Nucleic Acids A1.2
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Nucleic acid
A biological macromolecule made of nucleotide monomers that stores and transmits genetic information (DNA and RNA).
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid; the genetic material of all living organisms.
RNA
Ribonucleic acid; involved in protein synthesis and sometimes acts as genetic material in viruses.
Why are viruses not considered living even though some use RNA as genetic material?
They cannot carry out metabolism or reproduce independently as they need a host
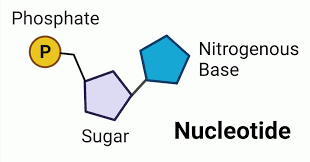
Nucleotide
The monomer of nucleic acids, consisting of a pentose sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
Components of a nucleotide
phosphate group + pentose sugar + nitrogenous base.
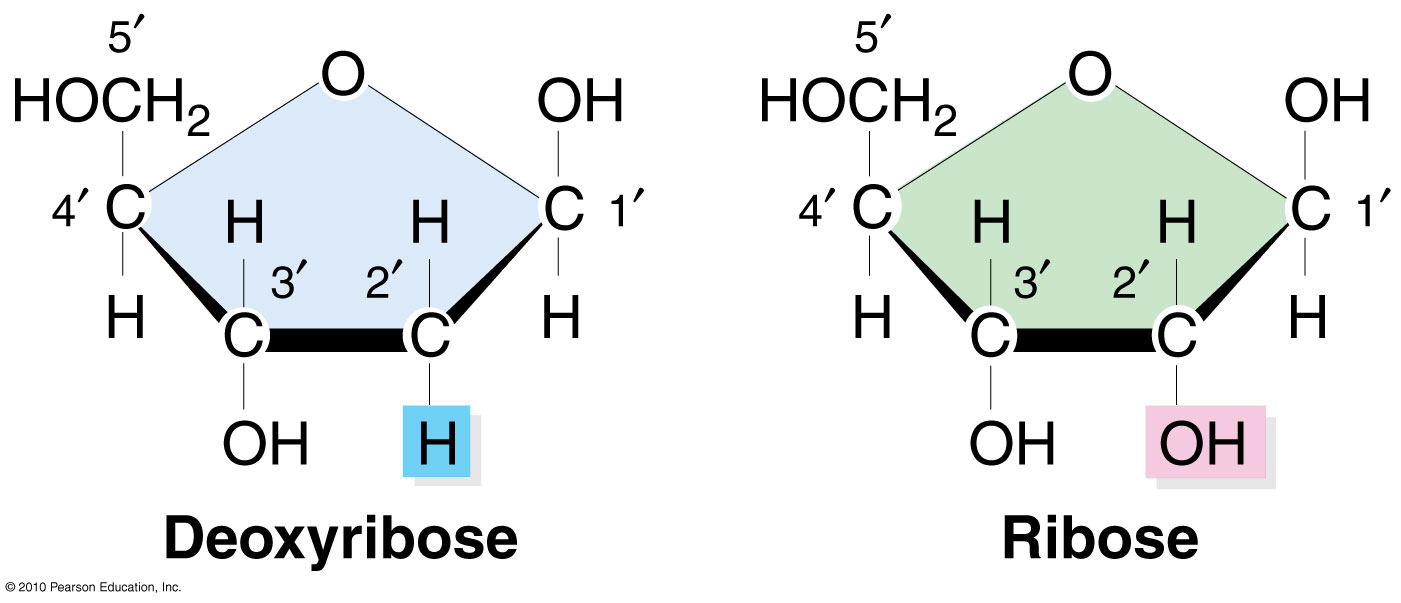
Pentose sugars in nucleic acids
DNA = deoxyribose
RNA = ribose
Deoxyribose vs ribose
Deoxyribose lacks one oxygen atom compared to ribose.
Nitrogenous base
A nitrogen-containing molecule that forms part of a nucleotide and carries genetic information.
Four nitrogenous bases in DNA
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), Cytosine (C)
Nitrogenous bases unique to RNA
Uracil (U) replaces thymine.
Sugar–phosphate bond
A covalent bond between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of another.
Sugar–phosphate backbone
A strong, continuous chain of alternating sugars and phosphates forming the structural framework of DNA and RNA.
RNA as a polymer
RNA is formed by condensation reactions linking nucleotide monomers together.
What type of reaction forms RNA polymers?
Condensation reactions
DNA double helix
A structure consisting of two antiparallel nucleotide strands twisted together.
Antiparallel
The two DNA strands run in opposite directions (5′→3′ and 3′→5′).
Complementary base pairing
Specific hydrogen bonding between bases: A–T (or A–U) and C–G.
What holds complementary base pairs together?
hydrogen bonds
Difference between DNA and RNA (overview)
DNA: double-stranded, deoxyribose, thymine
RNA: single-stranded, ribose, uracil
Why is complementary base pairing important for DNA replication?
It ensures accurate copying of genetic information.
Role of complementary base pairing in protein synthesis
It allows transcription and translation to occur accurately.
Triplet code
A sequence of three DNA or RNA bases codes for one amino acid.
Why does DNA have an enormous storage capacity for information?
Any length of DNA and any base sequence is possible.
What does “universal genetic code” mean?
The same genetic code is shared by almost all living organisms.
What does the universality of the genetic code provide evidence for?
A common ancestor for all life on Earth.
5′ to 3′ directionality
The direction in which nucleotides are added during replication and transcription.
Why is 5′→3′ directionality important?
It determines how DNA is replicated and how RNA is transcribed and translated.
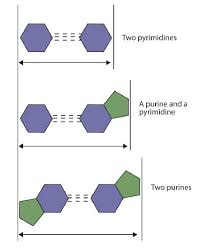
Purine vs pyrimidine
Purines: adenine, guanine
Pyrimidines: cytosine, thymine, uracil
Why does purine–pyrimidine pairing stabilize the DNA helix?
It ensures uniform width of the DNA molecule.
Nucleosome
DNA wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins, with linker DNA and an additional histone.
Histone
A basic protein that DNA coils around to form nucleosomes.
What did the Hershey–Chase experiment demonstrate?
That DNA, not protein, is the genetic material.
How did Chargaff’s data challenge the tetranucleotide hypothesis?
By showing base ratios vary between species but A=T and C=G.
Backbone
The sugar–phosphate structure forming the sides of DNA and RNA molecules.
Complementary
Bases that pair specifically due to hydrogen bonding.
DNA replication
The process by which DNA is copied before cell division.
Protein synthesis
The process by which genetic information is used to build proteins.