Laws of Motion and Momentum
1/11
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Mass
Amount of matter, a base quantity measured in kilograms (kg)
Inertia
The tendency of an object to resist a change in its state of motion
Newtons first law of motion
A body will remain at rest or keep travelling at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a resultant force
Newtons second law of motion
The rate of change of momentum of an object is directly proportional to the resultant force acting on the object and takes place in the direction of the resultant force
Newtons third law of motion
When two objects interact, each exerts an equal but opposite force of the same type on the other during the interaction
Linear momentum
The product of mass and velocity (of a particle), measured in kg ms-1 or Ns. It is a vector quantity as it is a product of a scalar (mass) and a vector (velocity)
Law / principle of conservation of momentum
For a system of interacting objects, the total momentum in a specified direction remains constant, as long as no external forces act on the system.
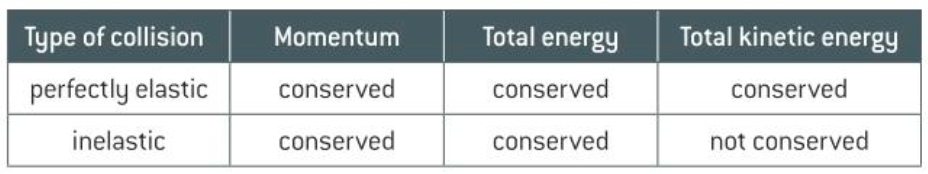
(Perfectly) Elastic collision
Collision in which momentum and total kinetic energy are both conseved
Inelastic collision
A collision in which momentum is conserved but some kinetic energy is transferred to other forms, e.g. heat
Difference(s) between perfectly elastic and inelastic collisions
Impulse
The area under a force-time graph - the product of force and the time for which the force acts (FΔt). Is equal to the change in momentum (Δp). The unit of impulse is Ns or kgms-1.
Deriving impulse from newtons second law of motion
According to Newton's second law of motion: net force = rate of change of momentum; F=Δp/Δt
Rearranging this equation gives: F × Δt = Δp
Impulse of a force is defined as the product of force and the time for which this force acts on an object. Therefore impulse of a force = change in momentum.