1 - Planes, Tissue, Muscle, Lymph
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
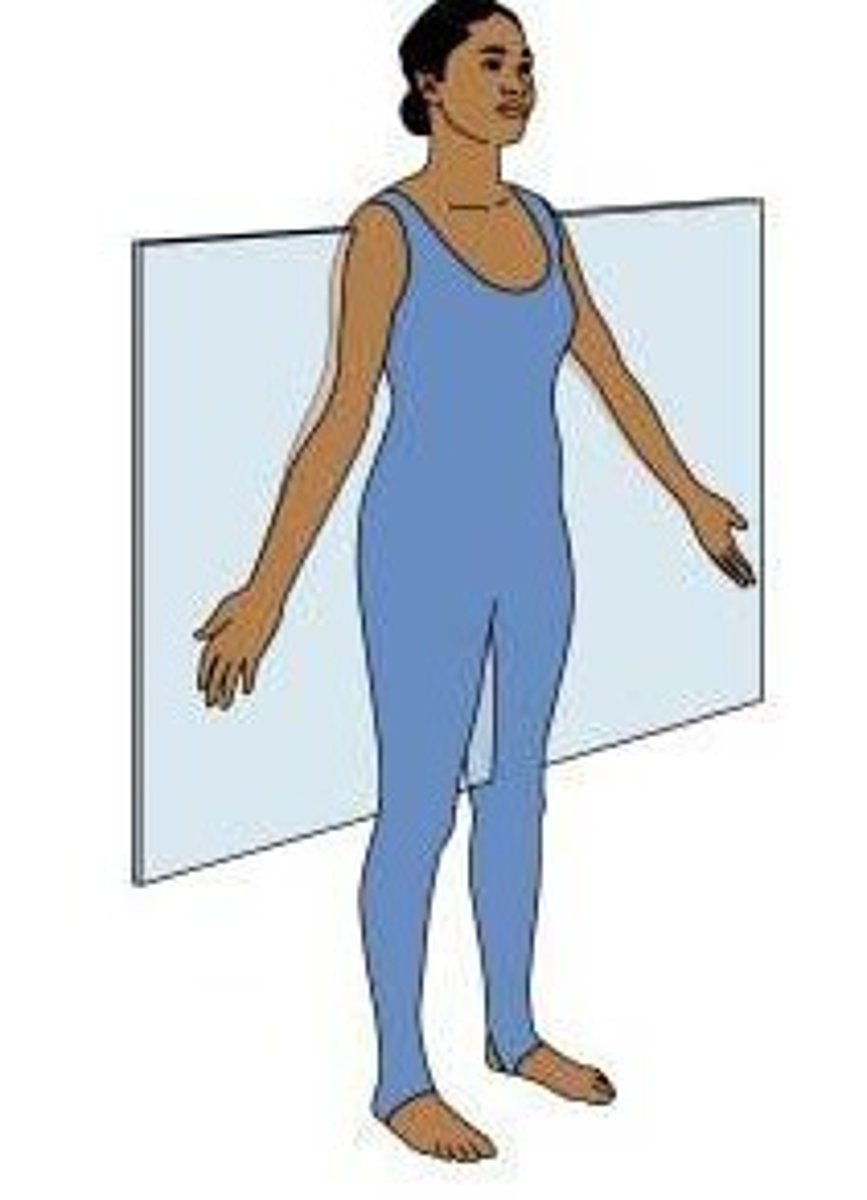
sagittal plane
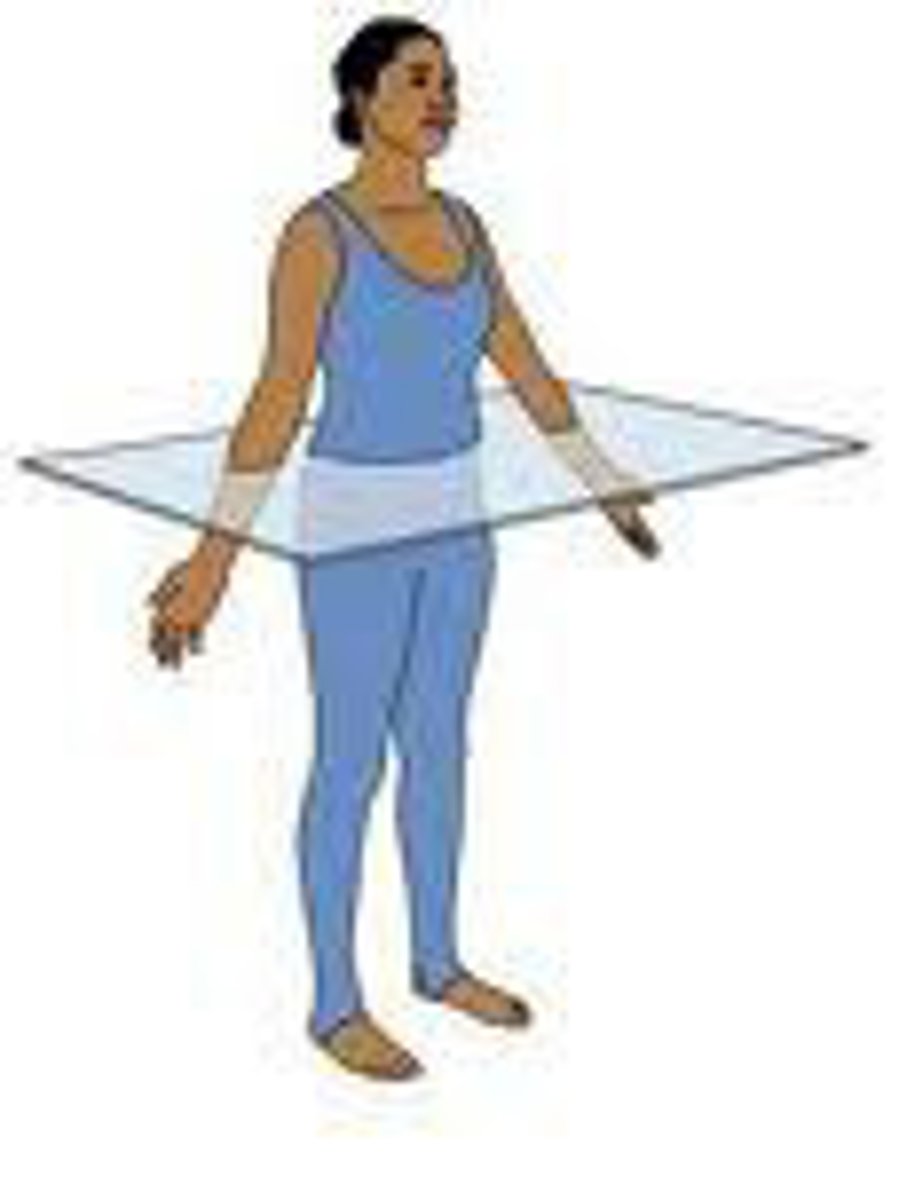
transverse plane
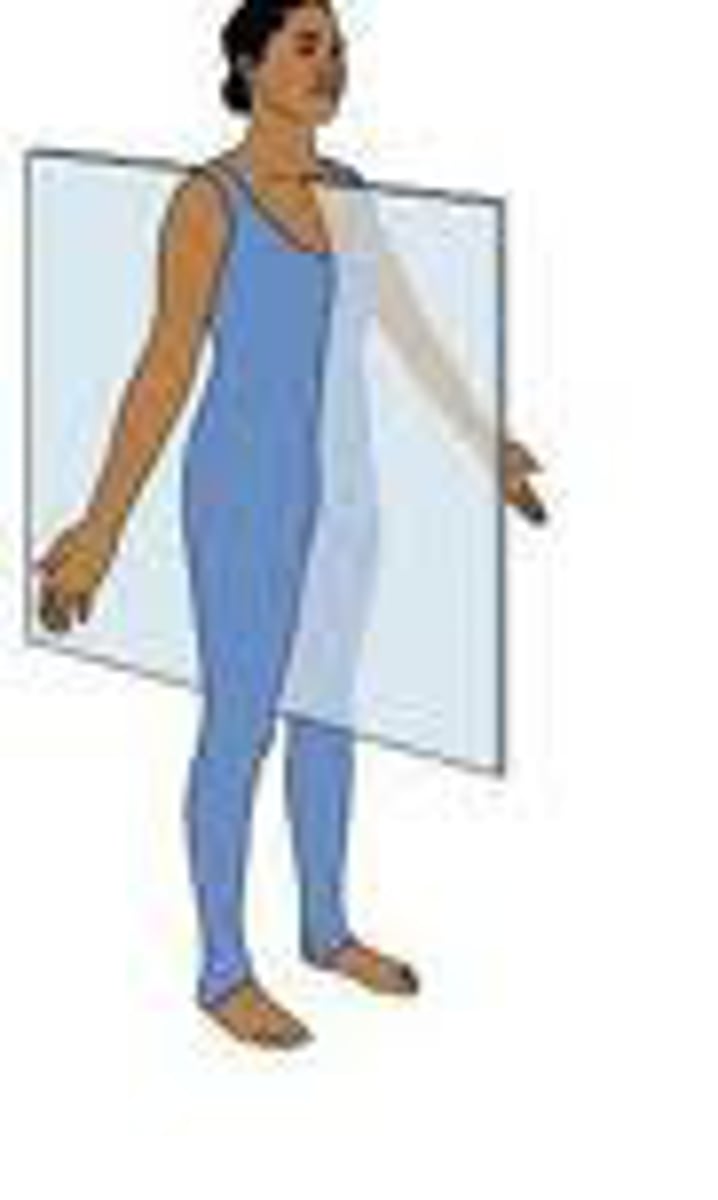
frontal plane
anatomical position
what is this position called
flexion, extension
what movements are these
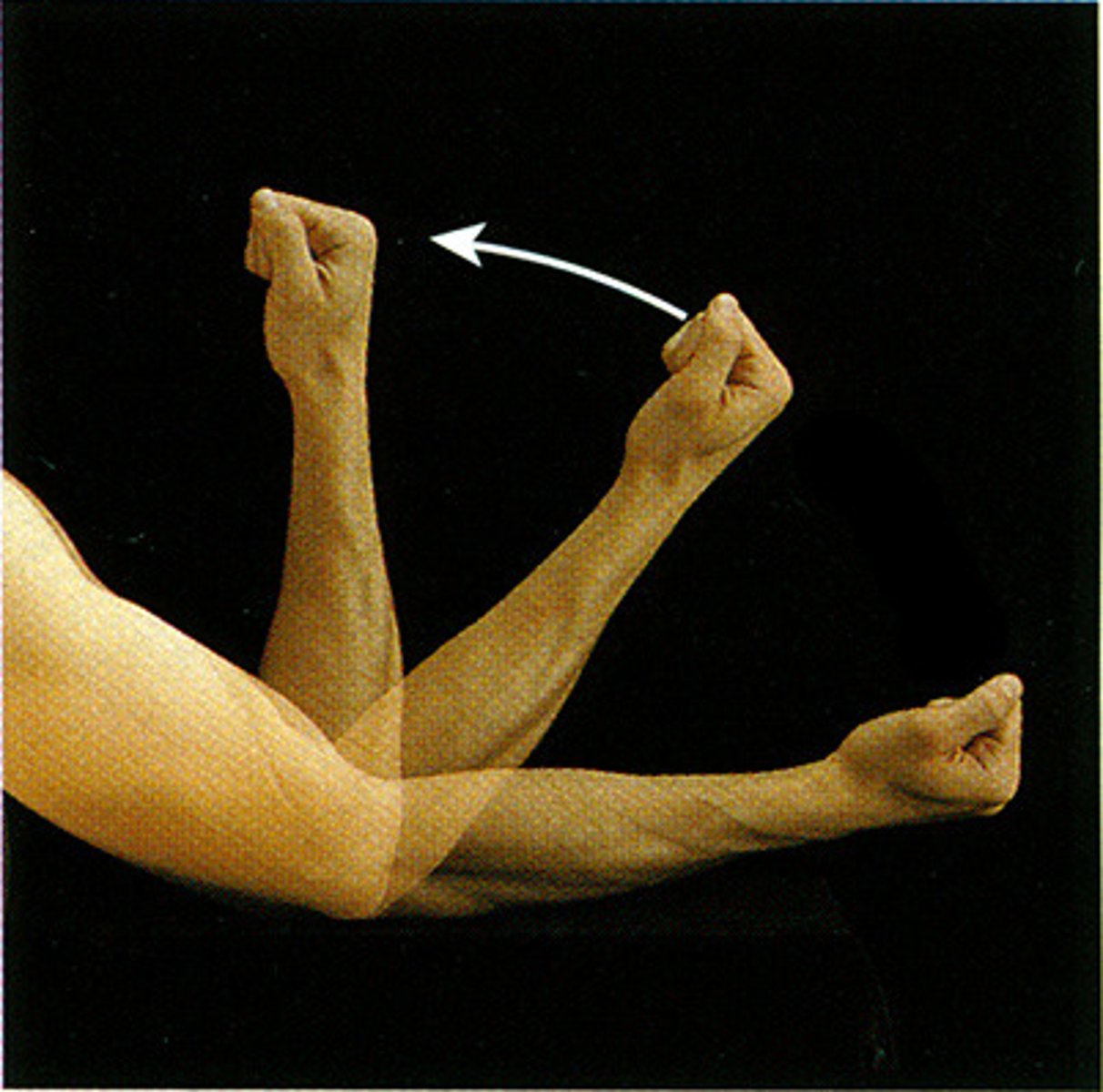
abduction, adduction
what movements are these
circumduction
what movement is this
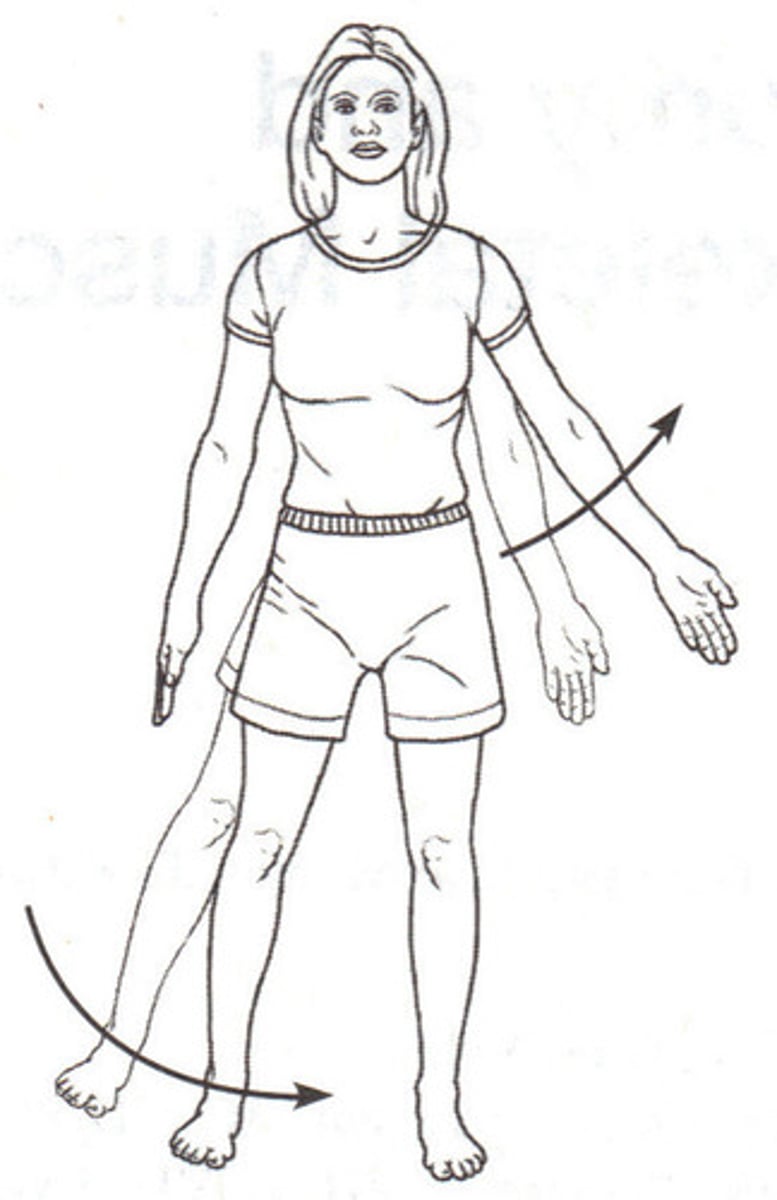
protraction, retraction
what movements are these
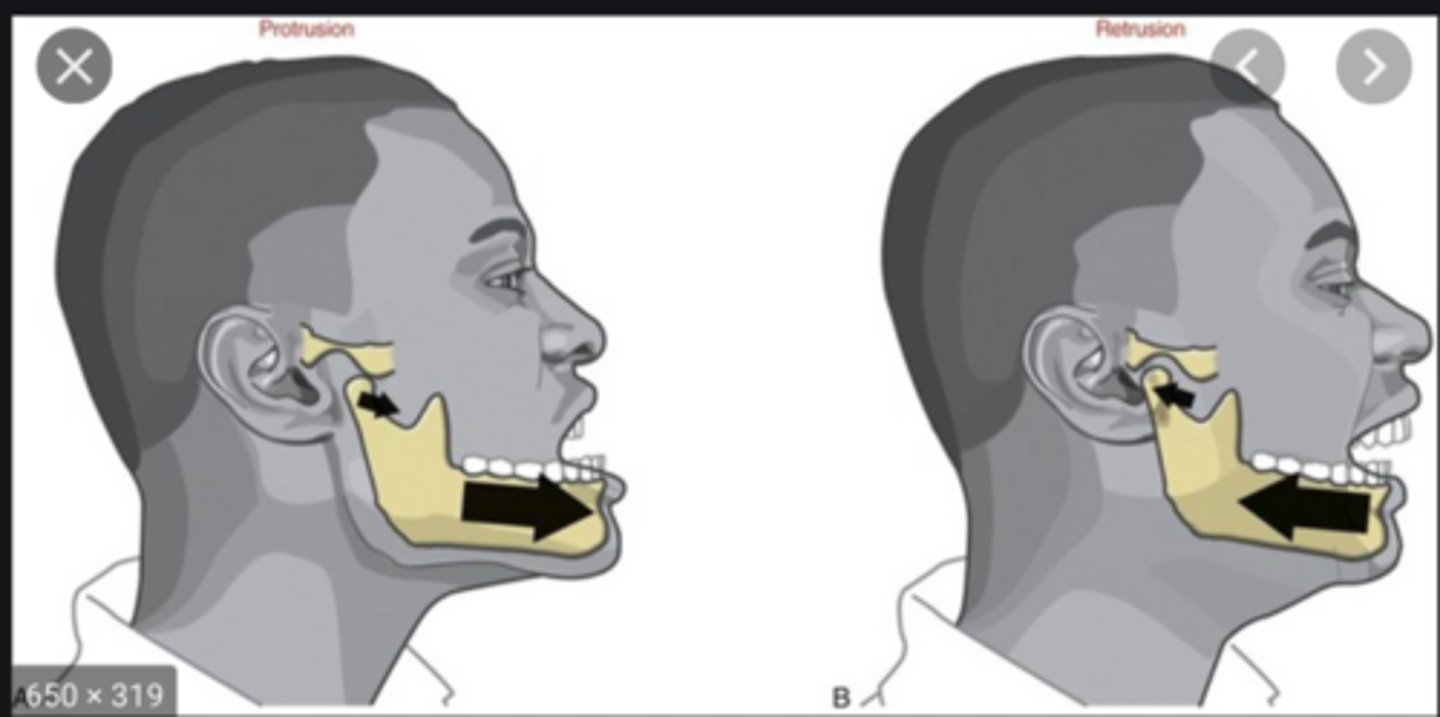
protrusion, retrustion
what movements are these & what parts of the body perform them?
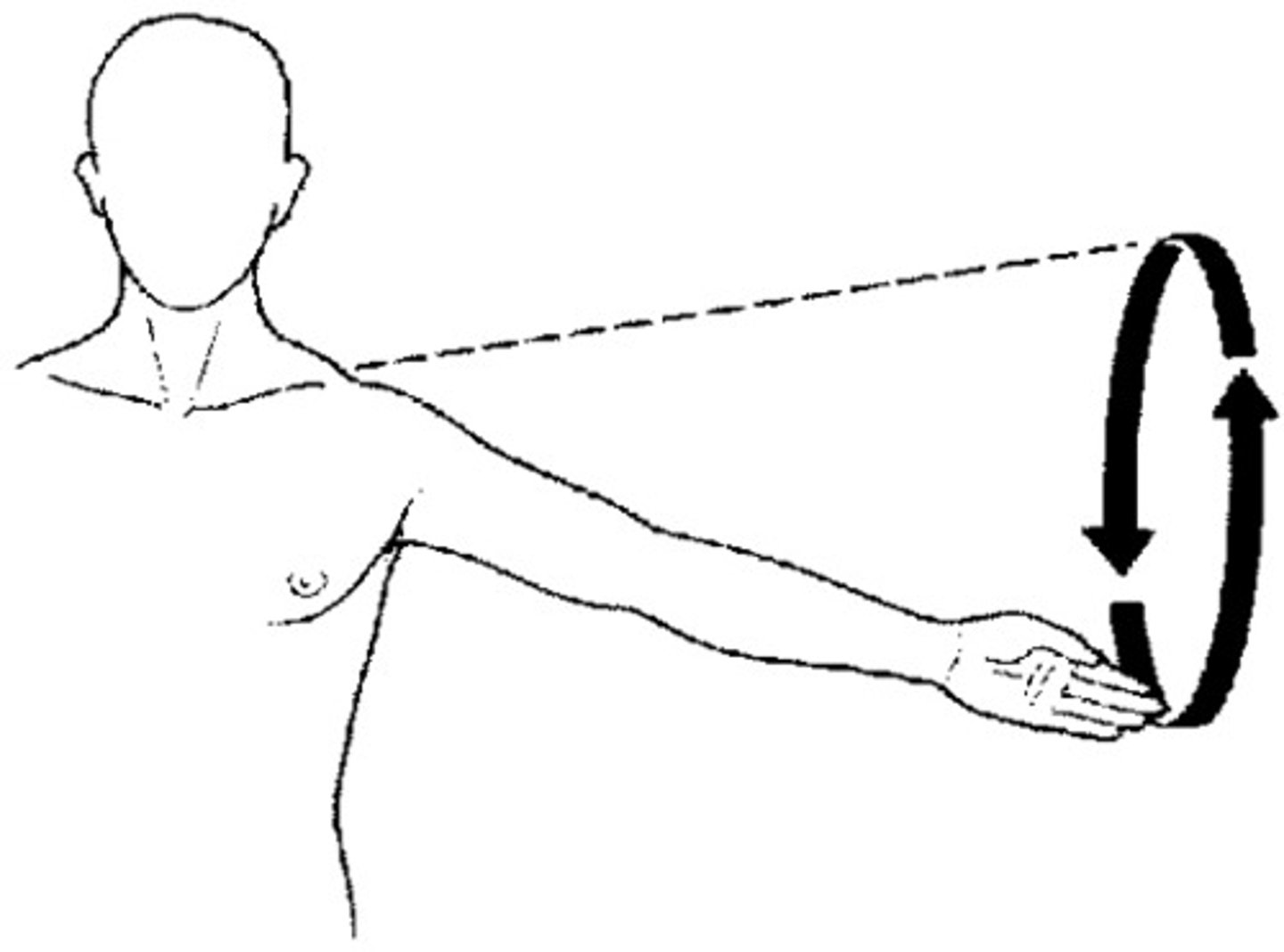
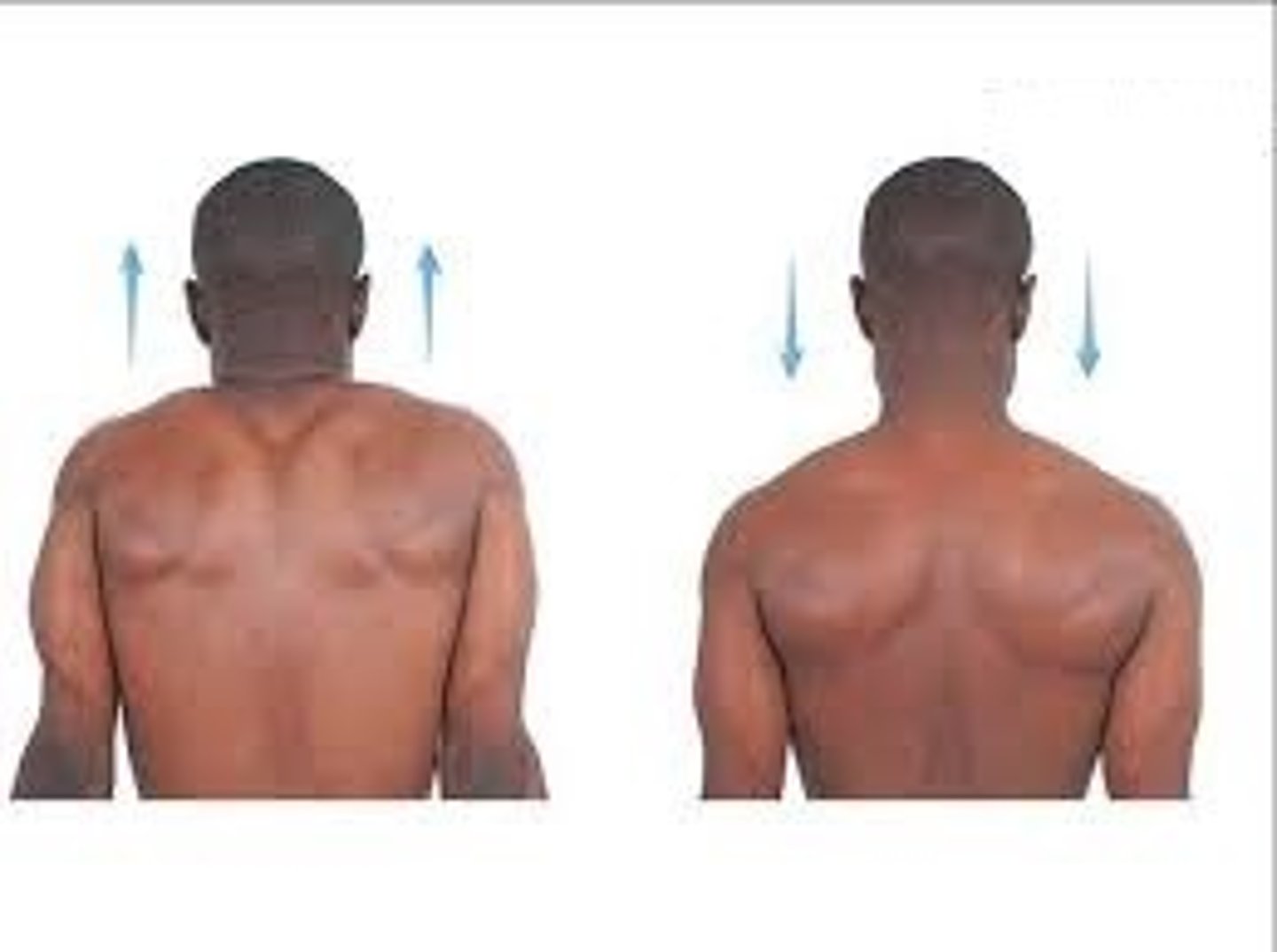
elevation, depression
what movements are these
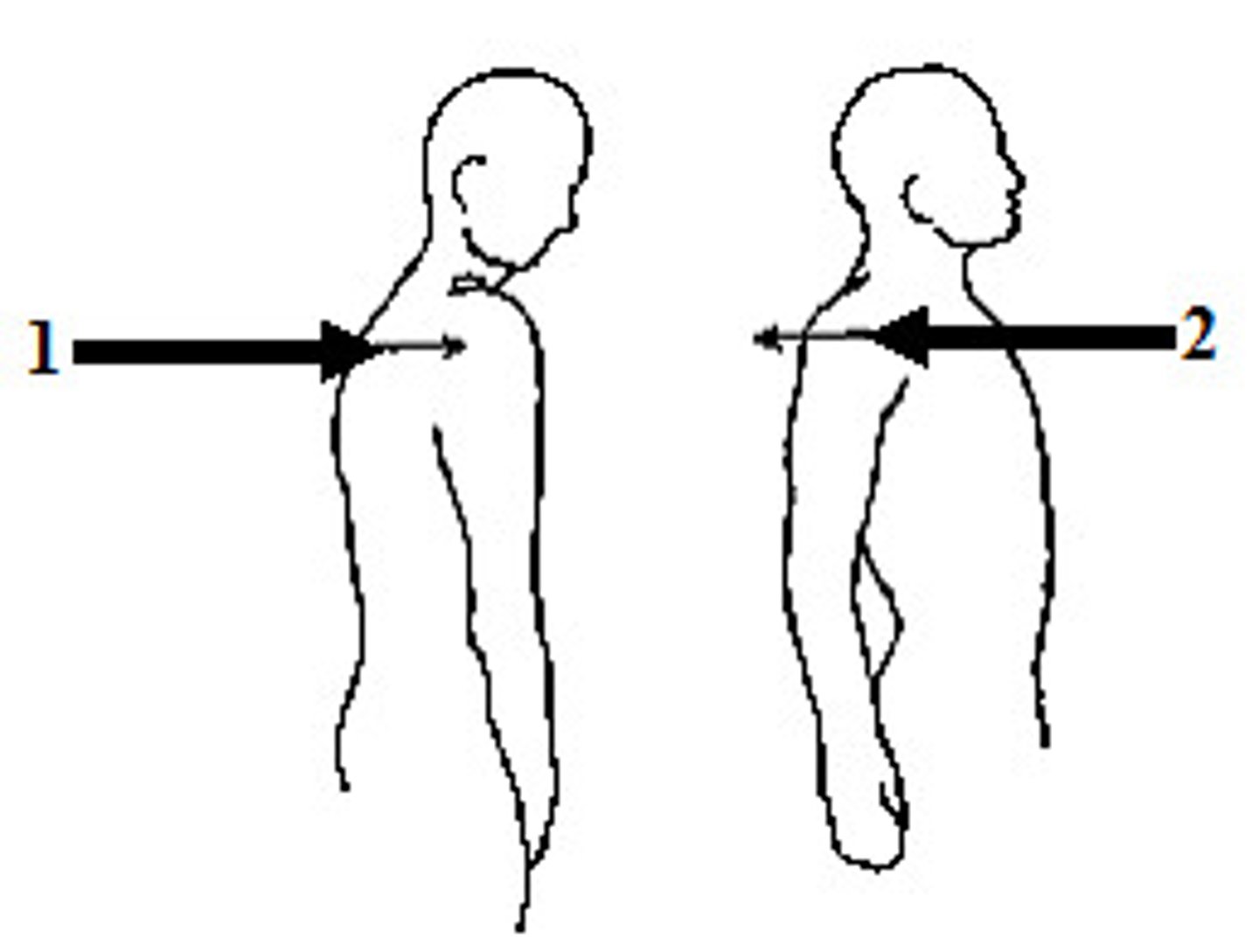
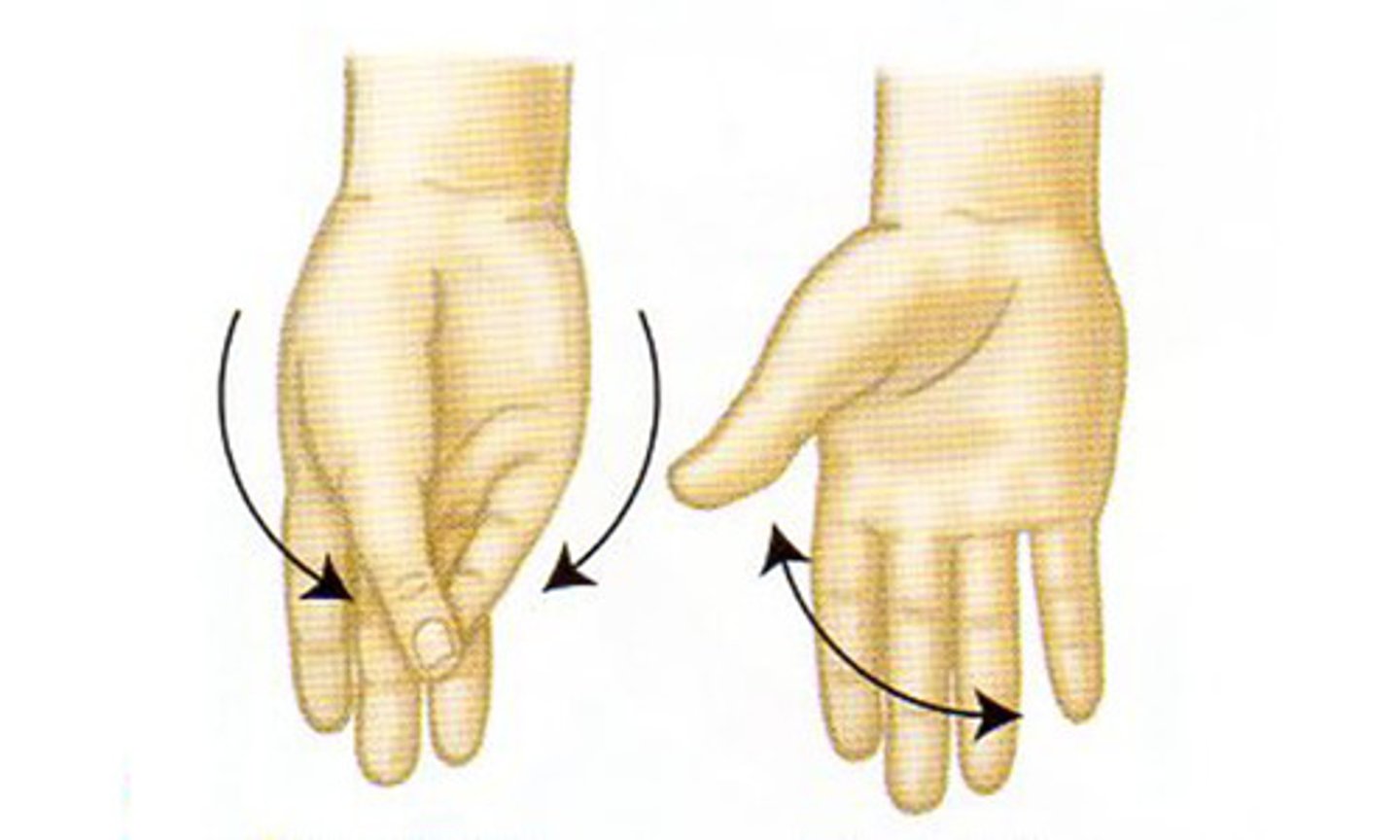
opposition, reposition
what movements are these
dorsiflexion, plantar flexion
what movements are these
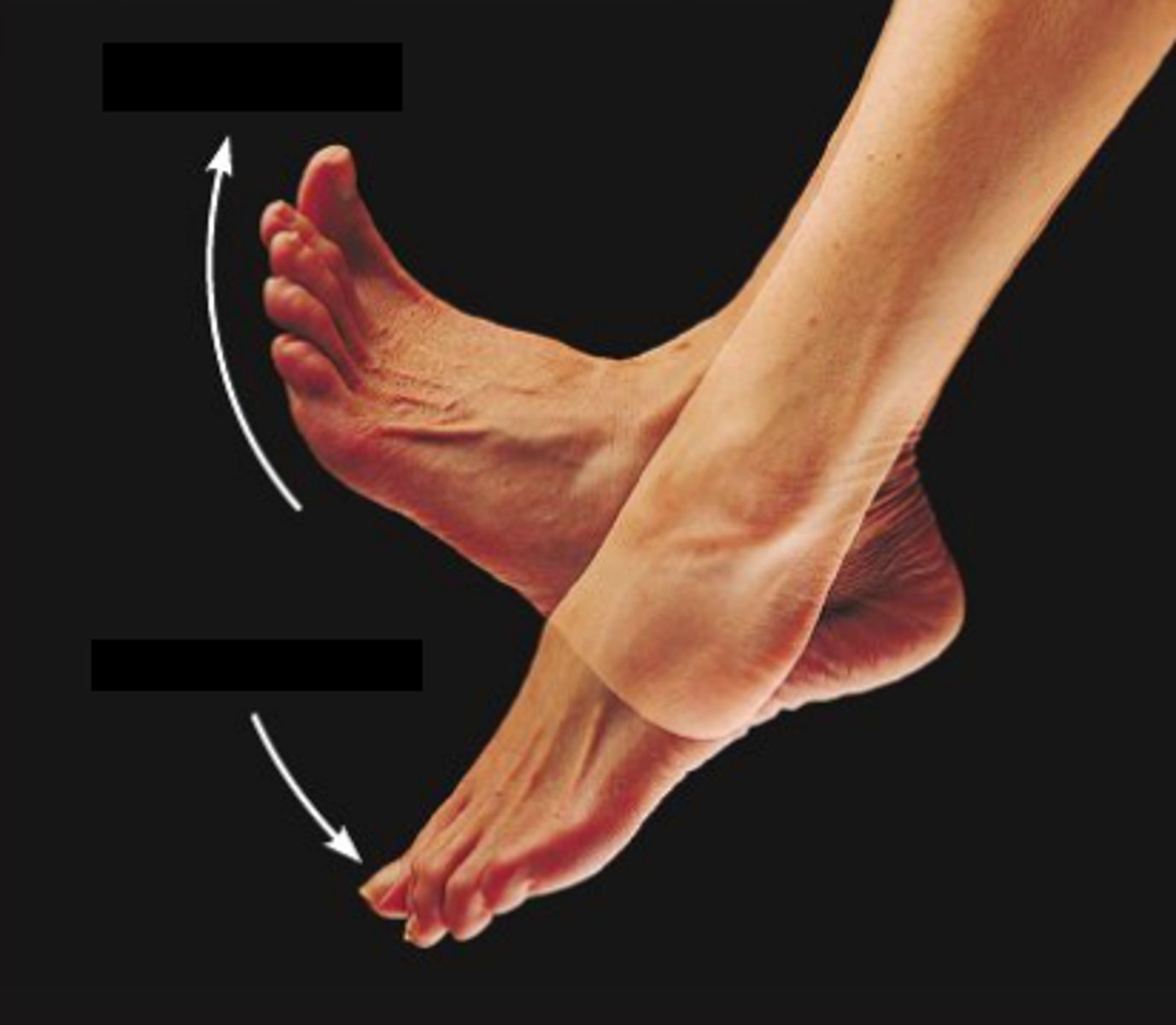
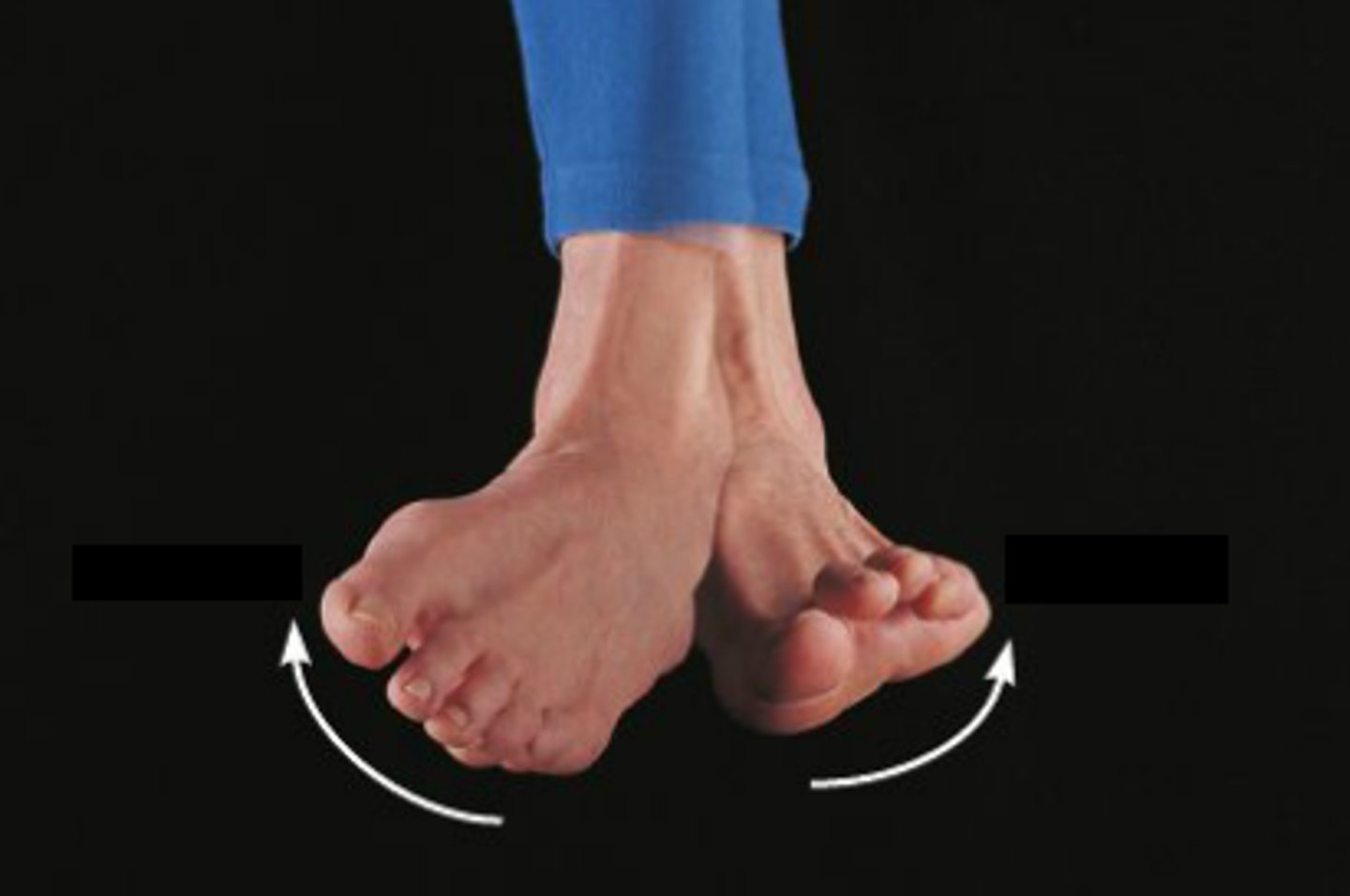
inversion, eversion
what movements are these
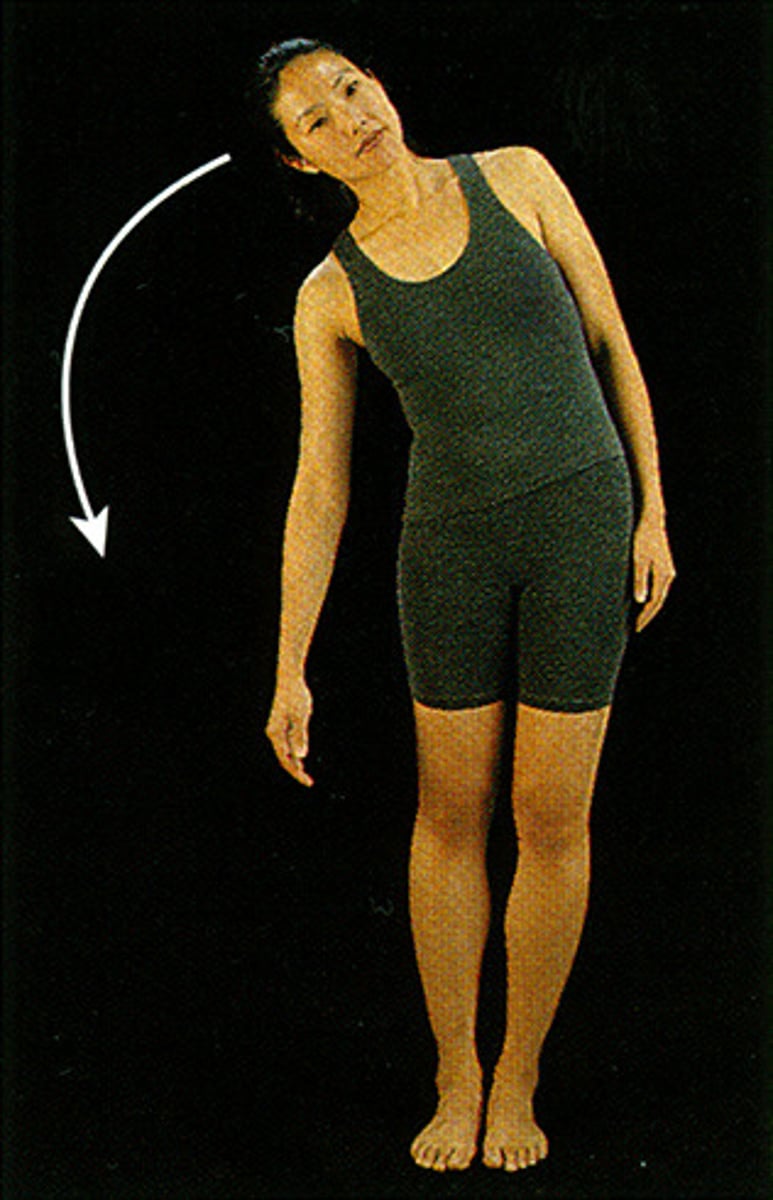
lateral/side bending
what movements are these
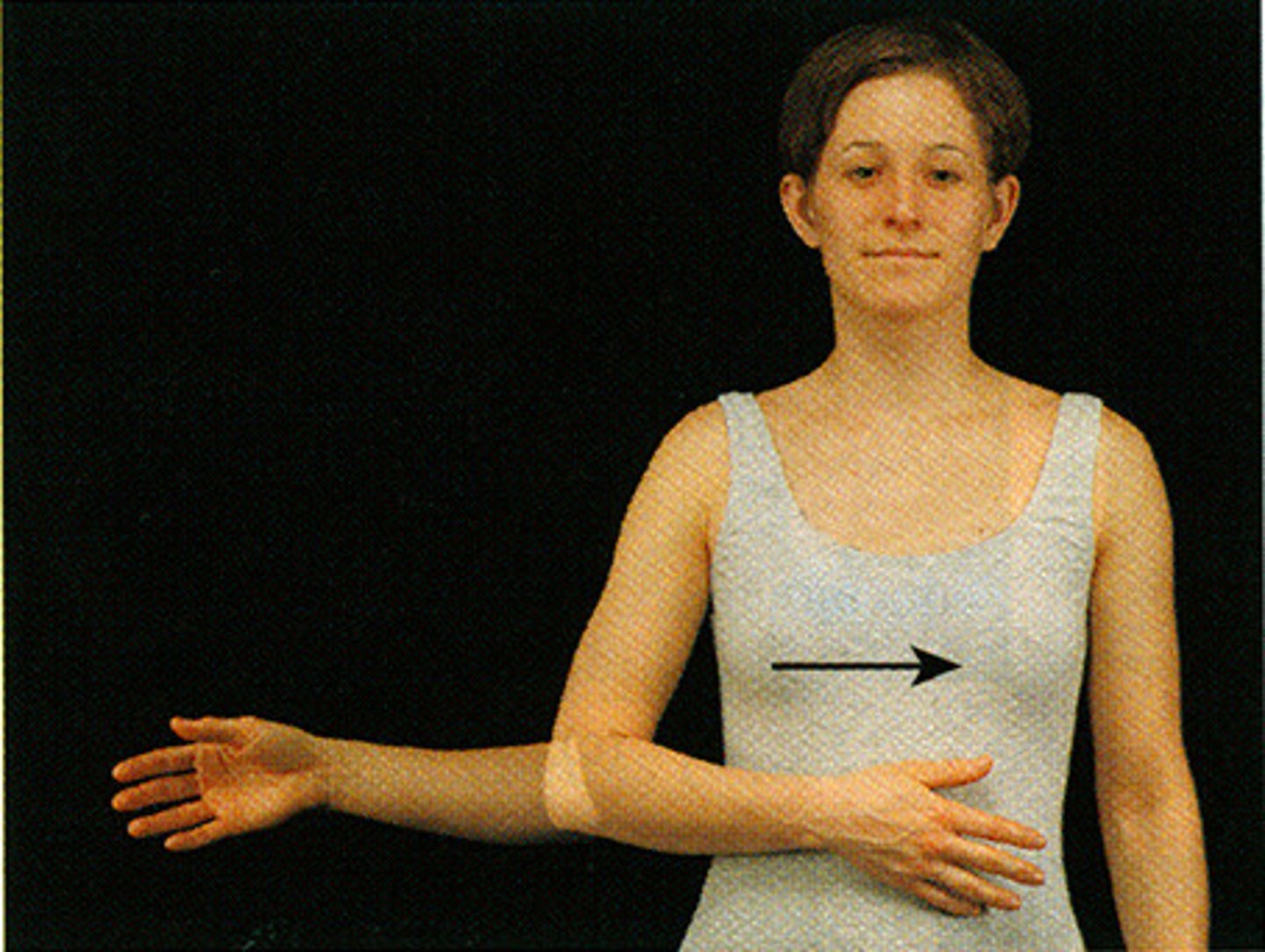
internal and external rotation
what movements are these
ipsilateral, contralateral, unilateral, bilateral
___ - same side
___ - opposite side
___ - one side
____ - both sides
proximal & distal
what terms do we use for the trunk vs. the limbs?
superficial
nearer to the surface
the muscles of the arm are ____ to the bone
intermediate
between a superficial & a deep structure
the biceps muscle is ____ between the skin and the humerus
deep
farther from the surface
the humerus is ___ to the arm muscles
medial
nearer to median plane
the 5th digit is on the ___ side of the hand
lateral
farther from the medial plane
the 1st digit is on the ___ side of the hand
posterior/dorsal
nearer to the back
the heel is ___ to the toes
inferior/caudal
nearer to the feet
the stomach is ___ to the heart
anterior/ventral
nearer to the front
the toes are ___ to the ankle
distal
farther from the trunk or origin
the wrist is ____ to the elbow,
superior/cranial
nearer to head
the heart is ___ to the stomach
palmar, dorsal
anterior hand
posterior hand
plantar, dorsal
inferior foot surface (sole)
superior foot surface (dorsum)
pronation, supination
what are these movements?
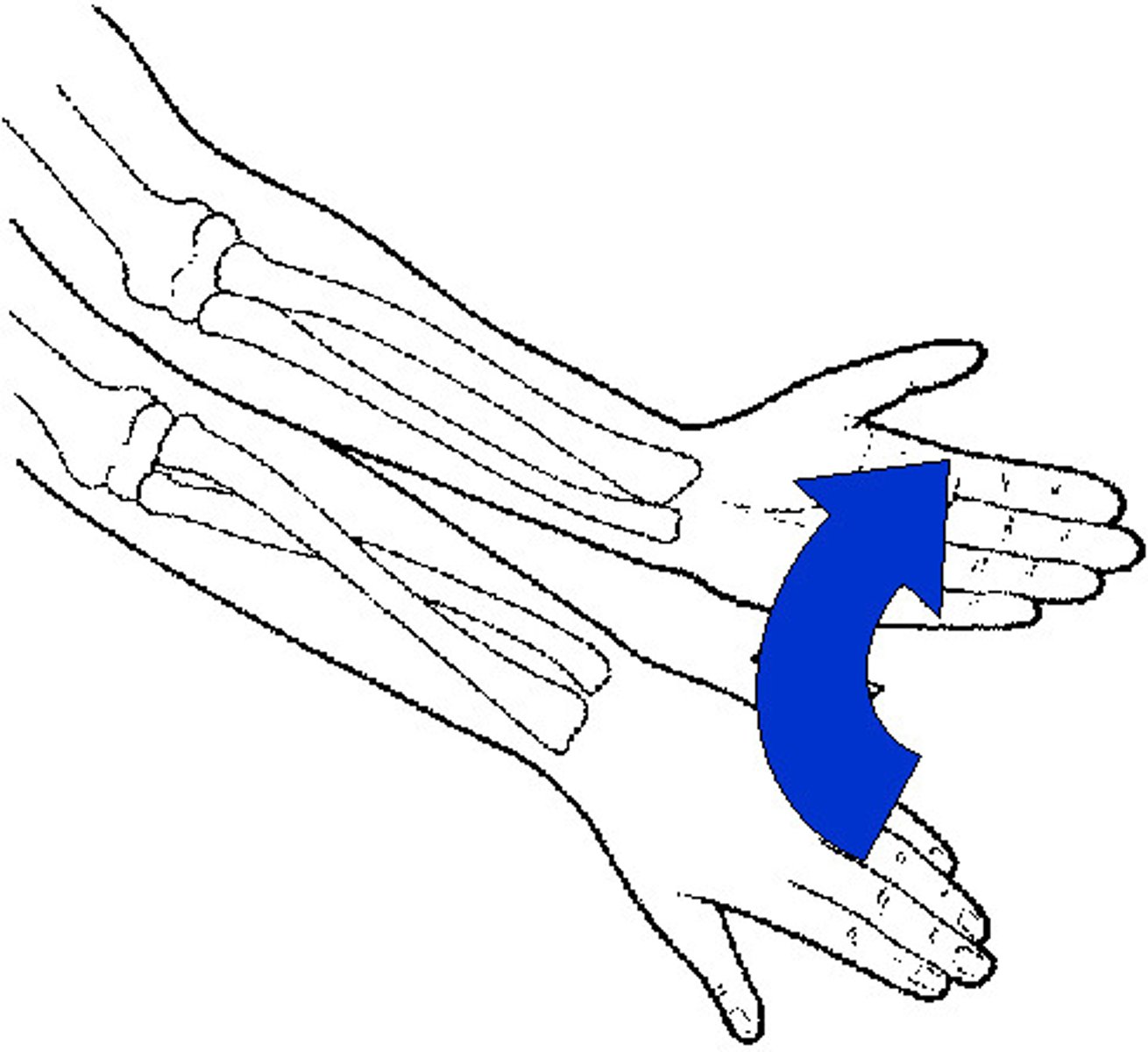
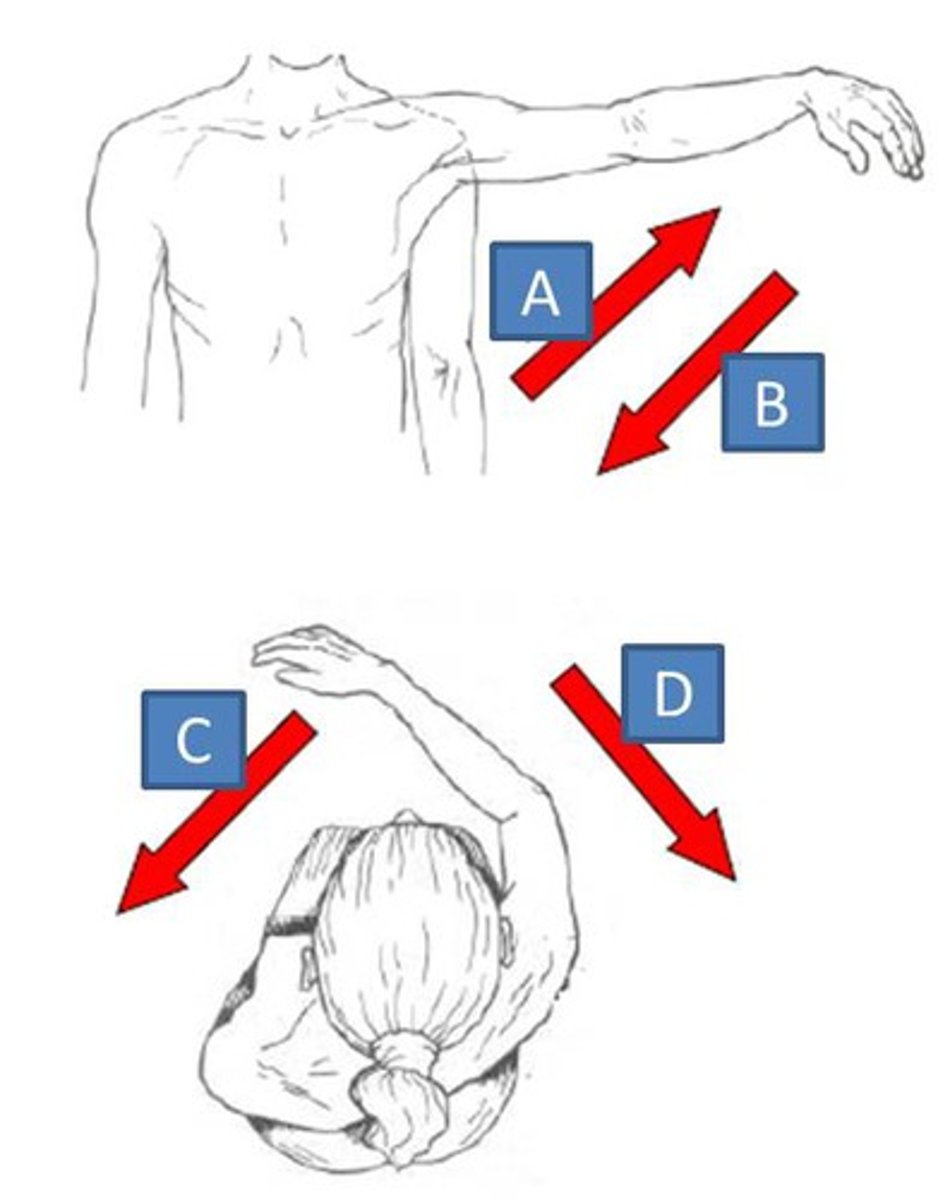
horizontal abduction, horizontal adduction
what are these movements
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
what are the 4 types of basic tissues?
collection of tissues that perform a function
what is an organ?
a group of organs that work together to perform a function
what is a system?
protective barrier, connect things within the body
what are the functions of epithelial and connective tissues respectively?
connective tissue
bone, blood, cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and joint capsules are examples of...
subcutaneous tissue/superficial fascia
where do vascular & lymph systems reside in the skin?
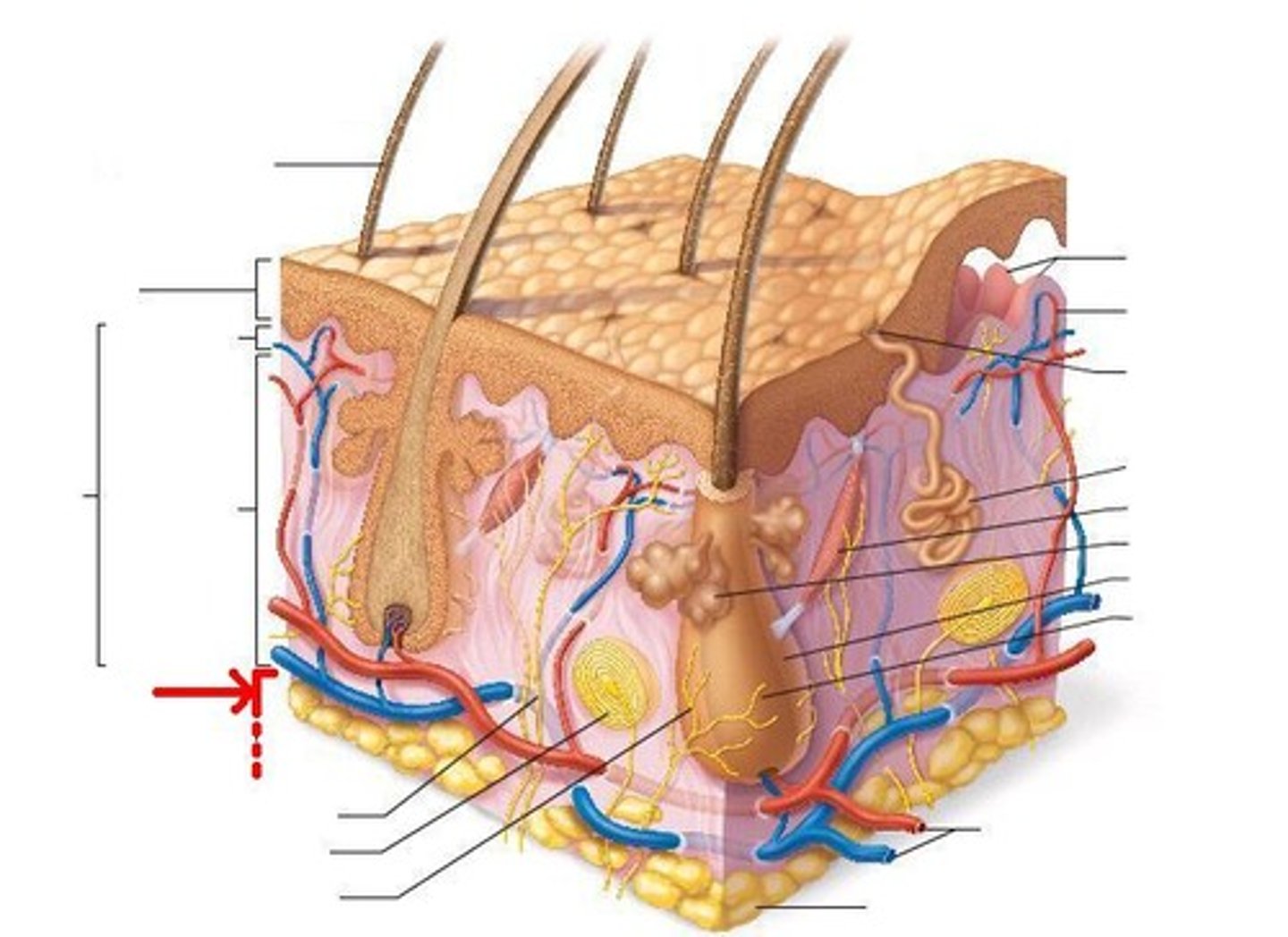
arrector pilli m.
what muscle activates goose bumps?
Subcutaneous tissue/deep fascia
other terms for the fat under the skin are...
it helps muscles move independently with little friction
why do we care about deep fascia?
epidermis, dermis, subcutaneous tissue (can also cut into muscle)
1st degree burns penetrate the ___
2nd degree burns penetrate the ____
3rd degree burns penetrate the ____
deep fascia
___ ___ attaches to periosteum covering bone and compartmentalizes functional groups of muscles
superficial fascia
muscles of facial expression & breast tissues are located within ____ ____
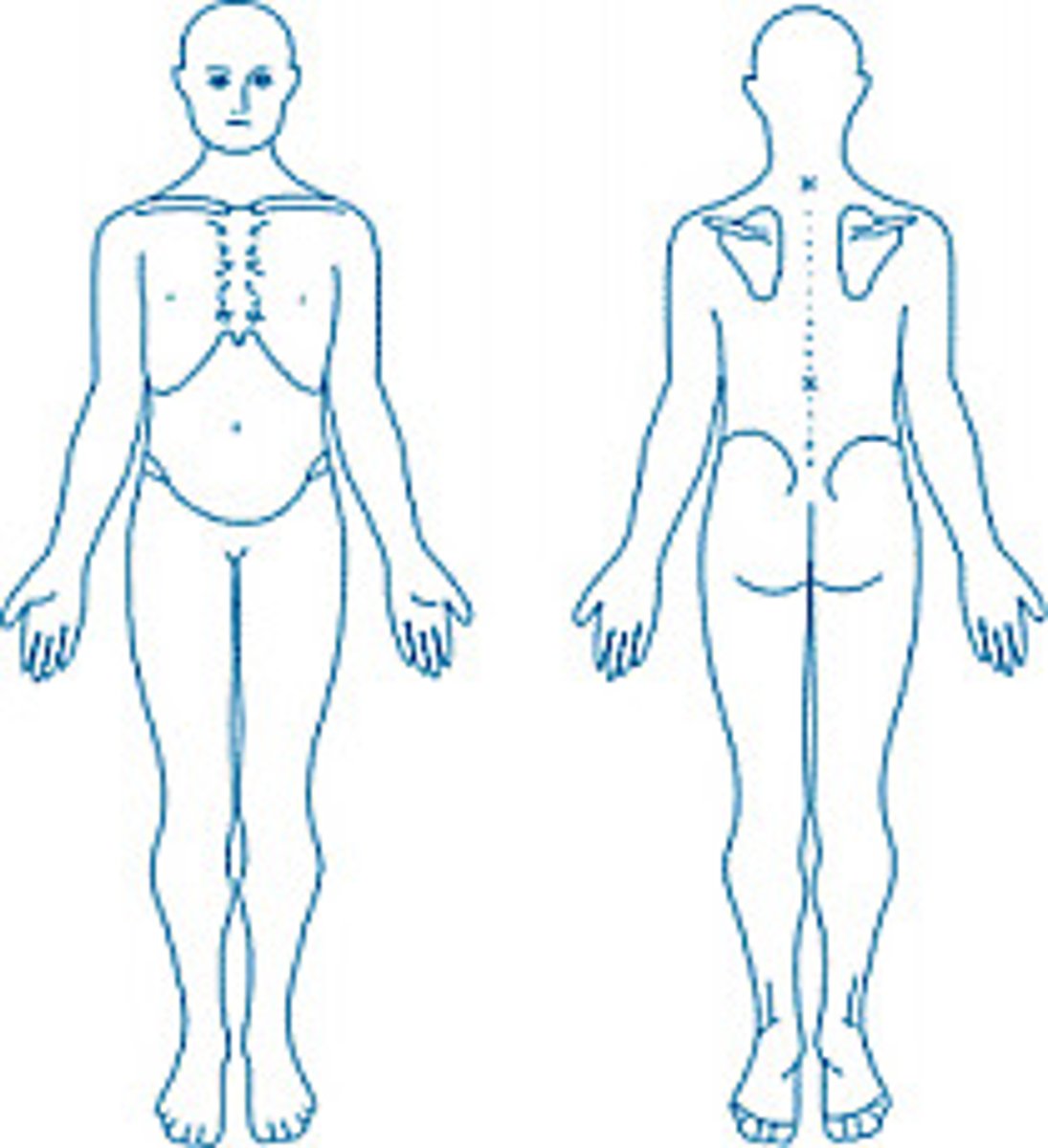
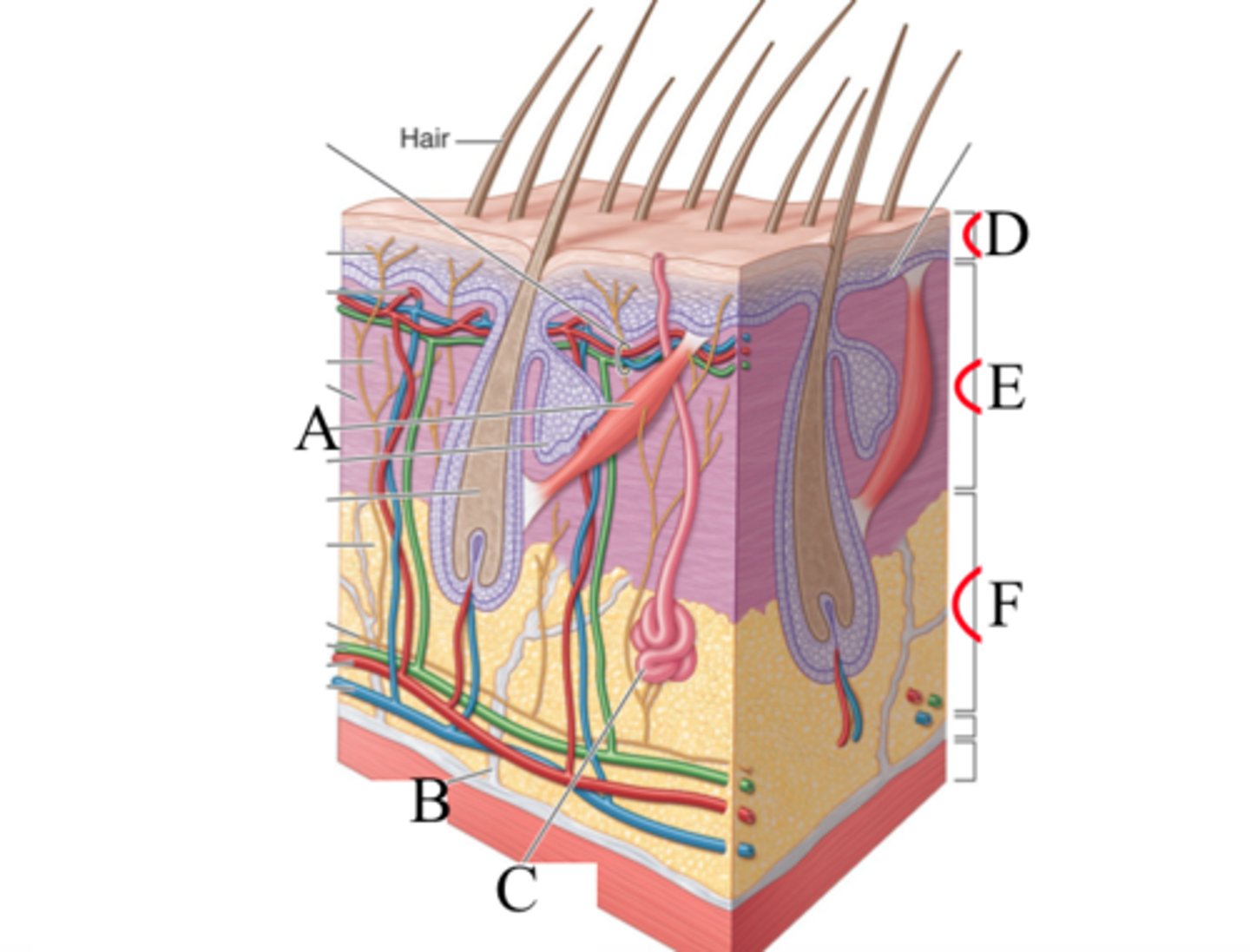
skin ligament
figure B in picture
small fibrous bands
through SQ tissue to dermis to deep fascia
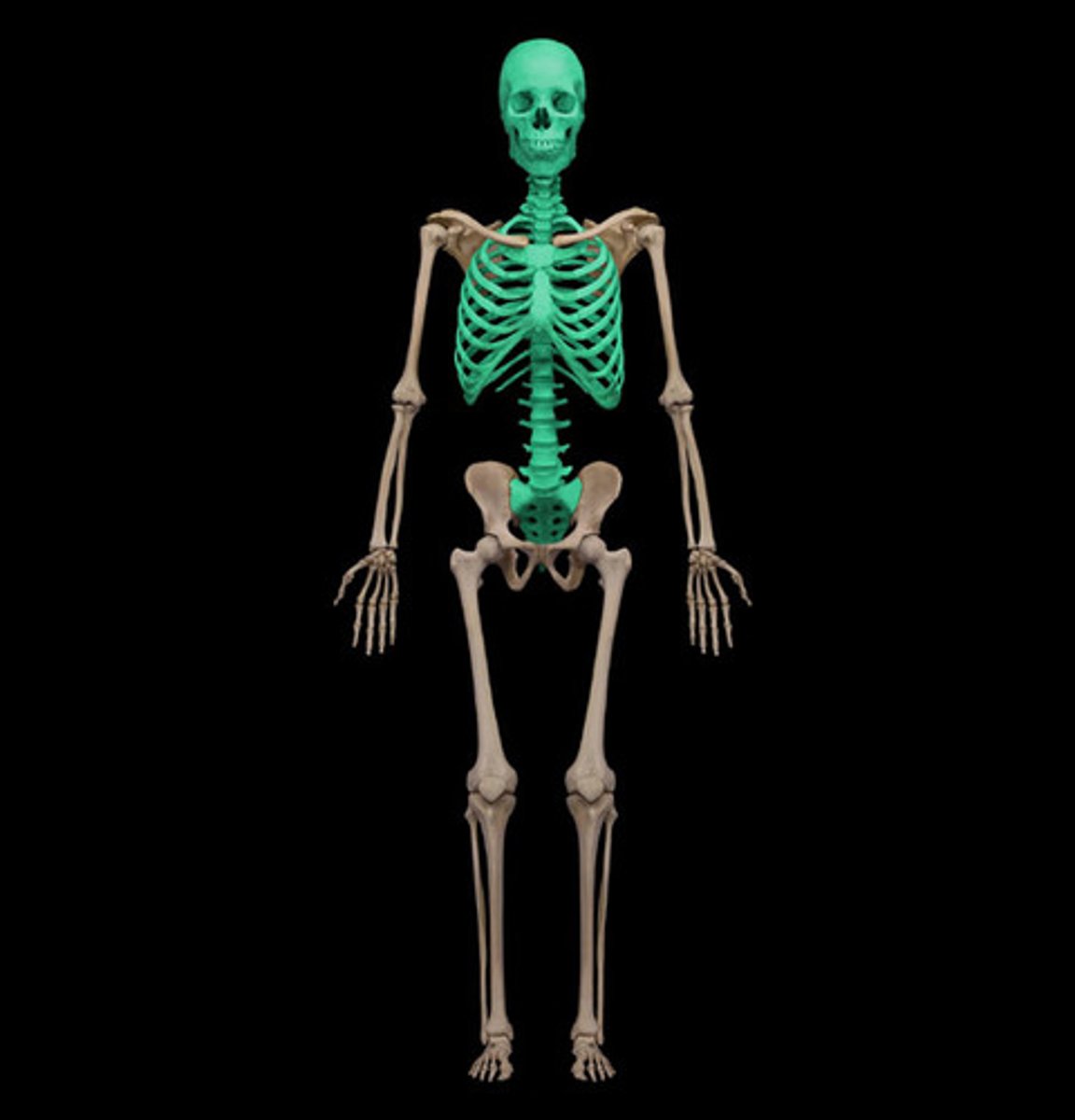
axial skeleton, cranium, vertebral column, sacrum, coccyx, ribs, sternum
identify
what bones comprise it
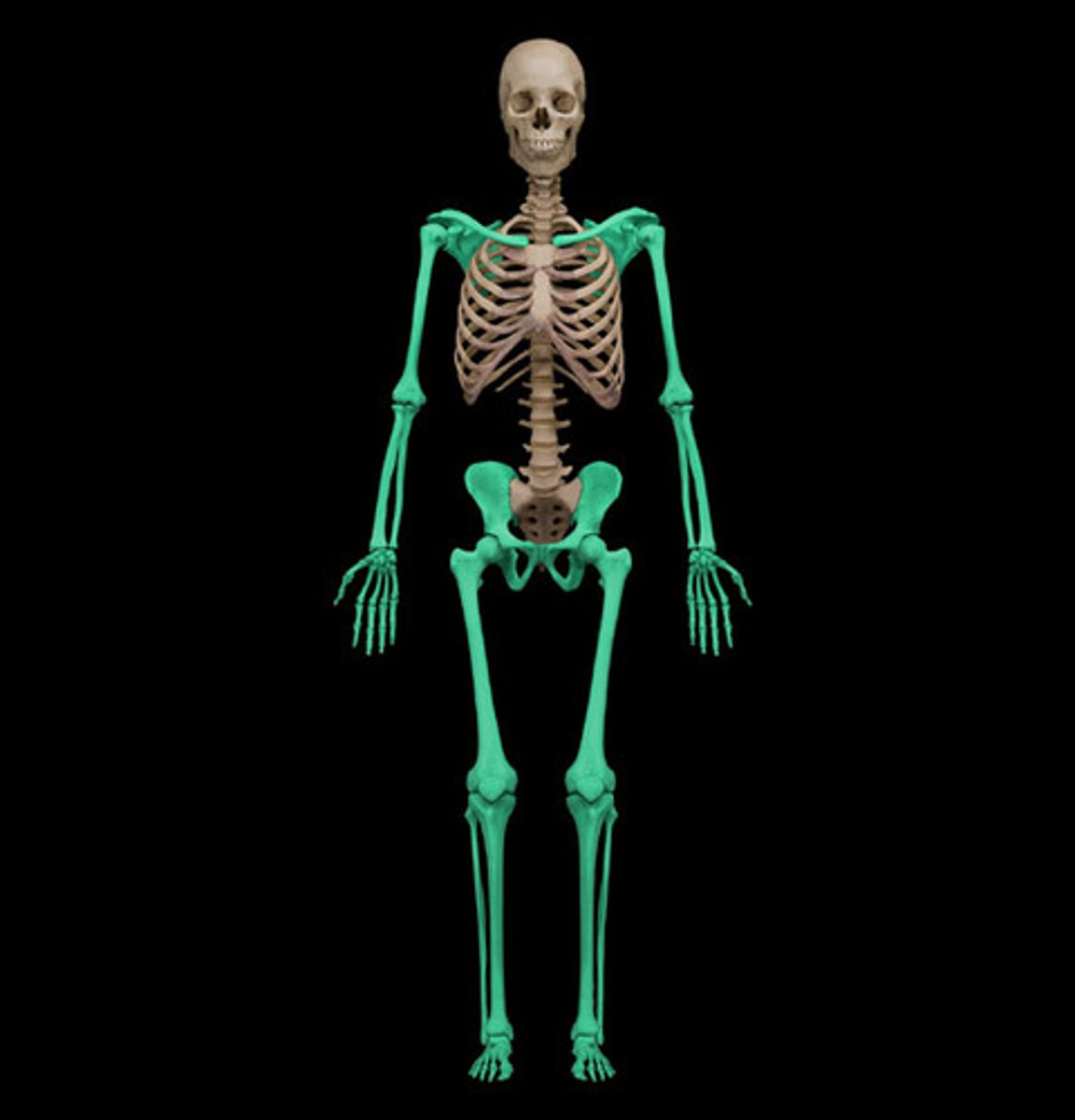
appendicular skeleton
identify
what bones comprise it
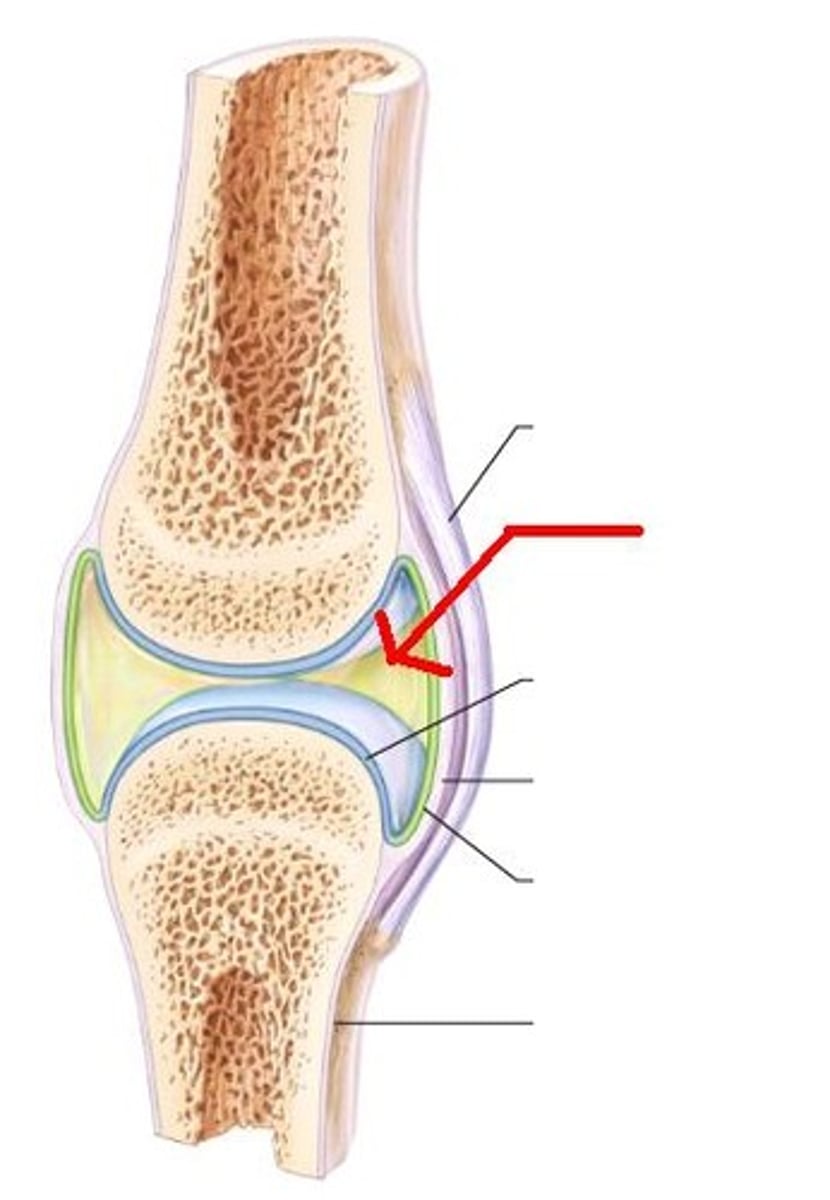
synovial joints
moveable
articular carilage on bone
fibrous joint capsule
synovial fluid for lubrication
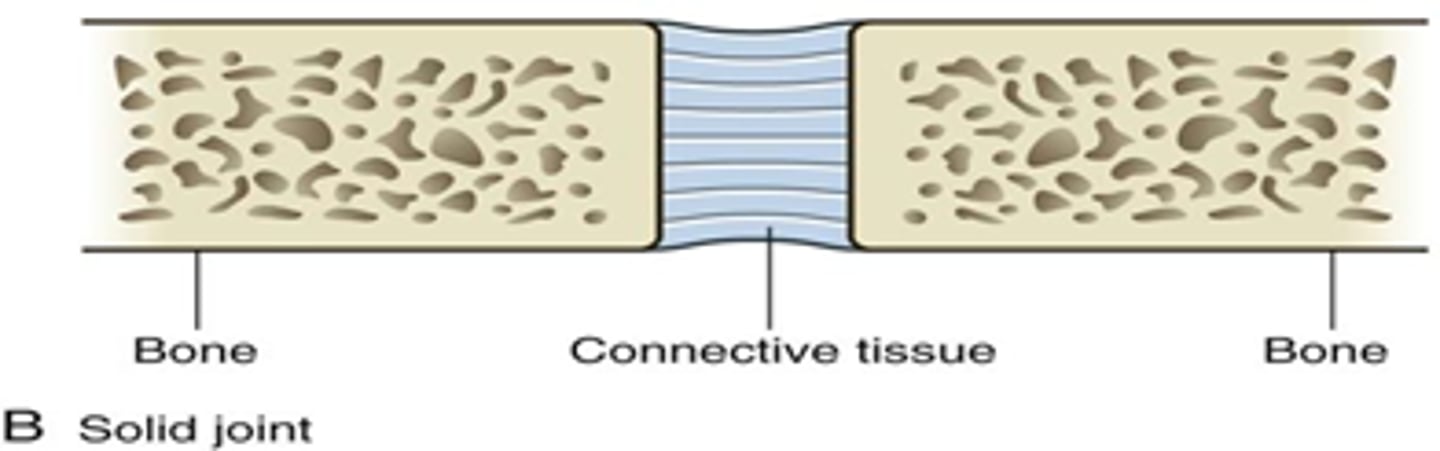
solid joints
limited mobility
fibrous
cartilaginous
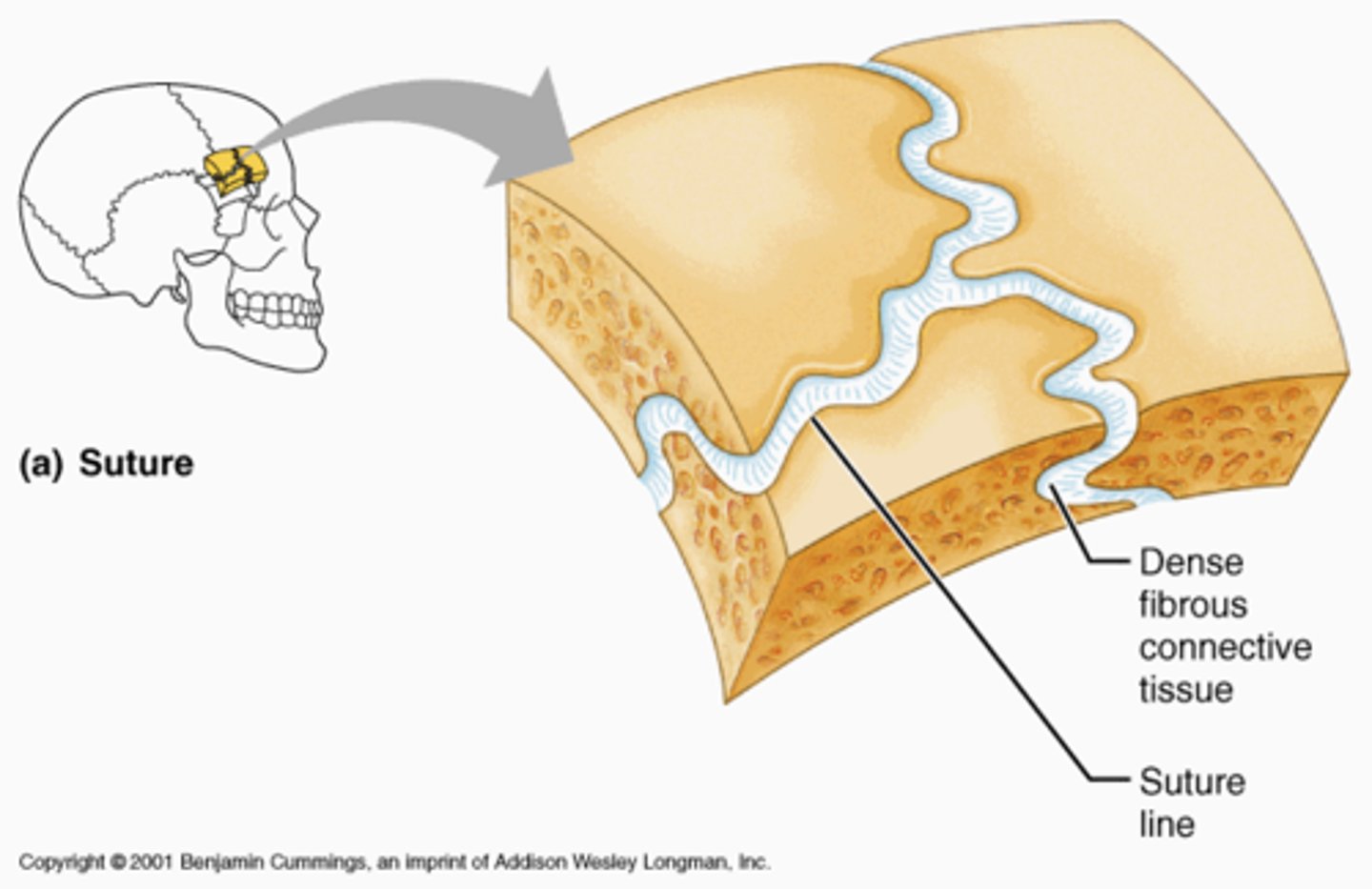
fibrous
Class of Joint
- united by collagen fibers
- types: suture, syndesmosis, gomphosis
^ immobile, slightly mobile, immobile
cartilaginous
class of joint
- bone ends united by cartilage
- types: synchondrosis, symphysis
^ immobile, slightly mobile
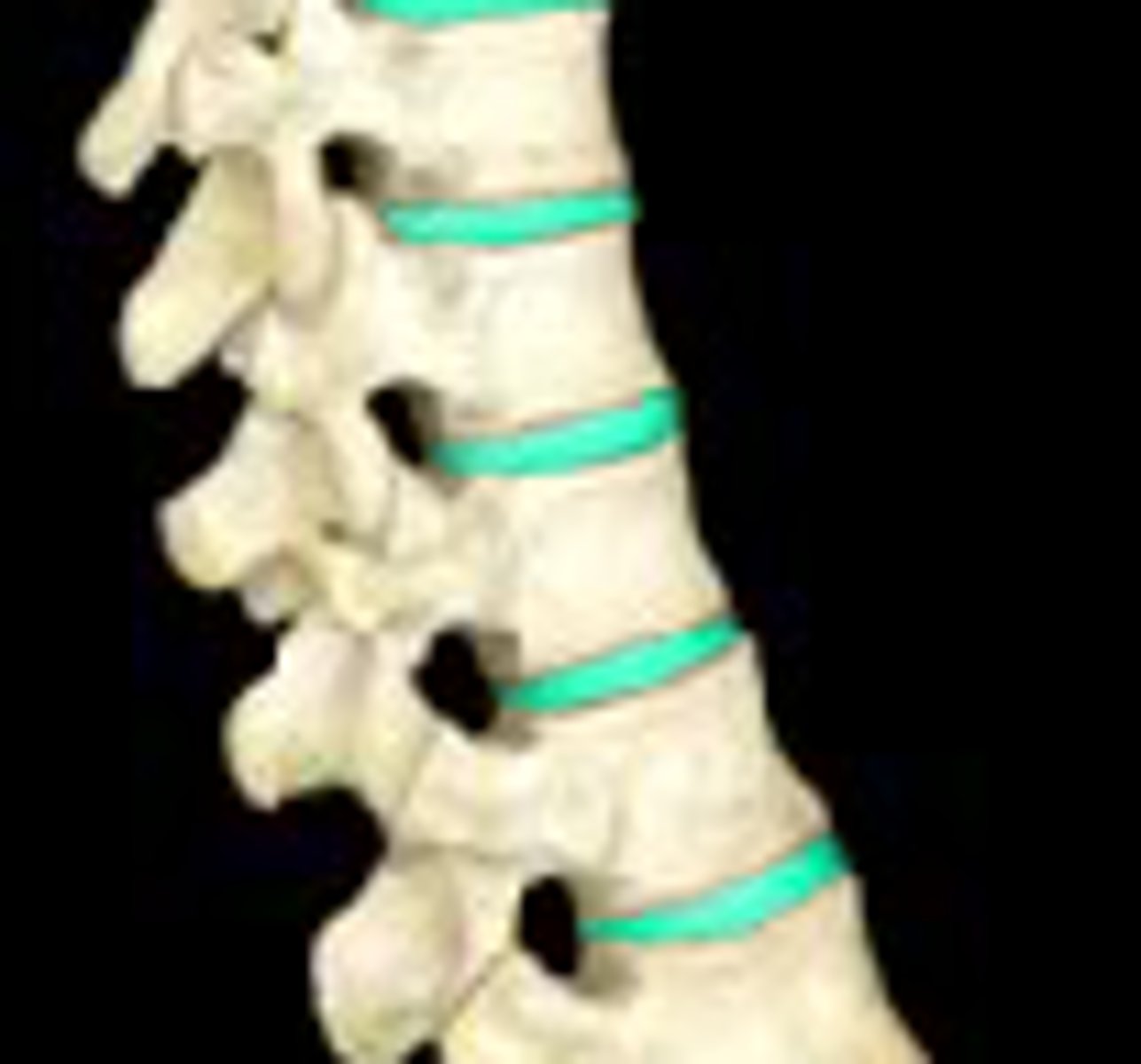
synovial
class of joint
- bone ends covered w/ articular cartilage
- enclosed in a capsule lined with ____ membrane
- types: plane, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, ball & socket
^ freely movable, depending on joint design

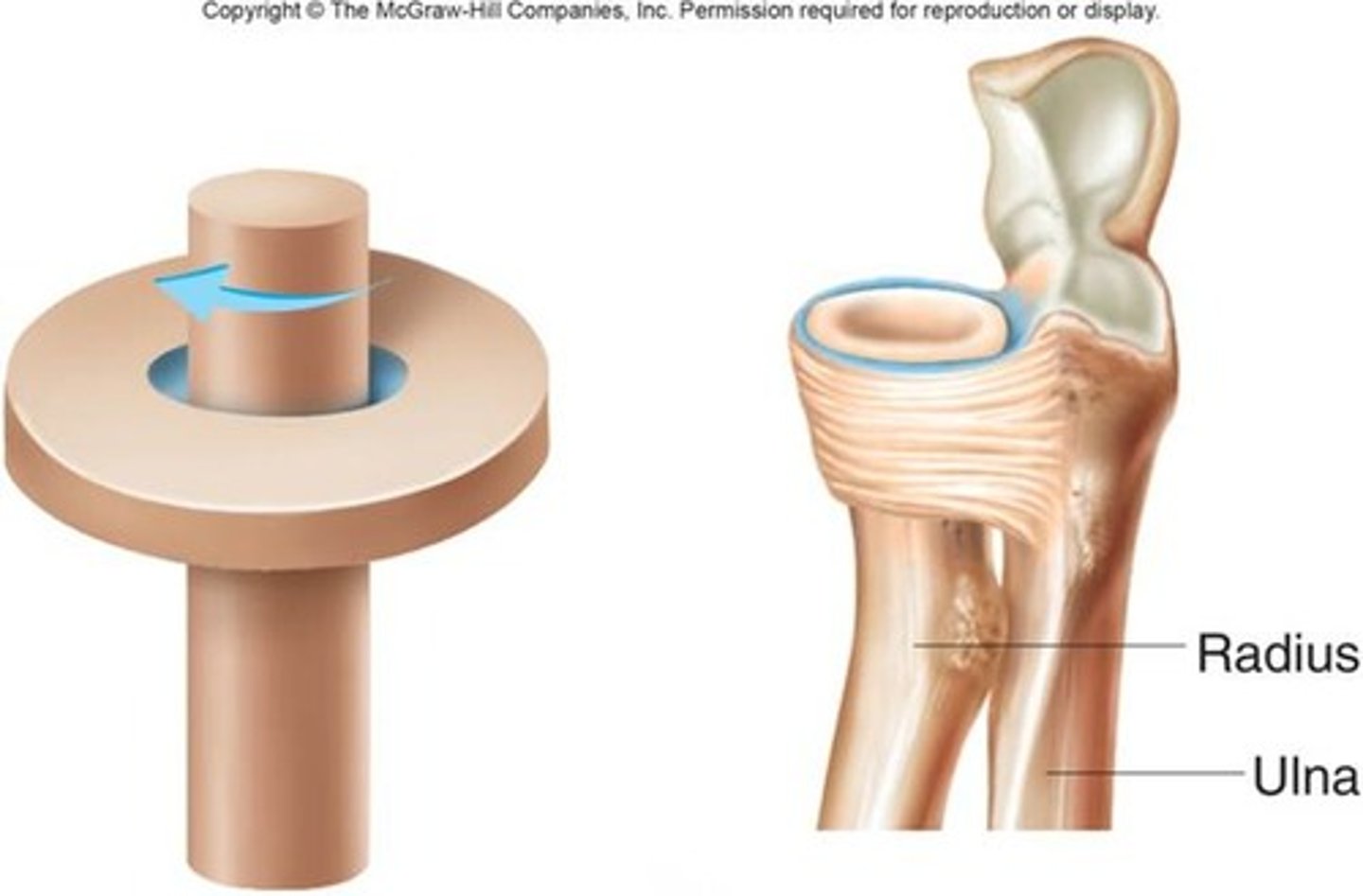
pivot joint
identify this synovial joint
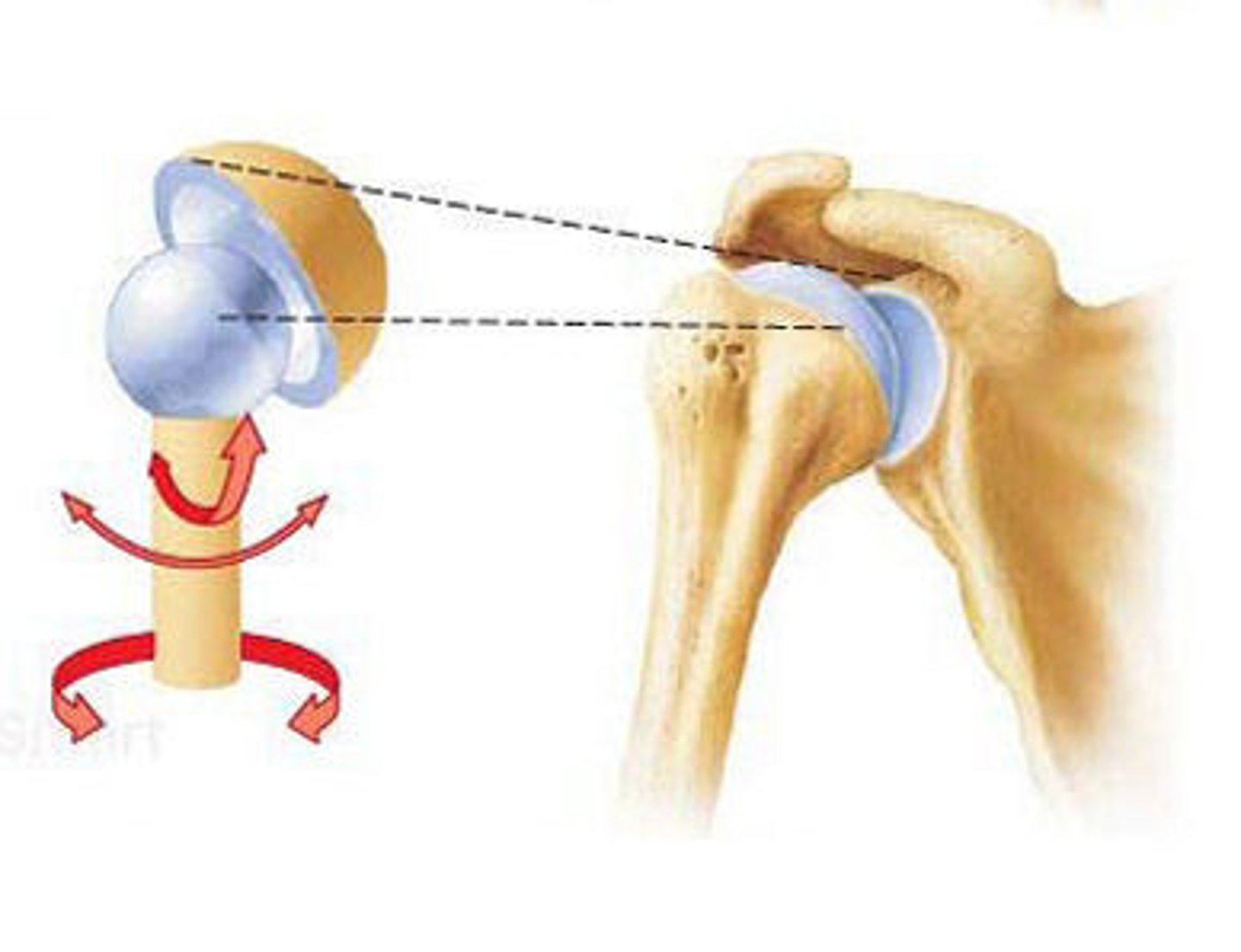
ball & socket
identify this synovial joint
condyloid joint
identify this synovial joint
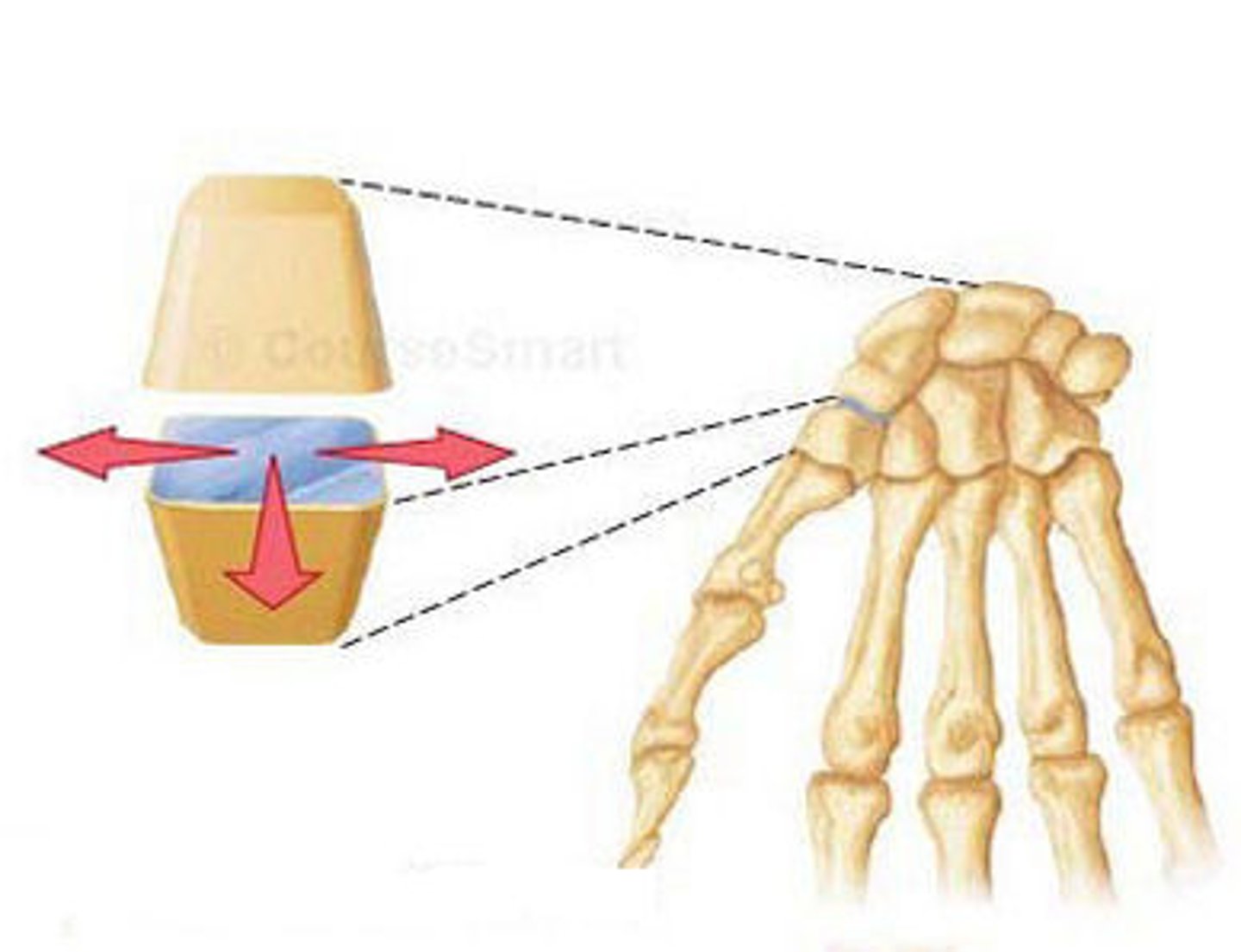
saddle joint
identify this synovial joint
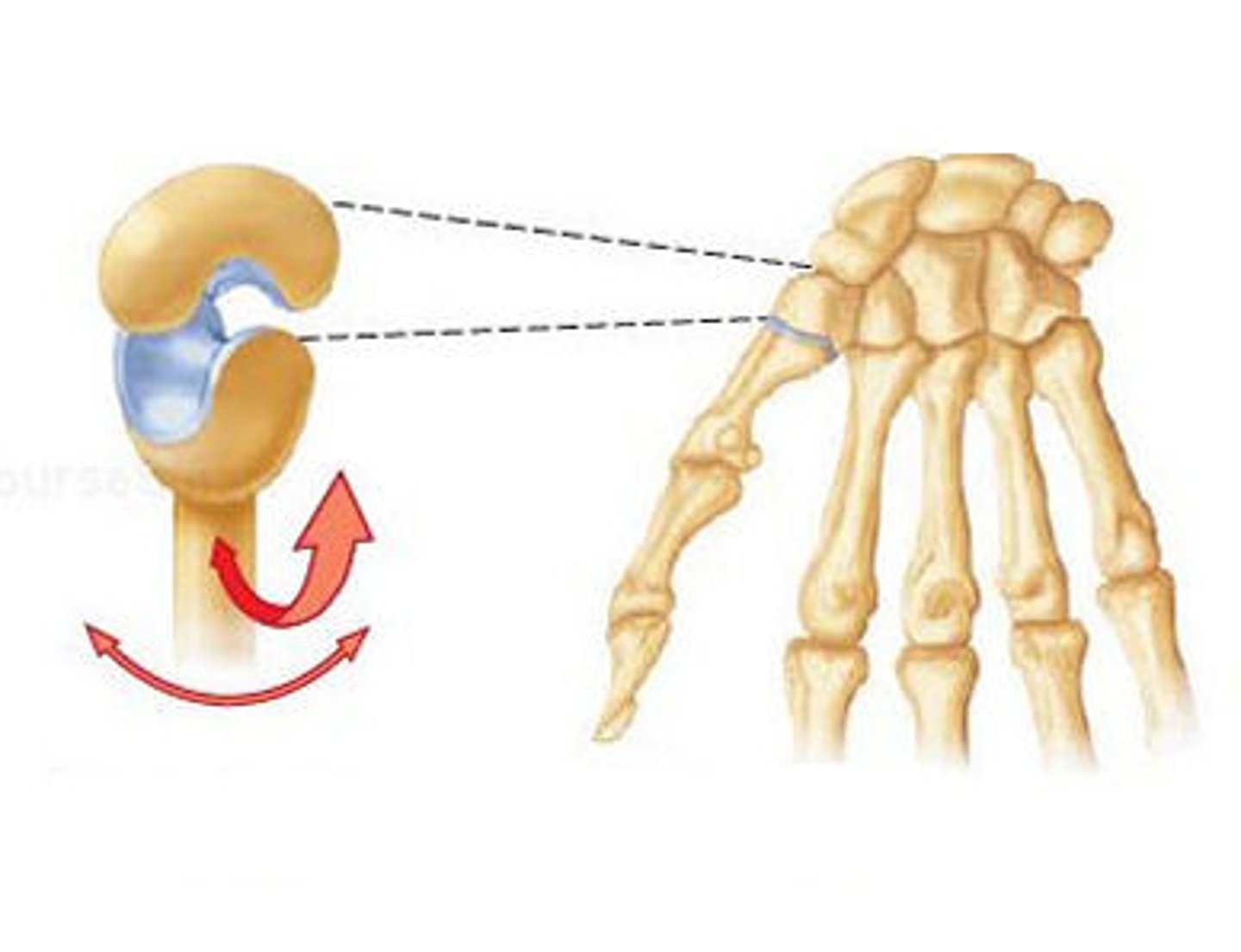
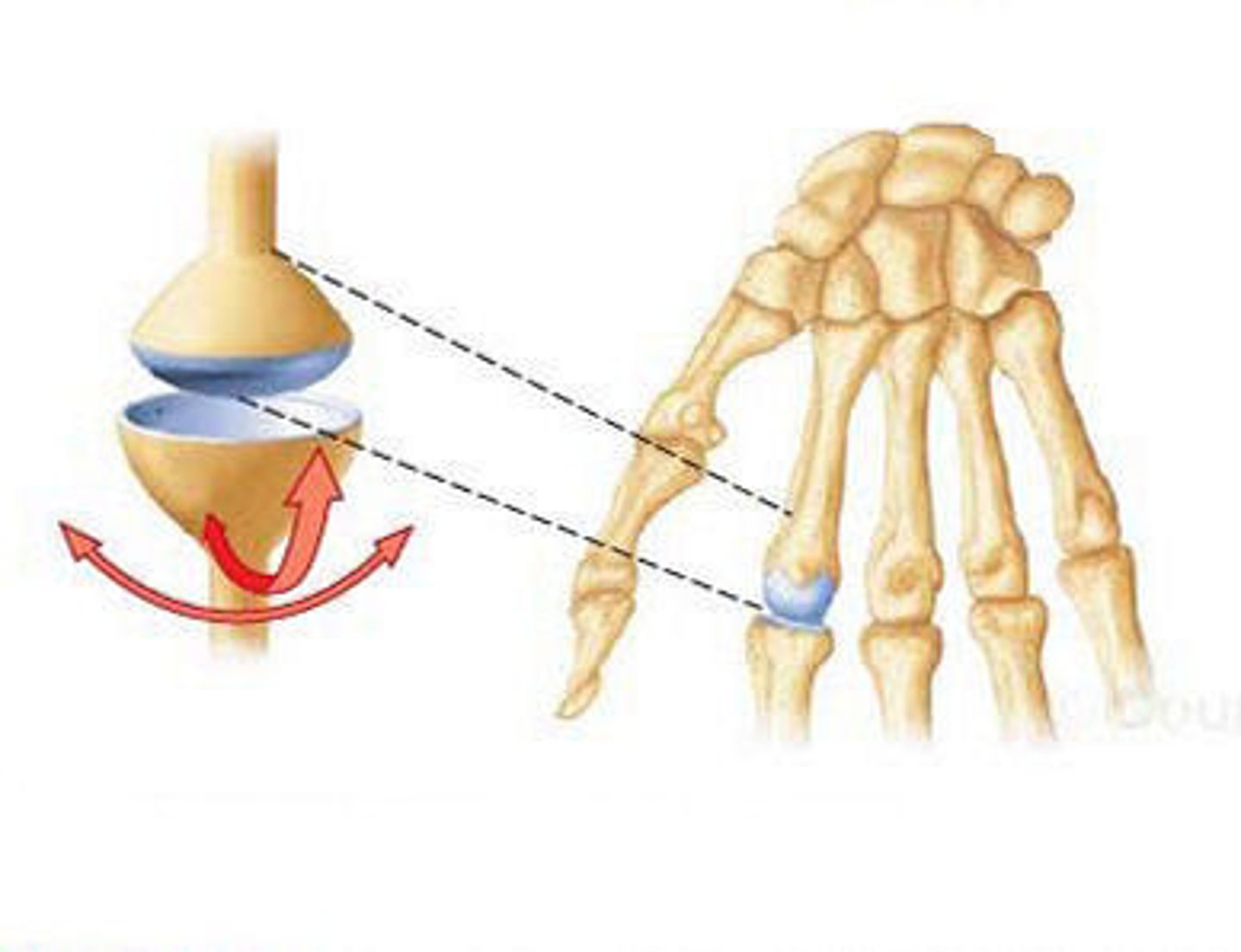
hinge joint
identify this synovial joint
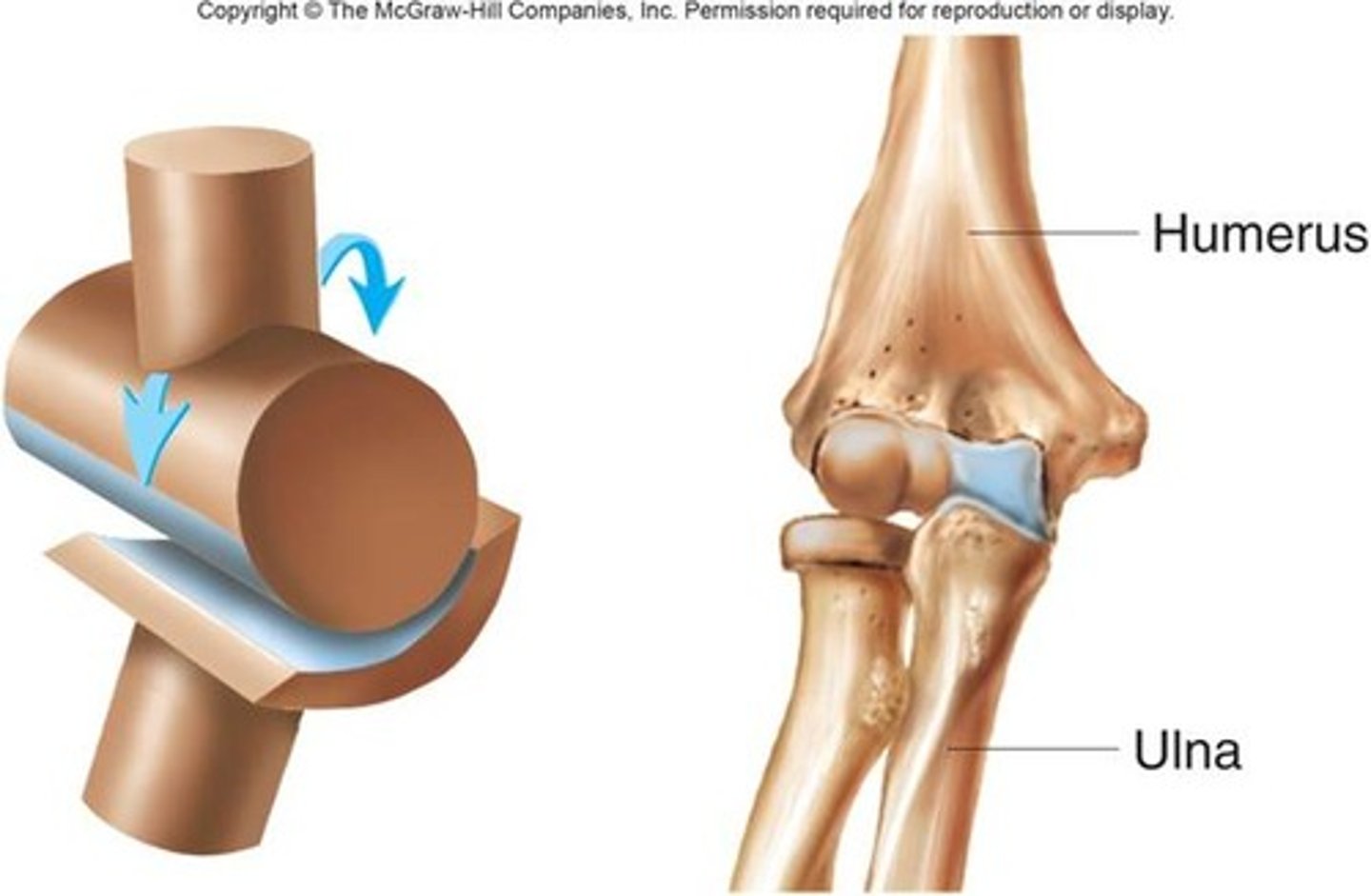
plane joint
identify this synovial joint
proximal attachment, distal attachment
____ : origin, often remains fixed
____: insertion, often moveable
true
T/F: some muscles can act in both directions, as both a proximal & distal attachment
posterior, anterior, sternum
the LA is ____ while the right side of the heart is ____
the RV is under the ___
blood enters the SVC to the RA, flows to the RV, passes through the PA to the lungs, from the lungs enter the pulmonary veins, flows to the LA then the LV, then flows through the AO to become systemic blood
describe the flow of blood through the heart
arteries, veins
____ are away from the heart while _____ are towards the heart
oxygenated, deoxygenated, deoxygenated, oxygenated
what blood resides in the brachail a.?
what blood resides in femoral vv.?
what blood is carried in pulmonary aa.?
what blood is carried in pulmonary vv.?
lymph
___ is plasm until in crosses from capillary to intersitium
it circulates in the lymphatic system
lymph capillaries
in interstitium, plasma is picked up by ___ ____
immune cells
lymph carries ___ ____
R upper trunk, R UE, R head & neck
the R lymphatic duct drains most of the R upper quadrant including...
while the L does the rest
R subclavian v., L subclavian v.
the R lymphatic duct enters into the ______ while the L subclavian duct enters into the _____