PY 131 Midterm 3 Study Guide
0.0(0)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/29
Earn XP
Last updated 3:58 AM on 4/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
Explain Frequency, Period, Wavelength, and Wave Speed.
**Frequency:** Number of waves passing a point in a given time. Frequency is a term used to describe the number of waves that pass a point in a given time. It is an important concept in the study of waves and is measured in hertz (Hz). The higher the frequency, the more waves that pass by in a given amount of time.
**Period:** Time taken for one complete wave cycle. Period is another important concept in wave theory. It is the time taken for one complete wave cycle to occur. This is measured in seconds and is inversely proportional to frequency. In other words, the higher the frequency, the shorter the period.
**Wavelength:** Distance between two consecutive points of similar phase. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points of similar phase. This is an important concept in wave theory because it is used to measure the distance between waves. The wavelength is measured in meters and is inversely proportional to frequency. This means that the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength.
**Wave Speed**: Rate at which a wave travels through a medium. Wave speed is the rate at which a wave travels through a medium. This is an important concept in wave theory because it determines how fast a wave will travel from one point to another. The wave speed is measured in meters per second and is dependent on the properties of the medium through which the wave is traveling. For example, sound waves travel at different speeds through different materials, such as air and water.
**Period:** Time taken for one complete wave cycle. Period is another important concept in wave theory. It is the time taken for one complete wave cycle to occur. This is measured in seconds and is inversely proportional to frequency. In other words, the higher the frequency, the shorter the period.
**Wavelength:** Distance between two consecutive points of similar phase. Wavelength is the distance between two consecutive points of similar phase. This is an important concept in wave theory because it is used to measure the distance between waves. The wavelength is measured in meters and is inversely proportional to frequency. This means that the higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength.
**Wave Speed**: Rate at which a wave travels through a medium. Wave speed is the rate at which a wave travels through a medium. This is an important concept in wave theory because it determines how fast a wave will travel from one point to another. The wave speed is measured in meters per second and is dependent on the properties of the medium through which the wave is traveling. For example, sound waves travel at different speeds through different materials, such as air and water.
2
New cards
Distinguish between Longitudinal and Transverse Waves.
Type of mechanical waves that move parallel to the direction of the wave's energy transfer are called **longitudinal** waves. Type of mechanical waves that move perpendicular to the direction of the wave's energy transfer are called **transverse** waves.
3
New cards
Explain Wave Interference.
When two waves meet, they interact and combine to create a new wave. This is called wave interference. If the waves are in phase, they will reinforce each other, creating a larger wave. If they are out of phase, they will cancel each other out, creating a smaller or no wave.
4
New cards
Describe the Doppler Effect.
The Doppler Effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is observed in sound and light waves and causes a shift in pitch or color.
5
New cards
Describe the sources of sound waves.
The origins of sound waves are vibrations or disturbances that occur in a medium. These disturbances can be caused by a variety of sources such as musical instruments, human voices, animals, and machines. The sound waves then travel through the medium, which can be air, water, or solids, until they reach our ears and are perceived as sound.
6
New cards
Compare the speed of sound through different mediums.
The speed of sound varies significantly depending on the medium through which it travels. In general, sound travels faster through denser materials, such as solids and liquids, than through gases.
For example, in dry air at room temperature, sound travels at approximately 343 meters per second (or 1,125 feet per second). In comparison, sound travels through water at around 1,482 meters per second (4,830 feet per second), and through iron at around 5,120 meters per second (16,800 feet per second).
The speed of sound can also be affected by other factors, such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. In general, as the temperature of a medium increases, the speed of sound also increases, while increasing pressure tends to increase the speed of sound as well.
For example, in dry air at room temperature, sound travels at approximately 343 meters per second (or 1,125 feet per second). In comparison, sound travels through water at around 1,482 meters per second (4,830 feet per second), and through iron at around 5,120 meters per second (16,800 feet per second).
The speed of sound can also be affected by other factors, such as temperature, pressure, and humidity. In general, as the temperature of a medium increases, the speed of sound also increases, while increasing pressure tends to increase the speed of sound as well.
7
New cards
Explain the reflection of sound waves.
Reflection of sound waves occurs when a sound wave encounters a surface and bounces back towards the source. The angle of incidence (the angle at which the sound wave hits the surface) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle at which the sound wave bounces back).
When a sound wave travels through a medium, it vibrates the particles of the medium in a particular direction, which then propagate in a wave-like pattern. When the sound wave reaches a boundary between two different media, some of the energy of the sound wave is reflected back into the original medium, while the rest of it is transmitted into the new medium. The amount of reflection and transmission depends on the difference in the acoustic impedance (a measure of the ability of a material to transmit sound waves) between the two media.
Reflection of sound waves is important in many everyday applications, such as echoes in a room, soundproofing materials, and the use of sonar to detect objects in water.
When a sound wave travels through a medium, it vibrates the particles of the medium in a particular direction, which then propagate in a wave-like pattern. When the sound wave reaches a boundary between two different media, some of the energy of the sound wave is reflected back into the original medium, while the rest of it is transmitted into the new medium. The amount of reflection and transmission depends on the difference in the acoustic impedance (a measure of the ability of a material to transmit sound waves) between the two media.
Reflection of sound waves is important in many everyday applications, such as echoes in a room, soundproofing materials, and the use of sonar to detect objects in water.
8
New cards
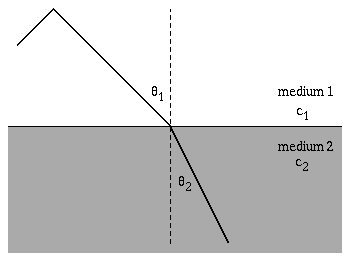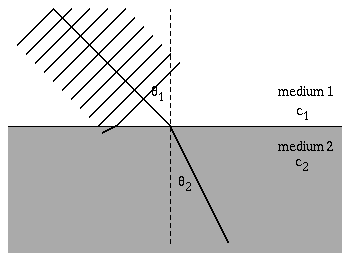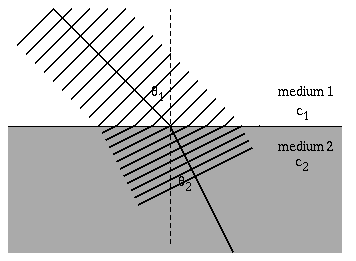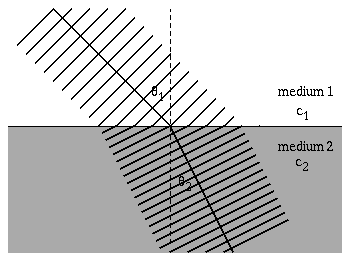
Diagram the refraction of sound waves.
When a sound wave travels through a medium such as air or water, it can encounter a boundary where the properties of the medium change, such as the density or temperature. When this happens, the sound wave can change direction, a process known as refraction.
The amount of refraction depends on the angle at which the sound wave hits the boundary and the difference in properties between the two media. If the sound wave hits the boundary at a right angle, it will continue straight through. However, if it hits at an angle, it will bend either towards or away from the normal line perpendicular to the surface of the boundary, depending on the relative densities of the two media.
This change in direction can also cause a change in the speed and wavelength of the sound wave. As a result, the frequency and pitch of the sound may also be affected.
The amount of refraction depends on the angle at which the sound wave hits the boundary and the difference in properties between the two media. If the sound wave hits the boundary at a right angle, it will continue straight through. However, if it hits at an angle, it will bend either towards or away from the normal line perpendicular to the surface of the boundary, depending on the relative densities of the two media.
This change in direction can also cause a change in the speed and wavelength of the sound wave. As a result, the frequency and pitch of the sound may also be affected.
9
New cards
Describe Forced Vibrations, Natural Frequency, Resonance, and Interference
**Forced vibrations** occur when an external force is applied to a system causing it to vibrate at a frequency different from its natural frequency.
**Natural frequency** is the frequency at which an object vibrates when it is disturbed without any external force.
**Resonance** occurs when a system vibrates at its natural frequency due to the presence of an external force or vibration that matches its natural frequency. This can result in a large amplitude of vibration, and it can cause damage if the amplitude becomes too large.
**Interference** occurs when two or more waves interact with each other. Constructive interference occurs when the waves add up to form a larger wave, while destructive interference occurs when the waves cancel each other out.
**Natural frequency** is the frequency at which an object vibrates when it is disturbed without any external force.
**Resonance** occurs when a system vibrates at its natural frequency due to the presence of an external force or vibration that matches its natural frequency. This can result in a large amplitude of vibration, and it can cause damage if the amplitude becomes too large.
**Interference** occurs when two or more waves interact with each other. Constructive interference occurs when the waves add up to form a larger wave, while destructive interference occurs when the waves cancel each other out.
10
New cards
Calculate the number of beats per second between two different frequencies.
To calculate the number of beats per second between two different frequencies, you can use the following formula: Number of beats per second = |f1 - f2| where f1 and f2 are the frequencies of the two sound waves.
Here, the vertical bars indicate absolute value, which means the result will always be a positive number.
Here, the vertical bars indicate absolute value, which means the result will always be a positive number.
11
New cards
Illustrate and explain the forces between different types of charges.
There are two types of charges: positive and negative. The forces between charges are determined by Coulomb's Law, which states that the force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The force between charges of the same sign (both positive or both negative) is repulsive, meaning that they push away from each other. The force between charges of opposite signs (positive and negative) is attractive, meaning that they pull toward each other.
The strength of the force is proportional to the magnitude of the charges. For example, if two charges have a magnitude of 1 Coulomb and 2 Coulombs, respectively, the force between them will be twice as strong as the force between two charges with a magnitude of 1 Coulomb.
The strength of the force is also inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. This means that as the distance between the charges increases, the force between them decreases rapidly.
The force between charges of the same sign (both positive or both negative) is repulsive, meaning that they push away from each other. The force between charges of opposite signs (positive and negative) is attractive, meaning that they pull toward each other.
The strength of the force is proportional to the magnitude of the charges. For example, if two charges have a magnitude of 1 Coulomb and 2 Coulombs, respectively, the force between them will be twice as strong as the force between two charges with a magnitude of 1 Coulomb.
The strength of the force is also inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges. This means that as the distance between the charges increases, the force between them decreases rapidly.
12
New cards
Describe Coulomb's Law and compare it with the Universal Law of Gravity.
Coulomb's law describes the electrostatic force between two charged particles and states that the force is directly proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. In contrast, the Universal Law of Gravity describes the gravitational force between two masses and states that the force is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. Both laws are similar in that they describe inverse square relationships between the forces and the distance between the interacting particles or masses, but they differ in that Coulomb's law applies to charged particles, while the Universal Law of Gravity applies to masses.
13
New cards
Distinguish between Conductors and Insulators.
In short, conductors are materials that allow electrons to move freely through them, while insulators are materials that resist the flow of electrons. Conductors typically have low resistance, meaning they allow electric current to flow easily, while insulators have high resistance and do not allow electric current to flow easily. Examples of conductors include metals like copper and aluminum, while examples of insulators include rubber and glass.
14
New cards
Describe two different ways of charging a conductor
Two different ways of charging a conductor are:
1. Charging by conduction: In this method, a charged object is brought in contact with a neutral conductor, allowing electrons to flow from one object to another until they reach equilibrium. For instance, if a negatively charged rod is touched to a neutral conductor, electrons will flow from the rod to the conductor until they reach the same charge.
2. Charging by induction: In this method, a charged object is brought near a neutral conductor, which causes the charges in the conductor to redistribute themselves. For example, if a negatively charged rod is brought close to a neutral conductor, the electrons in the conductor will be attracted to the rod and move away from the side nearest to the rod, resulting in a positively charged side closest to the rod and a negatively charged side farthest from the rod.
1. Charging by conduction: In this method, a charged object is brought in contact with a neutral conductor, allowing electrons to flow from one object to another until they reach equilibrium. For instance, if a negatively charged rod is touched to a neutral conductor, electrons will flow from the rod to the conductor until they reach the same charge.
2. Charging by induction: In this method, a charged object is brought near a neutral conductor, which causes the charges in the conductor to redistribute themselves. For example, if a negatively charged rod is brought close to a neutral conductor, the electrons in the conductor will be attracted to the rod and move away from the side nearest to the rod, resulting in a positively charged side closest to the rod and a negatively charged side farthest from the rod.
15
New cards
Explain Electric Potential and Voltage.
**Electric potential** is the amount of electric potential energy that a unit charge has at a particular point in an electric field. It is a scalar quantity that is measured in volts. The electric potential at a point is the work done per unit charge in bringing a positive charge from infinity to that point. Voltage, on the other hand, is the potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. It is a measure of the amount of energy required to move a unit of electric charge from one point to another in the circuit. **Voltage** is measured in volts, and it is the driving force that pushes electric current through a circuit. A voltage difference across a conductor causes a flow of electric charge, known as an electric current.
16
New cards
Describe Electric Energy Storage in Capacitors.
Electric energy storage in capacitors occurs due to the accumulation of charge on two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. When a voltage is applied to the capacitor, one plate becomes positively charged while the other becomes negatively charged. This creates an electric field between the plates, and energy is stored in the electric field. The amount of energy stored in a capacitor is proportional to the capacitance, which is determined by the size of the plates and the distance between them. Capacitors can store electric energy for short periods of time and can be used in a variety of electronic applications such as filters, timing circuits, and power supplies.
17
New cards
Explain the flow of charge as Electric Current.
Electric current is the flow of electric charge through a material. The charge can be carried by moving electrons in a wire, ions in a liquid or gas, or even by the movement of holes in a semiconductor. The amount of current is measured in amperes (A), and it represents the rate at which charge flows through a circuit. The direction of the current is defined as the direction of flow of positive charge, even though it is actually the negative electrons that are moving in the opposite direction. Electric current is a fundamental concept in electricity and is essential for the operation of electrical devices and systems.
18
New cards
Describe Electrical Resistance and Ohm’s Law
**Electrical resistance** is the measure of how much a material opposes the flow of electric current.
**Ohm's law** states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. This relationship is characterized by the equation I = V/R, where I is the current, V is the voltage, and R is the resistance. Ohm's law can be used to calculate the voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit.
**Ohm's law** states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. This relationship is characterized by the equation I = V/R, where I is the current, V is the voltage, and R is the resistance. Ohm's law can be used to calculate the voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit.
19
New cards
Distinguish between Direct and Alternating Current.
Direct current (DC) is a type of electrical current that flows in one direction only, while alternating current (AC) is a type of electrical current that periodically reverses its direction of flow. In DC, the electric charge moves continuously in the same direction, while in AC, the electric charge reverses direction periodically, typically 50 or 60 times per second. DC is commonly used in batteries and electronic devices, while AC is used in homes and businesses to power appliances and lighting.
20
New cards
Predict current flow through Series and Parallel Circuits using a provided model.
In a **series circuit**, the current flow remains the same throughout all components, while the voltage drops across each component. Therefore, if one component fails or is disconnected, the entire circuit is disrupted.
In a **parallel circuit**, the voltage remains the same across all components, while the current is divided among the branches. Therefore, if one component fails or is disconnected, the current can still flow through the other branches.
To predict current flow through series and parallel circuits, one can use Ohm's Law (I = V/R), where I is current, V is voltage, and R is resistance. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances, so the current can be calculated by dividing the total voltage by the total resistance (I = Vtotal/Rtotal). In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance, so the current can be calculated by adding the currents in each branch (I = I1 + I2 + I3 + ...).
In a **parallel circuit**, the voltage remains the same across all components, while the current is divided among the branches. Therefore, if one component fails or is disconnected, the current can still flow through the other branches.
To predict current flow through series and parallel circuits, one can use Ohm's Law (I = V/R), where I is current, V is voltage, and R is resistance. In a series circuit, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances, so the current can be calculated by dividing the total voltage by the total resistance (I = Vtotal/Rtotal). In a parallel circuit, the total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance, so the current can be calculated by adding the currents in each branch (I = I1 + I2 + I3 + ...).
21
New cards
Explain Magnetic Poles, Fields, and Domains.
**Magnetic poles** refer to the two ends of a magnet: the north pole and the south pole.
**A magnetic field** is the area around a magnet where its magnetic force is exerted. It is strongest at the poles and weaker farther away.
**Magnetic domains** are tiny regions in a magnetic material where the atoms are aligned with each other, creating a magnetic field. When these domains are aligned, the material becomes magnetized.
The direction of a magnetic field is defined by the direction of the force it would exert on a north pole if placed in the field. Like poles (north and north, or south and south) repel each other, while opposite poles (north and south) attract.
**A magnetic field** is the area around a magnet where its magnetic force is exerted. It is strongest at the poles and weaker farther away.
**Magnetic domains** are tiny regions in a magnetic material where the atoms are aligned with each other, creating a magnetic field. When these domains are aligned, the material becomes magnetized.
The direction of a magnetic field is defined by the direction of the force it would exert on a north pole if placed in the field. Like poles (north and north, or south and south) repel each other, while opposite poles (north and south) attract.
22
New cards
Explain the relationship between Electric Currents and Magnetic Fields.
The flow of **electric current** through a wire produces a magnetic field around the wire. The strength of the magnetic field depends on the magnitude and direction of the current flow.
Similarly, a changing **magnetic field** can induce an electric current in a nearby conductor. This relationship between electric currents and magnetic fields is known as electromagnetic induction and forms the basis of many electrical technologies, including generators, transformers, and motors.
The interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields is governed by the laws of electromagnetism, including Ampere's law, Faraday's law of induction, and Lenz's law.
Similarly, a changing **magnetic field** can induce an electric current in a nearby conductor. This relationship between electric currents and magnetic fields is known as electromagnetic induction and forms the basis of many electrical technologies, including generators, transformers, and motors.
The interaction between electric currents and magnetic fields is governed by the laws of electromagnetism, including Ampere's law, Faraday's law of induction, and Lenz's law.
23
New cards
Explain how electromagnets work.
**Electromagnets** are created by passing an electric current through a coil of wire. The wire becomes magnetized and produces a magnetic field around it. The strength of the magnetic field can be increased by increasing the current, the number of turns in the coil, or by using a magnetic core made of a material like iron. Electromagnets are used in many applications, including electric motors, generators, MRI machines, and in various types of industrial equipment. By controlling the electric current passing through the coil, the strength and polarity of the magnetic field can be changed, allowing for precise control in a wide range of applications.
24
New cards
Describe the Magnetic Force on Charged Particles and Current Carrying Wires.
The **magnetic force** on a charged particle moving in a magnetic field is perpendicular to both the direction of motion and the magnetic field. The force is proportional to the charge of the particle, its velocity, and the strength of the magnetic field. The direction of the force can be determined using the right-hand rule.
Similarly, a **current-carrying wire** in a magnetic field experiences a force that is perpendicular to both the direction of the current and the magnetic field. The force is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field, the current in the wire, and the length of the wire in the field. The direction of the force can also be determined using the right-hand rule.
Similarly, a **current-carrying wire** in a magnetic field experiences a force that is perpendicular to both the direction of the current and the magnetic field. The force is proportional to the strength of the magnetic field, the current in the wire, and the length of the wire in the field. The direction of the force can also be determined using the right-hand rule.
25
New cards
Describe the Earth’s Magnetic Field and Magnetic Poles.
The Earth has a **magnetic field** that extends from its core to the space surrounding it, known as the magnetosphere. The magnetic field is created by the motion of molten iron in the outer core of the Earth. The magnetic field is not static, but instead changes over time, and periodically reverses its polarity.
The **magnetic poles** of the Earth are the locations on the Earth's surface where the magnetic field lines are vertical. The North Magnetic Pole is currently located in northern Canada and is moving towards Siberia, while the South Magnetic Pole is located off the coast of Antarctica.
The Earth's magnetic field plays a critical role in protecting the planet from the solar wind, a stream of charged particles that flows from the Sun. The magnetic field deflects the solar wind, creating the auroras and protecting the Earth's atmosphere from erosion by the solar wind.
The **magnetic poles** of the Earth are the locations on the Earth's surface where the magnetic field lines are vertical. The North Magnetic Pole is currently located in northern Canada and is moving towards Siberia, while the South Magnetic Pole is located off the coast of Antarctica.
The Earth's magnetic field plays a critical role in protecting the planet from the solar wind, a stream of charged particles that flows from the Sun. The magnetic field deflects the solar wind, creating the auroras and protecting the Earth's atmosphere from erosion by the solar wind.
26
New cards
Describe Electromagnetic Induction.
**Electromagnetic induction** is the process of generating an electromotive force (EMF) in a conductor by varying the magnetic field around it. This phenomenon was first discovered by Michael Faraday in the 19th century. When a magnetic field around a conductor changes, it induces an EMF, which causes an electric current to flow in the conductor if there is a complete circuit. This process is the basis for electrical generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The amount of EMF induced is proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic field and the number of turns in the conductor. Faraday's law of induction states that the EMF induced in a closed loop is equal to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the loop. This law forms the basis of many important technologies, including transformers, motors, and generators.
27
New cards
Define Faraday’s Law.
Faraday's Law is a fundamental principle of electromagnetism that states that a changing magnetic field will induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a closed loop of wire. In other words, the rate of change of magnetic flux through a loop of wire is directly proportional to the magnitude of the induced EMF in the wire. This law is important for understanding the behavior of electric generators and motors, as well as many other applications of electromagnetism.
28
New cards
Explain the benefits of high voltage power lines.
**High voltage power lines** are used to transmit electrical power over long distances with minimal energy loss. This is because high voltage results in lower current, and lower current means less heat generated in the transmission lines due to resistance. This reduces the amount of energy lost as heat, making the transmission more efficient. Additionally, high voltage power lines are often used to connect different power grids or regions, allowing for more efficient distribution of power across larger areas.
29
New cards
Describe how transformers work and their benefits (both step-up and step-down).
**Transformers** are electrical devices used to change the voltage of an alternating current (AC) power supply. They work based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field in one coil induces a voltage in a nearby coil.
In a **step-up transformer,** the output voltage is greater than the input voltage. This is achieved by having more turns in the output (secondary) coil than in the input (primary) coil.
Conversely, in a **step-down transformer,** the output voltage is less than the input voltage, and the output coil has fewer turns than the input coil.
Transformers are essential in the transmission and distribution of electrical power over long distances. High voltage power lines use step-up transformers to increase the voltage of the electricity transmitted to minimize energy loss due to resistance in the wires. The higher voltage also allows for more efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. At the destination, step-down transformers are used to reduce the voltage to a safer and usable level for homes and businesses.
In a **step-up transformer,** the output voltage is greater than the input voltage. This is achieved by having more turns in the output (secondary) coil than in the input (primary) coil.
Conversely, in a **step-down transformer,** the output voltage is less than the input voltage, and the output coil has fewer turns than the input coil.
Transformers are essential in the transmission and distribution of electrical power over long distances. High voltage power lines use step-up transformers to increase the voltage of the electricity transmitted to minimize energy loss due to resistance in the wires. The higher voltage also allows for more efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. At the destination, step-down transformers are used to reduce the voltage to a safer and usable level for homes and businesses.
30
New cards