Atoms, compounds, ion
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Atoms
They are the basic building blocks of matter and the smallest units of an element that can combine with other elements. ____ are composed of even smaller particles called subatomic particles. Some of these subatomic particles are charged and follow the usual behavior of charged particles: Particles with the same charge repel one another, whereas particles with opposite charges are attracted to one another.
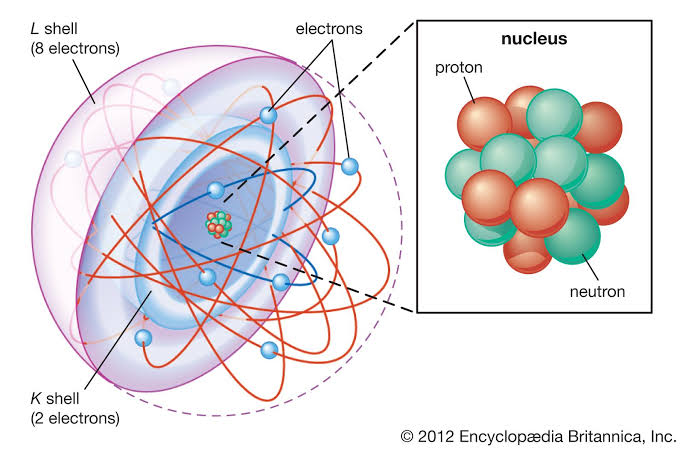

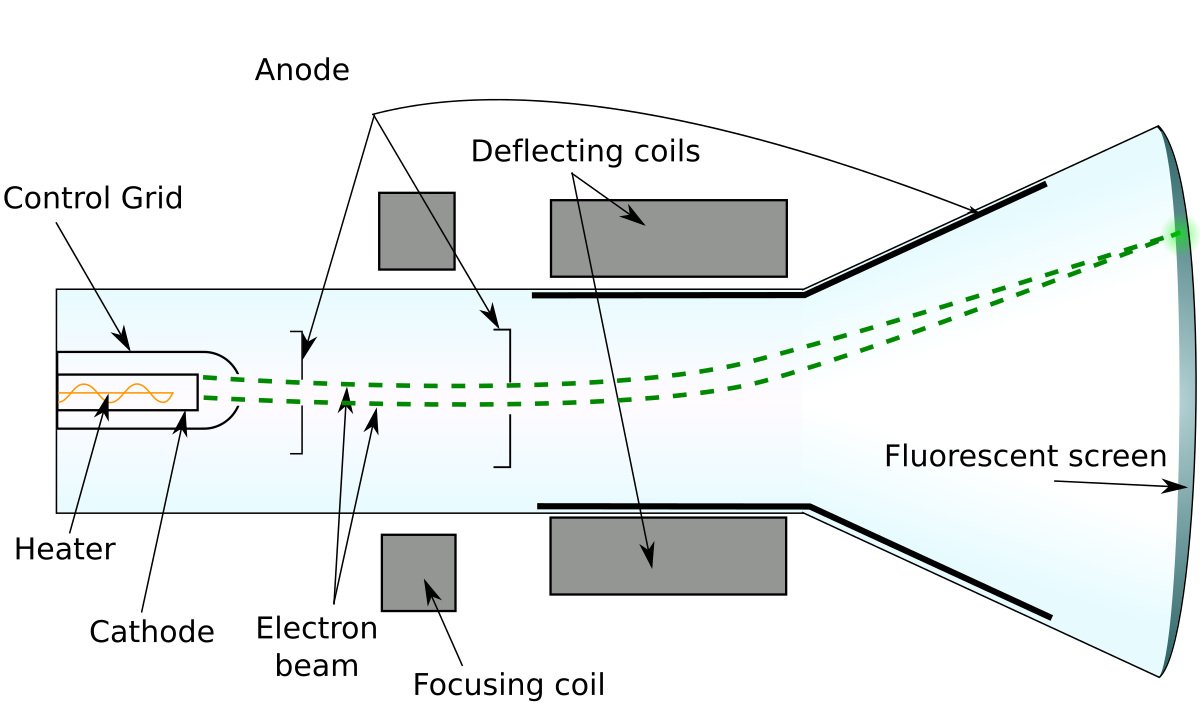
Joseph John Thomson's (JJ Thomson’s)
We considered some of the critical experiments that led to the discovery and characterization of subatomic particles. _____ ____ _____ experiments on the behavior of cathode rays in magnetic and electric fields led to the discovery of the electron and allowed its charge-to-mass ratio to be measured.

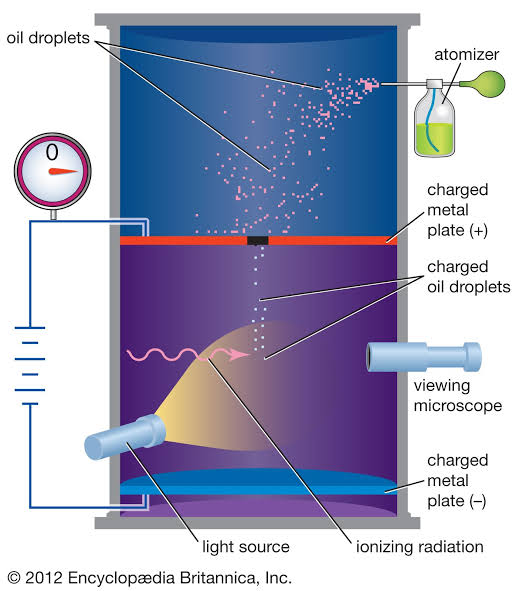
Robert Millikan's (R. A. Millikan)
_____ _____ oil-drop experiment determined the charge of the electron.

Henri Bequerel's
____ _____ discovery of radioactivity, the spontaneous emission of radiation by atoms, gave further evidence that the atom has a substructure. Though it was him that discovered radioactivity, it was Marie Curie who coined the term.

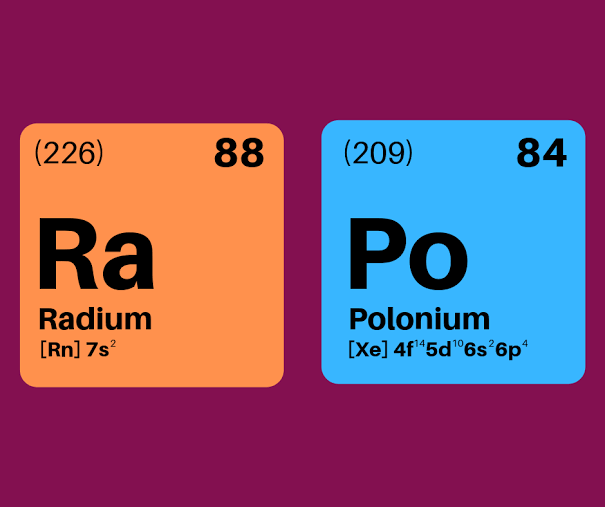
Marie Curie
____ _____ became the first woman to be for the discovery of Polonium and Radium in 1911. awarded the Nobel prize and the first person who received two Nobel prizes when she won the prize for the discover of the Polonium and Radium in 1911.

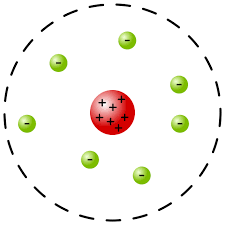
Ernest Rutherford's
______ _____ studies of how particles scatter when passing through thin metal foils led to the nuclear model of the atom, showing that the atom has a dense, positively charged nucleus.

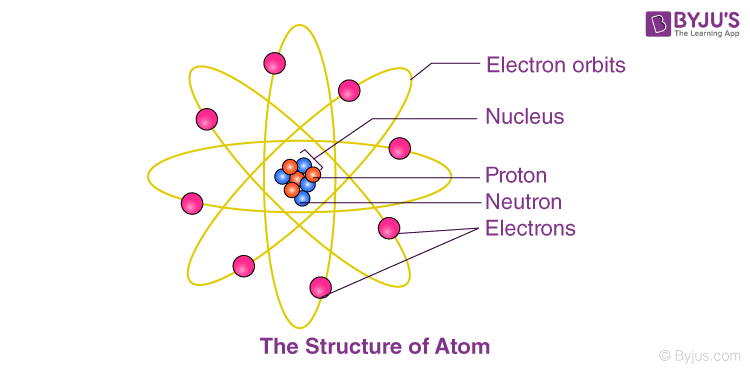
John Dalton’s
The main points of ____ _____ atomic theory are:
1. Everything is composed of atoms, which are the indivisible building blocks of matter and cannot be destroyed.
2. All atoms of an element are identical.
3. The atoms of different elements vary in size and mass.
4. Compounds are produced through different whole-number combinations of atoms.
5. A chemical reaction results in the rearrangement of atoms in the reactant and product compounds.

1.602 × 10^-19 C
The magnitude of the electron’s charge is:
___________
This is known as the elementary (electronic) charge.Charge values are usually expressed in multiples of this:
Electron: –1 charge
Proton: +1 charge
Neutron: 0 charge (neutral)
1.66054 × 10^-24 g
Atomic masses are typically measured in atomic mass units (amu).
1 amu is defined as:
_______________
angstroms
Atom sizes are often given in _______ (Å).
1 Å = 10^-10 meters
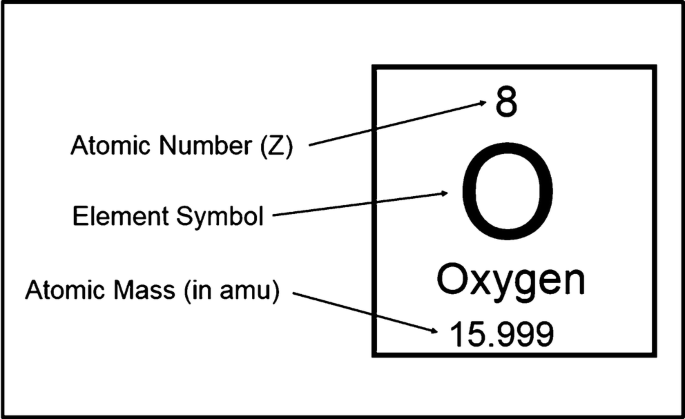
The role of the atomic number in identifying elements
the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. It uniquely identifies an element. For example, any atom with 6 protons is always carbon, no matter how many neutrons or electrons it has.
Why atoms of the same element always have the same atomic number
the atomic number = number of protons, and protons define the element, all atoms of the same element have the same atomic number. If the number of protons changes, it’s a completely different element.
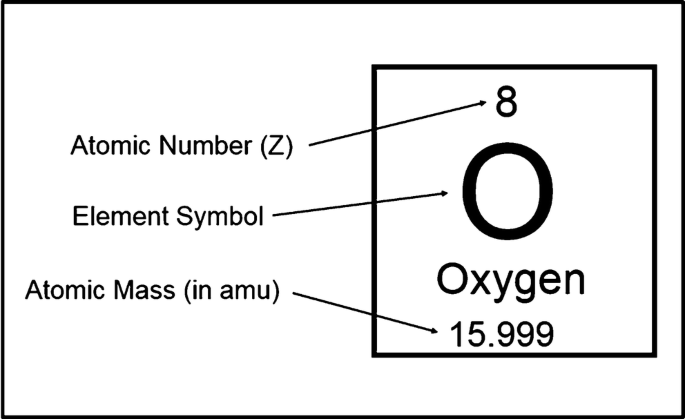
Meaning of an atom’s mass number
is the total count of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
Mass number = Protons + Neutrons
It represents the “massive” particles in the atom, since electrons have almost no mass.
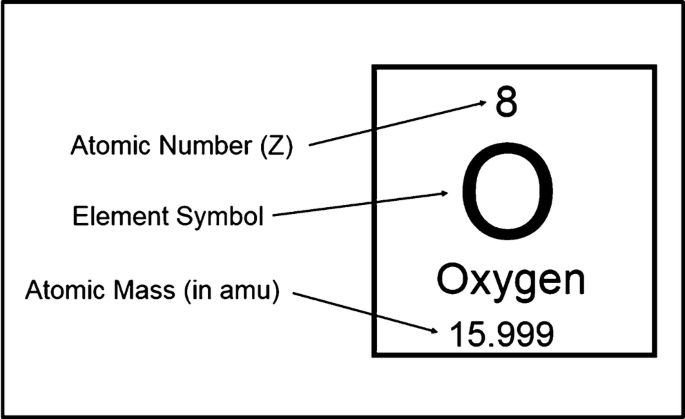
Definition and meaning of isotopes
are atoms of the same element (same number of protons) but with different numbers of neutrons, giving them different mass numbers. They behave chemically the same but may differ in stability or radioactivity.
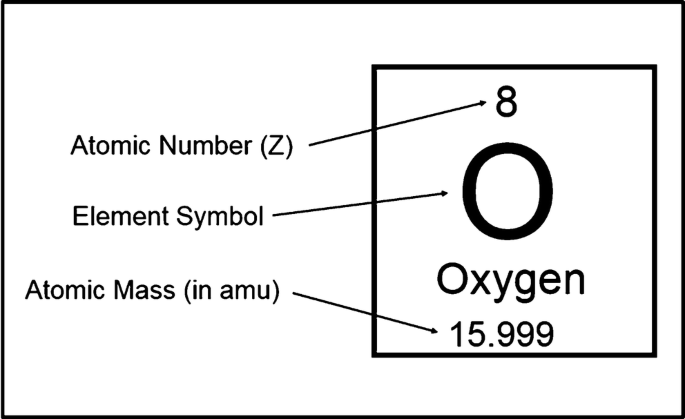
Example of isotopes and what they show
Carbon-12 has 6 protons and 6 neutrons.
Carbon-14 also has 6 protons but has 8 neutrons.
→ Both are carbon because they have 6 protons, but they’re isotopes due to different numbers of neutrons.
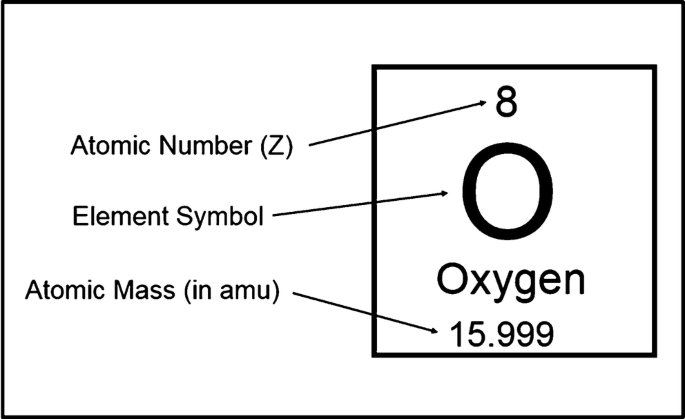
What stays the same and what changes among isotopes of an element
Stays the same: Number of protons (atomic number) and electron arrangement (if neutral).
Changes: Number of neutrons → this affects the mass number and can influence stability or radioactivity.
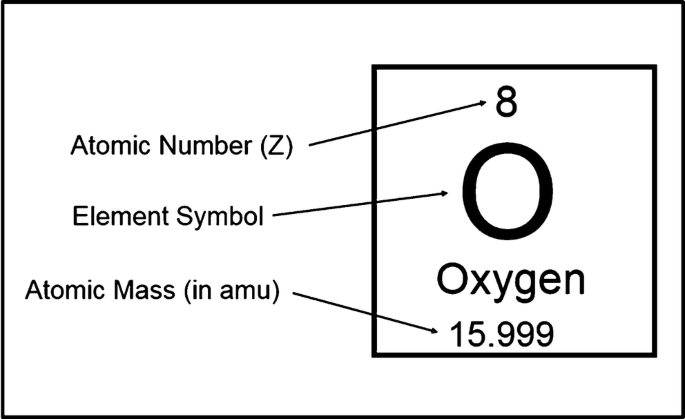
Atomic mass scale
Defined by assigning exactly 12 amu to a carbon (C) atom.

Atomic weight (average atomic mass)
Calculated using the relative abundances and masses of an element’s isotopes.

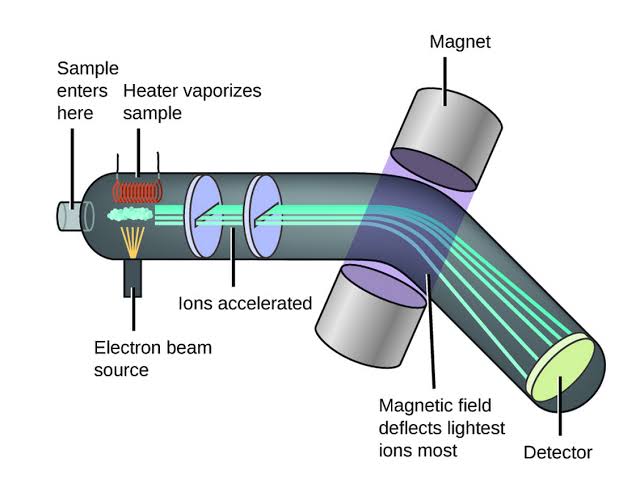
Mass spectrometer
The most direct and accurate tool for measuring atomic and molecular weights.
Arrangement of the periodic table
Elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number.
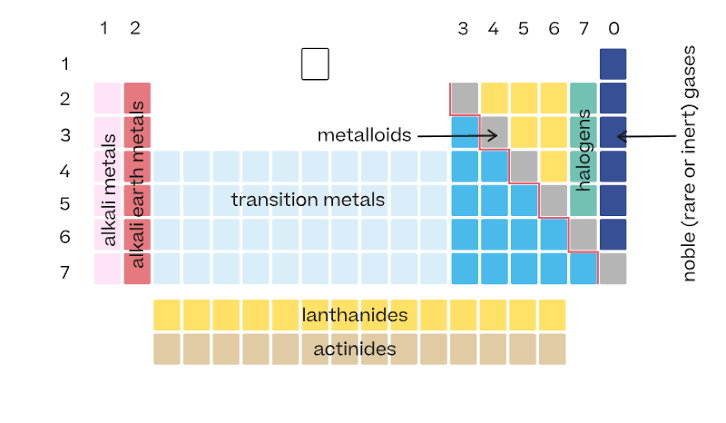
Vertical columns in the periodic table
Called groups. Elements in the same group have similar properties.
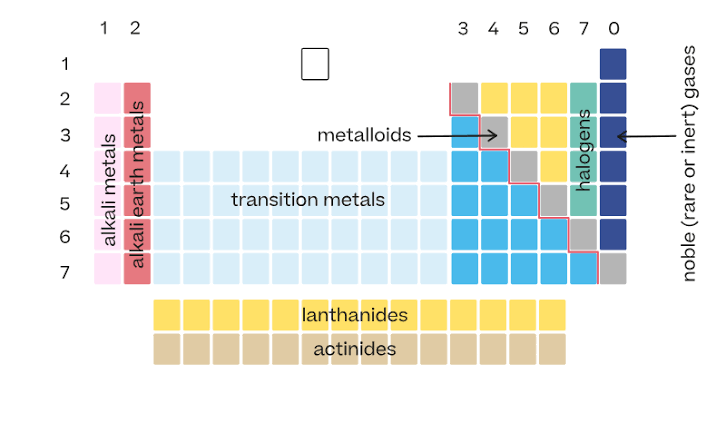
Horizontal rows in the periodic table
Called periods.
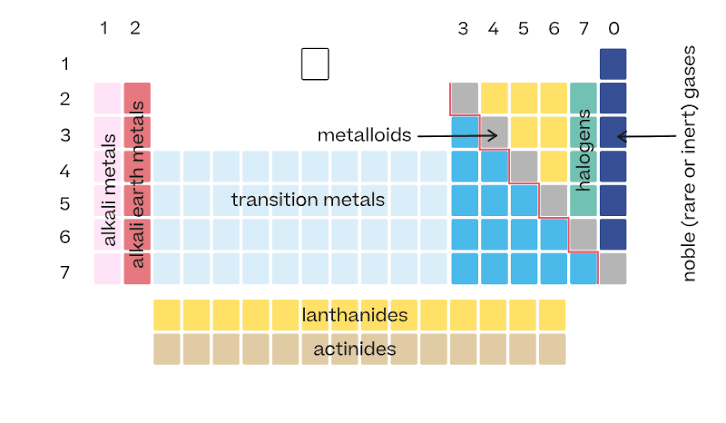
Location of metals on the periodic table
Found on the left side and middle. They make up most of the elements.

Location of nonmetals
Found on the upper right side of the table.
Metalloids
Elements along the zigzag line between metals and nonmetals. They have properties of both.
How atoms form molecules
Atoms combine to form molecules. These can make up molecular compounds.

Elements in molecular compounds
Usually contain only nonmetals.

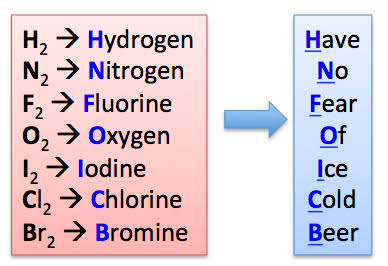
Diatomic molecule
A molecule that contains two atoms (can be same or different elements).
Chemical formula
Shows the composition of a substance using element symbols and subscripts.
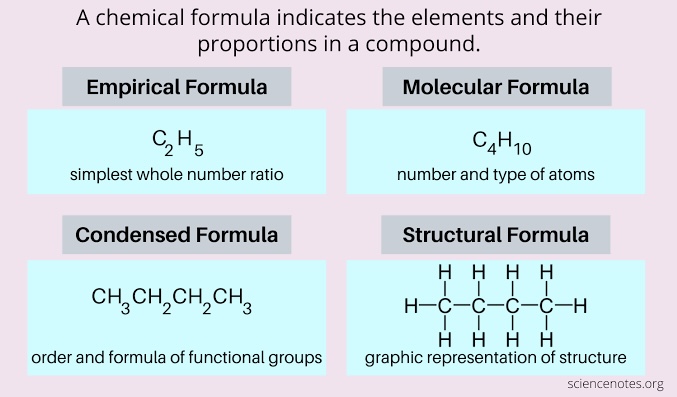
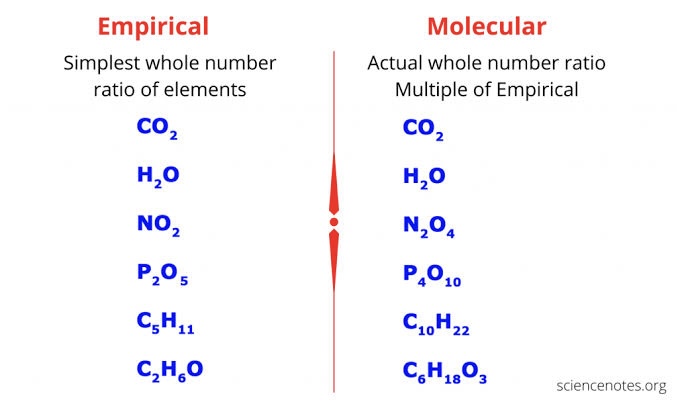
Empirical formula
Shows the simplest whole-number ratio of atoms in a compound.

Molecular formula
Shows the actual number of each atom in a molecule.
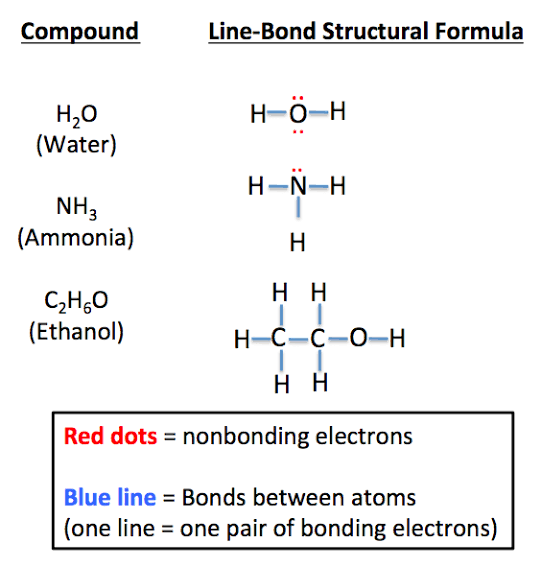
Structural formula
Shows how atoms are connected in a molecule.
Formation of ions
Atoms can gain or lose electrons, becoming charged particles called ions.
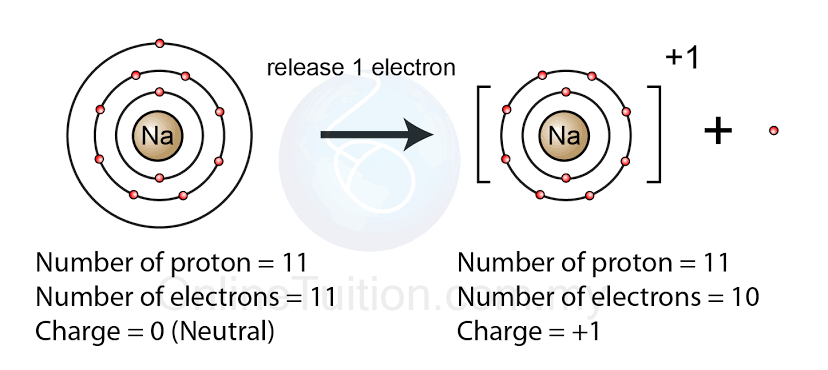
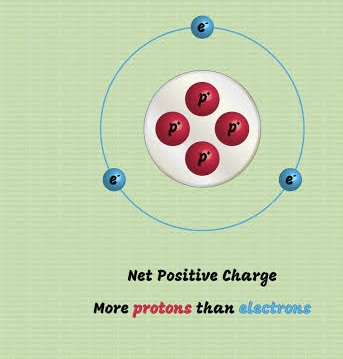
Cations (positive ions)
Metals tend to lose electrons, forming positively charged ions called ______.
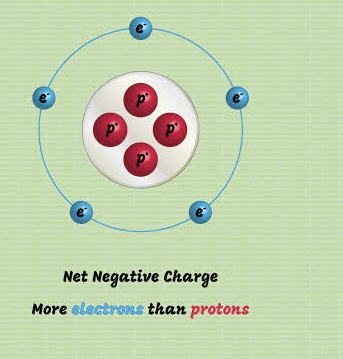
Anions (negative ions)
Nonmetals tend to gain electrons, forming negatively charged ions called ______.
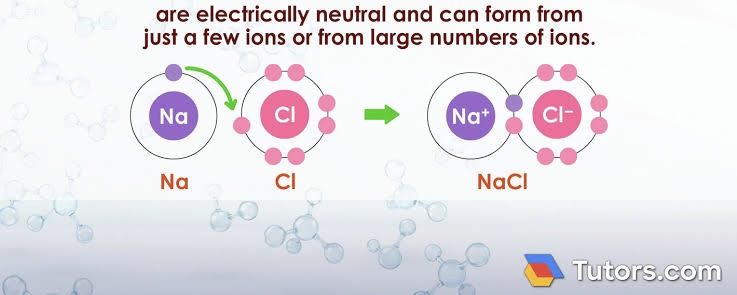
Composition of ionic compounds
Made of both cations and anions. They are electrically neutral overall and usually contain metals + nonmetals.
Polyatomic ions
A group of atoms bonded together with a net charge, acting like a single ion
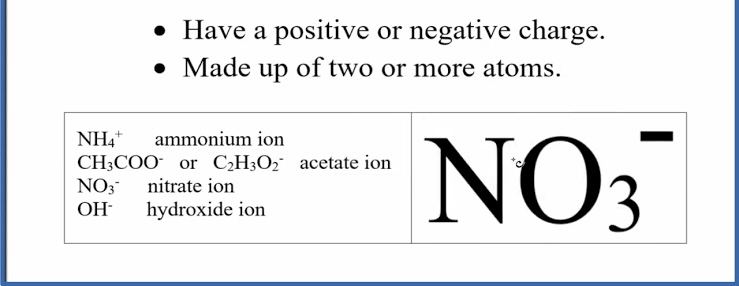
Chemical formulas of ionic compounds
Are empirical formulas, showing the lowest whole-number ratio of ions. You can write them if you know the ion charges.

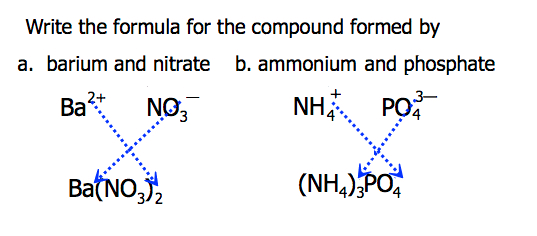
Balancing charges in ionic compounds
The total positive charge from cations must equal the total negative charge from anions to make the compound neutral.
Chemical nomenclature
The set of rules for naming chemical compounds.

3 types of inorganic compounds
Ionic compounds
Acids
Binary molecular compounds
Naming ionic compounds
Cation is named first, then anion.
Cations from metals keep the same name as the metal.
If a metal forms multiple ions, show the charge with Roman numerals.
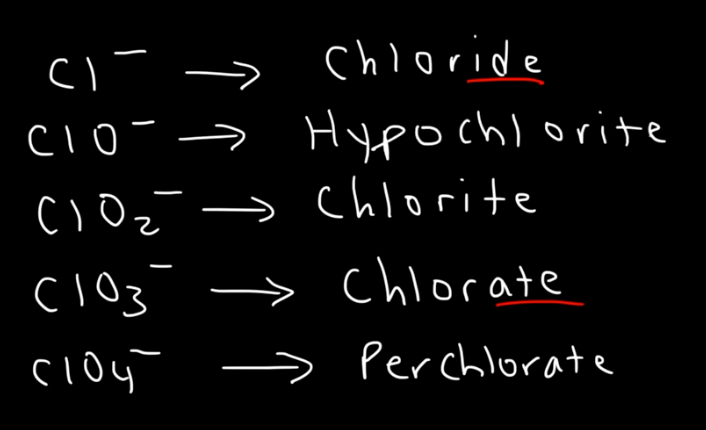
Naming monatomic anions (one atom)
End the element name with “-ide” (e.g., Cl⁻ → chloride, O²⁻ → oxide)
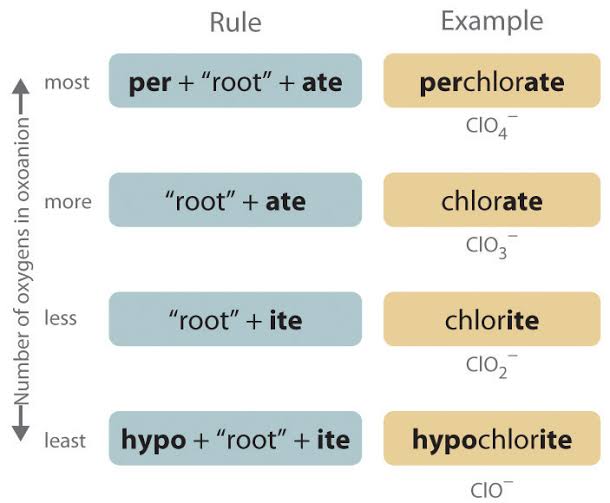
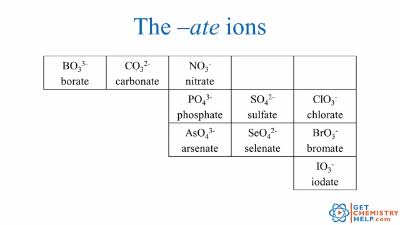
Naming polyatomic anions (oxyanions) - two or more atoms
Use “-ate” for more oxygen (e.g., sulfate, nitrate)
Use “-ite” for less oxygen (e.g., sulfite, nitrite)
Naming binary molecular compounds
Use Greek prefixes to show number of atoms (e.g., mono-, di-, tri-)
Name the element farther left on the periodic table first