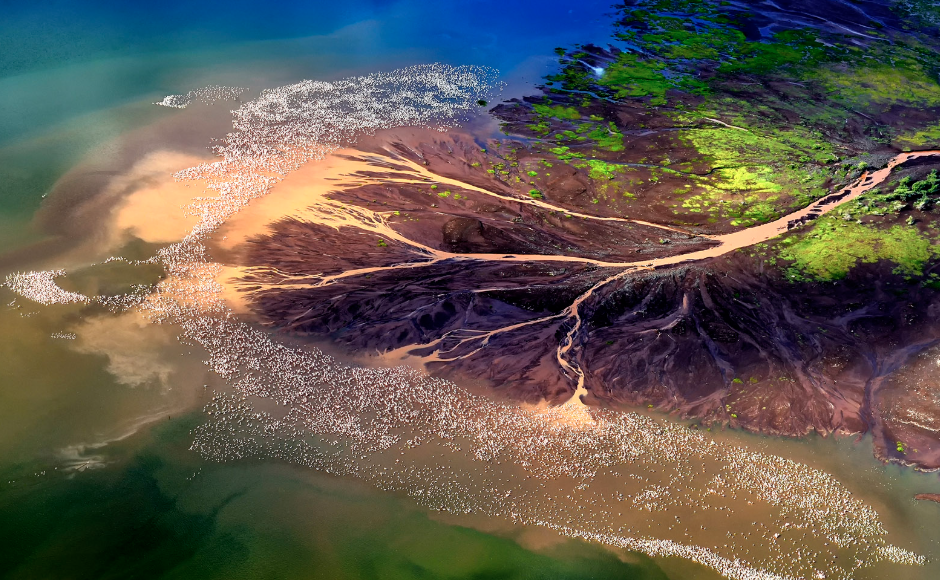
Delta
a landform, often triangular, that forms where a river enters a sea or lake, depositing sediment
Detritus
dead organic matter, including the bodies or fragments of dead organisms and fecal material, that accumulates in the water column or on the seafloor (helps for food and nutrition cycle)
Dissolved Oxygen (DO)
the amount of oxygen gas that is present in water (marine organisms use it for respiration)
Estuary
a semi-enclosed coastal body of water where freshwater from rivers and streams mixes with saltwater from the ocean
Euryhaline
able to tolerate a wide range of salinity
Eutrophication
the excessive enrichment of a marine ecosystem with nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, leading to an overgrowth of algae and other aquatic plants (can lead to things like a depletion of oxygen for organisms)
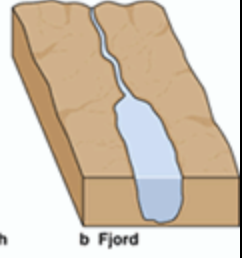
Fjords Estuary
a type of estuary characterized by being formed in a deep, U-shaped basin carved by glaciers, often with a shallow sill or submerged ridge near the mouth
Halophytes
a plant adapted to survive and thrive in highly saline environments
Isohaline
areas in the water that have equal salt concentrations, or salinities
Marginal Areas
ocean regions that connect coastal zones to the open ocean (found as indentations in continental landmasses and often separated by something like a peninsula)
Megalopa
a crucial developmental stage in the life cycle of certain crustaceans, particularly decapods (crabs) , that occurs after the larval stages, such as nauplius and zoea

NERRS
NERRS stands for Natonal Estuarine Research Reserve System.
Panne
a shallow depression in a salt marsh where the marsh is poorly drained. (high salinity) (halophytes live here)
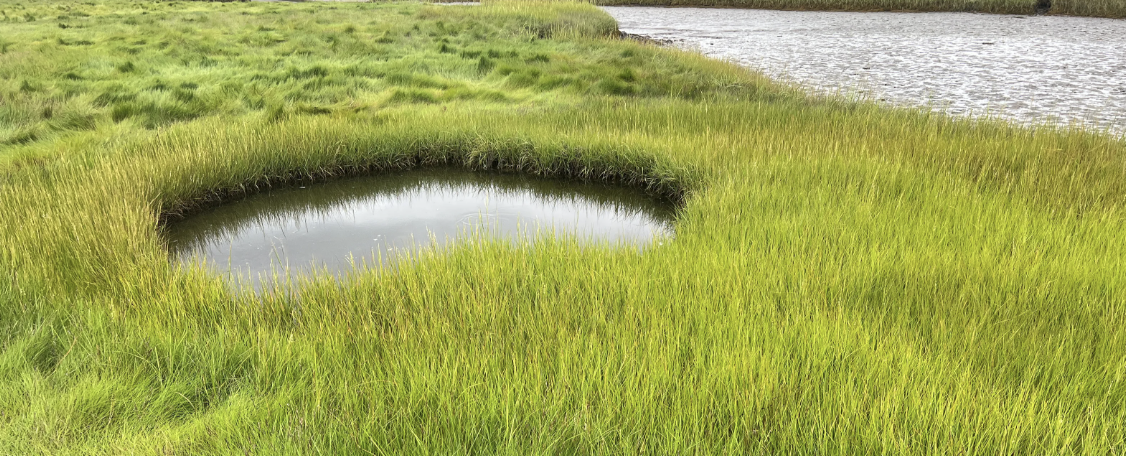

Pneumatophores
specialized aerial roots of mangrove trees that allow for respiration in waterlogged soil.
Prop Roots
a root that grows from and supports the stem above the ground in plants such as mangroves
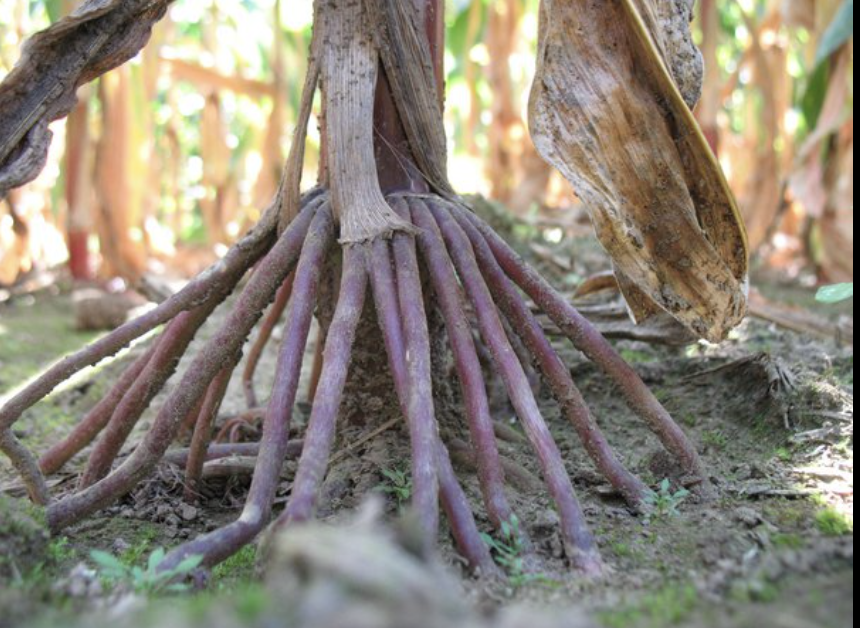

Propagules
any structure used by an organism to disperse to new areas or to the next stage of its life cycle (eg. seeds or algae spores)
Run Off
the flow of water, often contaminated with pollutants, from land into a sea or other body of water, typically due to rainfall or snowmelt that exceeds the soil's absorption capacity
Salt Marsh
coastal wetlands that are flooded and drained by salt water brought in by the tides
Salt Wedge
wedge-shaped layer of dense saltwater that moves upstream in an estuary beneath a layer of less dense freshwater (river volume>>tidal volume)
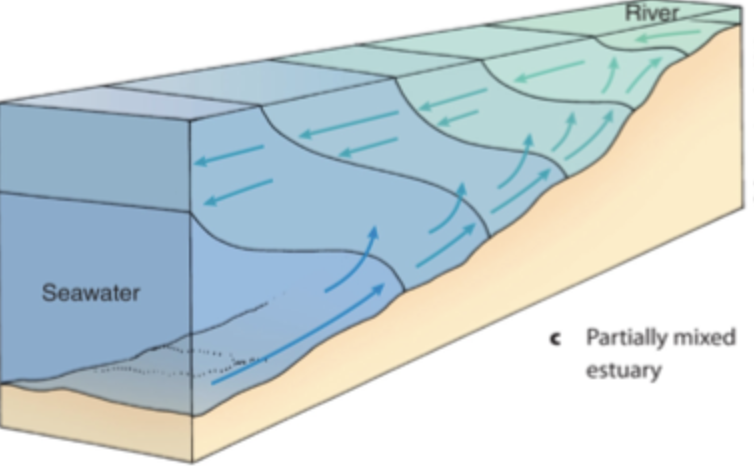
Slightly stratified
saltwater and freshwater mix at all depths; however, the lower layers of water typically remain saltier than the upper layers
Stenohaline
organisms, typically fish, that have a limited tolerance to salinity changes in their environment
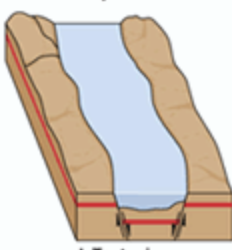
Tectonic estuary
created when a major crack or a large land sink in the Earth, often caused by earthquakes, produced a basin below sea level that filled with water
Tidal Creek
narrow inlet or estuary that is affected by the ebb and flow of ocean tide
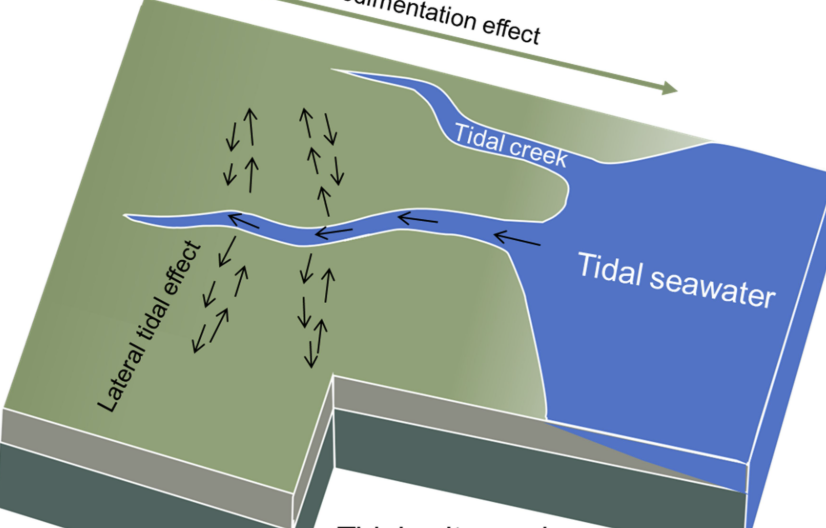
Ebb and flow
Ebb is high to low tide and flow is low to high tide
Vertically mixed
a situation where water in a body of water is evenly mixed from surface to bottom, meaning there's no significant stratification based on salinity or density (usually meaning strong tides but low river flow relative to tidal volume)
Wrack
natural organic material, primarily seaweed and seagrass, that is washed up on beaches by tides, waves, and wind
Zoea
a free-swimming larval stage of many decapod crustaceans, particularly crabs and lobsters
Zooplankton
tiny, animal-like organisms that drift or are carried by currents in the water (feed off of phytoplankton) (a food source to many other organisms)
Active coast
those located near a plate boundary, and thus in close proximity to tectonic activity
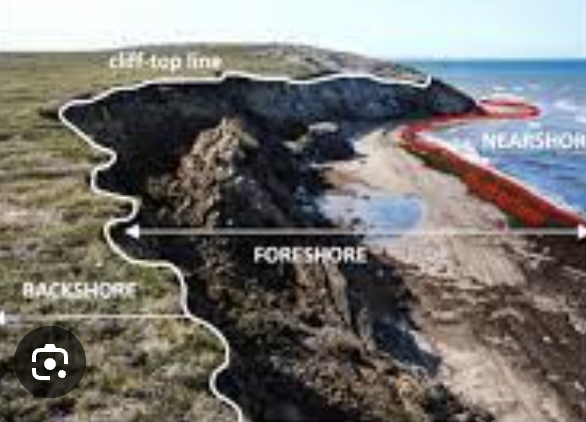
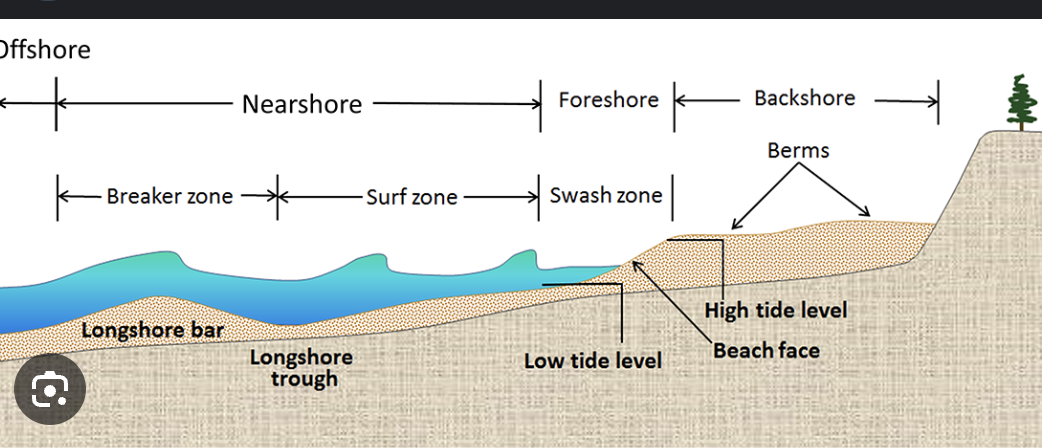
Backshore
the zone of the shore or beach above the high-water line, acted upon only by severe storms or exceptionally high tides
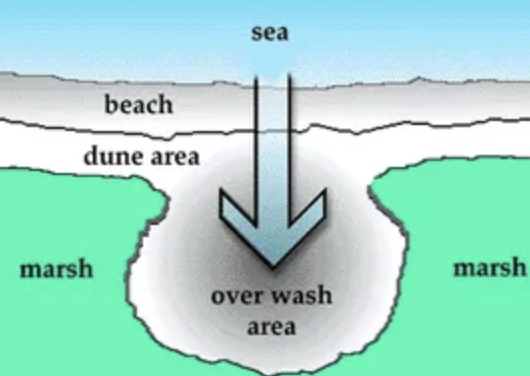
Barrier flat
formed by sediments that get pushed through the dune system by storms, such as hurricanes
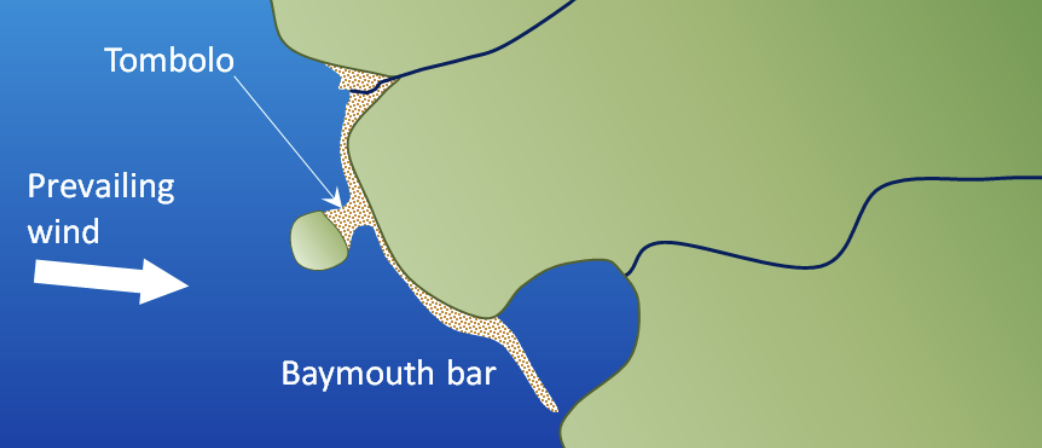
Bay mouth barrier
a sandbar that stretches across the mouth of a bay, effectively separating it from the open ocean or sea
Beach renourishment
the adding of sediment onto or directly adjacent to an eroding beach
Berm
terrace of a beach that has formed in the backshore, above the water level at high tide
Breakwaters
an offshore shore-parallel structure that “breaks” waves, reducing the wave energy reaching the beach and fostering sediment accretion between the beach and the breakwater (eg. a jetty)
Fault coasts
a coastline characterized by a fault line, where the land has been displaced along a fracture or crack in the Earth's crust
Foreshore
the part of a shore between high- and low-water marks, or between the water and cultivated or developed land
Groins
shore-perpendicular coastal engineering structure
Longshore drift
the transport of sediment (sand, pebbles, etc.) along a coastline due to waves approaching the shore at an angle
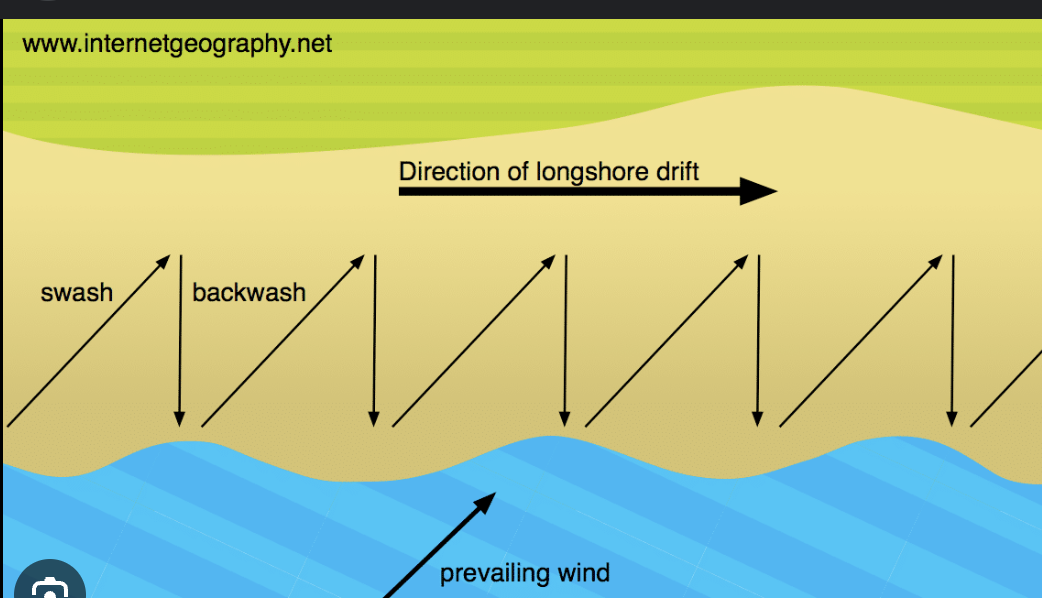
Low tide terrace
a flat, gently sloping area on a beach that is exposed at low tide
Passive coast
a continental margin located far from plate boundaries, characterized by a wider, flatter continental shelf and slope, and features like wide beaches and barrier islands
Primary coast
coast shaped by processes like erosion, deposition, and tectonic activity.
River dominated
very low wave energy and a very small tidal range
Secondary coast
marine-deposition coasts where sea movement causes accumulation of ocean sediments in a single place (eg. barrier island)
Tombolo
formed when a spit connects the mainland coast to an island

Know this
A high river flow relative to the tidal volume can lead to stratification, while a low river flow and strong tidal currents are more likely to result in a well-mixed estuary
Know this
Highly stratified R>V
Slightly stratified R<V
Vertically mixed R«V