Unit 1.5 & 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/162
Earn XP
Last updated 10:12 AM on 5/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
1
New cards
6 types of proteins
structural, enzyme, hormone, contractile, immunological & transport
2
New cards
Polypeptides
unbranched chain of amino acids
3
New cards
condensation reaction (draw)
removal of water links monomers together to combine smaller organic molecules to form larger moleculeU
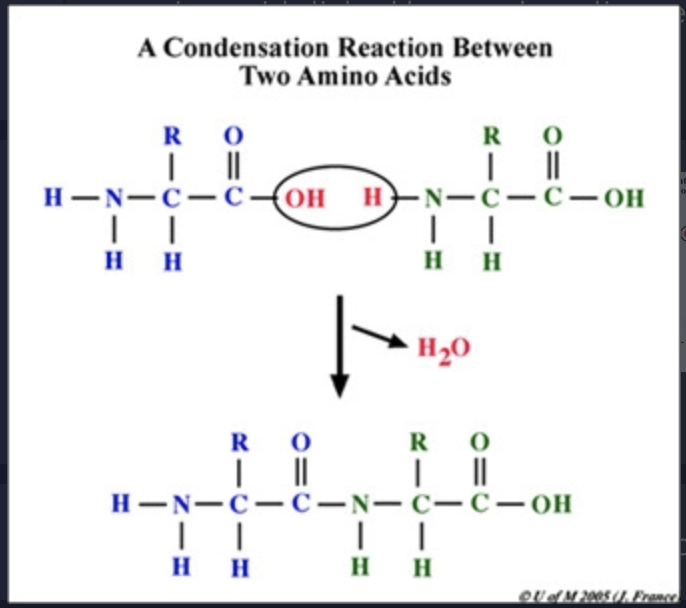
4
New cards
Proteins
single polypeptide or more than one polypeptide of amino acids linked together
5
New cards
Structure of an amino acid (draw)
an amino group, a carboxylic acid, and a R group (varies for each amino acid
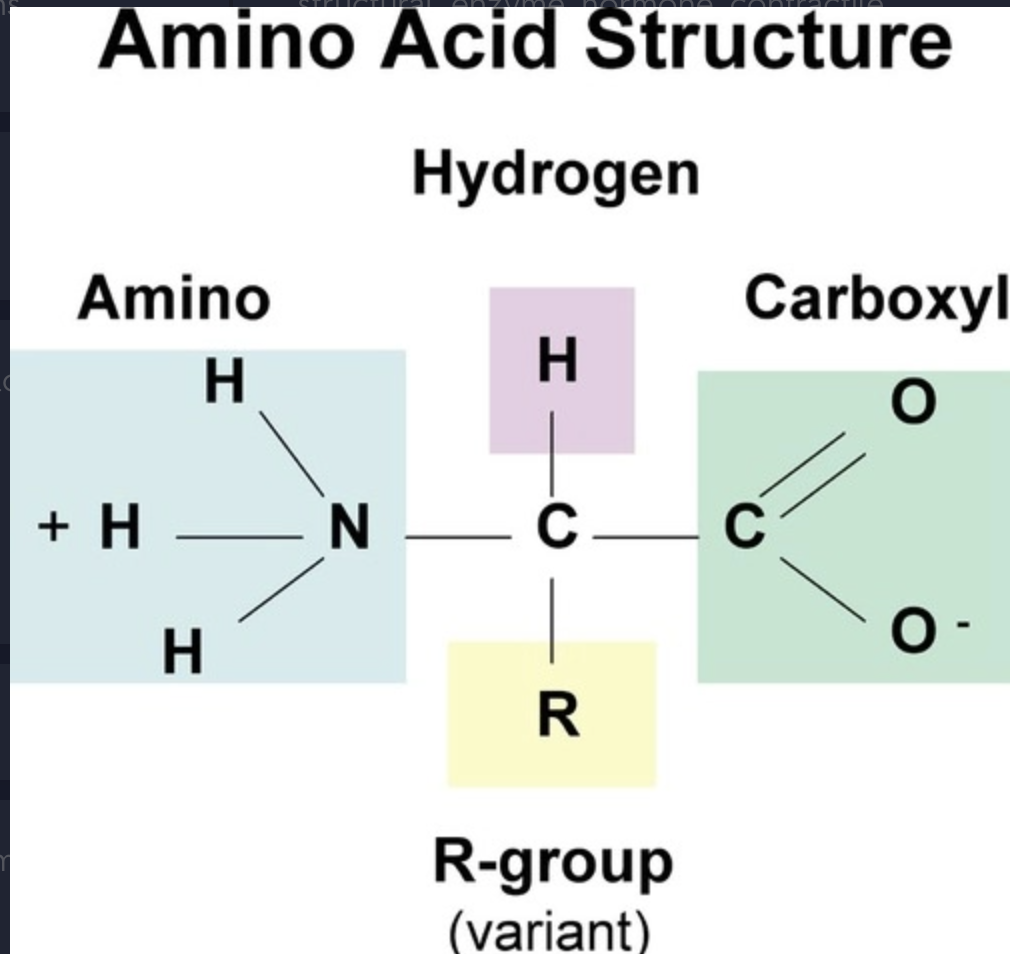
6
New cards
amino acid condensation reaction
* linked by condensation reaction
* new bond called peptide
* dipeptide; 2 amino acids
* tripeptide: 3 amino acids
* new bond called peptide
* dipeptide; 2 amino acids
* tripeptide: 3 amino acids
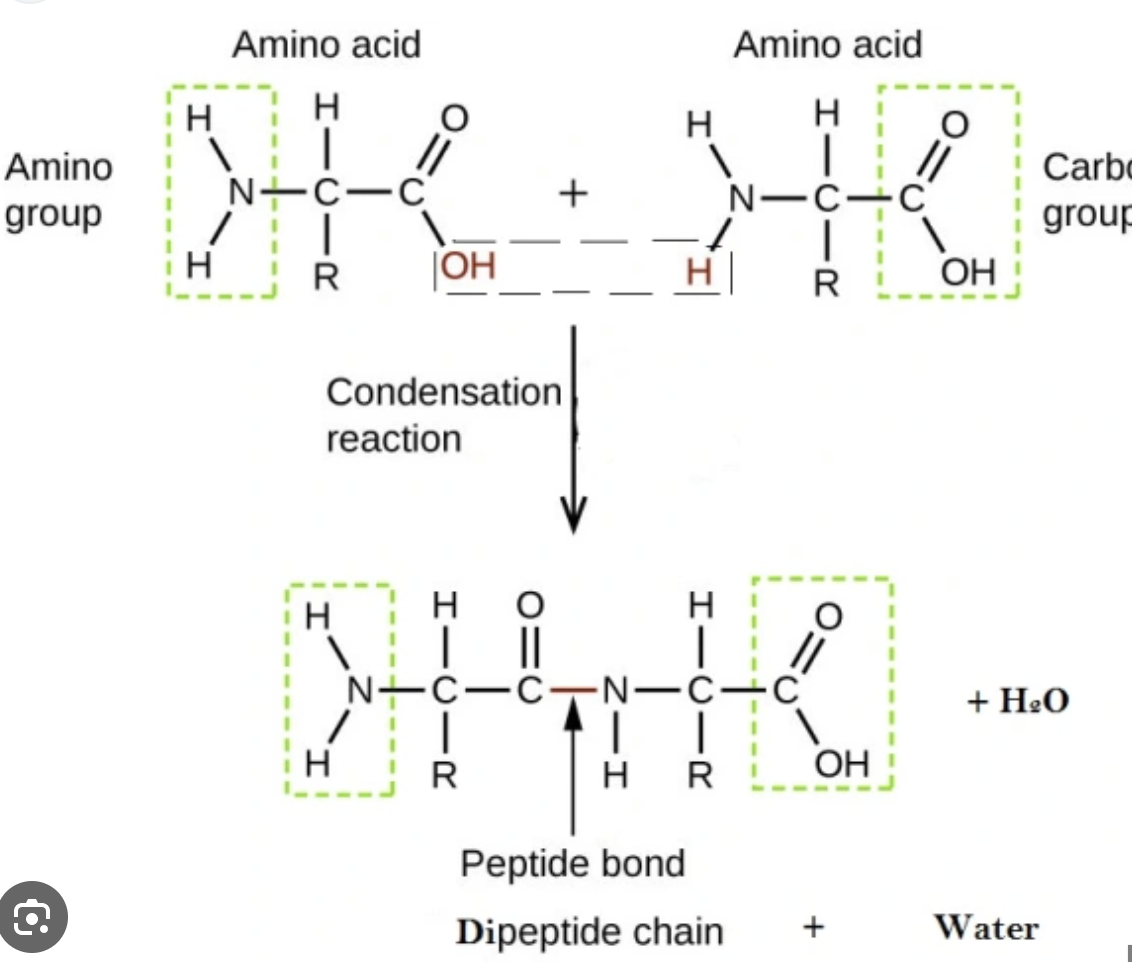
7
New cards
Number of amino acids
20
8
New cards
Synthesis of polypeptides
DNA provides info, transcribed into RNA, where the synthesis takes place in the ribosomes (translation)
9
New cards
Number of polypeptides in proteins
one or more
10
New cards
Polypeptide structures
* primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
* folding determined by amino acid sequence
* stabilized by intramolecular bonds between amino acids
* folding determined by amino acid sequence
* stabilized by intramolecular bonds between amino acids
11
New cards
Determinant of shape & function of protein
Order of amino acids
12
New cards
R group determines
types of bonds, interactions w/ other molecules, properties, function, structure
13
New cards
Conformation
three-dimensional shape of a proteinmolecule
14
New cards
Effect of gene mutation
changes protein's conformation, shape, loss of function
15
New cards
Primary structure
Simple linear sequence, defines all aspects of structure & function
16
New cards
Secondary structure
Folding chains on themselves (pleated sheet or alpha helix)
17
New cards
teritary structure
foils & coils to form complex 3d shape
18
New cards
Quarternary stucture
2 or more polypeptide chains held in a multi
19
New cards
Denaturation
Permanent loss of secondary, tertiary (sometimes quaternary) due to hydrogen bond disruption between R groups & amino groups
20
New cards
Cause of folding & touching of proteins
Ionic bonds between positively and negatively charged R groups
21
New cards
Genome
unique DNA content in every organism
22
New cards
Proteome
Unique set of proteins coded by genome
* varies because diff cells make diff proteins and depends on cell activity
* varies because diff cells make diff proteins and depends on cell activity
23
New cards
gel electrophoresis
Process to separate proteins
24
New cards
Divisions of protein
globular & fibrous
25
New cards
Determinant of divisions of protein
solubility in water
26
New cards
Globular proteins
Complex polypeptide chains linked to other chains, soluble in water cause hydrophobic R groups fold into the core away from surrounding water
27
New cards
Role of Globular proteins
active in cell metabolism
28
New cards
Fibrous proteins
Long polypeptide chains with hydrophobic R groups exposed therefore insoluble in water
29
New cards
Role of fibrous proteins
structural parts: tendons, skin, collages, keratin
30
New cards
Rubisco
* globular enzyme
* active site catalyzing photosynthesis reaction that fixes CO2 from atmosphere
* active site catalyzing photosynthesis reaction that fixes CO2 from atmosphere
31
New cards
Insulin
* globular, hormone, 2 diff polupeptide chains
* produced by pancreas
* carried, dissolved in blood
* binds specifically & reversibly to insulin receptors causing absorption pf glucose to lower blood glucose conc
* produced by pancreas
* carried, dissolved in blood
* binds specifically & reversibly to insulin receptors causing absorption pf glucose to lower blood glucose conc
32
New cards
Immunoglobulin
Globular, Y shaped, antibodies to fight infections by recognizing and binding to antigen molecules
33
New cards
Rhodopsin
* globular, pigment protein
* retina rod cells become light-sensitive to serve a nerve impulse
* retina rod cells become light-sensitive to serve a nerve impulse
34
New cards
Collagen
Fibrous, 3 diff polypeptide chains. structural protein, in muscles, tendons, ligaments to give tensile strength. In skin & bones to prevent tearing & fractures
35
New cards
Spider silk
Fibrous, structural protein, produced by spiders for webs, can be extended & resistant to breaking
36
New cards
Ways to denature proteins
higher temperatures, extreme pH of surrounding solution
37
New cards
3 properties of enzymes
substrate specific, optimum pH, optimum temperature
38
New cards
Why primary structures are not affected by denatueation
peptide bonds holding adjacent amino acids do not break
39
New cards
Reason for high fever danger
Some proteins start to denature, enzymes no longer function
40
New cards
Effect of temperature change on amino acids
Interaction between amino acids changed, affecting quaternary, tertiary & secondary
41
New cards
Effect of pH on amino acids
strong solutions can break bonds between non adjacent amino acids or between polypeptide chains
42
New cards
Coagulation: Structure when denatured
Hydrophilic attracts water molecules, hydrophobic portions unstable therefore associates with other hydrophobic molecules
43
New cards
Enzyme role
control metabolism of cell
* globular protein
* globular protein
44
New cards
Define Enzyme
biocatalyst that regulates the role of biochemical reactions without taking part
45
New cards
How is enzyme a catalyst
lowers minimum activation energy needed for reactants to react
46
New cards
Location of enzyme & substrate reactions
watery environment
47
New cards
Active site
location where substrate binds to enzyme to react
48
New cards
State of enzyme after reaction
unchanged & used again
49
New cards
Enzyme structure
large polypeptides with tertiary or quaternary structure, globular with specific active site
50
New cards
Induced fit
Once substrate binds to active site and during transition stage, enzyme changes slightly resulting in tighter binding
51
New cards
Role of induced fit
enzyme induces bond weakening within molecules thus reducing activation energy needed
52
New cards
Enzymatic reaction
1\. attraction of substrate to enzyme (diff shapes)
2\. conformational change reaction of substrate-enzyme complex
3\. enzyme revers to original shape and products leave reaction
2\. conformational change reaction of substrate-enzyme complex
3\. enzyme revers to original shape and products leave reaction
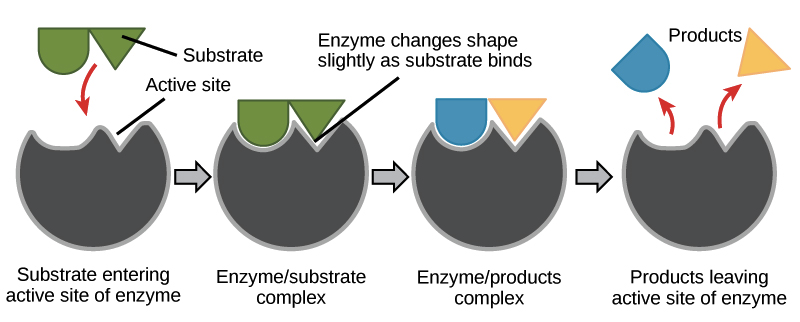
53
New cards
Active site structure
sequence of amino acids responsible for catalytic activity
54
New cards
Activation energy
minimum energy that reacting particles should possess for a reaction to make products
55
New cards
Collision theory
1. particles must collide to react together
2. need sufficient energy to break & form bonds
3. orientation (opposite charge molecules)
56
New cards
Exothermic or exergonic reation
product formation releases energy
57
New cards
Endothermic or endergonic
product formation associated with energy absorption (usually heat)
58
New cards
Causes of structural changes to active site
1\. temperature
2\. pH
3\. Substrate concentration
4\. Enzyme concentration
2\. pH
3\. Substrate concentration
4\. Enzyme concentration
59
New cards
Effect of temperature on collision theory
* Low temp = slowly, collision low
* High temp = rapid, collision high, denature
* High temp = rapid, collision high, denature
60
New cards
Low Substrate concentration
* more substrate than enzyme
* low rate of reaction
* low rate of reaction
61
New cards
High substrate concentration
* more collision chances
* rate of enzymatic reaction rises gradually
* increase halted when active sites occupied
* rate of enzymatic reaction rises gradually
* increase halted when active sites occupied
62
New cards
Graph structure of optimal temperature & pH
* increases due to more collisions of heat
* peak reached
* drops due to denature of heat and pH
* increase, peak and drop with pH
* peak reached
* drops due to denature of heat and pH
* increase, peak and drop with pH
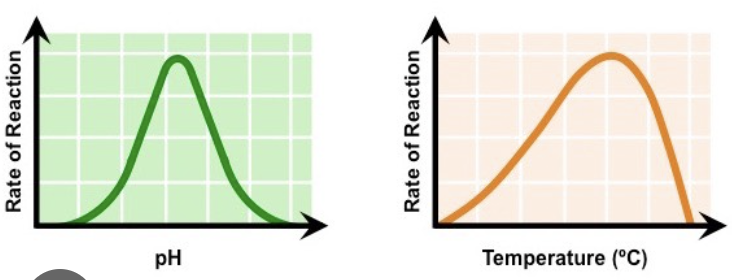
63
New cards
Graph structure of substrate/enzyme concentration
1. increases because more collisions between substrate and active site
2. plateau phase because most active sites are occupied
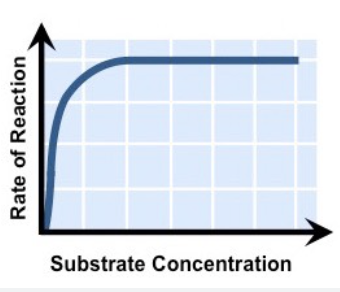
64
New cards
Immbolisation of enzyme
process of attaching enzyme to a material to restrict movement
65
New cards
Permit of immboilisation of enzyme
* not present in final product
* doesn't restrict conc
* avoid adverse effects to human consumption
* higher conc of enzymes
* faster rate of reaction
* immediate separation from reaction mixture
* recycled
* doesn't restrict conc
* avoid adverse effects to human consumption
* higher conc of enzymes
* faster rate of reaction
* immediate separation from reaction mixture
* recycled
66
New cards
How to increase pH as dependent variable
* increase rate of reaction!
* increase enzyme conc
* increase temp
* longer time
* increase enzyme conc
* increase temp
* longer time
67
New cards
Value of V(velocity) at start of reaction
Minimum since active sites are free
68
New cards
Amino acids
carbon center. monomers of proteins
69
New cards
Cell theory
1\. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells.
2\. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms
3\. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
2\. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms
3\. Cells arise from pre-existing cells.
70
New cards
Louis Pasteur method & results
Heated broth with swan necks \n 1. Sealed & upright: no growth \n 2. Unsealed: microbial growth \n 3. Tilted: growth
71
New cards
Louis Pasteur Conclusion
Air carries microbes but non-living conditions do not make living things
72
New cards
Spontaneous generation
Living things arise from non-living aka abiogenesis
73
New cards
Biogenesis
cells formed from pre-existing cells
74
New cards
Miller Urey Method
Recreated early earth conditions:
* atmosphere (low oxygen, high radiation, gasses)
* heating of water vapor
* electrical storm shocks
* atmosphere (low oxygen, high radiation, gasses)
* heating of water vapor
* electrical storm shocks
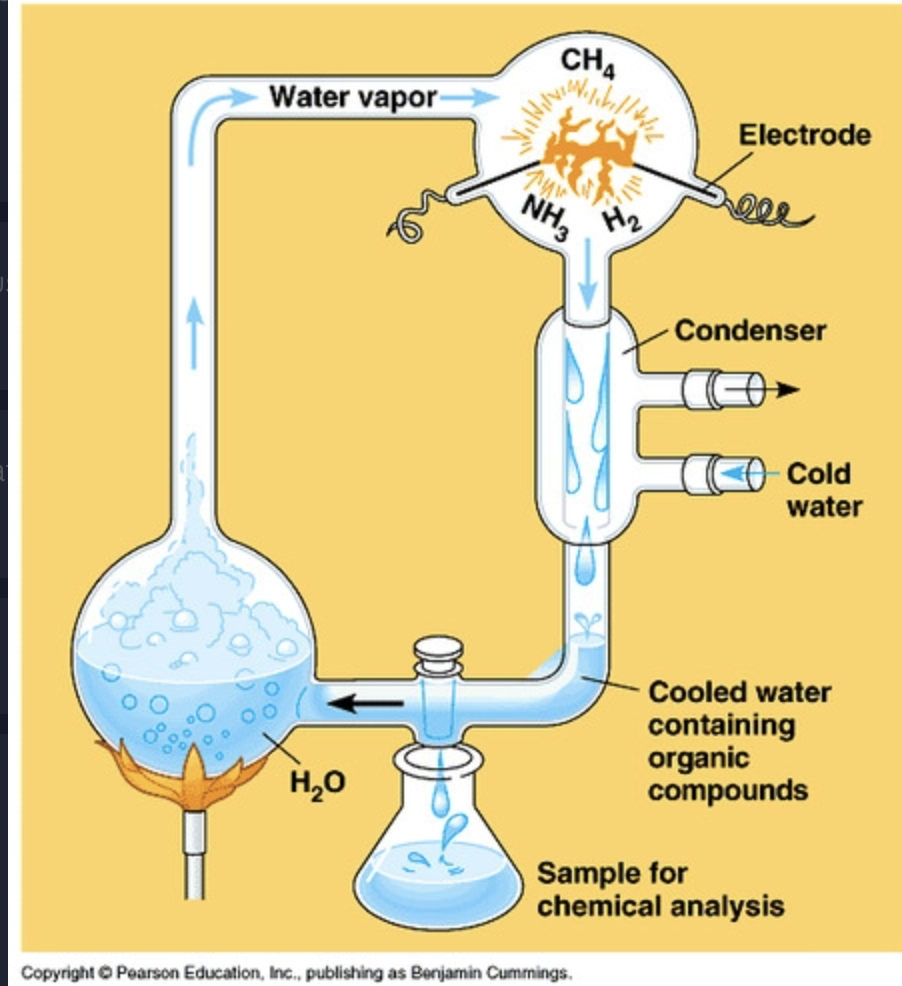
75
New cards
Miller Urey Conclusion
Solution found organic molecules including amino acids found in living organisms
76
New cards
4 conditions for life to emerge & persist
1\. Simple organic molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, carbohydrates)
2\. Larger organic molecules must be assembled from simpler molecules (DNA, phospholipids)
3\. Reproduction for replication
4\. Biochemical reactions require set conditions therefore self-contained structures need membranes
2\. Larger organic molecules must be assembled from simpler molecules (DNA, phospholipids)
3\. Reproduction for replication
4\. Biochemical reactions require set conditions therefore self-contained structures need membranes
77
New cards
endosymbiotic theory
Mitochondria (likely anaerobes) & chloroplasts (likely cyanobacteria) were prokaryotes taken by larger prokaryotes
78
New cards
evidence for endosymbiotic theory
In mitochondria & chloroplasts
* double membrane
* circular naked DNA like prokaryotes
* DNA as single chromosomes
* 70s ribosomes like prokaryotes
* binary fission like prokaryotes
* susceptible to some antibiotics
* double membrane
* circular naked DNA like prokaryotes
* DNA as single chromosomes
* 70s ribosomes like prokaryotes
* binary fission like prokaryotes
* susceptible to some antibiotics
79
New cards
How do living organisms control composition?
complex web of chemical reactions
80
New cards
Metabolism
web of all enzyme
81
New cards
Why is life carbon
based
82
New cards
4 types of macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins & nucleic acids
83
New cards
Lipids
* triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids
* carbon compounds made by living organisms
* mostly or entirely hydrophobic
* 2-3 hydrocarbon chains or quadruple ring structure (steroids)
* *stores energy for later use*
* carbon compounds made by living organisms
* mostly or entirely hydrophobic
* 2-3 hydrocarbon chains or quadruple ring structure (steroids)
* *stores energy for later use*
84
New cards
triglyceride
* fatty acid tails are flexible
85
New cards
fatty acids
* carboxyl group: acidic and -COOH
* unbranched hydrocarbon
* type of lipid
* 3 fatty acids form a triglyceride
* unbranched hydrocarbon
* type of lipid
* 3 fatty acids form a triglyceride
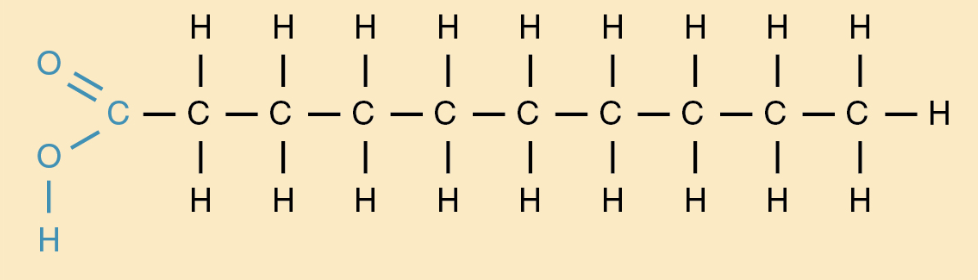
86
New cards
Macromolecules
organic compound made of smaller molecules
87
New cards
Role of macromolecules
build living cells & take part in biochemical reactions
88
New cards
glycerides
* lipids
* fatty acids linked to glycerol by condensation reaction
* fatty acids linked to glycerol by condensation reaction
89
New cards
Composition of carbohydrates
carbon, hydrogen & oxygen
90
New cards
Role of starch
energy storage in plants
91
New cards
Color of iodine solution if starch present
blue
92
New cards
Color of biuret test for proteins
purple
93
New cards
Color of benedict solution for carbohydrates
orange or brick red
94
New cards
Structure of Alpha Glucose (draw)
H top, OH down
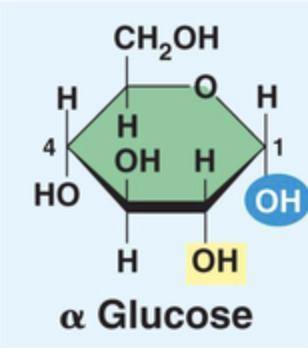
95
New cards
Structure of Beta glucose (Draw)
OH top, H down
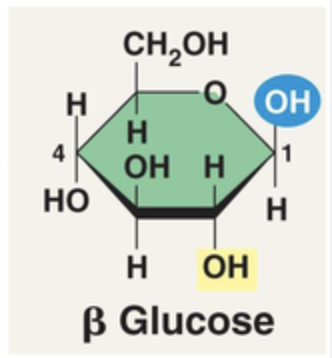
96
New cards
Anabolism
* synthesis of complex molecules to simpler molecules
* requires energy input
* requires energy input
97
New cards
Catabolism
* breakdown of complex into simpler molecules
* hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers
* hydrolysis of macromolecules into monomers
98
New cards
Hydrolysis reaction
breaking chemical bonds by adding water molecules
99
New cards
Urea formula
CO(NH2)2
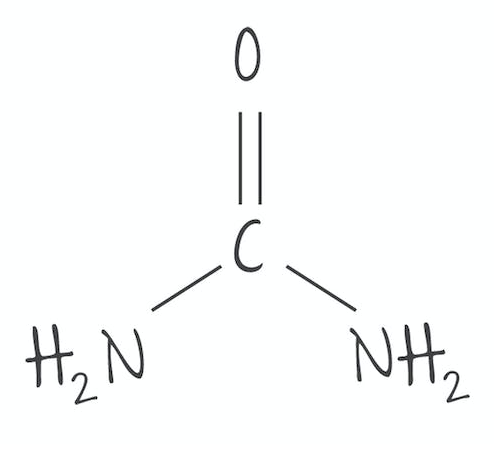
100
New cards
Use of urea
human body to excrete nitrogen because urea is non