Unit 10B - Bond Enthalpy and Enthalpy of Reactions
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
latent heat
the amount of heat energy required to push a substance through a phase change (overcome intermolecular forces)
latent heat equation
q = mΔH
ΔHf
heat of fusion (energy required to melt 1g of ice)
= 334 J/g or 79.9 cal/g
ΔHv
heat of vaporization (energy required to boil 1g of water)
= 2260 J/g or 540 cal/g
heat capacity (C)
the amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1 g of a substance 1 degree Celsius
Cice
2.05 J/gºC or 0.5 cal/gºC
Cwater
4.18 J/gºC or 1 cal/gºC
Csteam
2.01 J/gºC or 0.48 cal/gºC
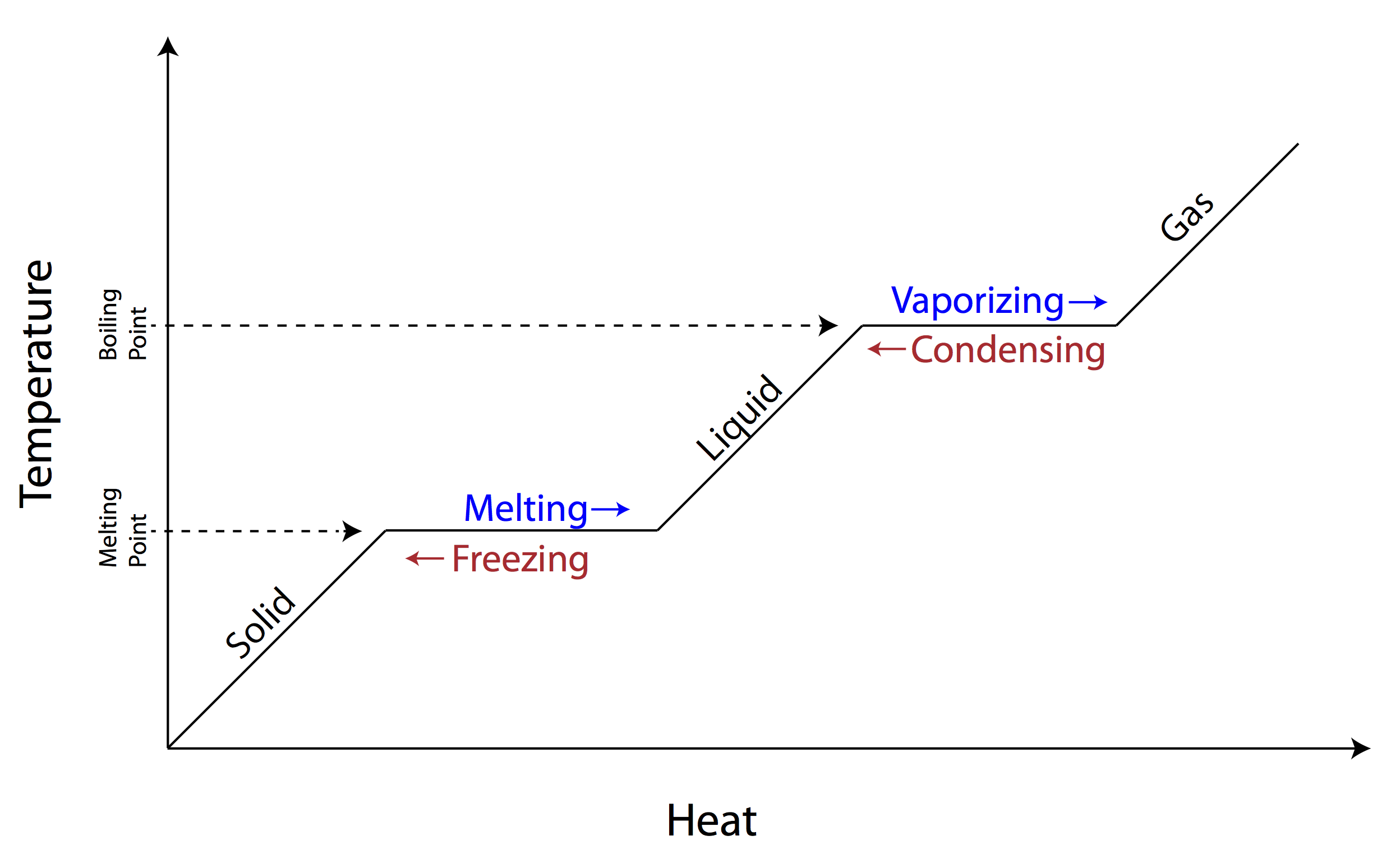
phase changes (when to use latent heat vs. heat capacity)
slope = changing temperature
no slope = phase change
when reactants form products
energy is released
when products are broken into reactants
energy is taken in
chemical bond
when two atoms are joined through the sharing of electrons
enthalpy (ΔH)
stored (potential) chemical energy in the form of heat
state function
a function (variable) whose value depends only on the current state of the system, and whose value is independent of the pathway
enthalpy is an example of a state function
G
gibbs free energy (overall energy)
H
heat
S
order
equation for gibbs free energy
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
bond energy
the energy required to break a chemical bond
homolytic dissociation
electrons are equally split between two atoms, electrons in the bonding pair “move” independently
(bond energies are lower than heterolytic dissociation)
heterolytic dissociation
electrons are not equally split between two atoms, electrons in bonding pair “move” together
(bond energies are higher than homolytic dissociation)
exothermic
system releases more energy than it takes in
endothermic
system releases less energy than it takes in
enthalpy is positive when
breaking a bond, endothermic, putting energy in
enthalpy is negative when
forming a bond, exothermic, releasing energy
enthalpy of formation
ΔHrxn for the formation of a compound from its elements in their natural state
the enthalpy of formation of any pure element in its natural state
0