Chapter 12: Managing Employee Benefits
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Types of Benefits
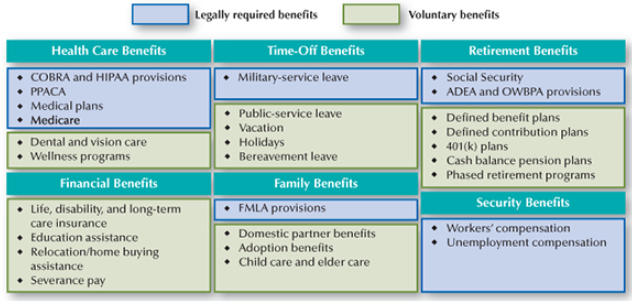
2
New cards
Benefit Design Decisions
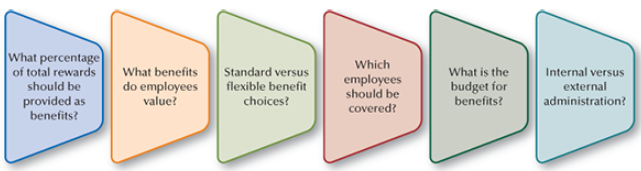
3
New cards
Flexible Benefit Plan
A program that allows employees to select the benefits they prefer from options established by the employer
4
New cards
Adverse Selection
A situation in which only higher-risk employees select and use certain benefits
5
New cards
Open Enrollment
A time when employees can change their participation level in various benefit plans and switch between benefit options
6
New cards
Third-Party Administrators (TPAs)
Vendors that provides enrollment, recordkeeping, and other administrative services to organizations
7
New cards
Self-Service
Technology that allows employees to enroll in and change their benefit choices, track their benefit balances, and submit questions to HR staff members and external benefit providers
8
New cards
Frequently Used Benefit Metrics
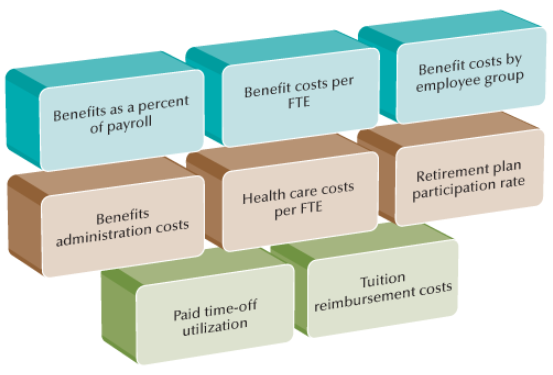
9
New cards
Legally Required Benefits
* **Social Security Act of 1935:** Provides old age, survivor’s, disability, and retirement benefits
* Funded by both employees and employers through a tax on employees’ wages or salaries
* Amount of wages subject to tax is reviewed and increased periodically
* **Medicare:** Government-operated health insurance for Americans aged 65 and above and for some citizens with disabilities
* Funded by a tax on employers and employees
* Long-term viability of funding is in question
* Funded by both employees and employers through a tax on employees’ wages or salaries
* Amount of wages subject to tax is reviewed and increased periodically
* **Medicare:** Government-operated health insurance for Americans aged 65 and above and for some citizens with disabilities
* Funded by a tax on employers and employees
* Long-term viability of funding is in question
10
New cards
Workers’ Compensation
Security benefits provided to workers who are injured on the job
11
New cards
Concepts Under Workers’ Compensation
* **No-Fault Insurance:** Injured worker receives benefits even if the accident was the worker’s fault
* **Exclusive Remedy:** Workers’ compensation benefits are the only benefits injured workers may receive from the employer to compensate for work-related injuries
* **Exclusive Remedy:** Workers’ compensation benefits are the only benefits injured workers may receive from the employer to compensate for work-related injuries
12
New cards
Unemployment Compensation
Established as part of the Social Security Act of 1935. Provides a minimum level of benefits for workers who are out of work. Each state operates its own system, so benefits differ by state
* Out-of-work and actively-looking employees can receive up to 26 weeks of pay at the rate of 50 - 80% of normal pay
* Out-of-work and actively-looking employees can receive up to 26 weeks of pay at the rate of 50 - 80% of normal pay
13
New cards
The 3-Legged Stool of Retirement Income
A model showing the three sources of income to fund an employee’s retirement
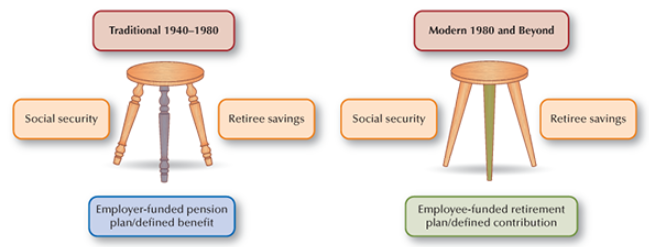
14
New cards
Vesting
A right that gives employees a benefit that cannot be taken away
15
New cards
Portability
A pension plan feature that allows employees to move their retirement benefits from one employer to another
16
New cards
Retirement Plan
A program established and funded by the employer and/or employees to fund employees’ retirement years. Organizations are not required to offer this to employees beyond contributions to Social Security
17
New cards
Defined Benefit Plan
Employees are promised a pension amount based on age and years of service

18
New cards
Defined Contribution Plan
Employer and/or employee makes an annual payment to an employee’s retirement account

19
New cards
401(k) Plan
Allows for a percentage of an employee’s pay to be withheld and invested in a tax-deferred account
* **Auto-enrollment:** Employee contributions are started automatically when an employee is eligible to join the plan
* **Auto-escalation:** Automatic increases of 1% a year
* **Auto-enrollment:** Employee contributions are started automatically when an employee is eligible to join the plan
* **Auto-escalation:** Automatic increases of 1% a year
20
New cards
Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA)
Ensures that private pension plans and other plans governed by this act meet minimum standards. Requires plans to periodically provide participants with information about plan features, funding, and benefit accrual amounts
21
New cards
Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA)
A 1986 amendment to this act states that most employees cannot be forced to retire at a specific age
22
New cards
Older Workers Benefit Protection Act (OWBPA)
Enacted as an amendment to the ADEA. Requires equal treatment for older workers in early retirement or severance situations. Sets specific criteria that must be met if older workers are asked to sign waivers promising not to sue for age discrimination in exchange for severance benefits during layoffs
23
New cards
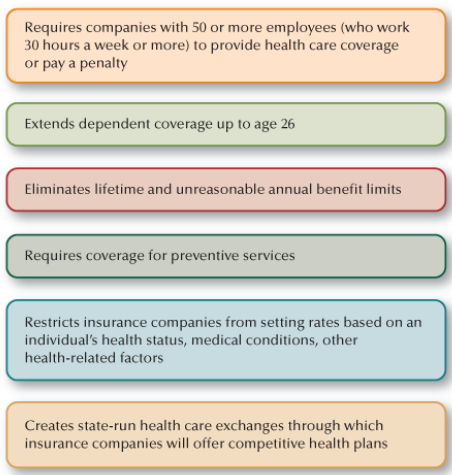
Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA)
Provisions were phased in over several years, culminating in universal coverage in 2014. Includes many important provisions intended to provide affordable health care for all citizens
24
New cards
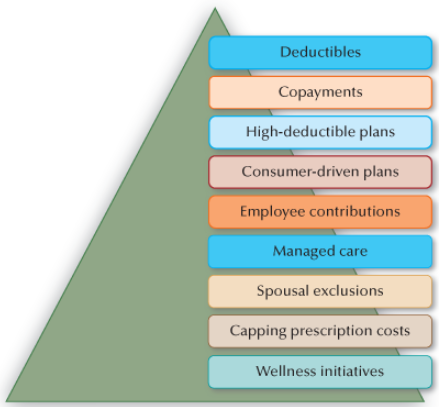
Health Care Cost Control Measures
25
New cards
Deductible
Money paid by an insured individual before a health plan pays for medical expenses
26
New cards
Copayments
Portion of medical expenses paid by an insured individual for medical treatment
27
New cards
Health Spending Account
A tax-favored savings plan to provide funds for paying medical expenses. These plans are subject to a number of regulations and limits and are available only to individuals in high-deductible health care plans
28
New cards
Consumer-Driven Health (CDH) Plan
A health plan that provides employer financial contributions to employees to help cover their health-related expenses
29
New cards
Managed Care
Consists of approaches that monitor and reduce medical costs through restrictions and market system alternatives. Emphasize primary and preventive care, the use of specific providers that charge lower prices, restrictions on certain kinds of treatment, and prices negotiated with hospitals and physicians
30
New cards
Well-Being
The overall level of employee physical, mental, financial, and social wellness
31
New cards
COBRA Provisions
Stands for Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act. Requires that most employers with 20 or more full-time and/or part-time employees offer extended health care coverage to certain groups of plan participants. These qualified beneficiaries are as follows:
* Employees who voluntarily quit or are terminated
* Widowed or divorced spouses and dependent children of former or current employees
* Retirees and their spouses and dependent children whose health care coverage ends
* Any child who is born or adopted by a covered employee
* Other individuals involved in the plan such as independent contractors and agents/directors
* Employees who voluntarily quit or are terminated
* Widowed or divorced spouses and dependent children of former or current employees
* Retirees and their spouses and dependent children whose health care coverage ends
* Any child who is born or adopted by a covered employee
* Other individuals involved in the plan such as independent contractors and agents/directors
32
New cards
Qualifying Events
An event that causes a plan participant to lose group health benefits
* Examples: reduction in work hours, divorce, death
* Examples: reduction in work hours, divorce, death
33
New cards
HIPPA Provisions
Allow employees to switch their health insurance plans when they change employers. Require employers to:
* Provide privacy notices to employees
* Carefully store sensitive employee personal information
* Not disclose employee health information without authorization
* Provide privacy notices to employees
* Carefully store sensitive employee personal information
* Not disclose employee health information without authorization
34
New cards
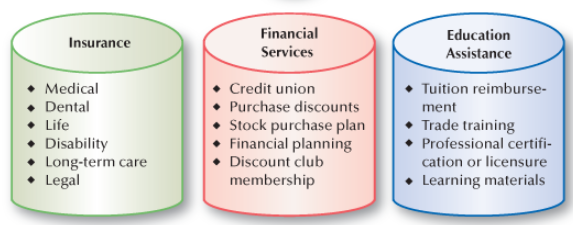
Common Types of Financial Benefits
35
New cards
Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA)
Enacted in 1993. Provides for unpaid leave. Covers:
* All federal, state, and private employers with 50 or more employees who live within 75 miles of the workplace
* Employees who have worked at least 12 months and 1,250 hours in the previous year
* All federal, state, and private employers with 50 or more employees who live within 75 miles of the workplace
* Employees who have worked at least 12 months and 1,250 hours in the previous year
36
New cards
FMLA Requirements
Requires employers to allow eligible employees to take a maximum of 12 weeks of unpaid, job-protected leave during any 12-month period for the following situations:
* Birth of a child and care for the newborn within one year of birth
* Adoption or foster care placement of a child
* Caring for a spouse, child, or parent with a serious health condition
* Serious health condition of the employee
* Military family members who must handle the affairs for military members called to active duty
* 26 weeks leave to care for a military servicemember injured while on active duty
* Birth of a child and care for the newborn within one year of birth
* Adoption or foster care placement of a child
* Caring for a spouse, child, or parent with a serious health condition
* Serious health condition of the employee
* Military family members who must handle the affairs for military members called to active duty
* 26 weeks leave to care for a military servicemember injured while on active duty
37
New cards
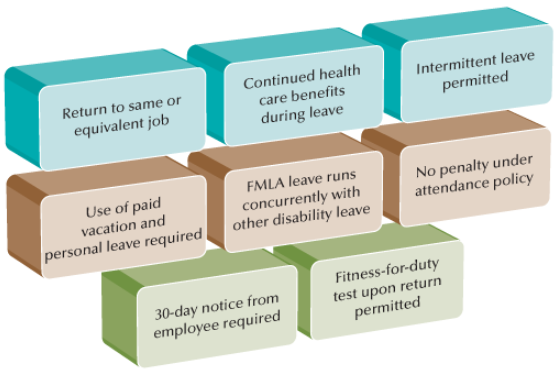
Guidelines Regarding FMLA Administration
38
New cards
Family-Care Benefits
* Adoption and fertility benefits
* Child-care assistance
* Elder-care assistance
* Child-care assistance
* Elder-care assistance
39
New cards
Child Care and Elder Care Programs
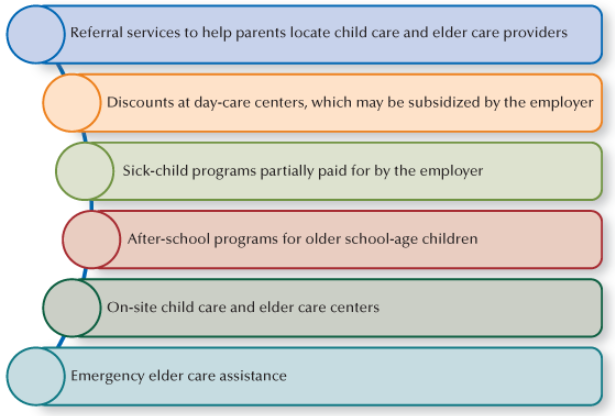
40
New cards
PTO Benefits
* Vacation and holiday leave
* Leaves of absence
* Family leave
* Sick leave
* PTO plans
* Employee-paid group benefits
* Leaves of absence
* Family leave
* Sick leave
* PTO plans
* Employee-paid group benefits