quiz 3 Sedimentary Rocks, Rivers and Floods
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
List the three categories of sedimentary rock discussed in the powerpoint slides:
clastic, biogenic, chemical
The four properties of clastic sedimentary rocks that we study are:
grain size- how big are the clasts
grain composition - what are the clasts made of
grain roundness - are the clasts round or angular
grain sorting - are the clasts the same size of mixed sizes
Biogenic rocks that have visible fossil fragments are described as ? whereas biogenic rocks that are made of microscopic fragments or calcite crystals are described as ?
fossiliferous, muddy
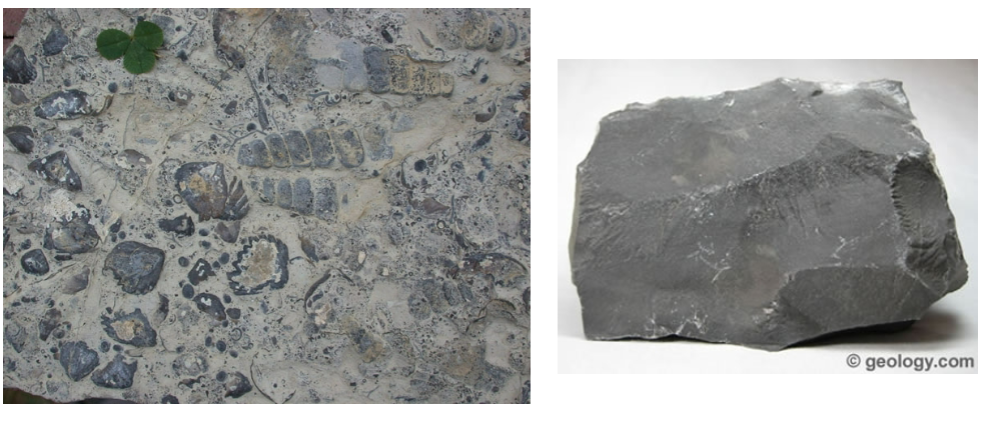

Chemical sedimentary rocks are
minerals that grow out of water as the water evaporates
>25% of grains are feldspar
arkosic(immature)

large clasts (gravel or larger)
conglomerate
>90% of grains are quartz
quart-rich (mature)
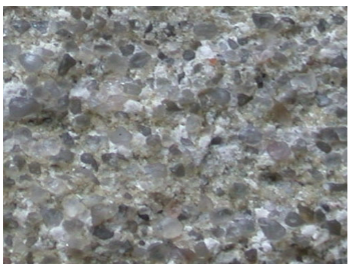
medium clasts (smaller than gravel but large enough to see)
sandstone
>25% of clasts are rock fragments
lithic (immature)

Clasts are mostly clay minerals
clay-rich(mature)

small clasts (too small to see)
mudstone
Which conditions are necessary for the life that produces biogenic rocks to flourish? In other words, when you see a biogenic rock, what does it tell you about conditions when the rock formed?
warm water not too hot, shallow water, clear water, not too salty
Which conditions are necessary for chemical sedimentary rocks to form? In other words, when you see a chemical sedimentary rock, what does it tell you about conditions when the rock formed?
dry climate, stagnant, mineral-rich water, hot climate, supply of minerals
two cleavage planes, not at 90 degrees
calcite gypsum
clear to white color
calcite gypsum
salty taste
halite
can scratch with fingernail
gypsum
too hard to scratch with fingernail
calcite, halite
effervesces (fizzes) in hydrochloric acid
calcite
3 cleavage planes, all at 90 degrees
halite
clear to white but with impurites can be pink/red/orange/brown
halite
make(s) biogenic sedimentary rocks
calcite
make(s) chemical sedimentary rocks
gypsum, halite
clastic definition
made from clasts(fragments) of weathered rocks
Biogenic definition
made from shells of organisms
chemical definition
direct precipitation of minerals dissolved in water when water evaporates (also often called evaporites)
what affects grain size?
grain size = energy of the environment = gradient
so conglomerates come from steep mountains, mudstones come from still water in lakes or oceans
Describes MAXIMUM grain size, rivers carry smaller sediments as well but never bigger than maximum size

clastic composition
clastic rocks are classified according to how much quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments there are in the rock
Why are arkosic and lithic rocks compositionally immature but quartz and clay rich rocks are compositionally mature
immature not procces much must have been deposited near source
mature sediment was processed alot, deposited far from source or is product of many cycle of weathering
What affects grain roundness
“river rocks” as sediments are moved by water they bounce and smash into each other wearing away sharp edges. More round further from source?
What makes grains angular?
angular sediments never got the chance to have the sharp edges broken off, so these were either transported by glacier ice or never travelled far from source
what affects grain sorting?
from glacier will be poorly sorted ie mixed sizes
river sediment is medium to ewll sorted depending on how far the sediment travelled, more travel = better sorting
wind is best as sorting, large clasts aren’t moved, small clasts blown away as dust so only medium clasts are piled in dunes. wind moved sediment is always well sorted
The force of moving water plucks up and tears away material from the channel, including solid rock
scouring, breaking and lifting
Sediment carried by the river acts as sandpaper, scouring away material from the channel bottom
abrasion
Slightly acidic river water dissolves the rock of the river channel
dissolution
steep gradient
straight river
wide, shallow valleys
meandering river
high sinuosity
meandering river
transition from steep to gentle gradient (or too much sediment)
braided river
carries large, sand-sized, and mud-sized clasts, deposits large clasts
straight river
deep narrow valleys
straight river
primarily horizontal erosion
meandering river
caries coarser sand-sized and mud-sized clasts, deposits sand-sized clasts
braided river
carries finder sand-sized and mud-sized clasts, deposits finer sand-sized and mud-sized clasts
meandering river
low energy
meandering river
gentle gradient
meandering river
primarily vertical erosion
straight riverd
deep, narrow valleys
straight river
high energy
straight river
medium energy
braided river
low sinuosity
straight river
how can superposed drainage come to be?
change in river gradient
uplift of mountains around a river
differential weathering of rocks around a river
the base level of a river is
the elevation at the rivers mouth and
the lowest elevation a river can erode to
a rise in base level ____________
decreases a river's energy, leading to an increase in deposition
A drop in base level
increases a river's energy, leading to an increase in erosion
How horizontal erosion happens?
Current is fast at the outsides of the bends where erosion happens
current is slow at the insides of bends where deposition happens
eventually creates oxbow lake
How does superposed drainage come to be?
change in gradient over time
differential weathering and erosion (river was there before top layers eroded away)
uplift around river (river was there before mountain was raised)
drainage patterns
dendritic- treelike; equally resistant beds and gradual slope
trellis - ridges of resistant and soft beds
radial - outward from an isolated peak
rectangular - following perpendicular sets of joints
parallel - consisten, relatively steep slope
characteristics of seasonal flood
too much water from a long period of rain or snowmelt
relatively slow development and long duration
can linger for months before floodwaters recede
characteristics of a flash flood
relatively quick development and short duration
water comes too quickly to soak into ground, or for rivers to move away
can occur too quickly for a person to escape
Where does flooding occur in a meandering river system?
The flood fills the entire river valley
What can be done to protect against seasonal floods?
build dams to regulate water flow,
build dikes and levees
breach levees and flood less valuable areas to protect more valuable areas
What can be done to protect against flash floods?
get to high ground if it rains
watch the weather forecasts and avoid flood-prone areas if rain is forecast
get to high ground immediately if river flow increases or turns muddy
build flood control basins
What is monitored to predict flooding?
predicted precipitation
current snowpack
ground saturation
current streamflow