Aromatic compounds
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
What is Benzene?
An aromatic hydrocarbon/arene with the molecular formularC6H6
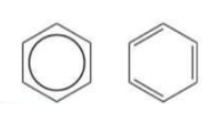
What does the kekule structure suggest about benzene?
That the structure of benzene was based on a 6-membered ring of carbon atoms, joined by alternate single and double bonds
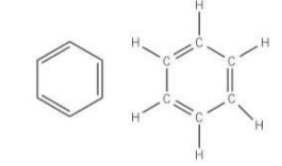
Why is the Kekule structure wrong (electrophilic addition)
Because if benzene contained C=C bonds, it should decolourise bromine in an electrophilic addition, however benzene does not undergo electrophilic addition reactions and so does not decolourise bromine under normal conditions therefore it cannot have any C=C bonds in its structure.
What was found when the bond lengths of benzene was measured/how were the bond lengths measured?
Using x-ray diffraction, it is possible to measure bond lengths in a molecule, when benzene was examined, it was found that all bonds were the same length (0.139nm). This bond length is between the length of a single bond (0.153nm) and a double bond (0.134nm)
What is the bond length of a double bond?
0.134nm
What is the bond length of a single bond?
0.153nm
What is the bond length of benzene?
0.139nm
If benzene had the kekule strucuture, then how many times more would it be expected to have an enthalpy change of hydrogenation than cyclohexene?
3 times (because 3 double bonds)
Complete the sentence
When cyclohexene is ——————, one double bond reacts with H2 to form ————— and the enthalpy change of hydrogenation is ——kJmol-1. In reality, the enthalpy change of hydrogenation of benzene is ——kJmol-1, indicating benzene is —— stable than the kekule model suggested.
When cyclohexene is hydrogenated, one double bond reacts with H2 to form cyclohexane and the enthalpy change of hydrogenation is -120kJmol-1. In reality, the enthalpy change of hydrogenation of benzene is -208kJmol-1, indicating benzene is more stable than the kekule model suggested.
How does the delocalised model show benzene?
As a planar cyclic, hexagonal hydrocarbon containing 6 C atoms and 6 H atoms.
In benzene what does each electron from 1 C bond to?
2 C and 1 H. Each C atom has 1 electron in the p orbital at right angles to the plane of the bonded carbons and hydrogens
How is a ring of electron density formed in benzene, what does this do?
When adjacent p orbitals overlap sideways in both directions above and below the plane of the C atoms to form a ring of electron density. The overlapping p orbitals creates a system of pi bonds which spread over all the carbon atoms in the ring structure. The 6 electrons occupying the system of pi bonds are delocalised.

How do you name a benzene compound with 1 substituent group?
In aromatic compounds, the benzene ring is considered the parent chain. Alkyl groups, halogens and nitro groups are considered prefixes to benzene.
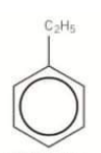
What would this compound be called?
Ethylbenzene
What would this compound be called
chlorobenzene
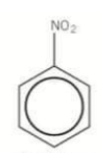
What would this compound be called?
Nitrobenzene
How would you name the compound when benzene is attaches to an alkyl chain with a functional group or with 7 or more carbons?
Benzene is considered the substituent groups. Instead of benzene the prefix is phenyl.
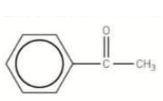
What would this compound be called?
Phenylethanone
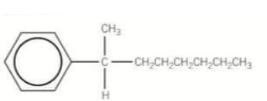
What would this compound be called?
2-phenyloctane
How are aromatic compounds with more than 1 substituent group named?
The substituent groups are listen in alphabetical order, using the smallest numbers possible.
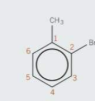
How would this compound be named?
The molecule is based on the methybenzene, with a bromine substituent. When naming compounds you always use the lowest combination of number possible, therefore bromine is on carbon 2. The compound is 2-bromomethylbenzene
What are the exception in naming aromatic compounds?
True or false benzene undergoes addition reactions in which a H atom on the benzene ring is replaced by another atom/group of atoms
False it undergoes substitution reactions in which a H atom on the benzene ring is replaced by another atom/group of atoms
True or false benzene reacts with electrophiles
True
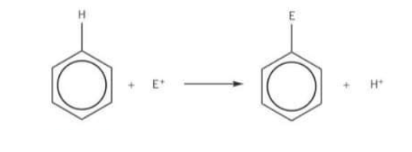
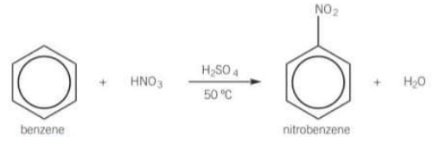
What does benzene react with to form nitrobenzene? What are the conditions for the reaction?
HNO3
Catalysed with H2SO4 and heated to 50°C to obtain a good rate, a water bath is used to maintain a steady temperature
What happens during nitration of benzene?
One of the H atoms is replaced with a nitro group
Describe the reactivity of benzene
Benzene does not react with Br2 unless halogen carrier present because benzene has delocalised pi electrons spread above and below plane. - electron density around 2 carbons in benzene ring less than in C=C bond so cannot polarise bromine
Compare the reactivity of alkenes and arenes
alkenes decolourise bromine by electrophilic addition, bromine adds across the c=c bond in cyclohexene
Pi bond in alkene contains localised electrons above and below plane of 2 other carbons in c=c bond produces an area of high electron density
Localised. Electrons in pi bond induce dipole in non-polar bromine molecule making one slightly positive and one slightly negative
Slightly positive bromine enables Br molecule to act as electrophile
What is a nitro group?
NO2
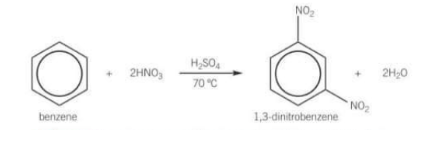
What happens in nitration of benzene if the temperature exceeds 50 degrees?
Further substitution reactions may occur forming dinitrobenzene
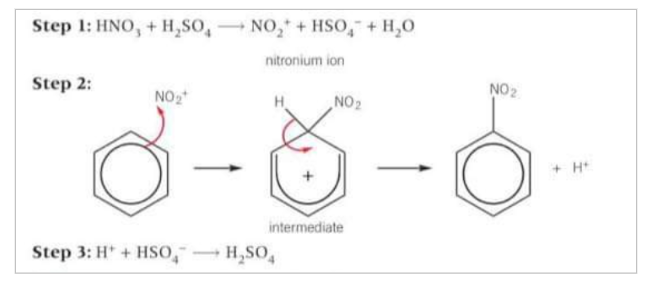
How is the electrophile made in the nitration of benzene?
Nitric acid is not an electrophile. The electrophile in the reaction is the nitronium ion (NO2+), Produced by the reaction of concentrated nitric acid with concentrated sulfuric acid in step 1
How does nitration of benzene take place?
The electrophile NO2+ accepts a pair of electrons from the benzene ring to form a dative covalent bond. The organic intermediate formed is unstable and breaks down to form the product, nitrobenzene and an H+ ion. A stable benzene ring is reformed. Finally, the H+ ion reacts with the HSO4- to regenerate the H2SO4 catalyst.
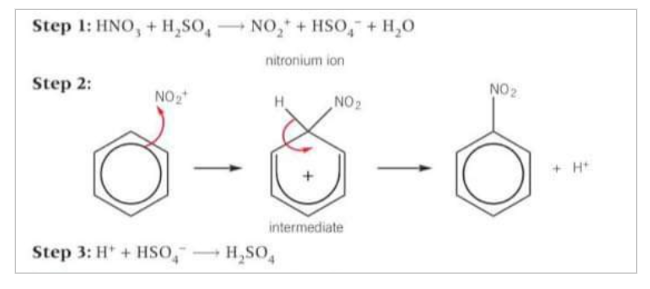
Write out the steps of nitration of benzene
True or false halogens always readily react with benzene?
False they don’t react with benzene unless a catalyst called a halogen carrier is present
What are the halogen carriers?
AlCl3
FeCl3
AlBr3
FeBr3
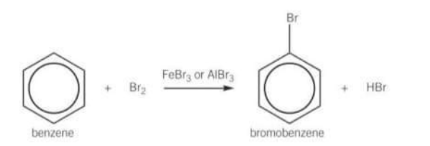
What are the conditions for the bromination of benzene?
Room temperature and pressure, in the presence of a halogen carrier
What type of reaction is bromination of benzene?
Electrophilic substitution
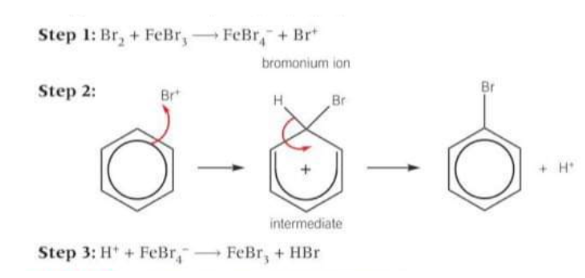
In the bromination of benzene: benzene is too stable to react with a non-polar bromine molecule so how does it react?
The electrophile is the bromonium ion Br+, which is generated when the halogen carrier catalyst reacts with bromine.
What happens in the bromination of benzene?
The bromonium ion accepts a pair of electrons from the benzene ring to form a dative covalent bond. The organic intermediate is unstable and breaks down, forming the organic product, bromobenzene and a H+ ion. The H+ ion formed reacts with FeBr4- to regenerate the FeBr3 catalyst.
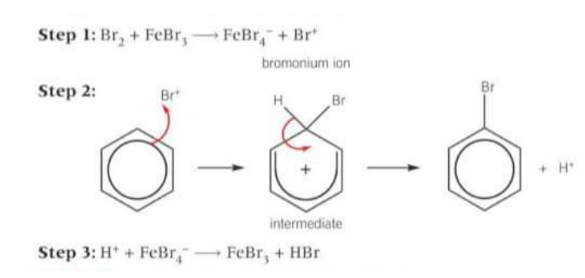
Draw the mechanism for bromination of benzene
What is the overall equation for the chlorination of benzene?
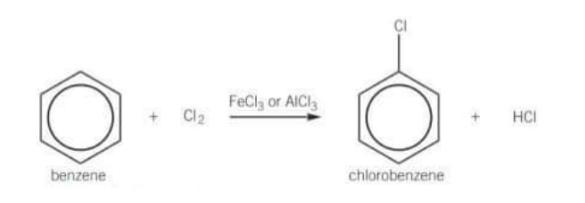
What is an alkylation reaction of benzene?
The substitution of a H atom in the benzene ring by an alkyl group
How is an alkylation reaction carried out? What is it known as?
Benzene is reacted with a haloalkane in the presence of AlCl3, generating the electrophile. Alkylation increases the number of carbon atoms in a compound by forming C-C bonds. It is known as Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
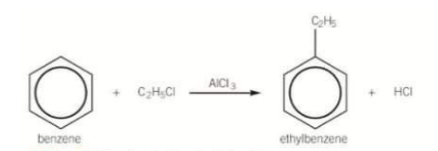
Complete the sentence:
When benzene reacts with an acyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3 an aromatic _________ is formed
When benzene reacts with an acyl chloride in the presence of AlCl3 an aromatic ketone is formed
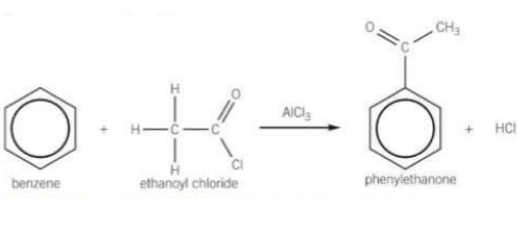
Compare the reactivity of alkenes and arenes pt1 - how does cyclohexene react with Br2
Alkenes decolourise bromine by electrophilic addition, bromine adds across the C=C bond in the cyclohexene
The pi bond in the alkene contains localised electrons above and below the plane of the 2 other carbons in the C=C bond. This produces an area of high electron density. The localised electrons in the pi bond include a dipole in the non-polar bromine molecules, making 1 Br atom slightly positive and the other slightly negatice
The slightly positive bromine atom enables the bromine molecules to act like an electrophile
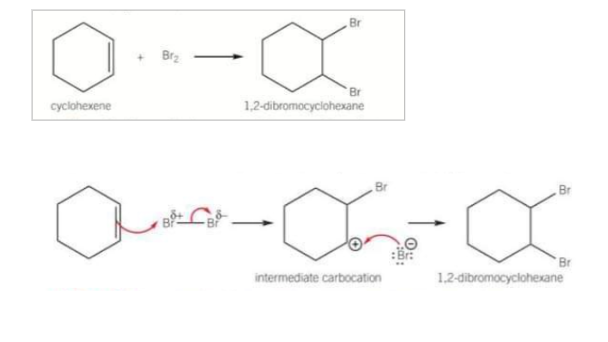
Compare the reactivity of alkenes and arenes pt2 Describe aromatic reactivity
Benzene does not react with Br2 unless a halogen carrier is present. This is because the benzene has delocalised pi electrons that are spread above and below the plane of the carbon ring.
The electron density around any two carbons in the benzene ring is less than that in a C=C bond in an alkene.
When non-polar molecules like Br2 approach benzene, there is insufficient pi-electron density around any two carbon atoms to polarise the bromine molecule. This prevents the reaction from taking place
The mechanism for the reaction of bromine with benzene in the presence of a halogen carrier is electrophilic substitution