BC Calculus Yellow Board
AB Topics
Inverse Trig Derivatives
arcsin = 1/√1-u² * u’
arccos = -1/√1-u² * u’
arctan = 1/1+u² * u’
arccot = -1/√1+u² * u’
arcsec = 1/u√u²-1 * u’
arccsc = -1/u√u²-1 * u’
logau = 1/(u ln a) * u’
au=aulna*u’
d/dx[f-1(x)]=1/f’(f-1(x))
e and ln rules
f’(x) ∫f(x)
eu eu *du eu/du
lnu 1/u * du
1/u power rule lnu/du
Integral to Summation
a∫bkp = ∑ᵇ⁻ᵃ⁄ₙ(a+⁽ᵇ⁻ᵃ⁾ᵏ⁄ₙ)p
Trig Identities
sin²x+cos²x=1
tan²+1=sec²x
cot²x+1=csc²x
VOLUME FORMULAS
Disk: π∫(r²)
Washer: π∫(big r)²-(small r)²
Shells: 2π∫r*h
Shells with gap: 2π∫r(big height-small height)
Cross Sections:
Semi-circle: ∫½πr² r= ᶠ⁽ˣ⁾⁻ᵍ⁽ˣ⁾⁄₂
Equilateral Triangle: ∫(√3)/4 s² s=f(x)-g(x)
Isosceles Right Triangle: ∫½s² s=f(x)-g(x)
Logistic Growth:
dP/dt=kP(1-P/L) or dP/dt=kP((L-P)/L)
k=constant, P=population at time t, L=carry capacity
BC Topics
Euler’s Method: ynew=yold-y’∆x
Integration by Parts: ∫udv=uv-∫vdu
Arc Length: ∫√1+(f’(x))²
Parametric Formulas
Slope: (dy/dt)/(dx/dt) = dy/dx
Equation: y-y1=m(x-x1)
2nd Derivative: d²y/dx²= (d/dx (dy/dx)) / (dx/dt)
Arc Length: ∫√(dy/dt)²+(dx/dt)²
Speed: √(dy/dt)²+(dx/dt)²
Position: x(t)+∫x’(t) , y(t)+∫y’(t)
Polar Formulas
x=rcosθ
y=rsinθ
r=asin(nθ)
r=acos(nθ)
a=radius; n=odd → #of petals; n=even → 2n=petals; cos begins on x axis; sin begins @ 90/petals
r=2asinθ → circle centered on y axis
r=2acosθ → circle centered on x axis
Limacons: r=a±b(sin or cos)θ
a/b < 1 → inner loop
a/b = 1 → cardioid
1<a/b<2 → dent
a/b > 2 → bulge
Lemniscate: r²=a²(sin or cos) 2θ
Spiral: r=aθ
Basic Area: ½∫r² dθ
Arc Length: ∫√r²+(dr/dθ)²
Series
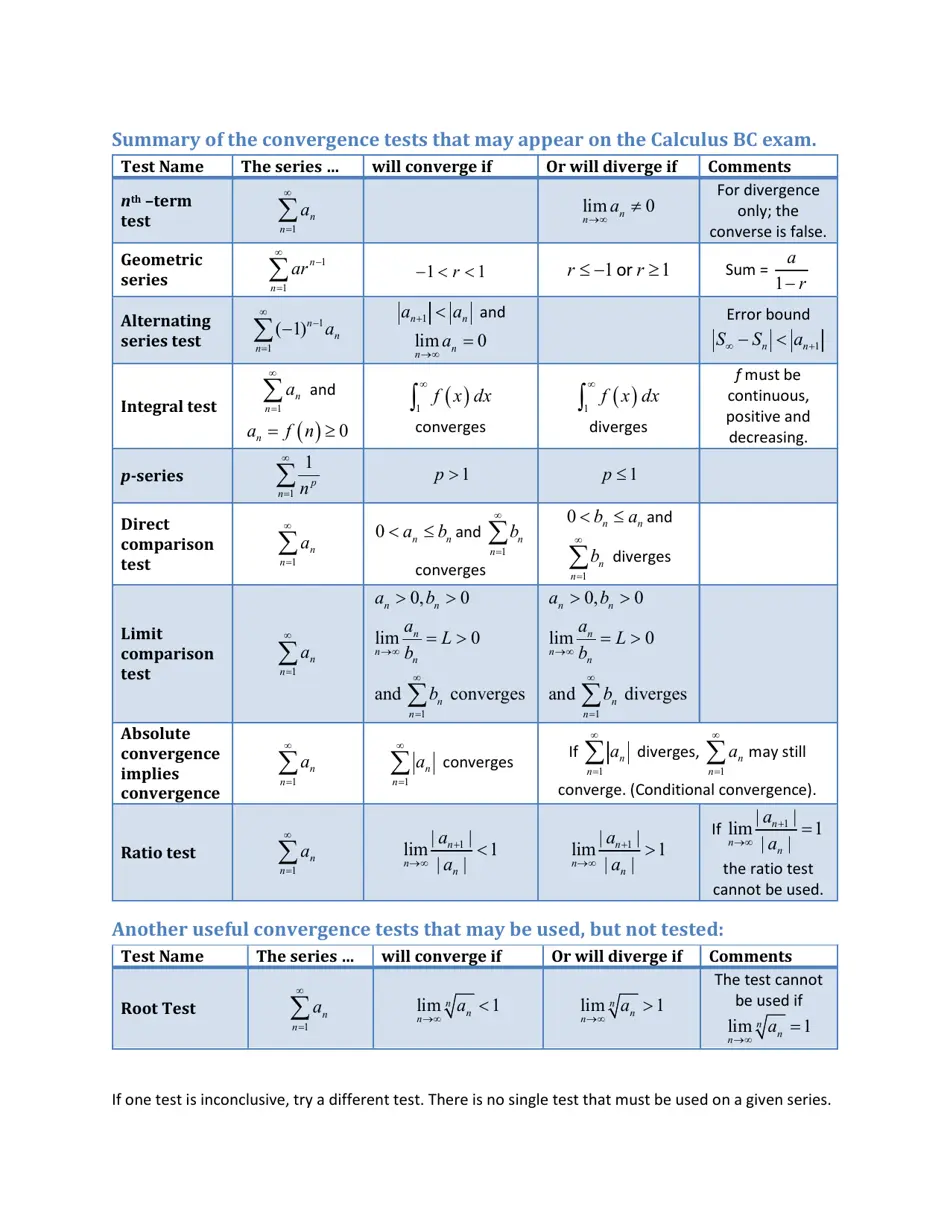 La Grange Error Bound:
La Grange Error Bound:
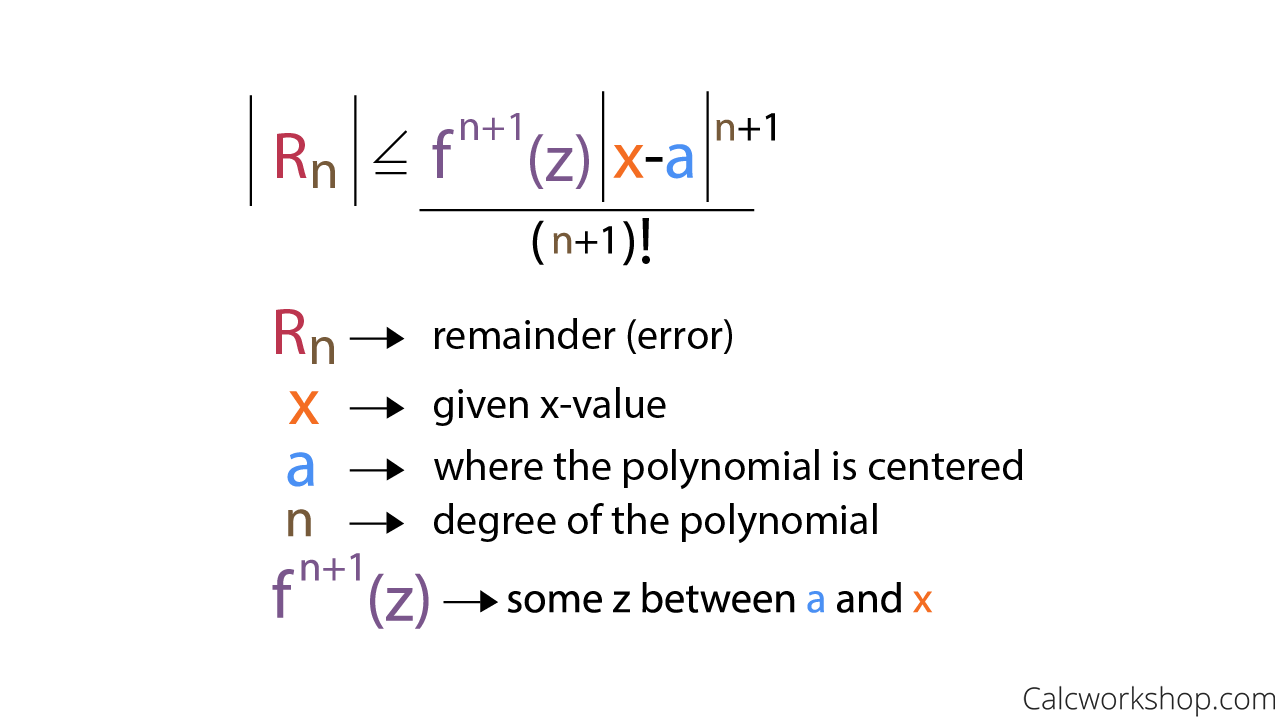
Alternating Series Error Bound:

Maclaurin Series:
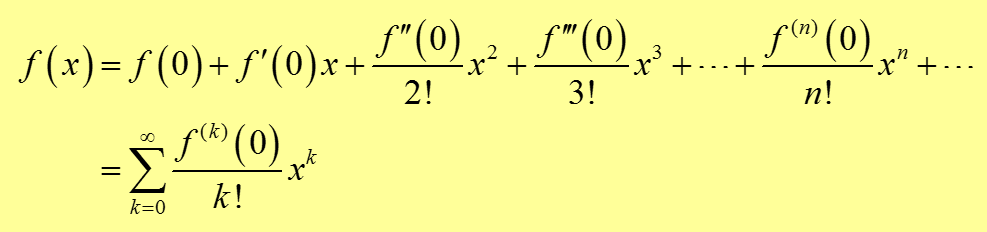
Taylor Series:
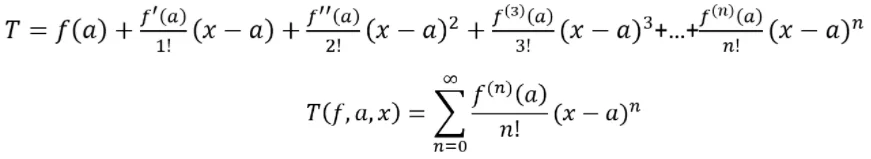
Power Series: (*memorize)
