BM - Cardiovascular Biomechanics
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Laws governing fluids
Law of conservation of mass, navier sokes law
Navier stokes equation is for flow in a…
Cylinder
The sum of forces per unit volume is equal to…
density times acceleration
The Navier Stokes law governs what 4 properties?
velocity, pressure, viscocity, height
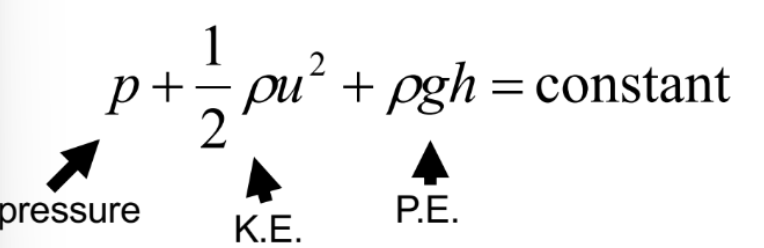
This equation describes…
Steady inviscid flow
The Bernouli equation describes what 3 properties?
velocity (constant), pressure, height
If the Reynolds number of a fluid is < 2300, it is considered _____ flow.
Laminar
If the Reynolds number of a fluid is >= 2300, it is considered _____ flow.
Turbulent
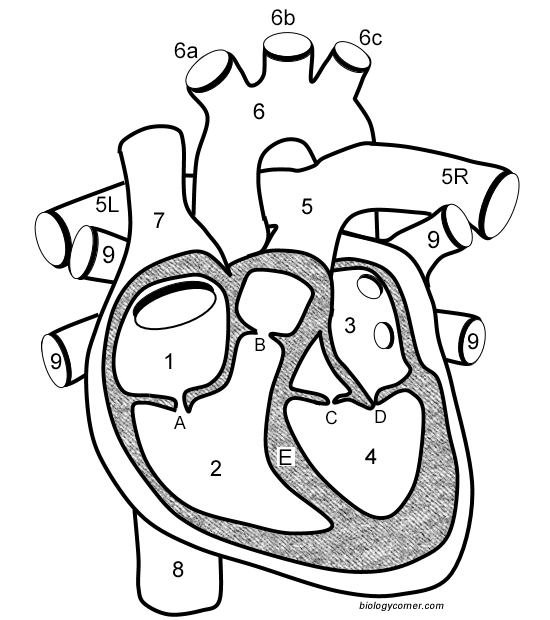
Number 1
Right atrium
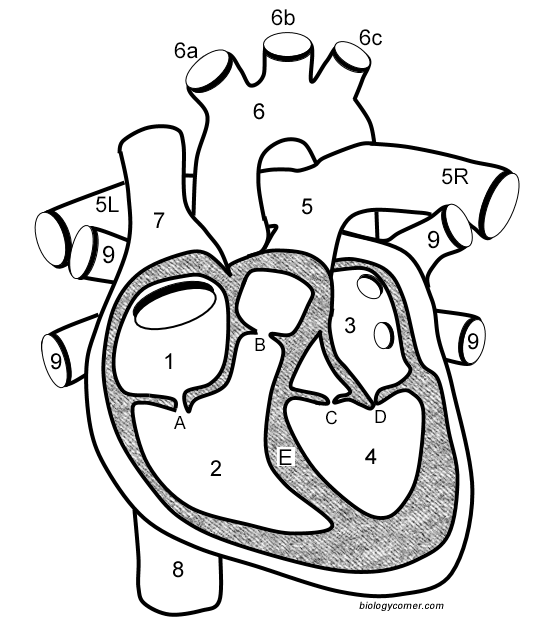
Number 2
Right ventricle
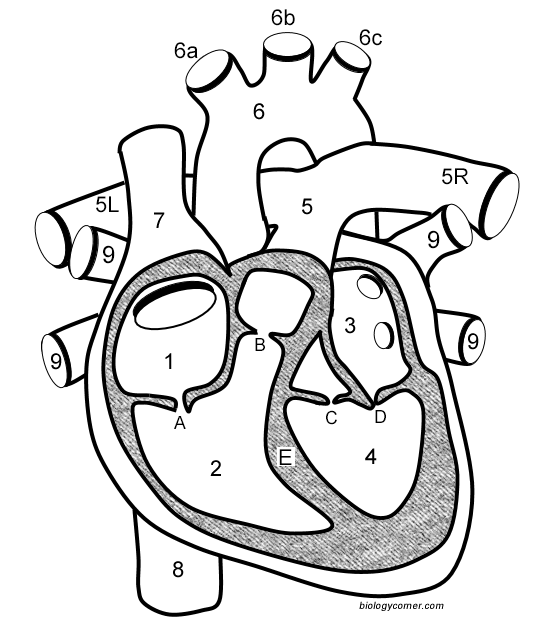
Number 3
Left Atrium
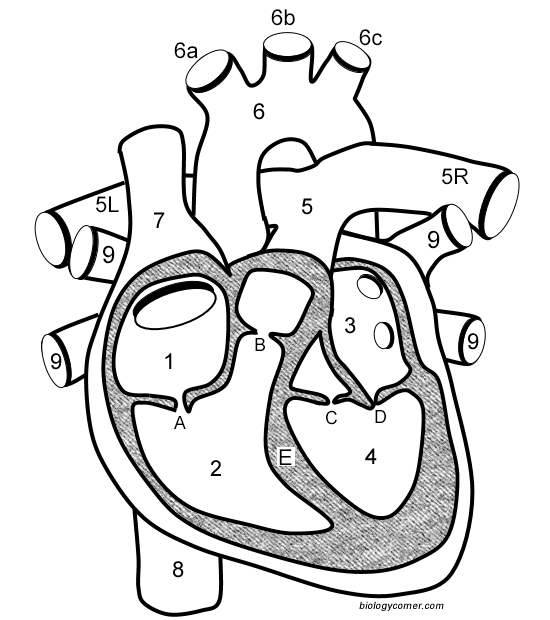
Number 4
Left ventricle
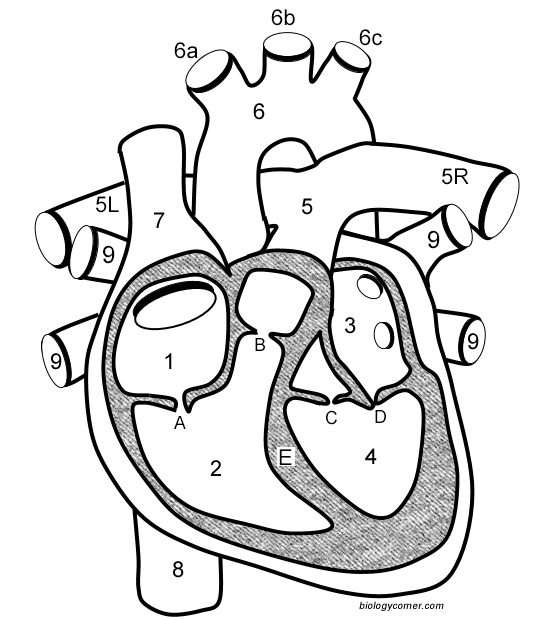
Number 5 (5L & 5R)
Pulmonary artery
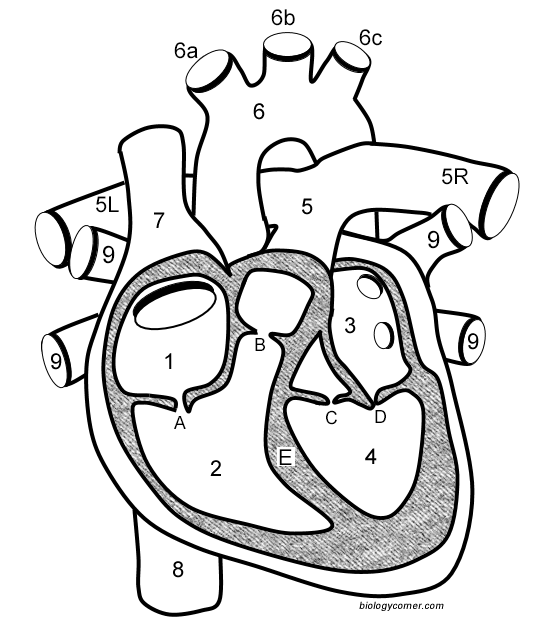
Number 6
Aorta
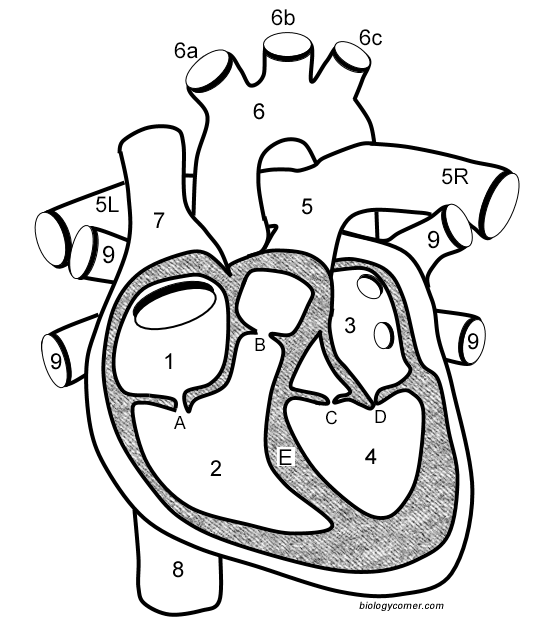
Number 7
Superior vena cava
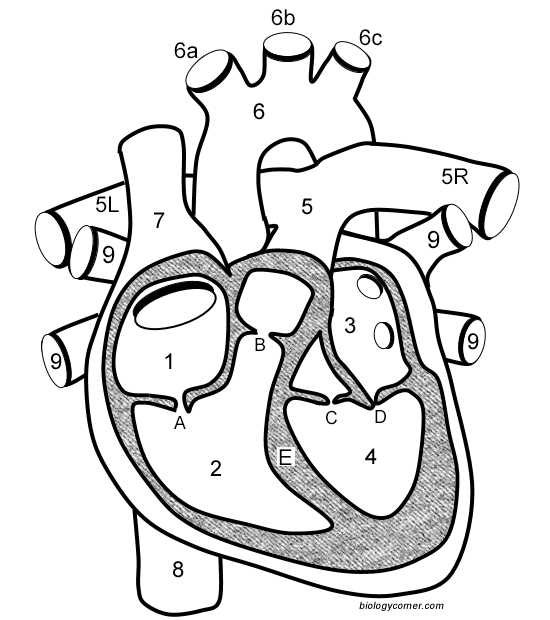
Number 8
Inferior vena cava
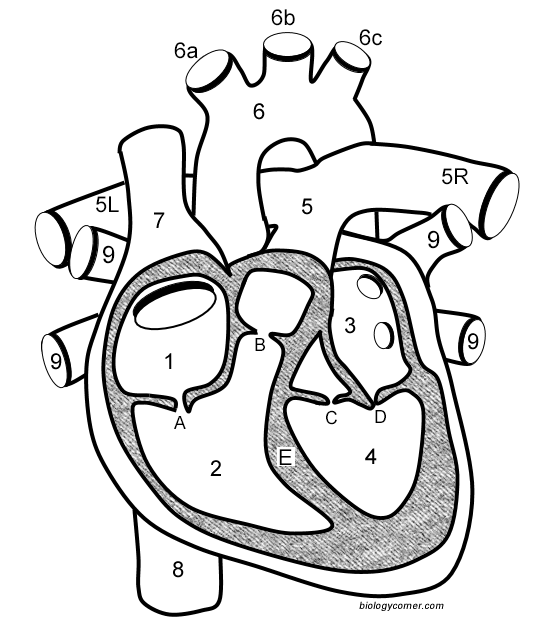
Number 9
Pulmonary veins
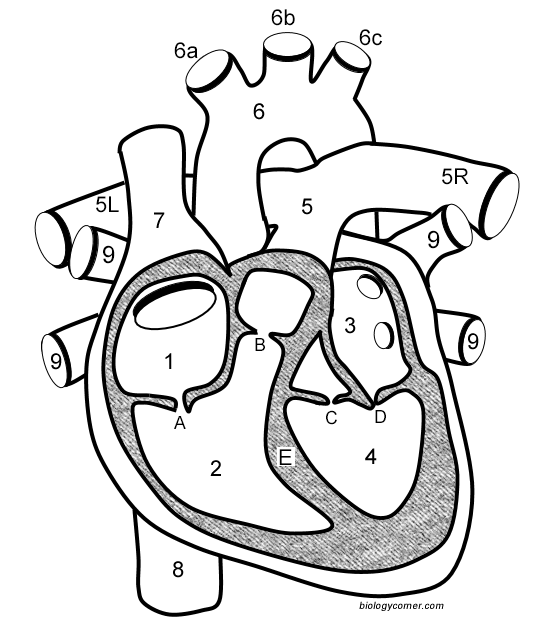
Letter A
Tricuspid valve
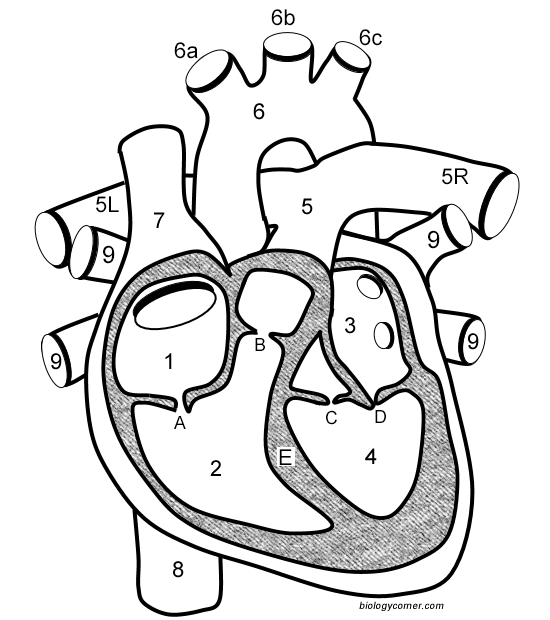
Letter B
Pulmonary valve
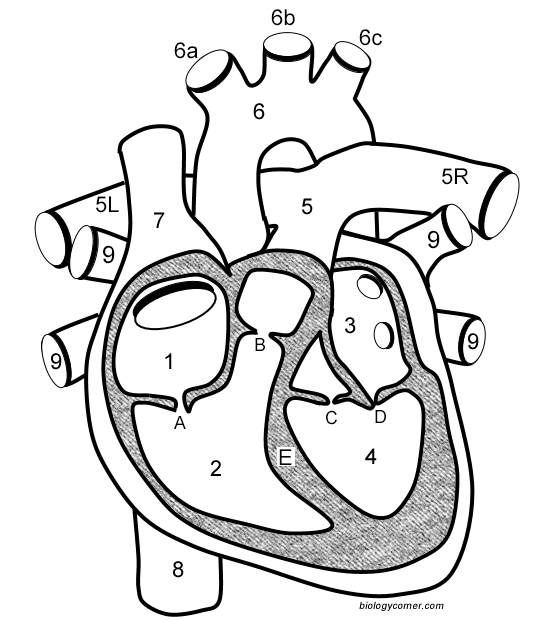
Letter C
Aortic valve
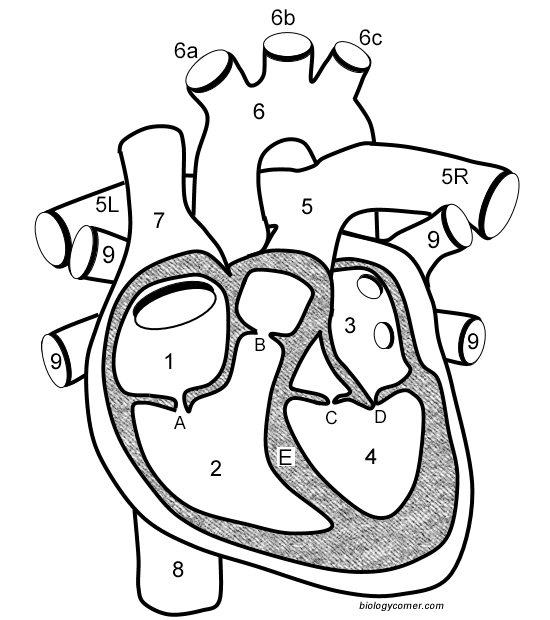
Letter D
Mitral valve
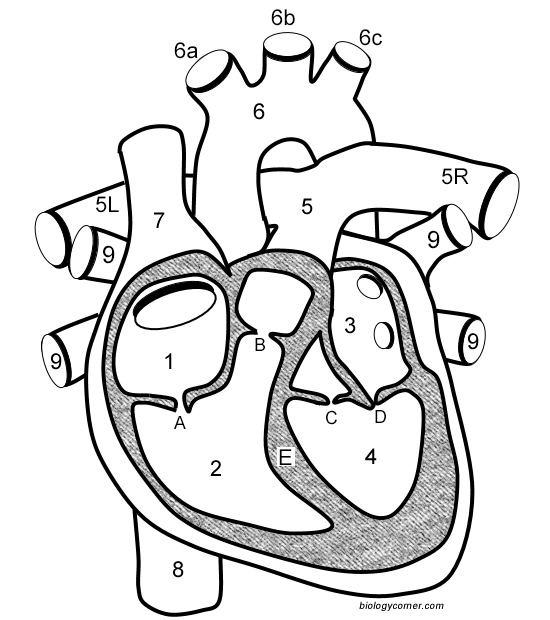
Letter E
Septum
The aorta pumps blood into the…
Left ventricle
The right ventricle is in a _________ shape.
Semilunar
The left ventricle is a _______ shape.
Globular shape
The right ventricle contracts…
Top to bottom
The left ventricle contracts…
Diameter and logitudinal
The myocardium makes up ____% of cardiac thickness.
95
Myocardium is made up of 90% _______ and 5% ______.
Fiber bundles, collagen
Myocardial cells are connected to each other by specialized gap junctions called ______________.
Intercalated disks
The only node that is electrically connected
AV Node
The SA node has how many action potentials per minute?
60-80 per minute (same as heartbeat)
The QRS complex occurs at the end of…
Atrial systole
In an EKG, the R peak occurs when the…
AV valve closes
In an EKG, the S dip occurs when the…
Semilunar valve opens
Bottom LEFT of a pressure/volume graph
Mitro valve opens
Top LEFT of a pressure/volume graph
Atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve closes
Top RIGHT of a pressure/volume graph
Atrioventricular (tricuspid) valve opens
Bottom RIGHT of a pressure/volume graph
Mitro valve closes
The cardiac cycle moves in a ________ direction on a pressure/volume graph.
Counterclockwise
Clockwise
Counterclockwise
The stroke work is the ______ of a pressure/volume graph.
Area
Change in volume
Change in pressure
Pressure at the top right curve
Maximum pressure
Area
The stroke volume is the ______ of a pressure/volume graph.
Area
Change in volume
Change in pressure
Pressure at the top right curve
Maximum pressure
Change in volume
The diastolic blood pressure is the ______ of a pressure/volume graph.
Area
Change in volume
Change in pressure
Pressure at the top right curve
Maximum pressure
Pressure at the top right curve
The systolic blood pressure is the ______ of a pressure/volume graph.
Area
Change in volume
Change in pressure
Pressure at the top right curve
Maximum pressure
Maximum pressure
Mean arterial pressure formula
(1/3)(SBP + 2DBP)
Stroke volume
Change in volume
Cardiac output
Stroke volume * Heart Rate
Cardiac index
Cardiac output / body surface area
Stroke work
Stroke Volume * (mean arterial pressure)
Power (of the heart)
Stroke work * Heart rate
Frank-Starling Law: Ventricular contractility (_________) is proportional to ventricular filling volume (_________)
Stroke volume, pre load
In a normal heart, as after-load increases, stroke work __________.
Increases
Stroke volume will only drop if the after load becomes…
Extremely high
In a pipe-circuit mock, the resistance is the…
Resistance
In a pipe-circuit mock, the change in pressure is the…
Voltage
In a pipe-circuit mock, the current is the…
Flow rate
In parallel, the flow rates are…
Summed
In parallel, the pressure drops are…
Equal
In series, the voltage drops are…
Summed
In series the flow rates are…
Equal
Systemic vascular resistance is
1 PRU
Pulmonary vascular resistance is
0.1 PRU
Δp =
Res * Q
The following properties describe what type of flow?
Newtonian fluid
Laminar flow
Rigid walls
No slip at walls
Fully developed, steady flow
Cylindrical vessel
Hagen-Poiseuille
High shear stress causes what on the blood?
Platelet activation, hemolysis
Low shear stress causes what on the blood?
Platelet aggregation/adhesion
RBC destruction occurs at 10³ (dynes,cm2). This leads to…
Poor oxygen supply
Platelet activation/destruction starts occuring at 10², but can cause…
Clotting
The peak Reynolds number in the body is 5100, which occurs when…
The aortic valve closes
Normal blood flow in the arteries is turbulent or laminar?
Laminar
Freely floating entity in the blood
Emboli
Buildup of plaque in arteries
Atherosclerosis
The three types of ___________ are regurgitation, stenosis, and atresia.
Valvular diseases
Expansion and eventual bursting of arteries.
Aneurysms
Which type of cells actually experience wall shear stress in the circulatory system?
Endothelial cells
Doppler limitations
Many layers of arteries
Velocity is different throughout the body
We have to assume neglibile viscosity
Any sort of narrowing of a tube, can be caused by atherosclerosis
Stenosis
Atherosclerotic lesions occur at…
Curvature, bifurcation, branches
2/3 of the time the blood vessels experience some pressure is in the _____ region.
Diastolic
Pulse Pressure
SBP - DBP
As a rule of thumb, PP should be…
SBP * 1/3