4. Endo/Repro Exam 2: Medicine Pregnancy and Lactation, Oral Contraceptives (Dr. Cammock)
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
What are the perinatal oral health practice guidelines?
- Benefits far outweigh potential risks
- Good oral health and control of oral disease
- - Protects woman's health and quality of life
- - Potential to reduce transmission of pathogenic bacteria from mother to child
- Provide preventative services early in pregnancy
- Treat infection or sources of sepsis at any stage of pregnancy
- No increased risk of miscarriage or preterm delivery by treating (there is risk to not treating!)

What are three categories of barriers to dental care in pregnancy?
- Patients (~50% reported cleanings during pregnancy; some believed dental treatment was harmful)
- Oral health professionals (some thought it was dangerous)
- Prenatal care providers

T/F: The 2000 Surgeon General’s report Oral Health in America, stated that a “silent epidemic of oral diseases is affecting our most vulnerable citizens,” including the poor and many members of racial and ethnic minority groups
True

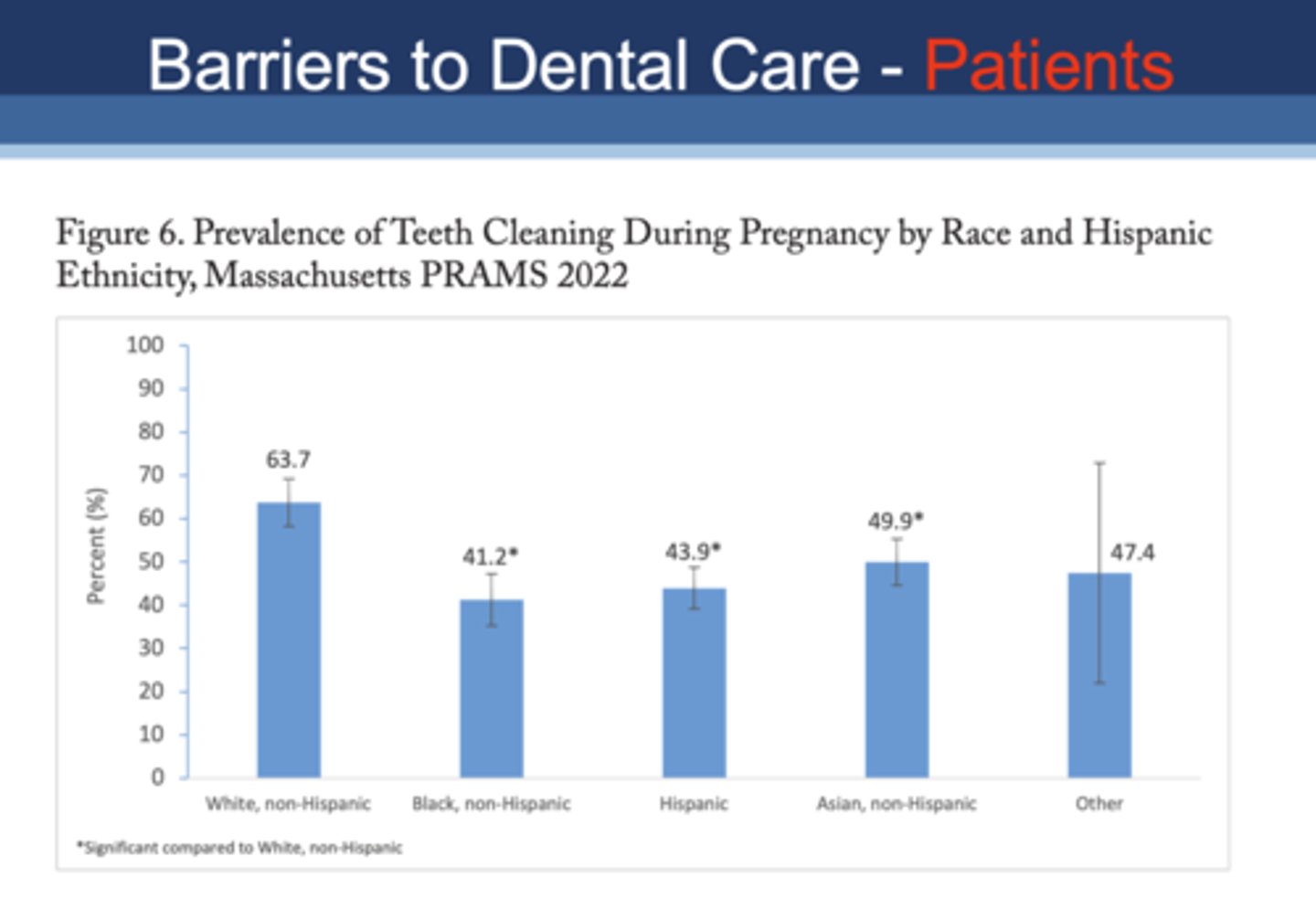
Which population had the lowest percentage of teeth cleaning during pregnancy?
A. White, non-hispanic
B. Black, non-hispanic
C. Hispanic
D. Asian, non-hispanic
B. Black, non-hispanic
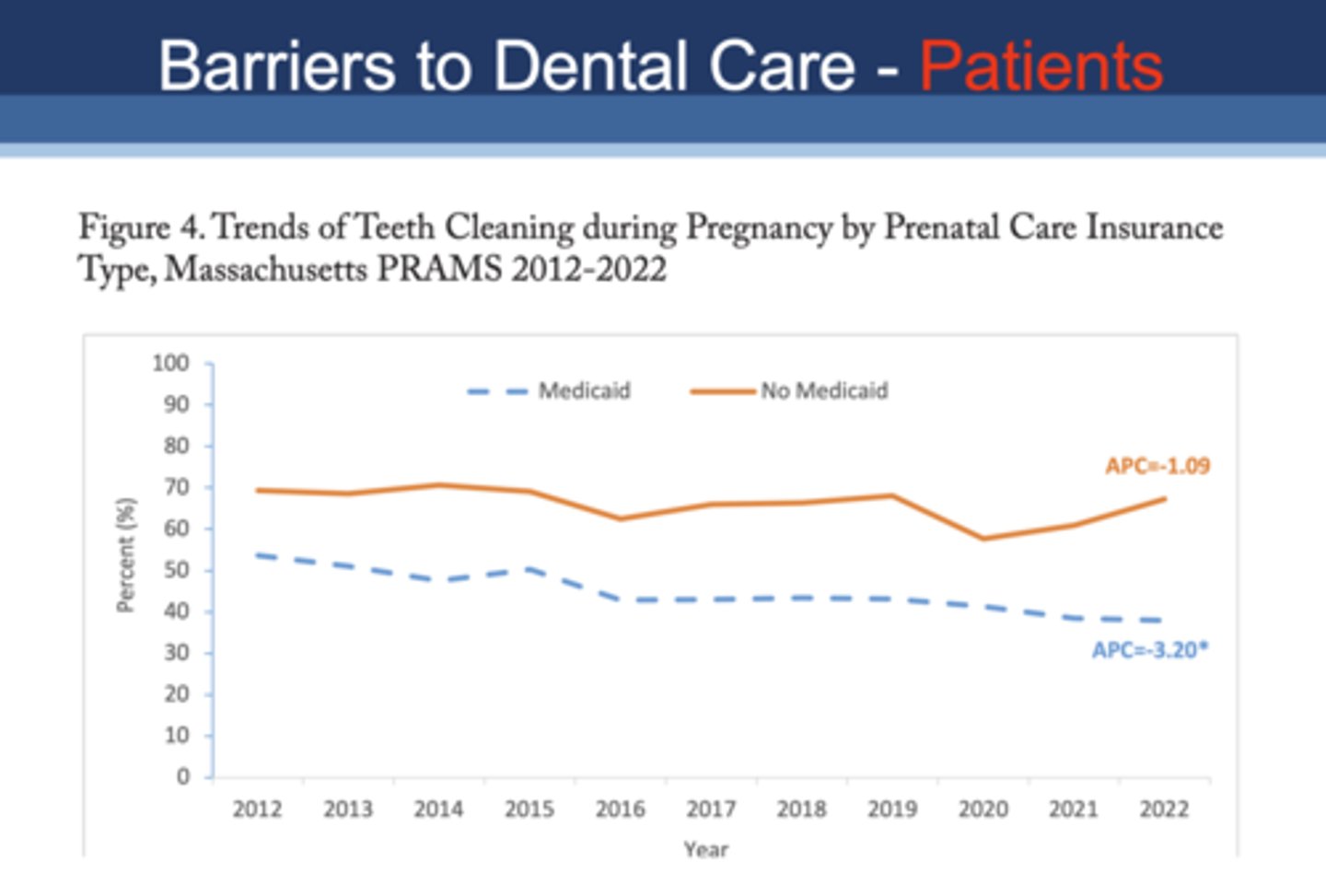
Who is more likely to have teeth cleaning during pregnancy?
A. Medicaid patients
B. Non-medicaid patients
B. Non-medicaid patients
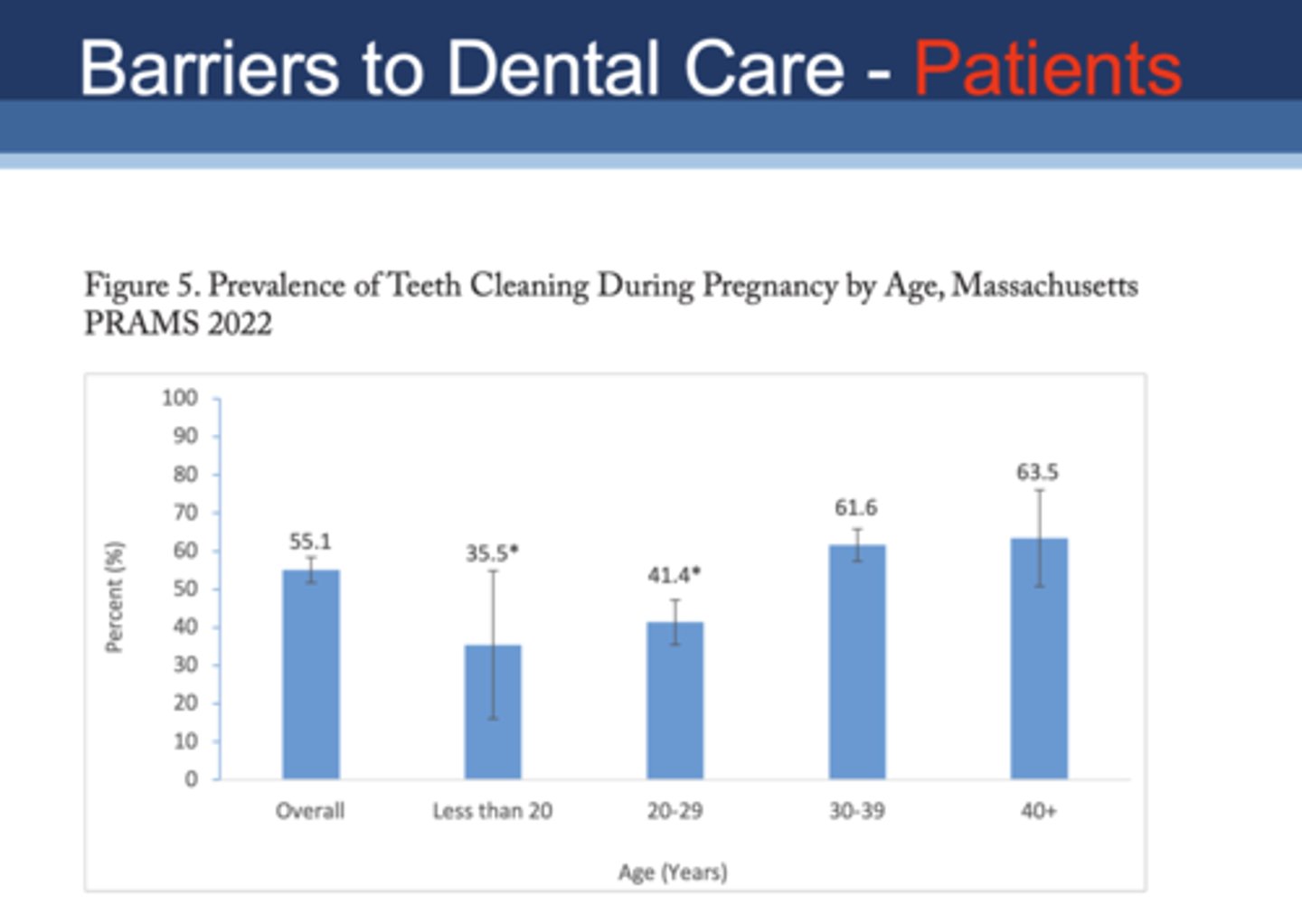
Which age group had the lowest percentage of teeth cleaning during pregnancy?
A. Less than 20
B. 20-29
C. 30-39
D. 40+
A. Less than 20
What percentage of obstetricians did not hear about the oral health practice guidelines?
74%

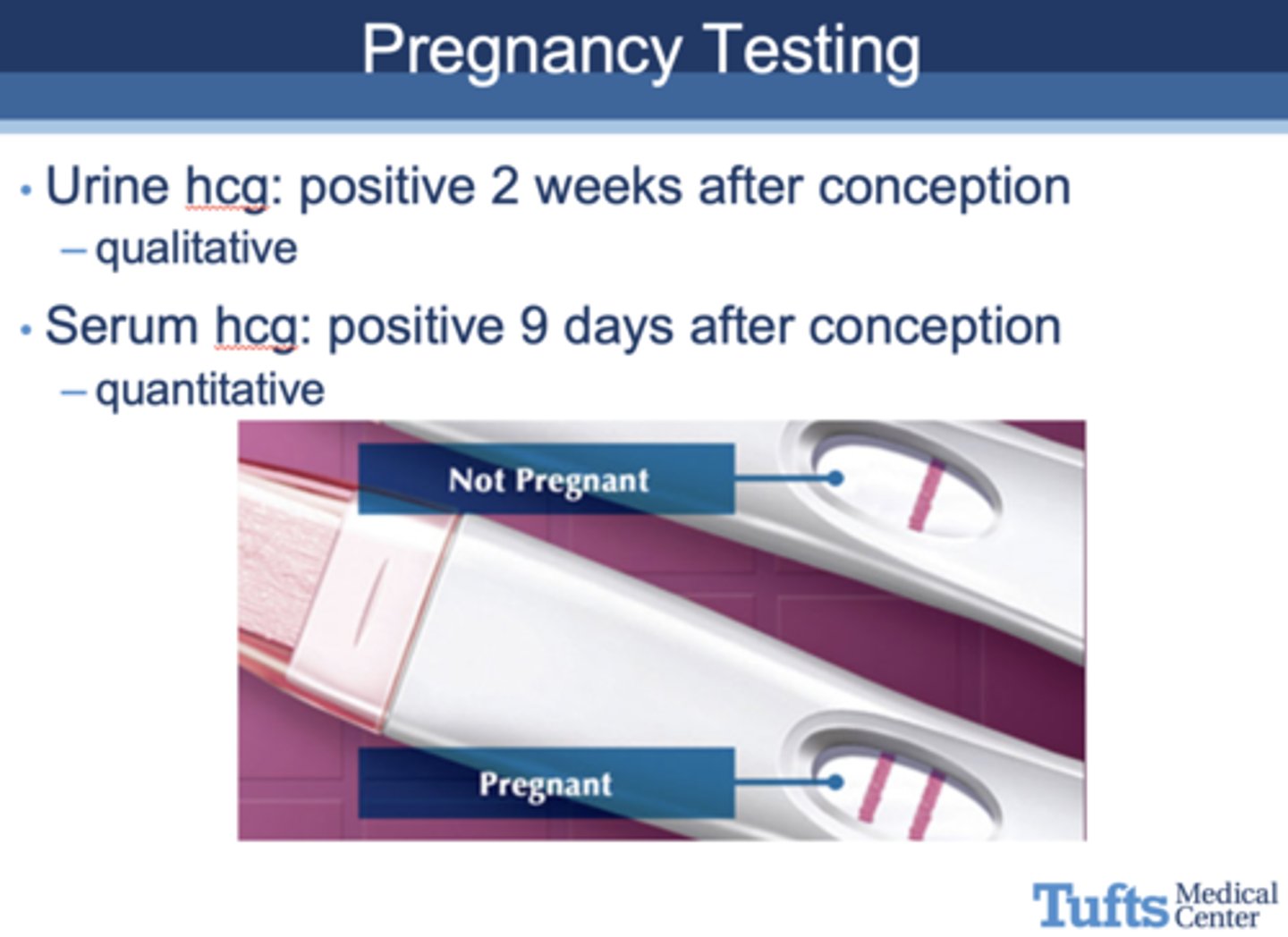
which type of pregnancy test will test positive 2 weeks after conception?
urine hCG test (qualitative)
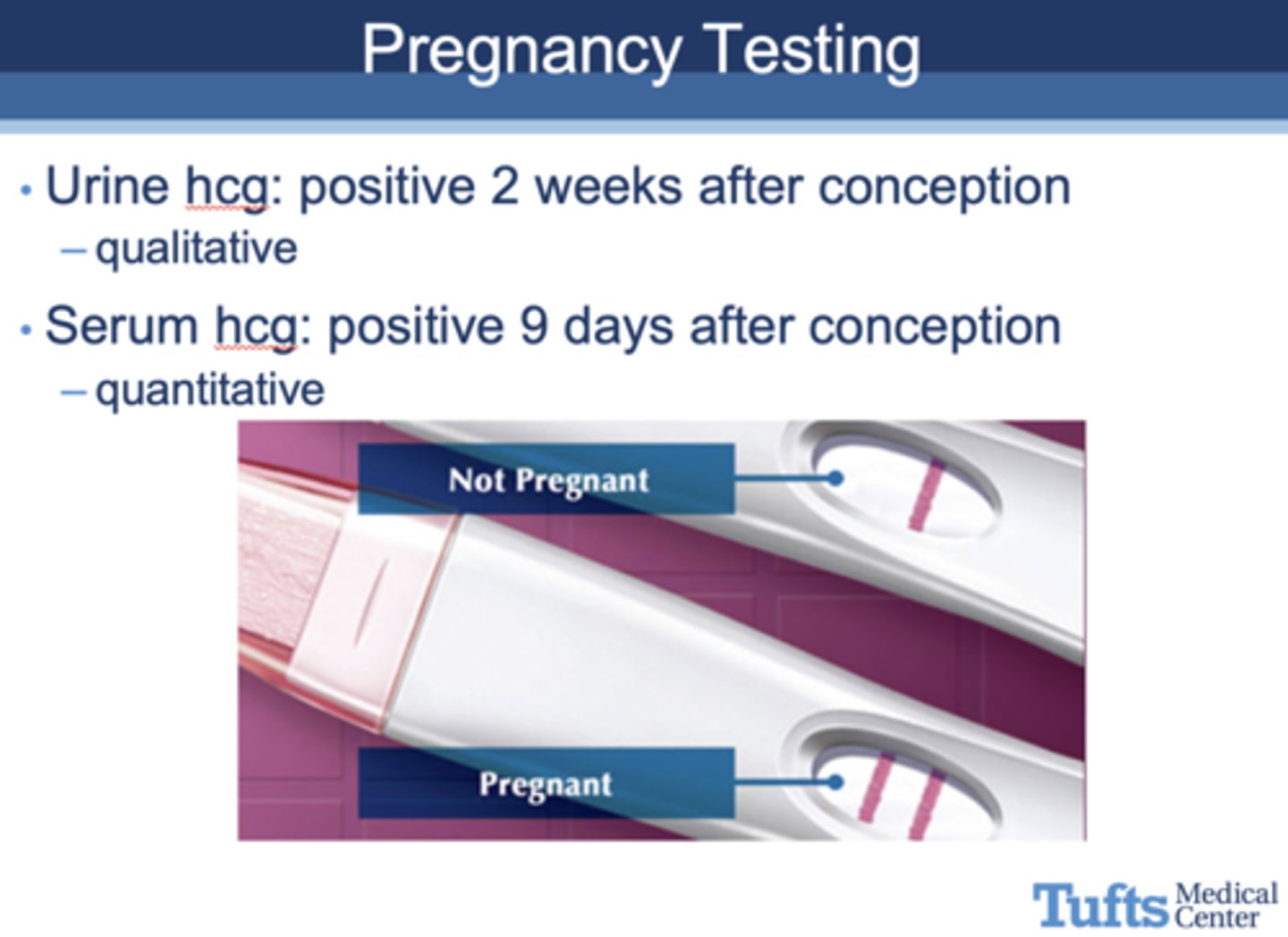
which type of pregnancy test will test positive 9 days after conception?
serum hCG test (quantitative)
What are early signs and symptoms of a patient being pregnant?
- Amenorrhea (period stops)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Urinary frequency
- Breast tenderness and enlargement
- Fatigue

When is the due date of a pregnancy?
1st day of period + 280 days

When does the dating of pregnancy begin?
1st day of last menstrual cycle

Pregnancy discovered at first missed menses, which is a –Gestational age of _______ weeks
5

Pregnancy discovered at first missed menses, which is a –Embryonic age of _______ weeks
3

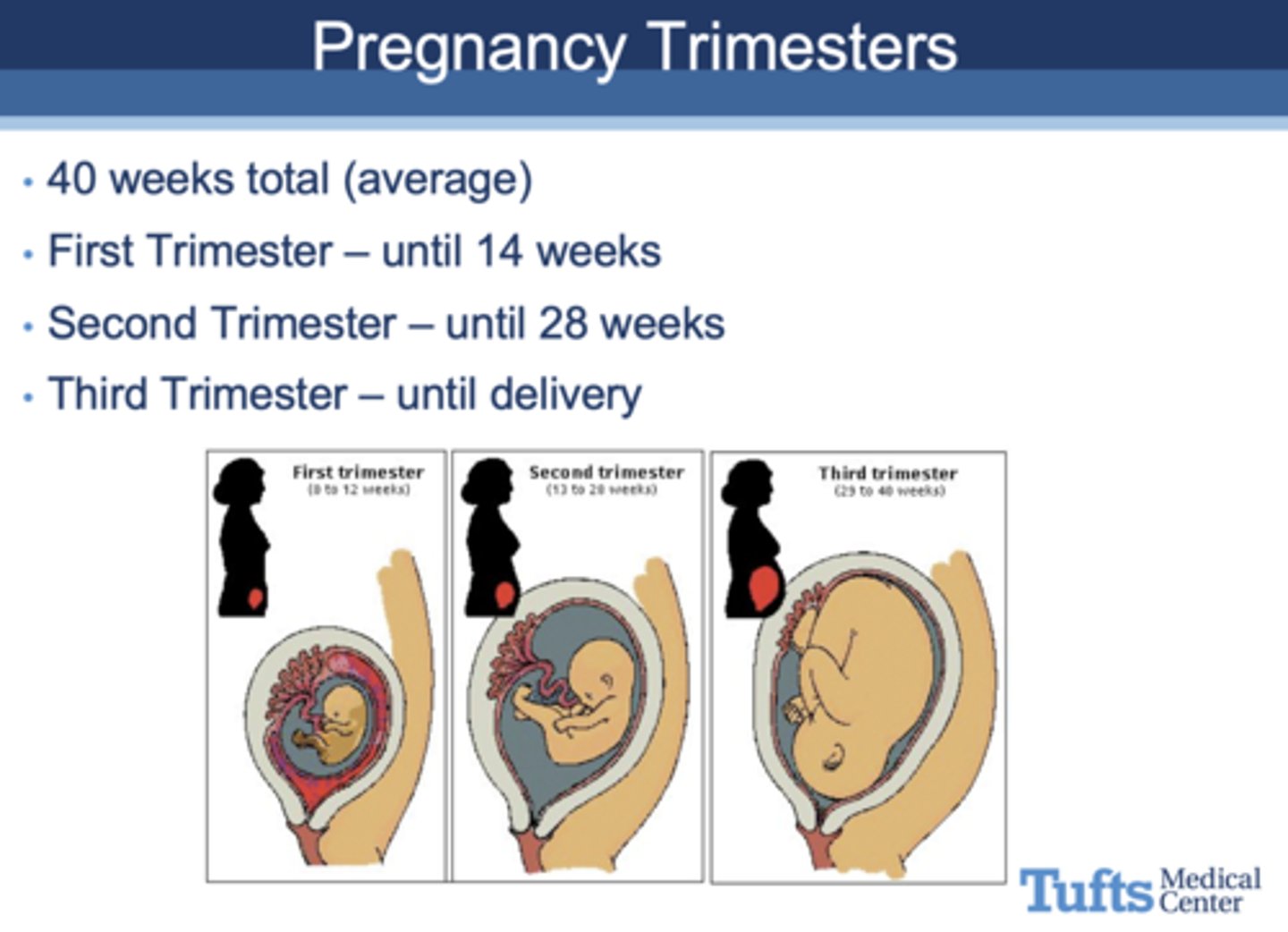
the average pregnancy last about _______ weeks
40
how long is the 1st trimester?
until 14 weeks
how long is the 2nd trimester?
until 28 weeks
how long is the 3rd trimester?
until delivery
What is typical dental care in the 1st trimester?
- Evaluate dentition
- Perform established dentistry regimen
(Slight risk with procedures)

What is typical dental care in the 2nd trimester?
Any routine or major necessary procedures

What is typical dental care in the 3rd trimester?
- Continue established maintenance programs
- Perform major procedures as required

T/F: Conditions that require immediate treatment, such as extractions, root canals, and restoration (amalgam or composite) of untreated caries, may be managed at any time during pregnancy. Delaying treatment may result in more complex problems.
True

What is the idea weight gain in pregnancy for non-obese woman?
25-35 lbs

pregnancy normally causes a _______ in plasma volume:
increase
pregnancy normally causes a _______ in cardiac output (HR and SV):
increase
pregnancy normally causes a _______ in peripheral vascular resistance:
decrease
pregnancy normally causes a _______ in blood pressure:
decrease
pregnancy normally causes a _______ in minute ventilation:
increase
pregnancy normally causes a _______ in tidal volume
increase
T/F: In 3rd trimester, reclining position does not impair respiratory function
False (can impair)
GI changes from pregnancy include:
- Hyperemic gums
- Decreased motility of GI tract
- Relaxed esophageal sphincter

Why are pregnant individuals not put to sleep for surgery?
Risk of aspiration

What is a dental consequence of hyperemesis gravidarum?
Surface enamel loss

What is a recommended remedy after vomiting to prevent enamel erosion?
Rinsing with 1 tsp baking soda in 1 cup water

Up to 40% of pregnant women experience ____________ as an oral complication
periodontal disease

50-70% of pregnant women experience ________ as an oral complication
gingivitis
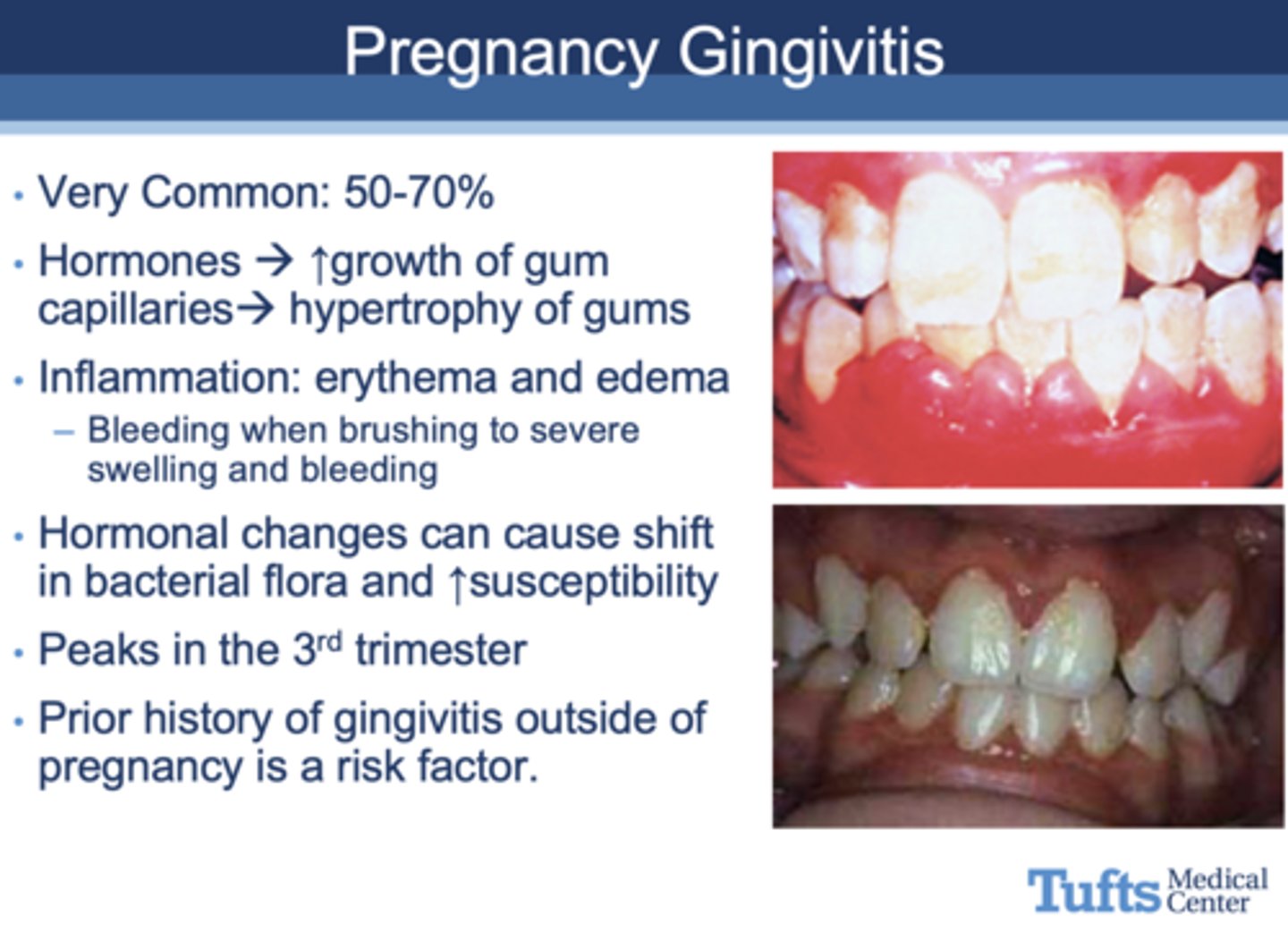
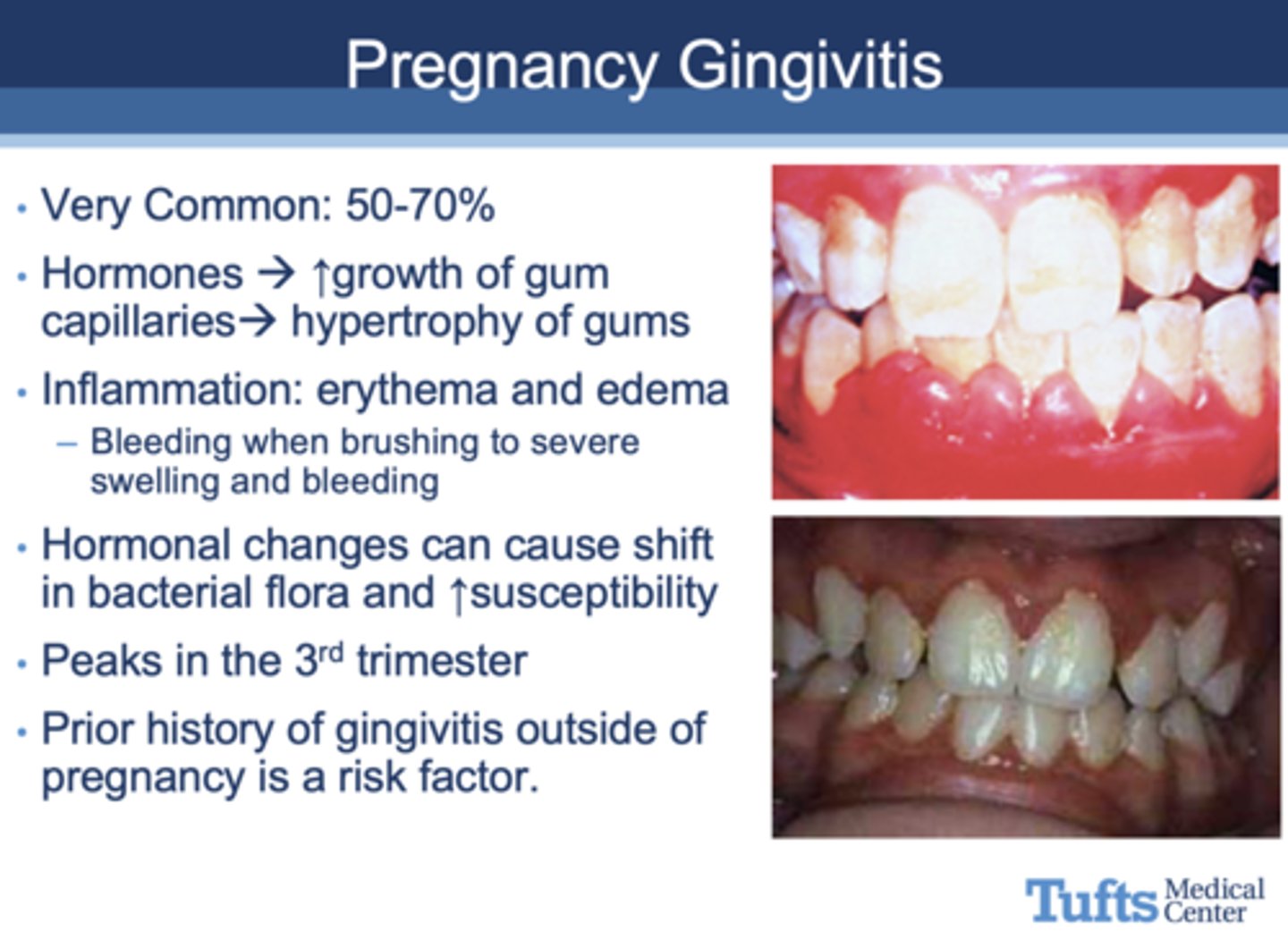
All of the following are seen in what oral complication of pregnancy?
- Hormones ↑
- Growth of gum capillaries --> hypertrophy of gums
- Inflammation: erythema and edema
- - Bleeding when brushing to severe swelling and bleeding
- Hormonal changes can cause shift in bacterial flora and ↑susceptibility
- Prior history of gingivitis outside of pregnancy is a risk factor.
Gingivitis
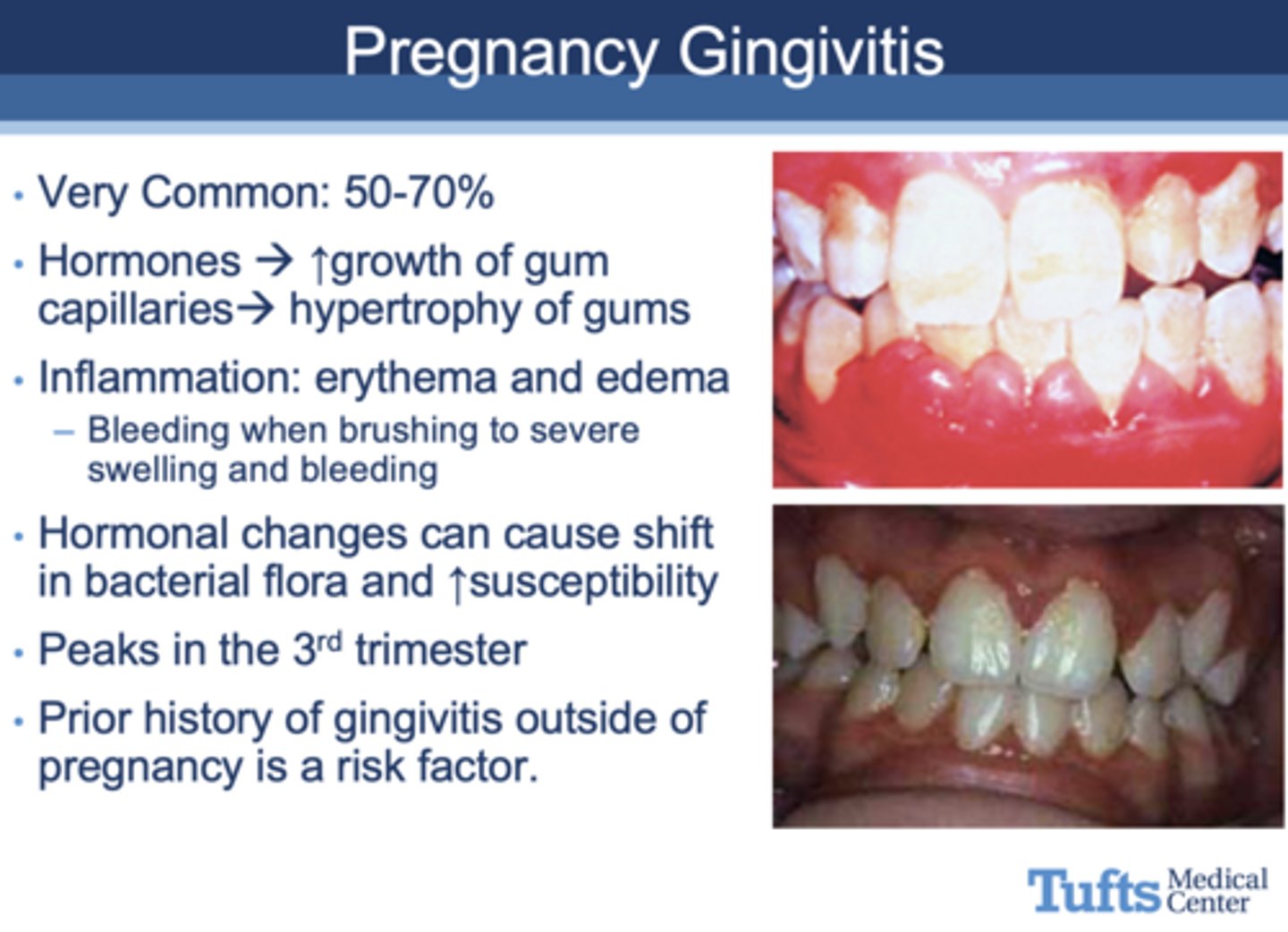
in what trimester do incidents of gingivitis peak in pregnant women?
3rd
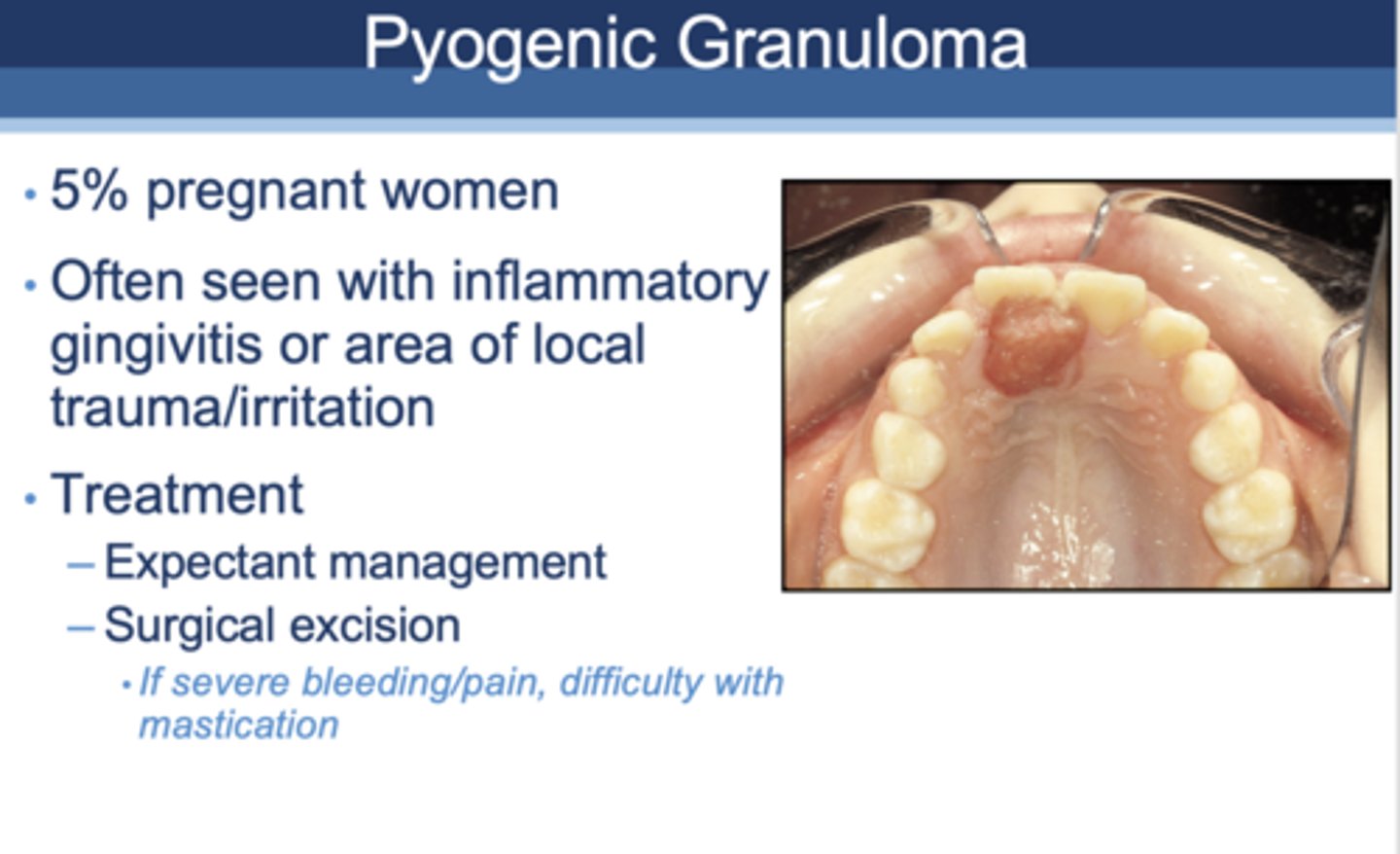
All of the following are seen in what oral complication of pregnancy?
- Pregnancy Tumor
- Found in oral cavity (anterior & maxillary)
- Soft, painless
- Smooth or lobulated red-purple
- A pedunculated outgrowth from interproximal gingiva
- Up to 2cm in diameter
Pyogenic granuloma
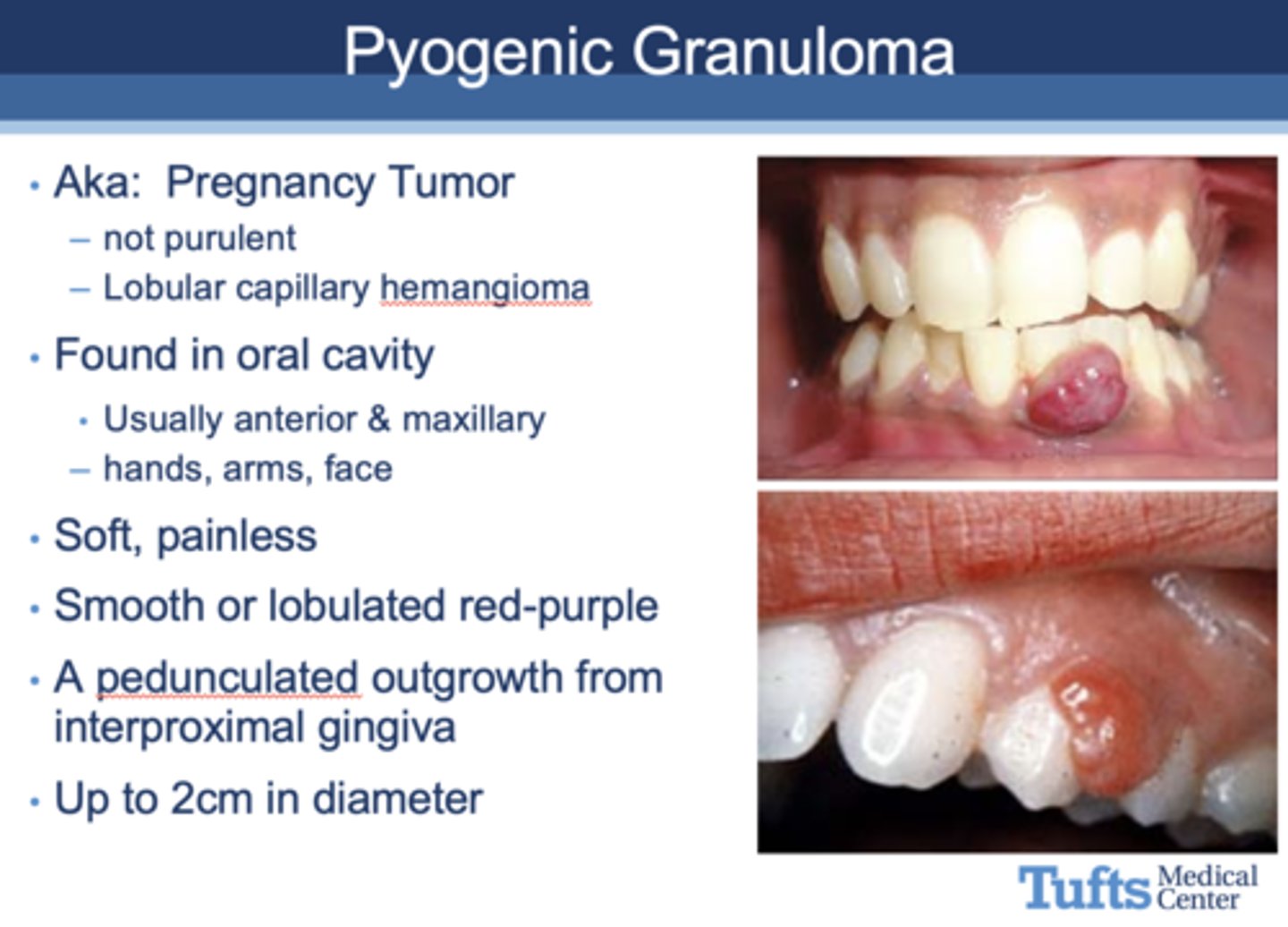
5% of pregnant women experience ________ as an oral complication, often seen with inflammatory gingivitis or area of local trauma/inflammation
Pyogenic Granuloma
t/f: increase in tooth loss can be associated with pregnancy
false

t/f: increase in tooth mobility can be associated with pregnancy
true

t/f: increase in tooth erosion can be associated with pregnancy
true

t/f: increase in dental caries can be associated with pregnancy
false, BUT pre-existing dental disease may become exacerbated due to pregnancy influences (increased acidity, more sugary cravings)

Which of the following is false regarding periodontal care in pregnancy?
A. It is very important
B. General maternal health maintenance is necessary
C. It is not recommended due to risks to the fetus
D. Studies show it is safe
C. It is not recommended due to risks to the fetus

t/f: Current available data says there is no change in preterm birth rates or neonatal morbidity with scaling and root planning
True

t/f: Current available data do not support treatment of patients with periodontal disease during pregnancy as an intervention to decrease preterm birth rates
true, no change in preterm births or adverse events

Is it safe to treat periodontal disease in pregnancy?
Yes

T/F: A study from UPenn stated that if treatment is successful, there is a 6-fold decrease rate in preterm birth rates
True
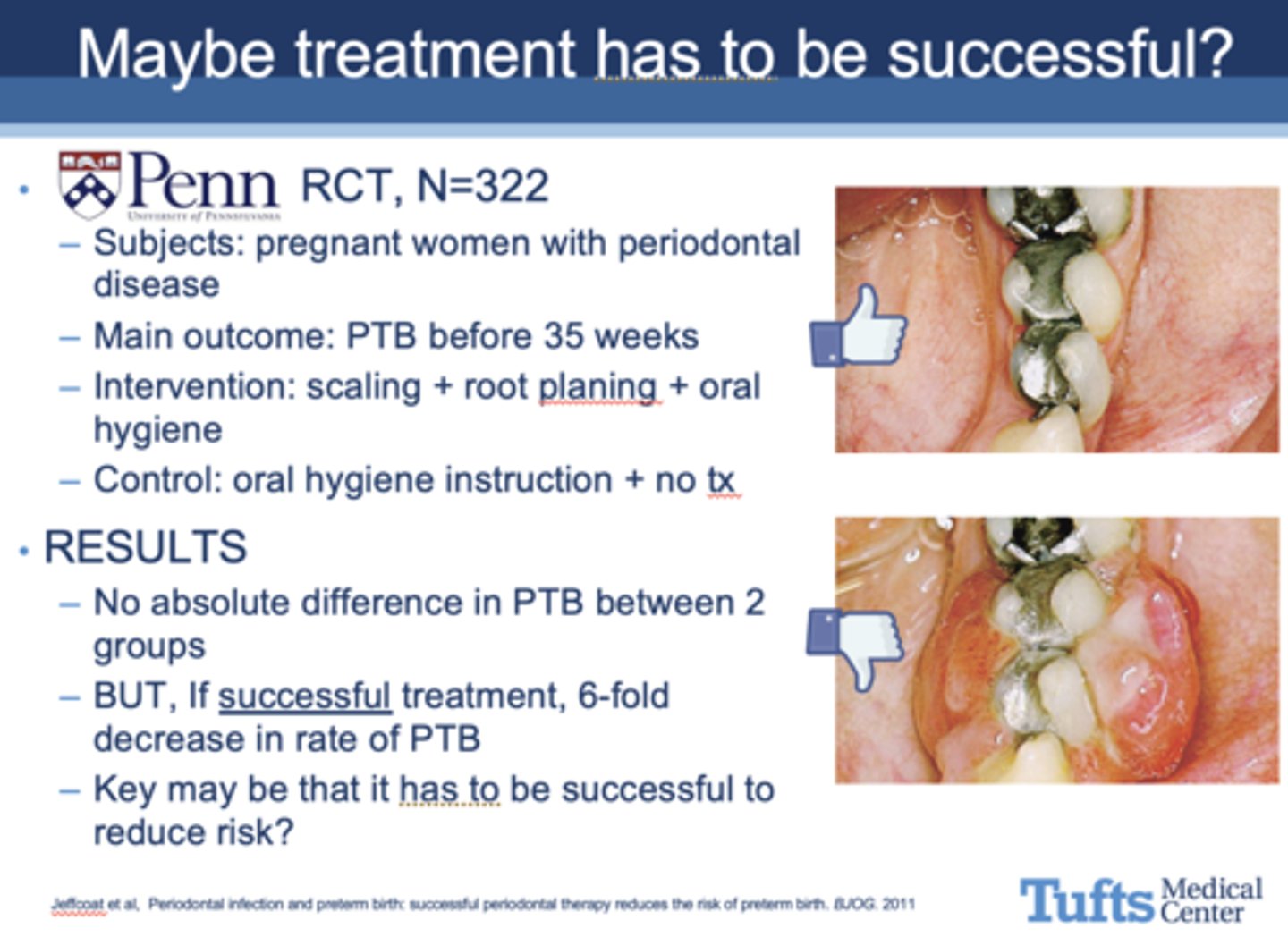
Which of the following is incorrect about periodontal treatment during pregnancy?
A. Decreased risk of perinatal mortality
B. Reduced risk of preterm birth
C. Significantly increased birthweight
D. Was NOT associated with preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, cesarean section, SGA, or congenital malformations
E. None of the above
E. None of the above

What does current data conclude about periodontal treatment during pregnancy?
Current available data reveals mixed results with periodontal disease during pregnancy as an intervention to decrease preterm birth rates.
Importantly data does NOT show harm.

According to RCTs, which of the following is not considered safe during pregnancy?
A. Surgical periodontal procedures
B. Routine, essential dental care
C. Non-surgical periodontal procedures
D. Use of topical/local anesthesia
A. Surgical periodontal procedures

What products are commonly prescribed for periodontal disease during pregnancy?
- Chlorhexidine
- Fluoridated mouth rinses
- Xylitol-containing chewing gum

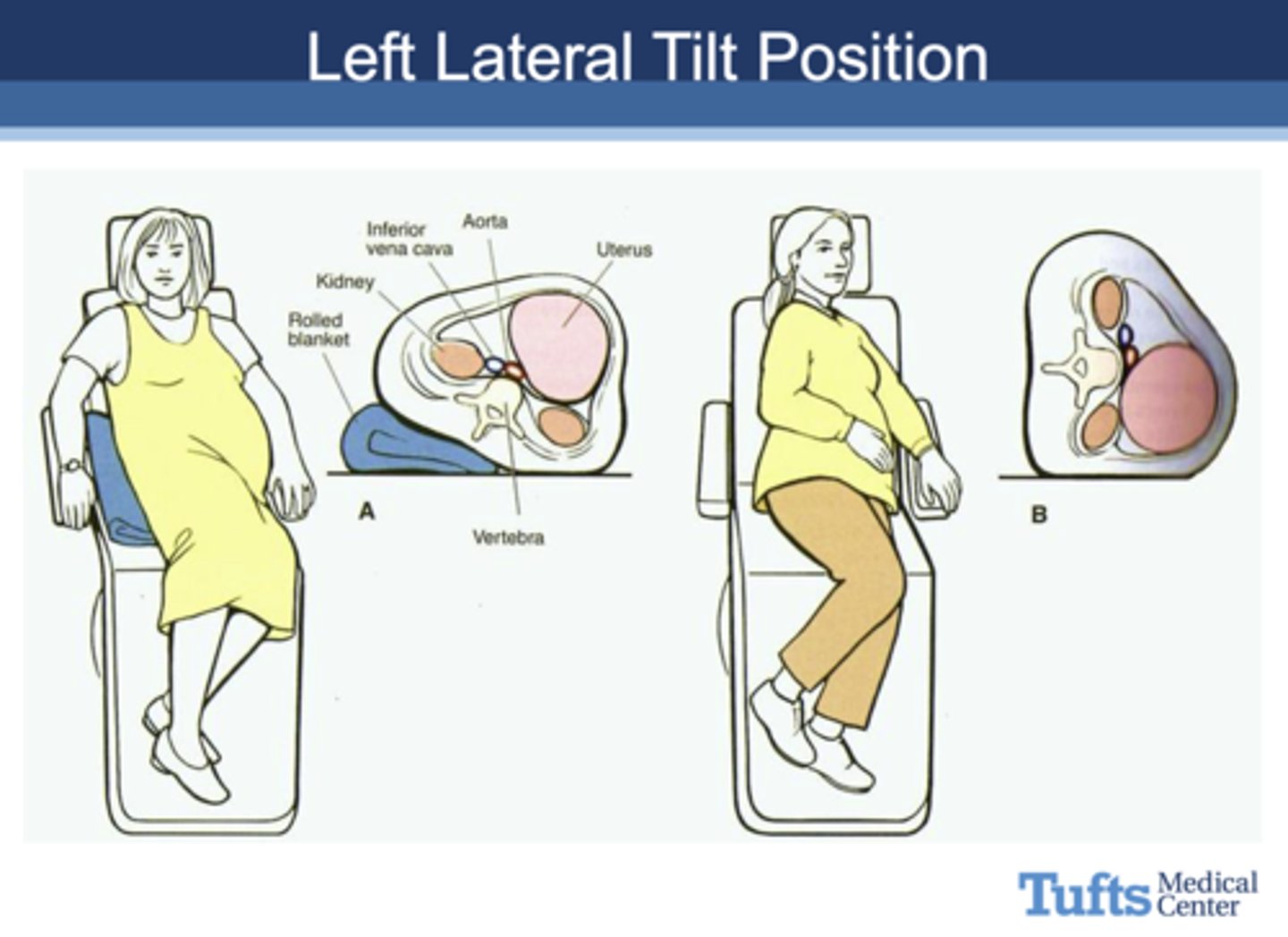
Which of the following is correct about positioning a pregnant patient?
a. Use a semi-reclining position as tolerated
b. Encourage frequent position changes
c. Place small pillow under right side to tilt patient to the left
d. All are true
d. All are true

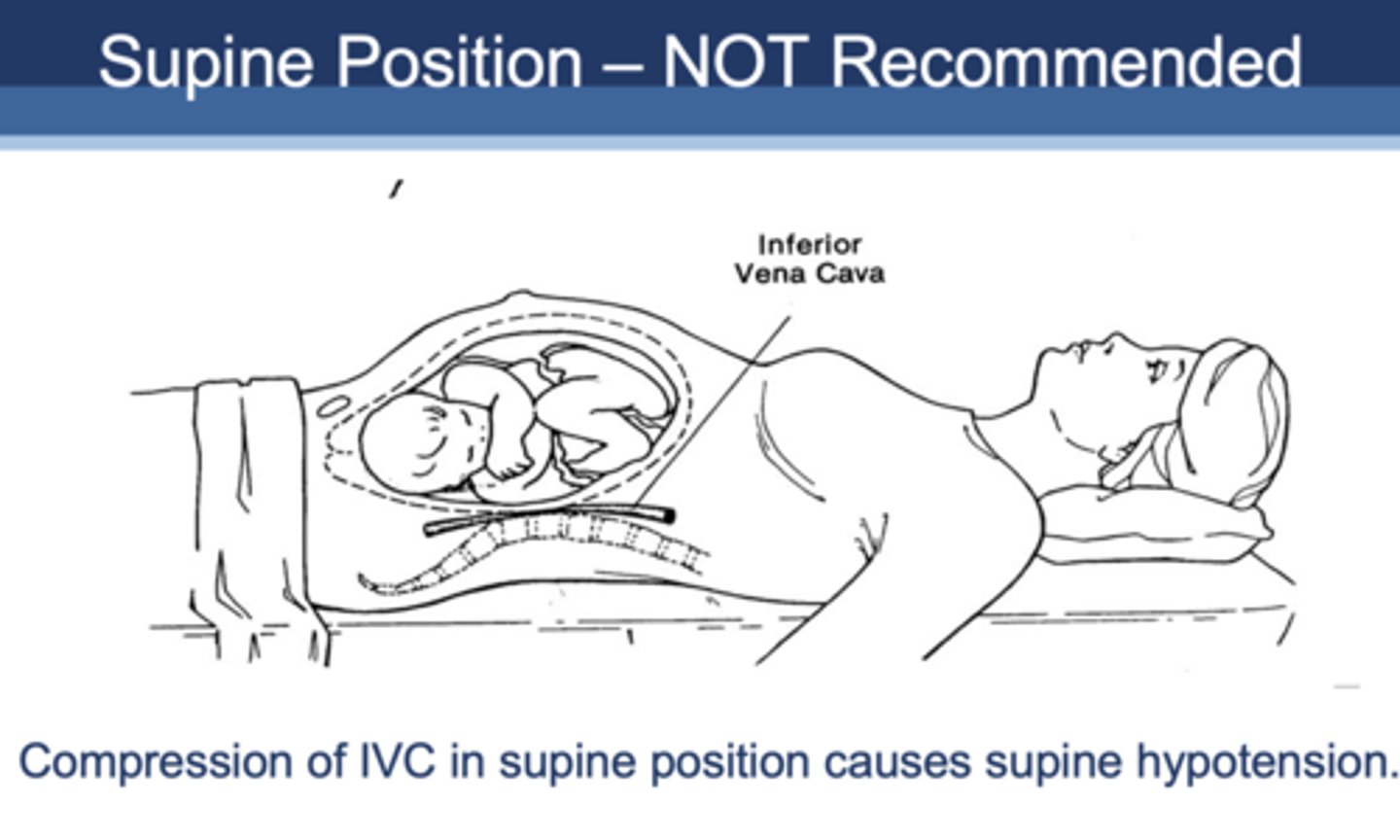
which position is not recommended for pregnant patients and why?
Supine position not recommended due to compression of IVC causes supine hypotension
what is the optimal position for a pregnant woman to sit in during a dental appointment?
Left Lateral Tilt Position
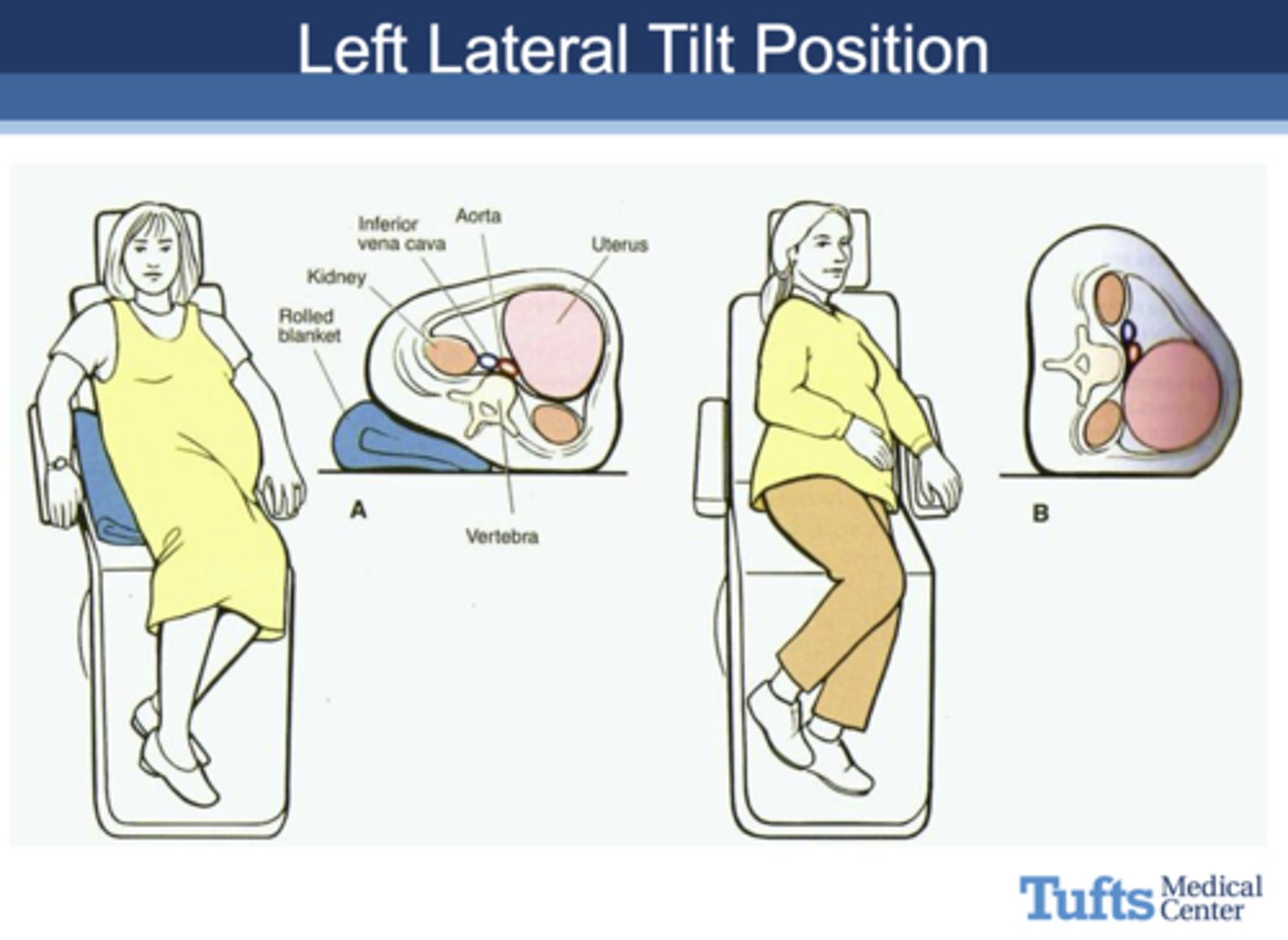
the Left Lateral Tilt Position is used pregnant woman to sit in during a dental appointment to avoid _______
Compression of IVC in supine position causing supine hypotension.
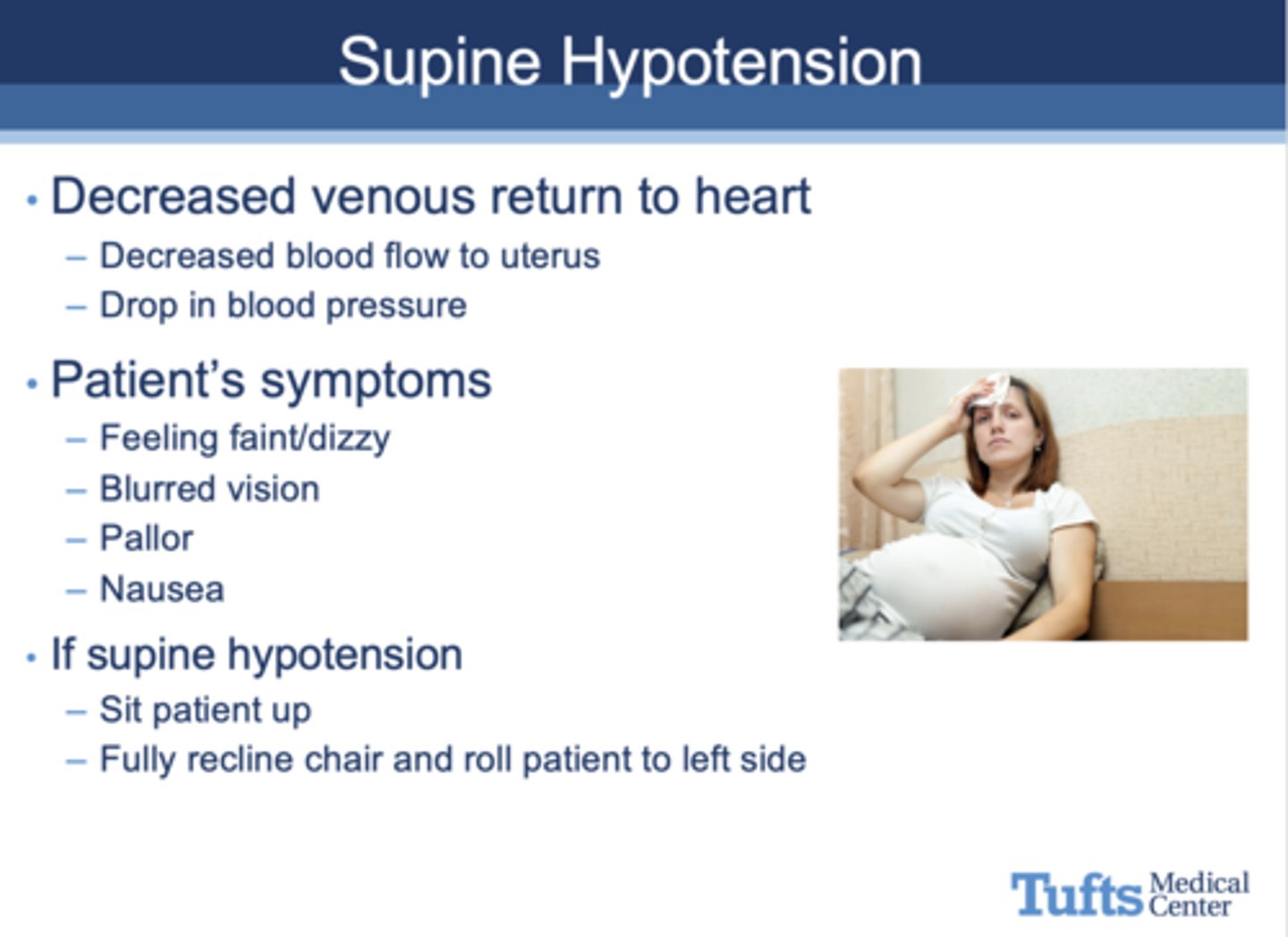
What are the following characteristics signs of?
- Decreased venous return to the heart and blood flow to the uterus
- Drop in blood pressure
- Symptoms: dizzy/faint, blurred vision, pallor, nausea
supine hypotension
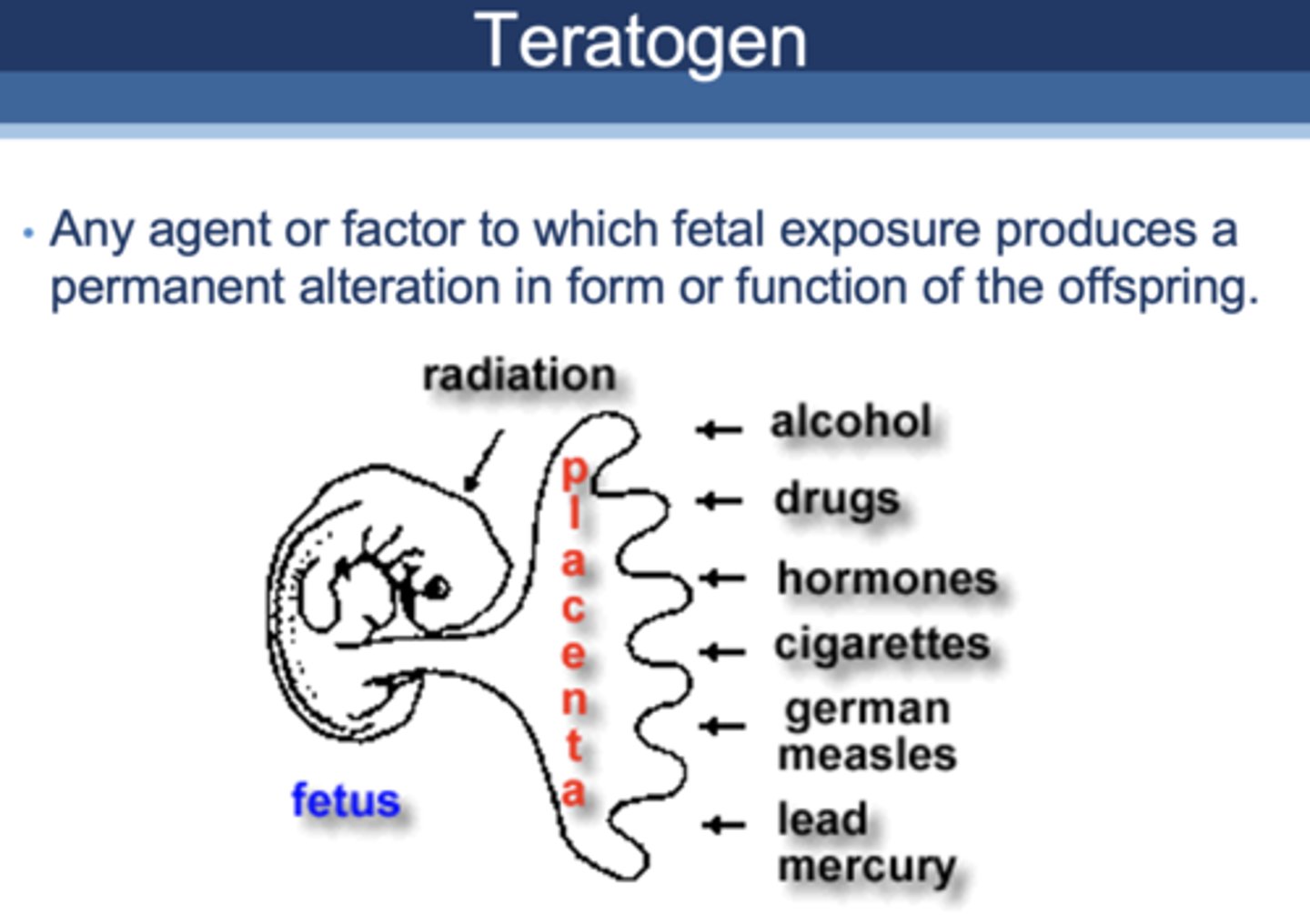
Define the following:
Any agent or factor to which fetal exposure produces a permanent alteration in form or function of the offspring
teratogen
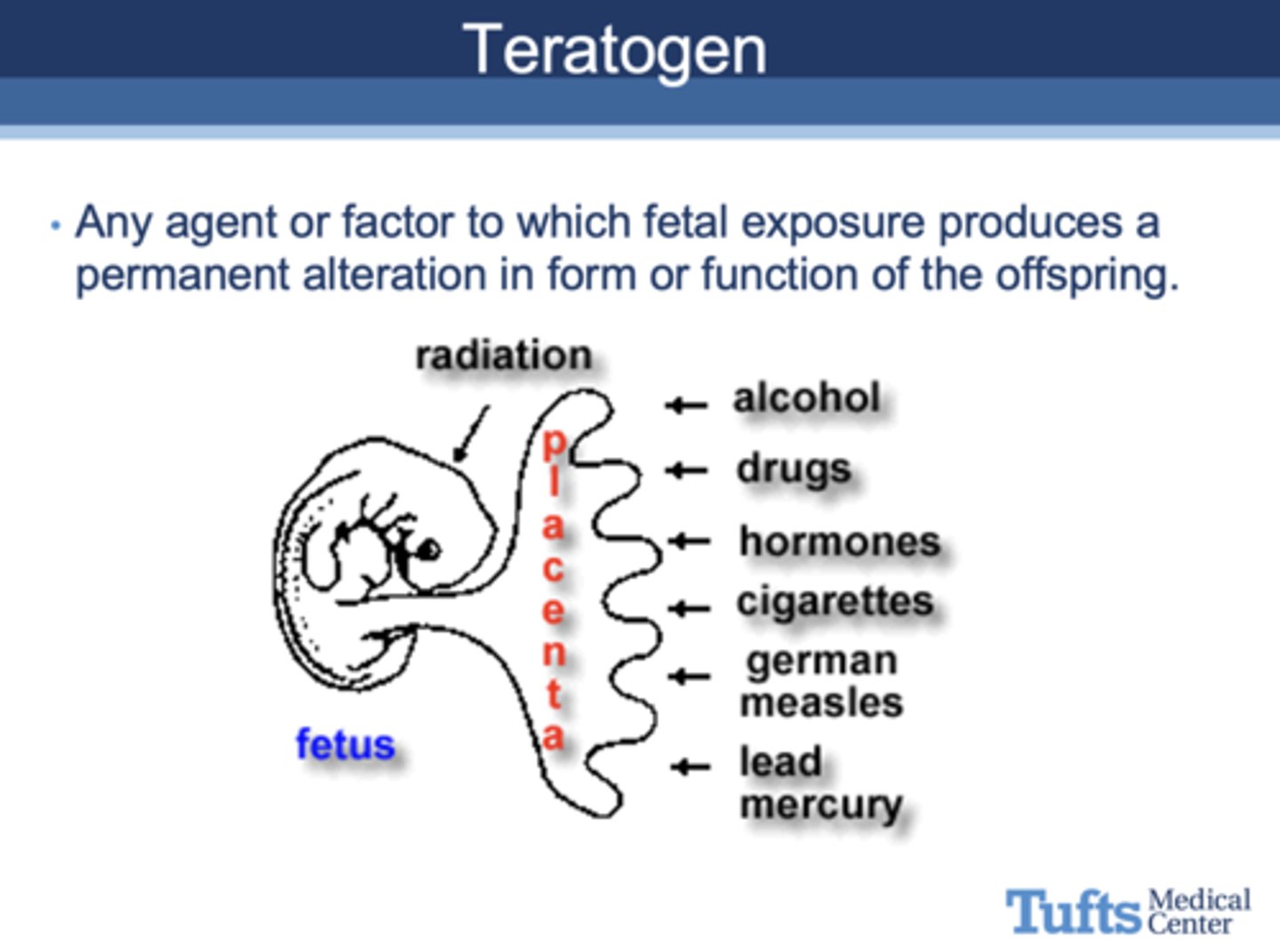
alcohol, drugs, hormones, cigarettes, german measles, lead mercury are all examples of ____________
teratogens
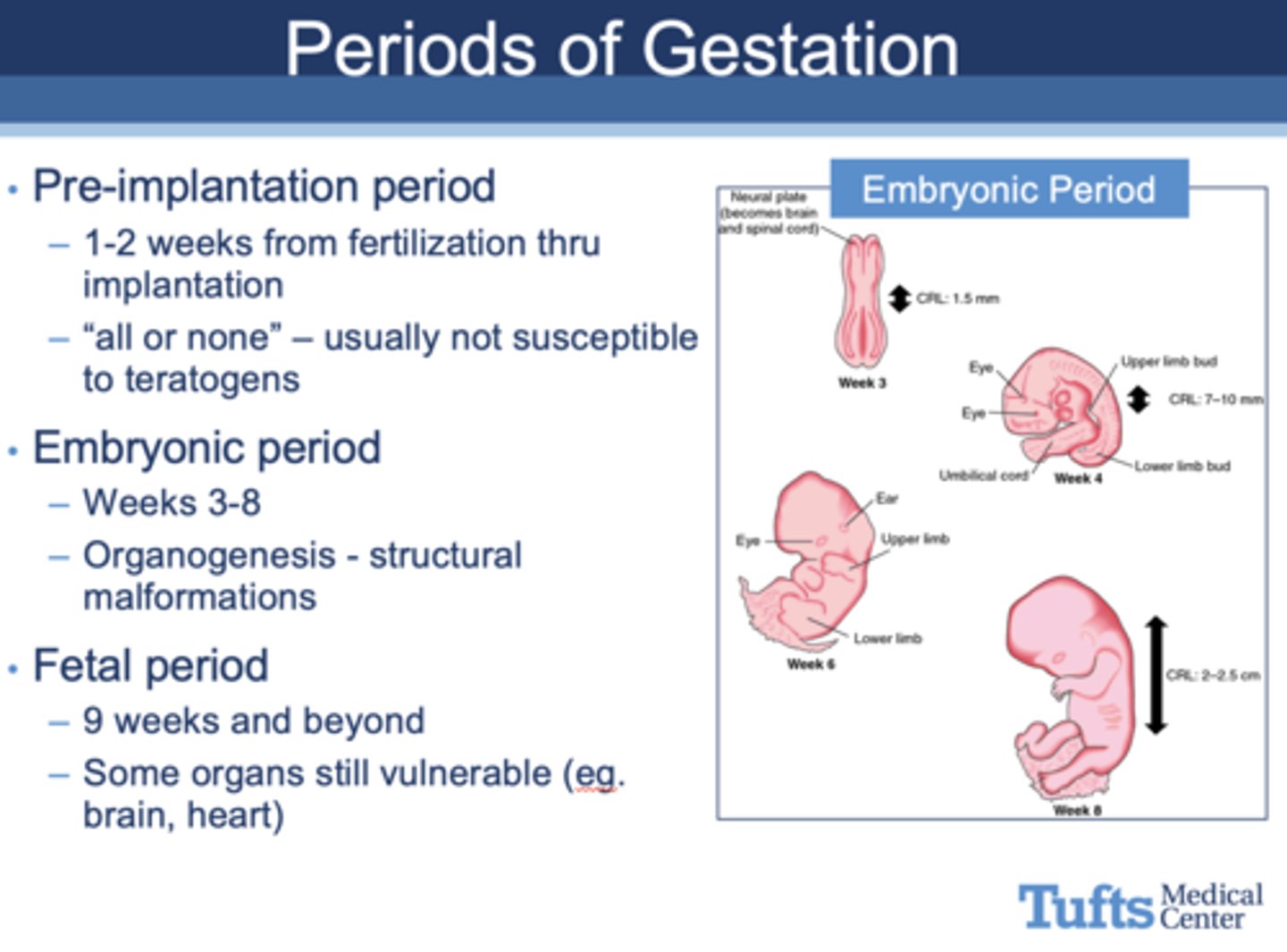
What period of gestation?
- “All or none” – usually not susceptible to teratogens
- 1-2 weeks from fertilization thru implantation
Pre-implantation period
What period of gestation?
- Weeks 3-8
- When exposure to teratogens may cause organogenesis - structural malformations
Embryonic period
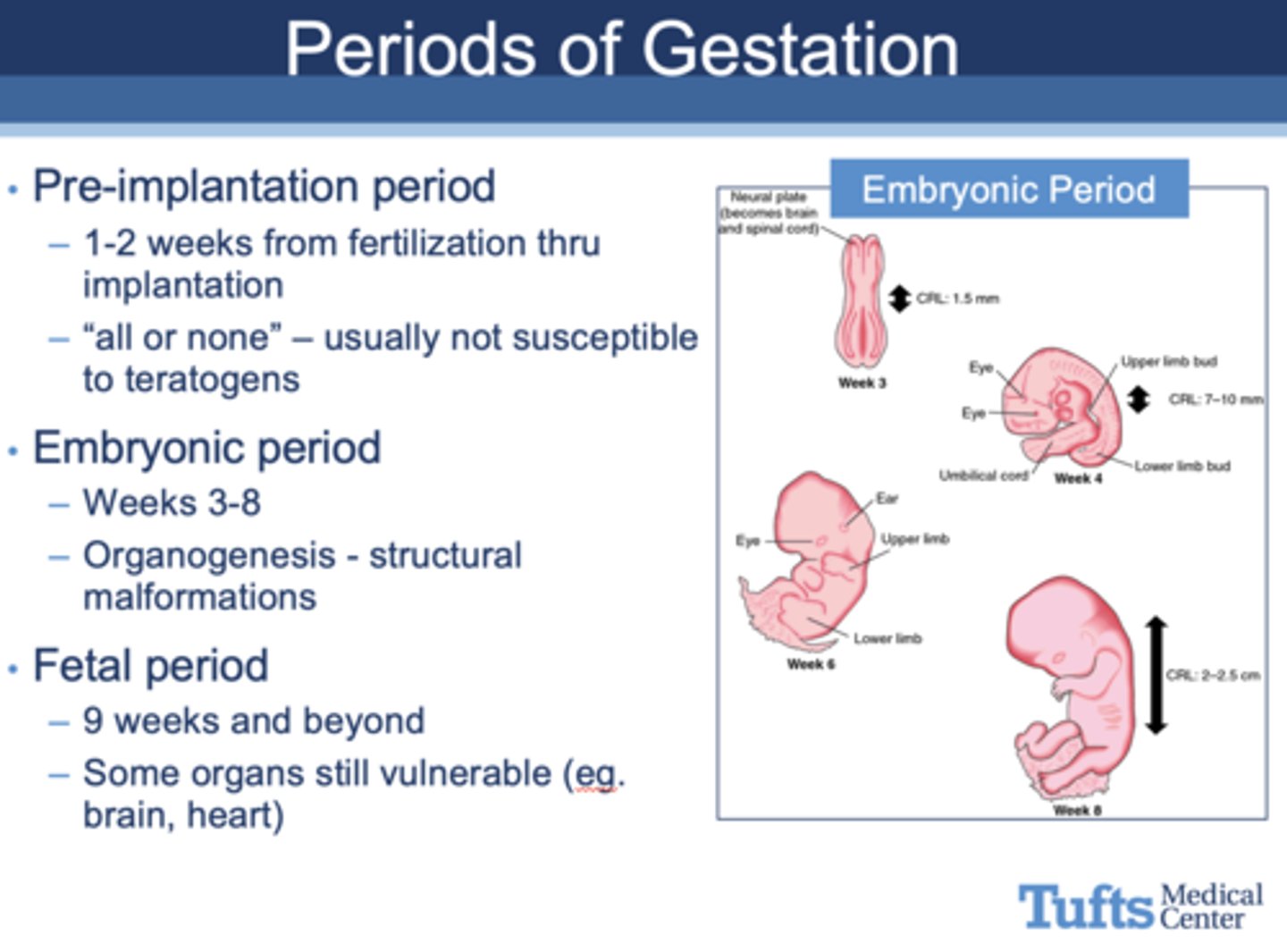
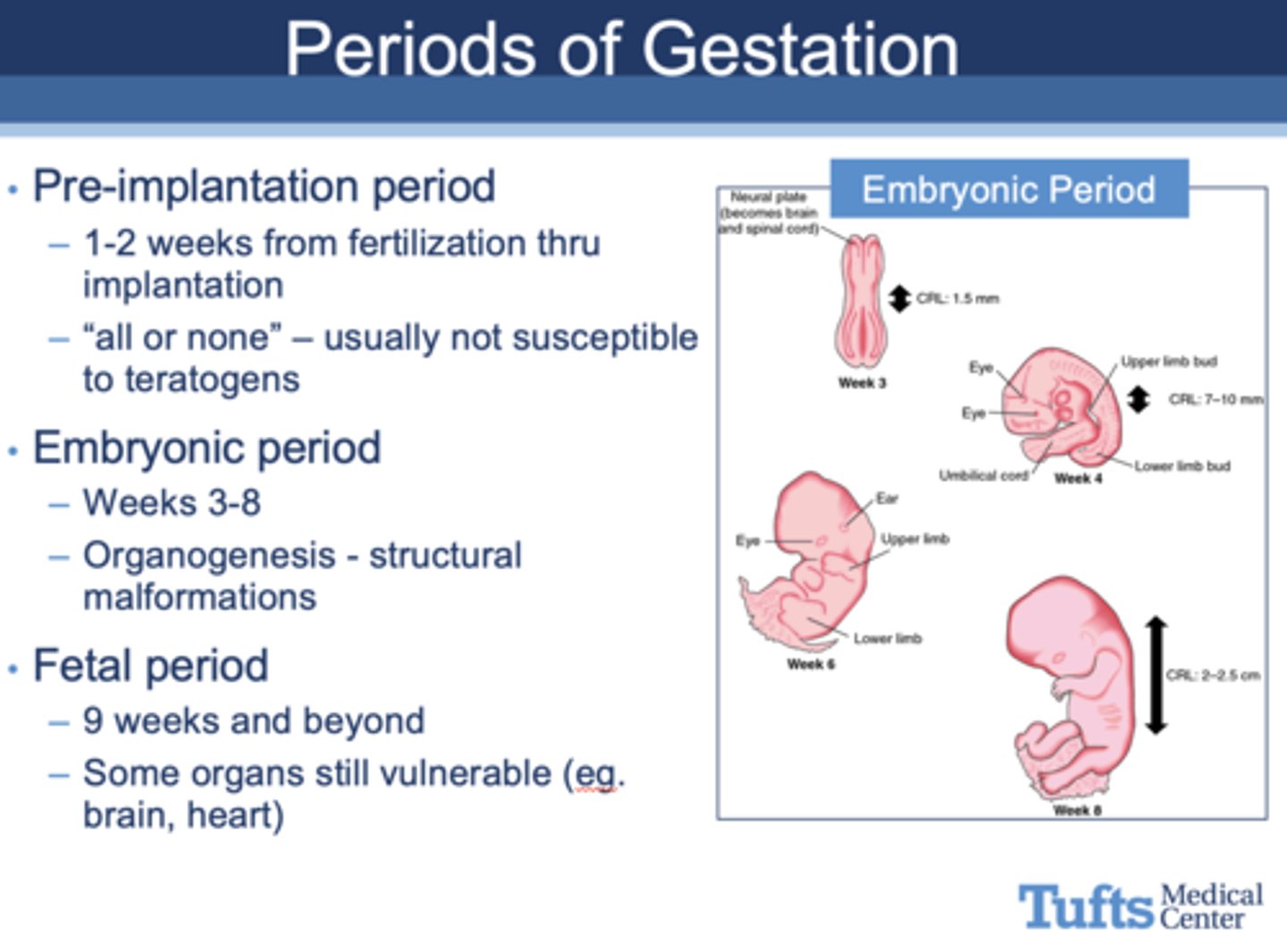
What period of gestation?
- 9 weeks to birth
- When exposure to teratogens, some organs still vulnerable (eg. brain, heart)
Fetal Period
What are three examples of teratogens?
•Thalidomide
•Warfarin
•Alcohol

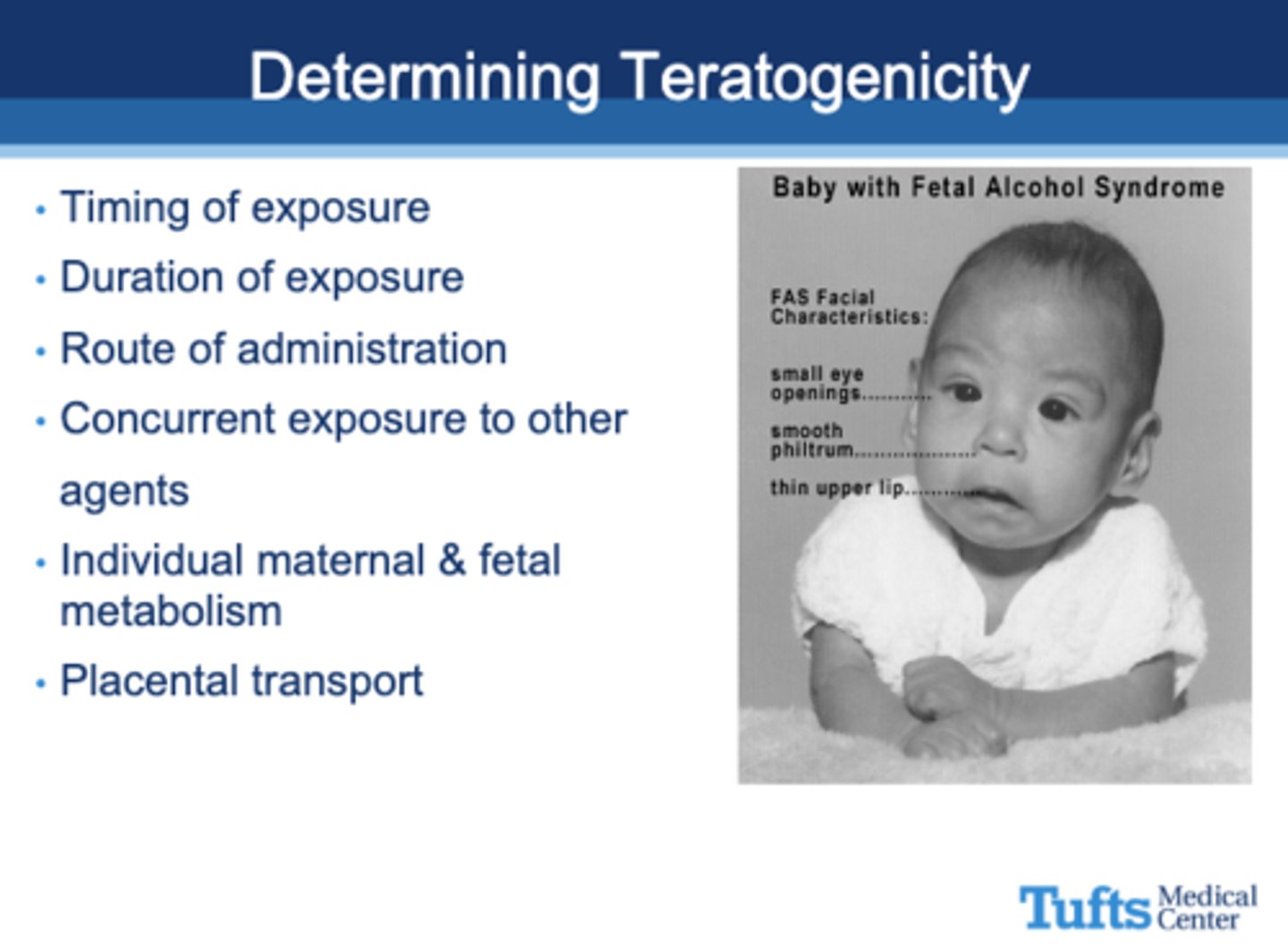
All of the following are used to determine what?
- Timing of exposure
- Duration of exposure
- Route of administration
- Concurrent exposure to other agents
- Individual maternal & fetal metabolism
- Placental transport
Teratogenicity
What replaced the A, B, C, D, and X FDA study categories in 2015?
Descriptive text
which of the following meds is NOT contraindicated in pregnancy?
a. anticonvulsants
b. wafarin
c. ACE inhibitors
d. retinoids
e. androgens
f. antineoplastic agents
g. some antimocirobials
h. all contraindicated medications
h. all contraindicated medications

What drug causes yellow-brown discoloration of deciduous teeth?
Tetracyclines
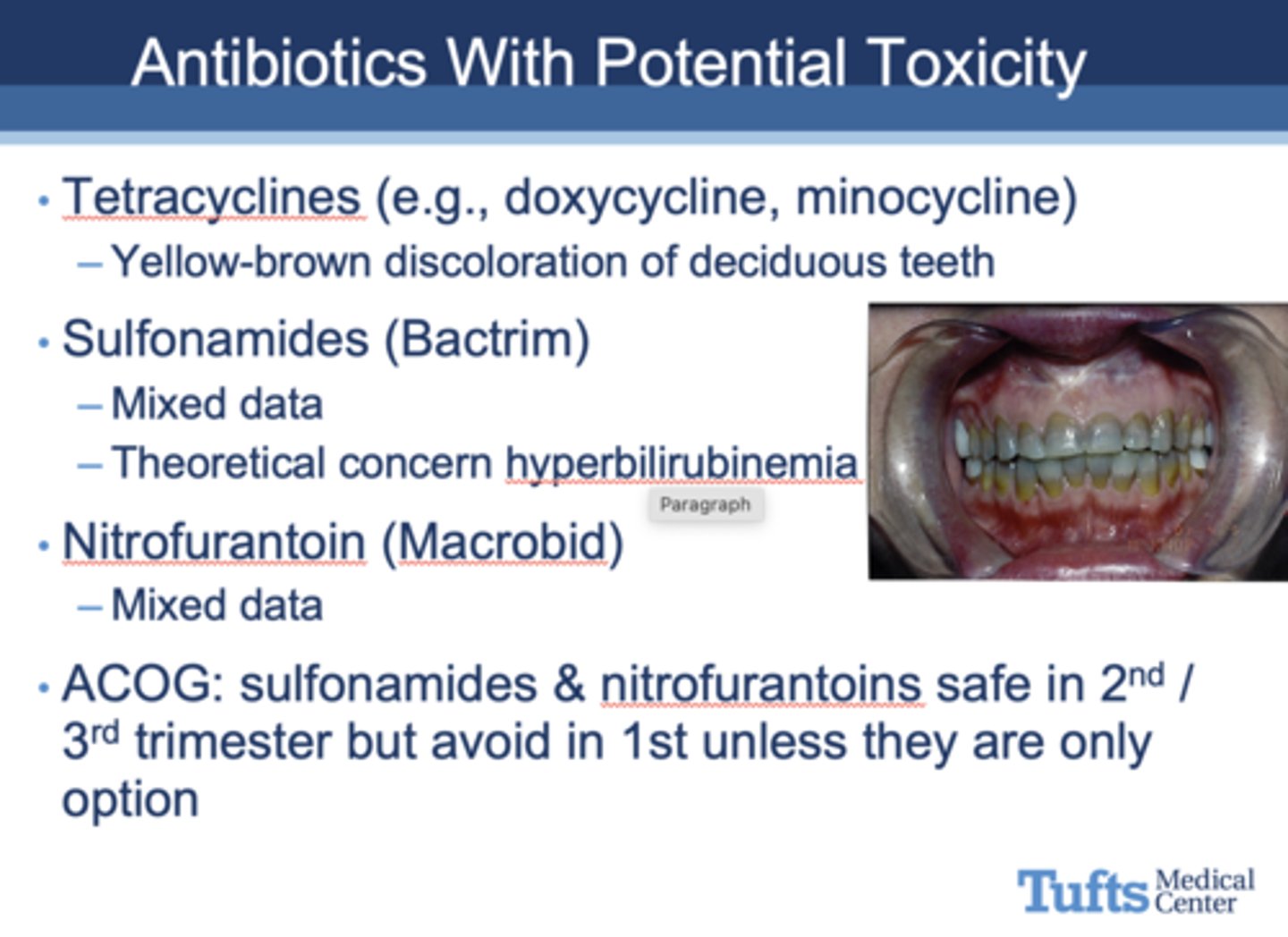
What drug causes fetal hyperbilirubinemia?
Sulfonamides
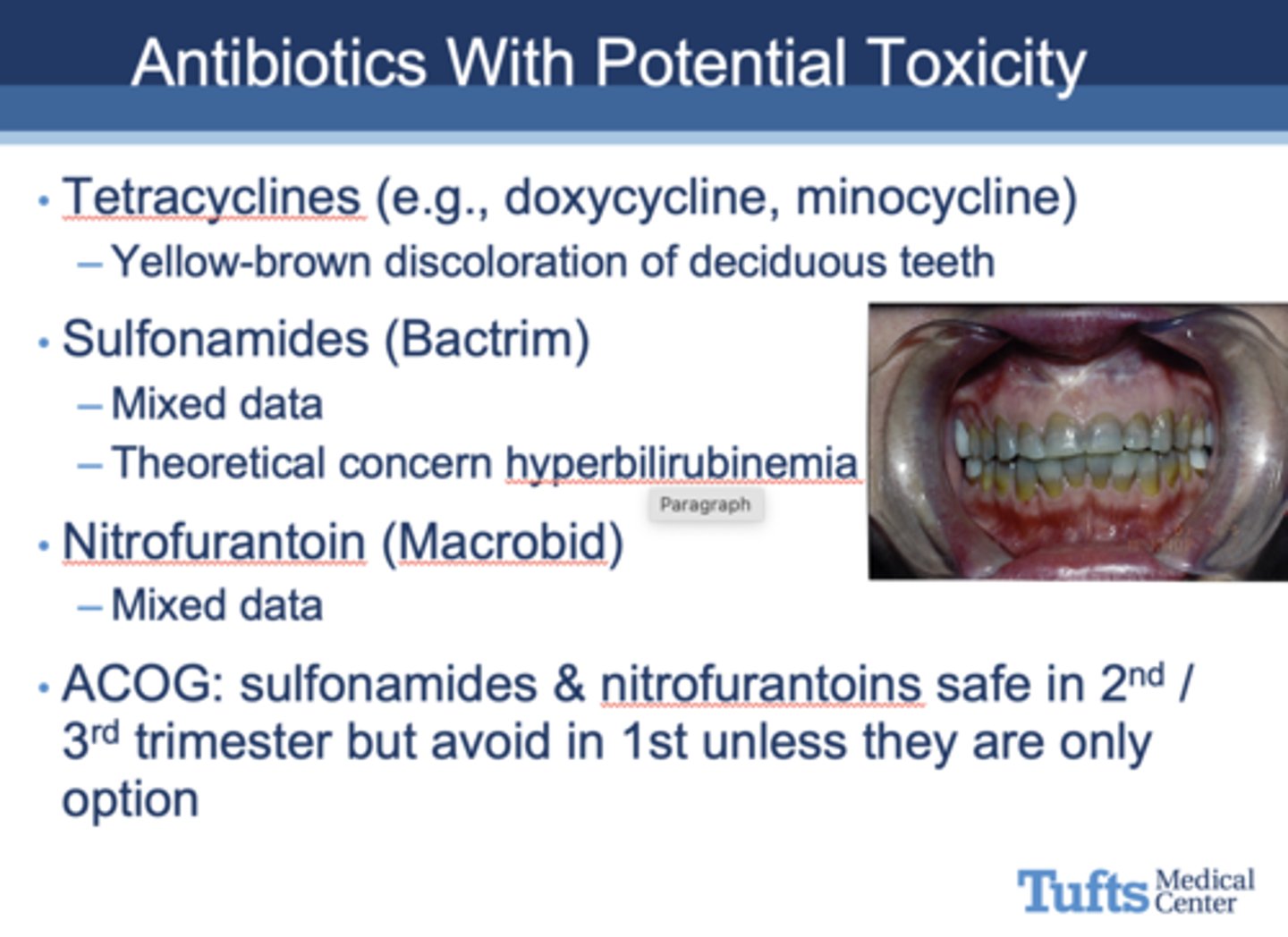
T/F: sulfonamides & nitrofurantoins are safe in 2nd and 3rd trimester but must be avoided in the 1st trimester
true
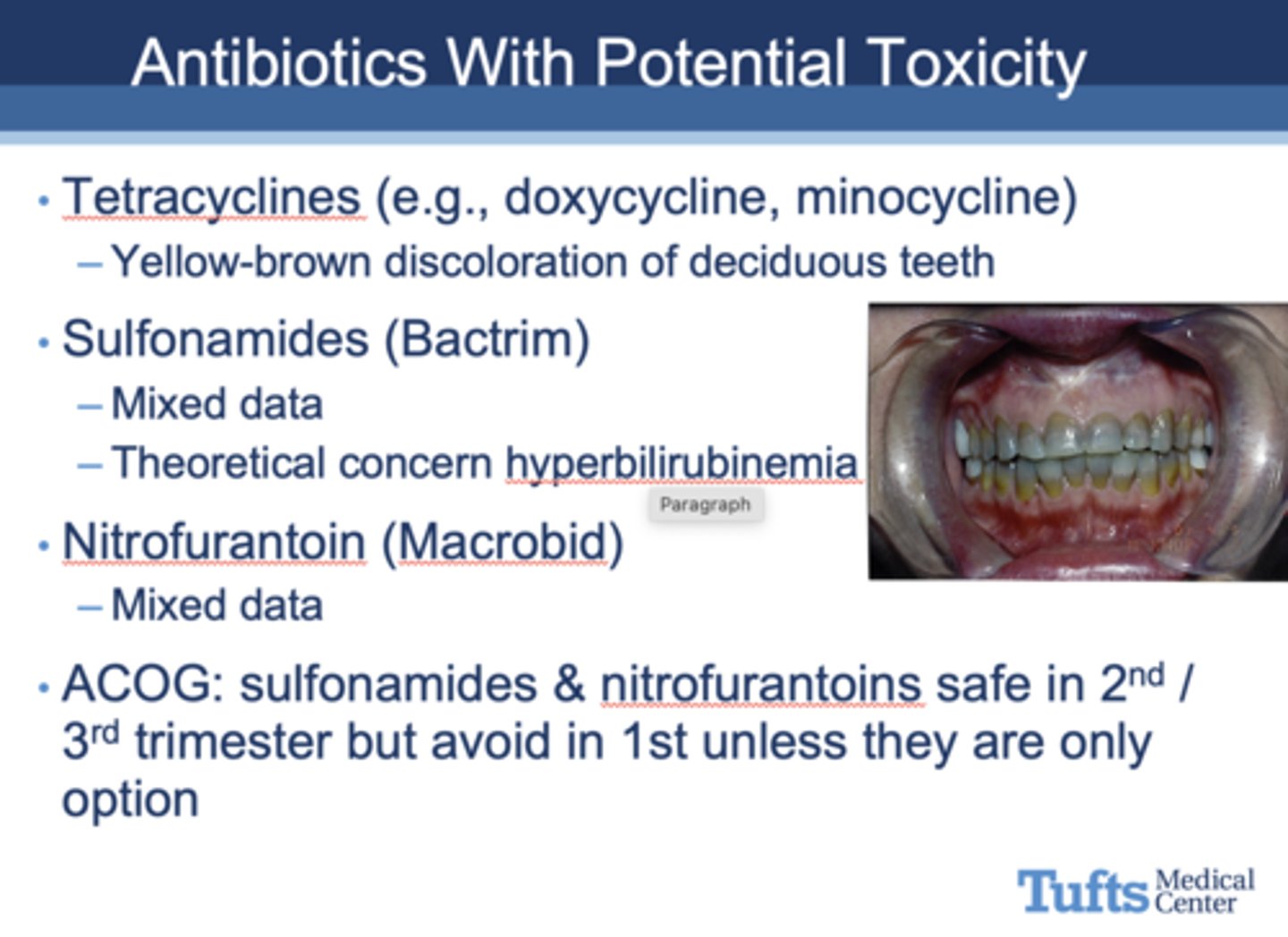
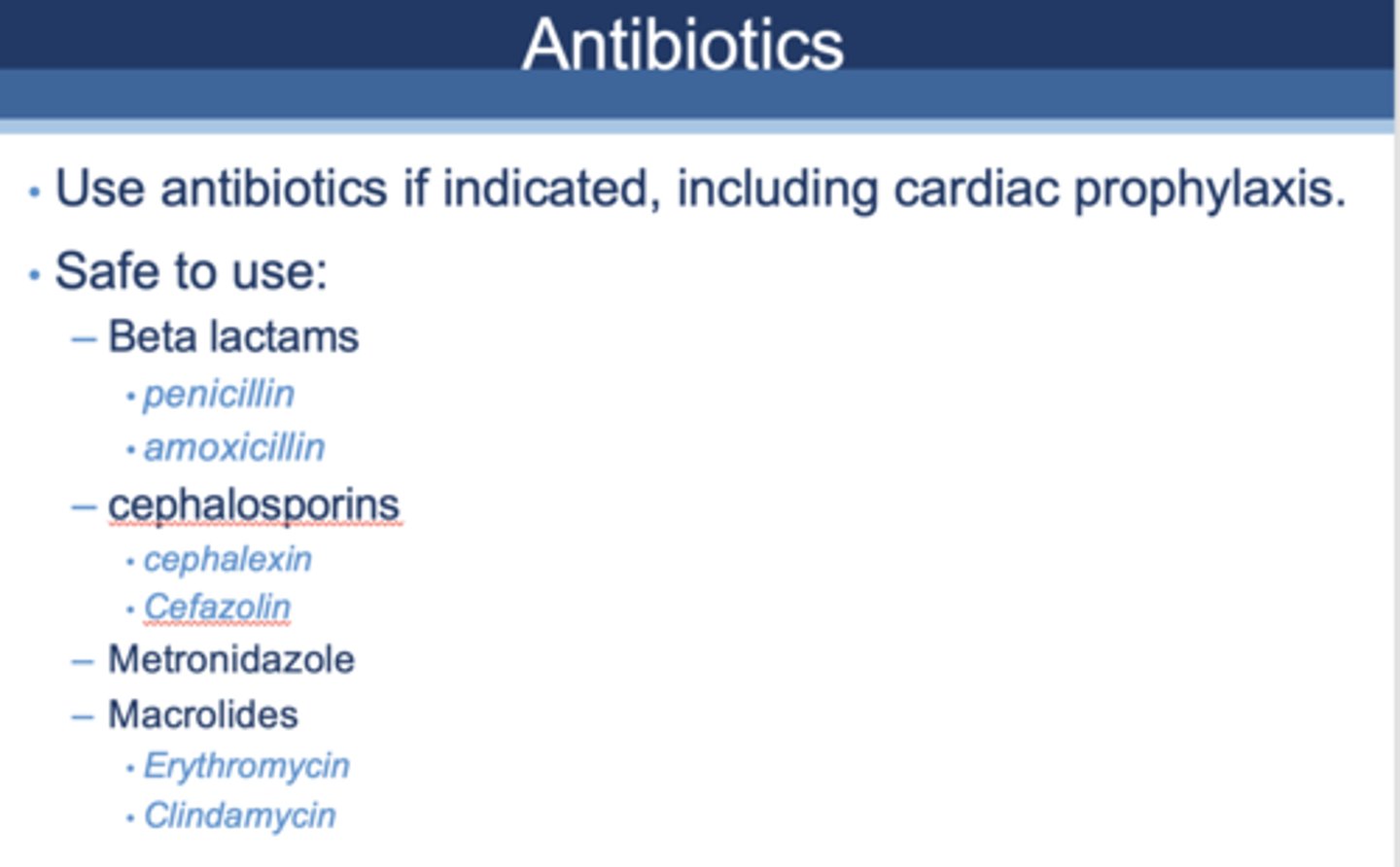
T/F: Use antibiotics if indicated, including cardiac prophylaxis in patients who are pregnant
True (see image for safe antibiotic examples)
What drug is prohibited in pregnant woman due to concerns of premature closure of ductus arteriosus, renal insuffciency, decreased fetal urine output?
salicylates (aspirin), NSAIDS
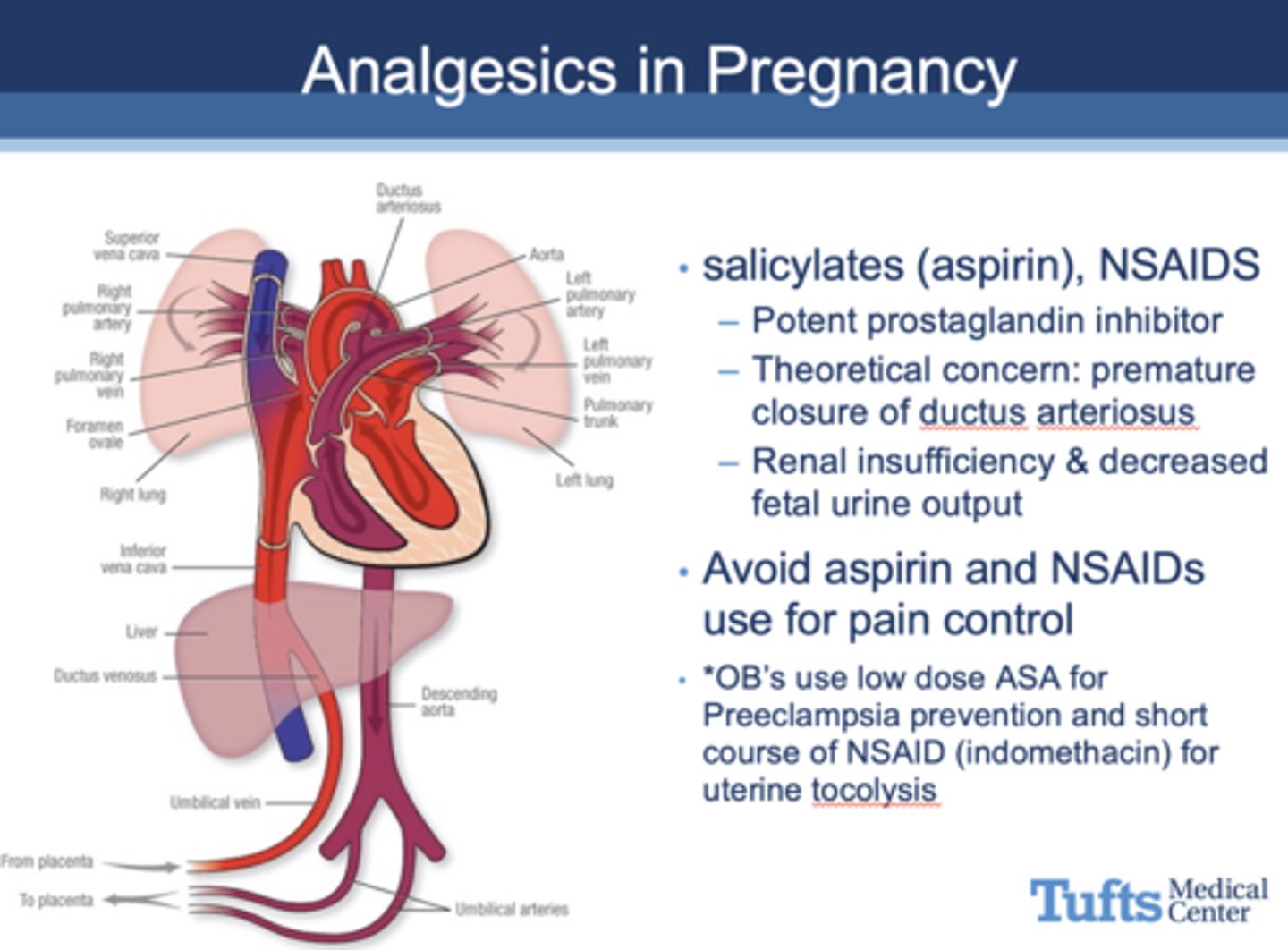
Are NSAIDS safe for pregnant women?
No
Is acetaminophen safe for pregnant women?
Yes

Are narcotics (oxycodone, codeine) safe for pregnant women?
Yes, in short term use but not long term use

Is lidocaine (with or without epinephrine) safe during pregnancy?
Yes
What happens if general anesthesia crosses CNS of a pregnant woman?
It will cross the placenta and depress CNS of fetus

What happens to the airway during pregnancy?
- Increased swelling and friability of oropharyngeal tissues
- Reduced size of glottis
- Worse at end of pregnancy
- Can lead to difficulty ventilating and intubating

Is nitrous oxide safe during pregnancy?
Yes

What are three helpful sources online for information about pregnant women?
– REPROTOX
– TERIS (U of WA)
– Uptodate.com
Are the use of dental x-rays contraindicated in pregnant women?
No

T/F: X-rays during pregnancy is a frequent cause of anxiety for providers and patients
True

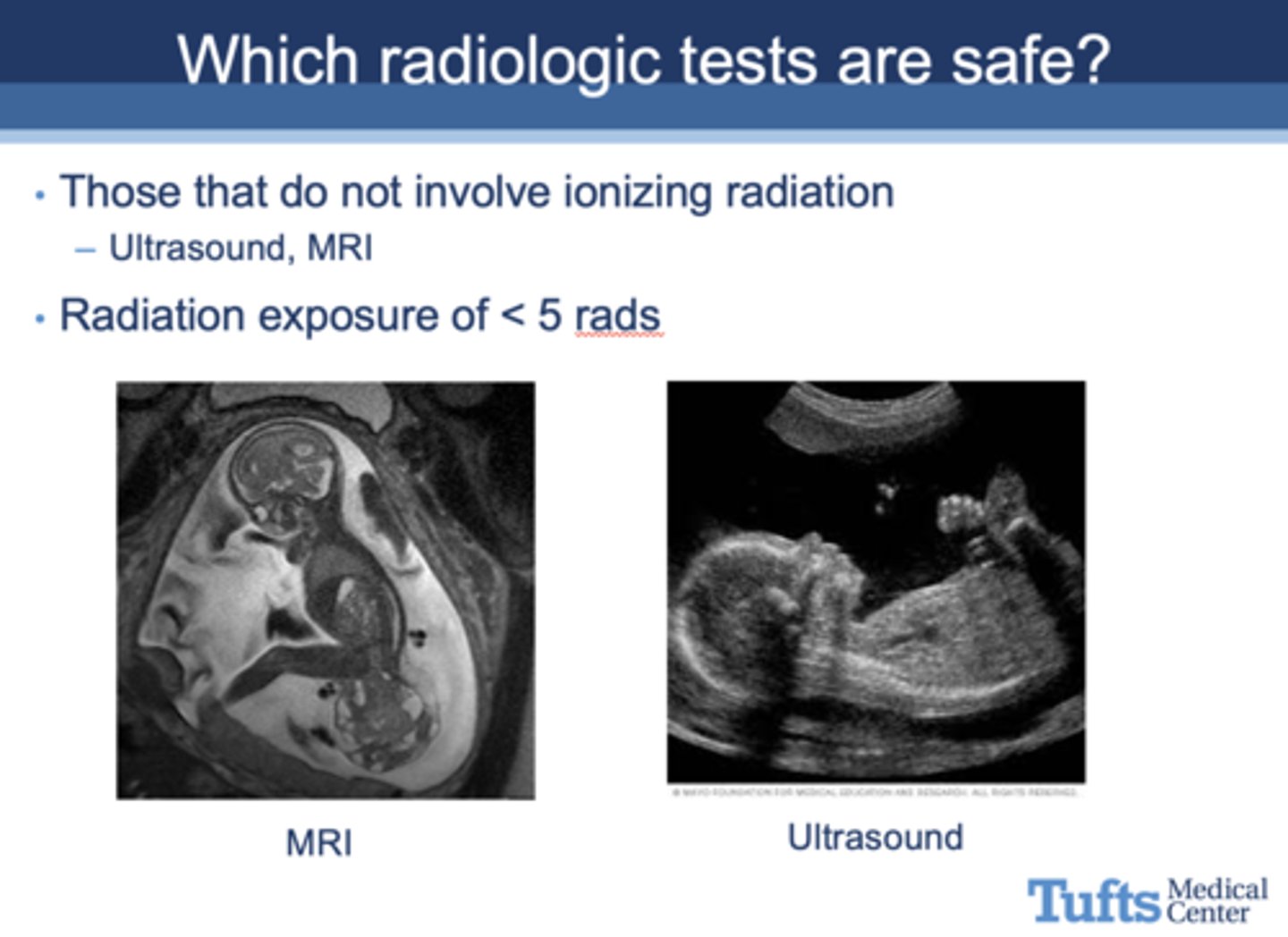
Which radiologic tests are safe?
Those that do not involve ionizing radiation, such as ultrasound and MRI
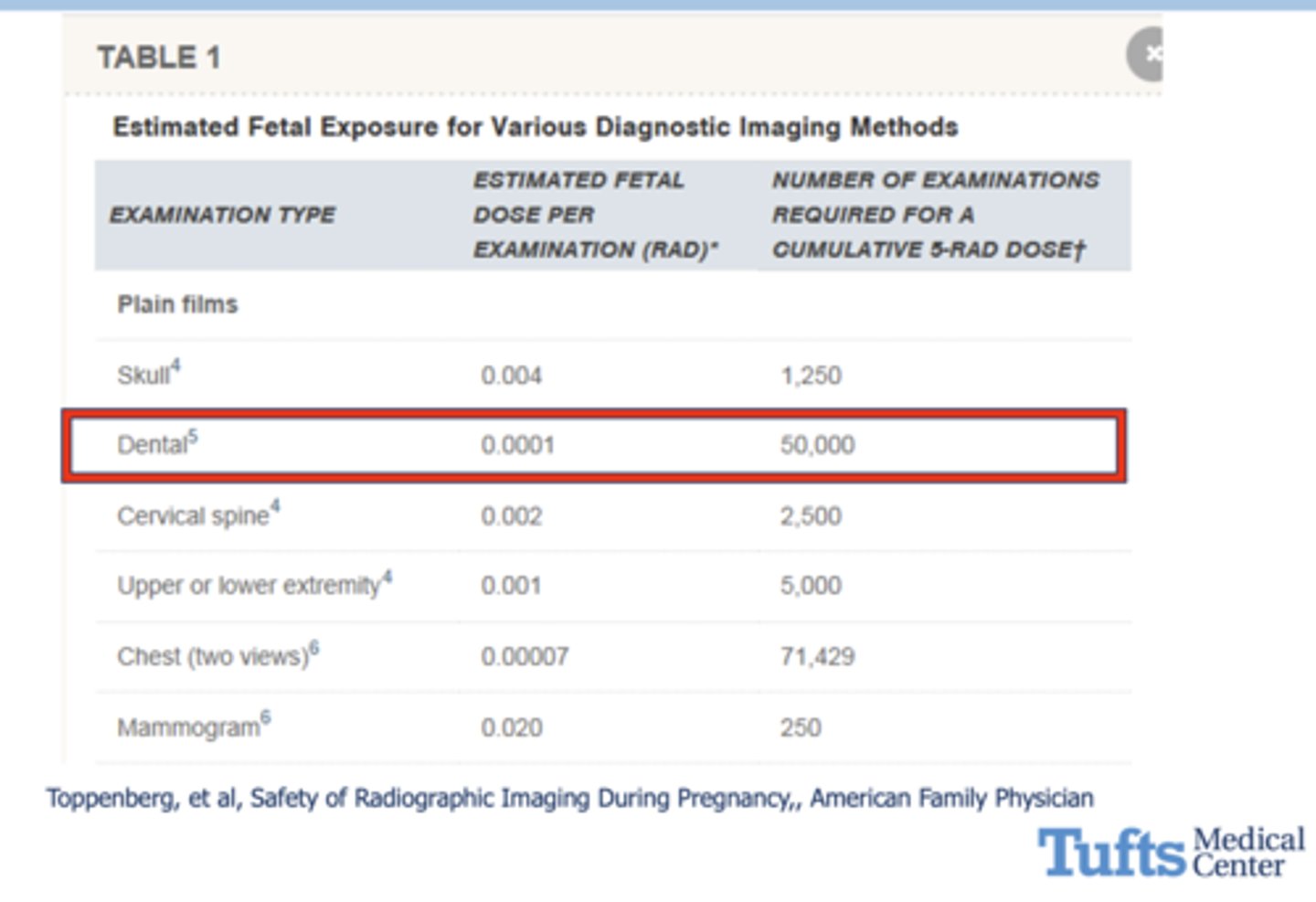
what is the estimated fetal radiation exposure for a dental x-ray?
0.0001
Which imaging studies are NOT safe for pregnant women?
radioactive iodine

Radioactive iodine can be especially unsafe in pregnant women especially if used after how many weeks?
10-12 weeks

Radioactive iodine is unsafe for pregnany women because it crosses placenta and can affect what fetal organ?
thyroid

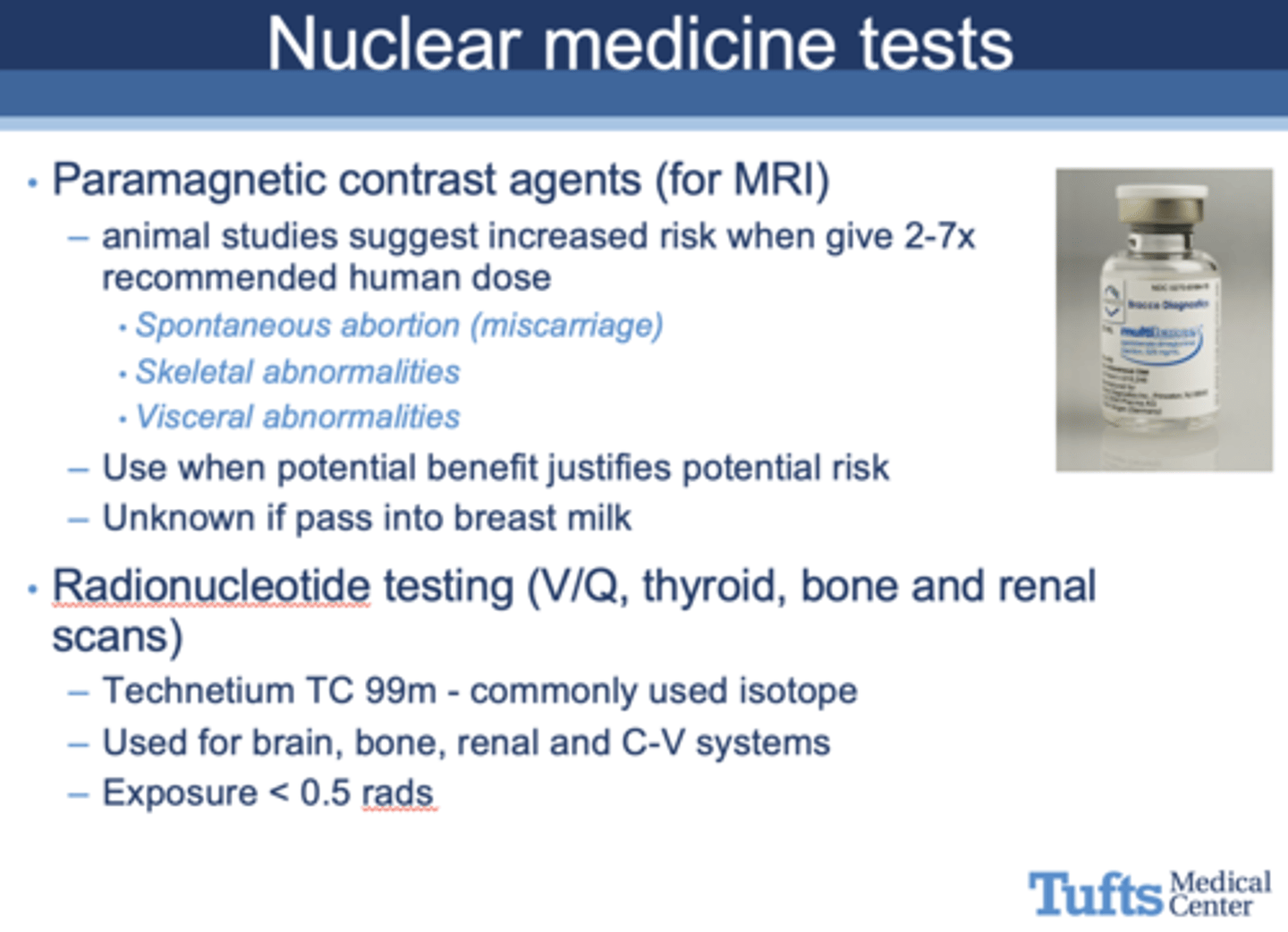
Can nuclear medicine tests be used for patients who are pregnant?
Yes, but use cautiously

Animal studies suggest increased risk when give ______-______x recommended human dose for paramagnetic contrast agents, resulting in:
- Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Skeletal abnormalities
- Visceral abnormalities
2-7
All of the following can result from what?
- Embryonic death - all or non phenomenon
- Teratogenic effects
- Carcinogenesis
- Genetic effects or germ cell mutations
- Adverse genetic effects on future generations
- Intrauterine fetal growth restriction
High-dose radiation exposure

Does carcinogenesis pose a risk to fetus?
Unclear risk, but probably small

T/F: Multiple X-ray exposures seldom result in a high-dose radiation exposure
True

Risk of anomalies/growth restriction/abortions is not increased with exposure <___ rads
5

If radiographic testing is medically necessary, how can you avoid putting the fetus at risk?
Shield the fetus and limit exposure

Highest risk from radiographic testing for fetus is during what period?
organogenesis (3-10 weeks)

AAP Recommendations: Infants should be breastfeed exclusively for first _____ months.
6

AAP Recommendations: Breastfeeding should continue until ______ of age with supplementation of solid foods after 6 months
1 year

All of the following are benefits of what?
- Colostrum aids digestive system
- Antibodies that help immune system
- Lower risk of asthma, obesity, allergies
- Protein/fat better used than formula
- Less gas, feeding issues, constipation
- Less SIDS (sudden infant death)
Breastfeeding

When should medications be taken when breastfeeding?
Timing doses immediately after a feeding

Are the following safe or unsafe with breastfeeding?
- Antibiotics
- Antihistamines
- Nasal decongestants
- Analgesics
- IV contrast agents
Safe
