Core Concepts- Lecture 5- Phagocytes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
describe the differences between neutrophils and macrophages
macrophages- round nucleus and irregular shape and cytoskeleton
neutrophils- multilobed nucleus with lots of chromatin and has granules
discuss macrophage and neutrophil phagocytosis and effector functions
Neutrophils
rapid/short lived professional killers
release antimicrobial granules enzymes and peptides to kill extracellular pathogens
can release NETS- webs of chromatin and microbial proteins
produces superoxide and reactive oxygen
macrophages
cleanup/ surveillance and APC
also efferocytosis- removing dead and dying cells
has lysosomes- acidification by vacuolar ATPases
generates reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species
produces cytokines
slower and long lived
describe the steps of phagocytosis- neutrophils and macrophages
recognition of the target via phagocytic receptors- recognise PAMPs
target is engulfed into a phagosome- membrane bound vesicle
phagosome has V-ATPases that pump H+ ions in and make it more acidic, early phagosome is Rab5+ and late is 7+ positive and V-atpases
phagosome fuses with the primary and secondary granules/lysosomes. lysosomes have AMP and is acidified. makes a phagolysosome
NADPH oxidase assembles the phagosome membrane and makes superoxide and other reactive oxygen- highly antimicrobial environment- low pH, lysosomal enzymes to kill pathogen
degranulation in neutrophils
discuss the neutrophils fate
short lived and for a rapid response- after using their effector function they degranulate and die
may die by apoptosis: regulated death and expose DAMPs to signal macrophages for clean up. non inflammatory resolution
may die of netosis- release DNA and chromatin into the extracellular space- pro inflammatory
necrotic/uncontrolled death- cellular contents are released and make inflammatory signalling
how are phagocytic compartments trafficked?
RAB GTPases- determine the identity and trafficking routes
SNAREs- mediate membrane fusion for the phagolysosome
actin binding proteins- control movement and shape and changes of vesicles
discuss phagocytic receptors(5)
C type lectin- dectin-1 recognises beta glucans on fungal cell walls
mannose receptors- sugar on bacterial surfaces
scavenger receptors- bind glycoproteins on bacteria and host DAMPs- MARCO, SRA
complement receptors- CR3 binds fungal beta glucans or opsonised microbes
PRRs- TLRs- don’t activate phagocytosis but activates pro inflammatory signalling and NLRs= regulate phagosome maturations
discuss phagocytosis autophagy and xenophagy definition
autophagy: special form where cell captures cytoplasmic to destroy organelles
xenophagy: targets intracellular pathogens and not just exracellular microbes and makes double membrane organelles called autophagosomes
discuss xenophagy process
recognition- intracellular pathogen is ubiquinated
recruitment of adapter proteins such as p62 binds to the ubiquitinated cargo and recruits autophagosome
autophagosome formation- Atg5 and LC3- makes double membrane
fusion with the lysosome
discuss phagocyte killing mechanisms
pro inflammatory signalling by TNF-alpha, IL-1, IFN-gamma- enhance phagocytosis and promote lysosome maturation. induce iNOS to make nitrous oxide for antimicrobial activity and up regulate ROS
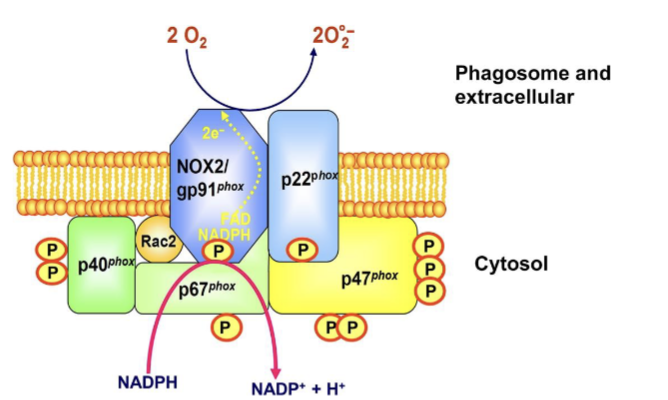
respiratory burst- make reactive oxygen species to kill pathogens inside the phagosome. NADPH complex made of membrane bound cytochrome b558 and cytosolic subunits p40/p47.
describe the respiratory burst steps
NADPH oxidase complex- composed of cytochrome b558(gp91 and Nox2) and cytosolic subunits p40/p47/p67
activated by PRRs sensing PAMPs. G-protein coupled receptors signal activation. Rac2 GTPase critical for assembly for NADPH complex
phagosome forms and cytosolic subunits translocate to the phagosomal membrane and NADPH catalyses to make super oxide and made into hydrogen peroxide and hypochlorite
fuses with the lysosome and low pH acidification with ROS kill pathogen
what is efferocytosis?
process by which phagocytes recognise, engulf and digest dead or dying cells such as apoptotic neutrophils, cellular debris or infected cells
steps in efferocytosis
recognition of the dying cell- dying cells have eat me signals
phagocyte engulfs cell and makes an intracellular vesicle and then digested by lysosomal enzyme
cytokines that are anti inflammatory are made: IL-10 suppress pro-inflammatory responses and TGF-beta promotes tissue repair
discuss macrophage activation states
classic pro inflammatory activation
M1 like
makes TNF-alpa, IL-1beta and IL-6
to kill microbes and promote inflammation and promote Th1 T cell responses
use arginine to make nitric oxide via iNOS
alternative anti inflammatory
M2 like
induced by IL-4, IL-13 and macrophages produce iL-10, TGF-beta
repair tissues and clearance of dead cells and promote Th2
uses arginine to make ornithine
name types of resident macrophages in different tissues
brain- microglia
liver- kupffer cells
lung- alveolar macrophages
skin-lanerhans cells
bone- osteoclasts
what are some things that make scientists believe innate macrophages may also have memory?
epigenetic programming- exposure to a stimulus marks the chromatin so response genes like chemokine are more easily reactivated