1.4.2: Many proteins are enzymes
1/5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
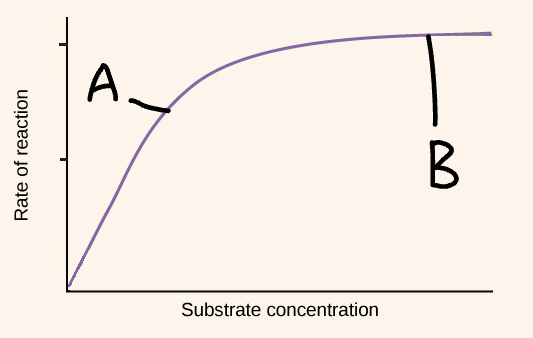
Explain part A of this graph (substrate concentration)
Available / free active sites
Increase in substrate concentration
Increase in enzyme-substrate complexes
Increase in rate of reaction
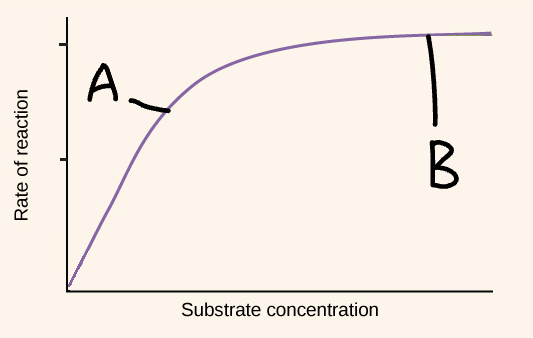
Explain part B of this graph (substrate concentration)
No available active site
Increase in substrate concentration
No increase in enzyme-substrate complexes
Rate of reaction stays constant
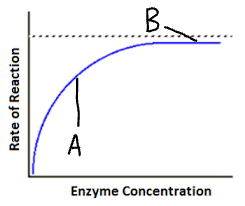
Explain part A of this graph (enzyme concentration)
Available substrates
Increase in enzyme concentration
Increase in enzyme-substrate complexes
Increase in rate of reaction
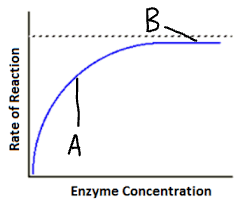
Explain part B of this graph (enzyme concentration)
No available substrate molecules
Increase in enzyme concentration
No increase in Enzyme-substrate complexes
Rate of reaction stays the same
How do competitive inhibitors work?
Their molecular shape is similar to the substrate
The molecules can bind to the outside of an enzyme
The inhibitor is not permanently bonded to the enzyme, so a substrate can still the active site once the inhibitor leaves
An increase in the concentration of substrates decreases the effect of the inhibitor
Less enzyme-substrate complexes are formed which leads to a lower rate of reaction
How do non-competitive inhibitors work?
Bind to the enzyme at a location other than the active site
The inhibitor then changes the shape of the enzyme so the substrate is no longer complimentary to the active site
Less enzyme-substrate complexes form so the rate of reaction islower
An increase in the concentration of substrates has no effect on how these inhibitors work