Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
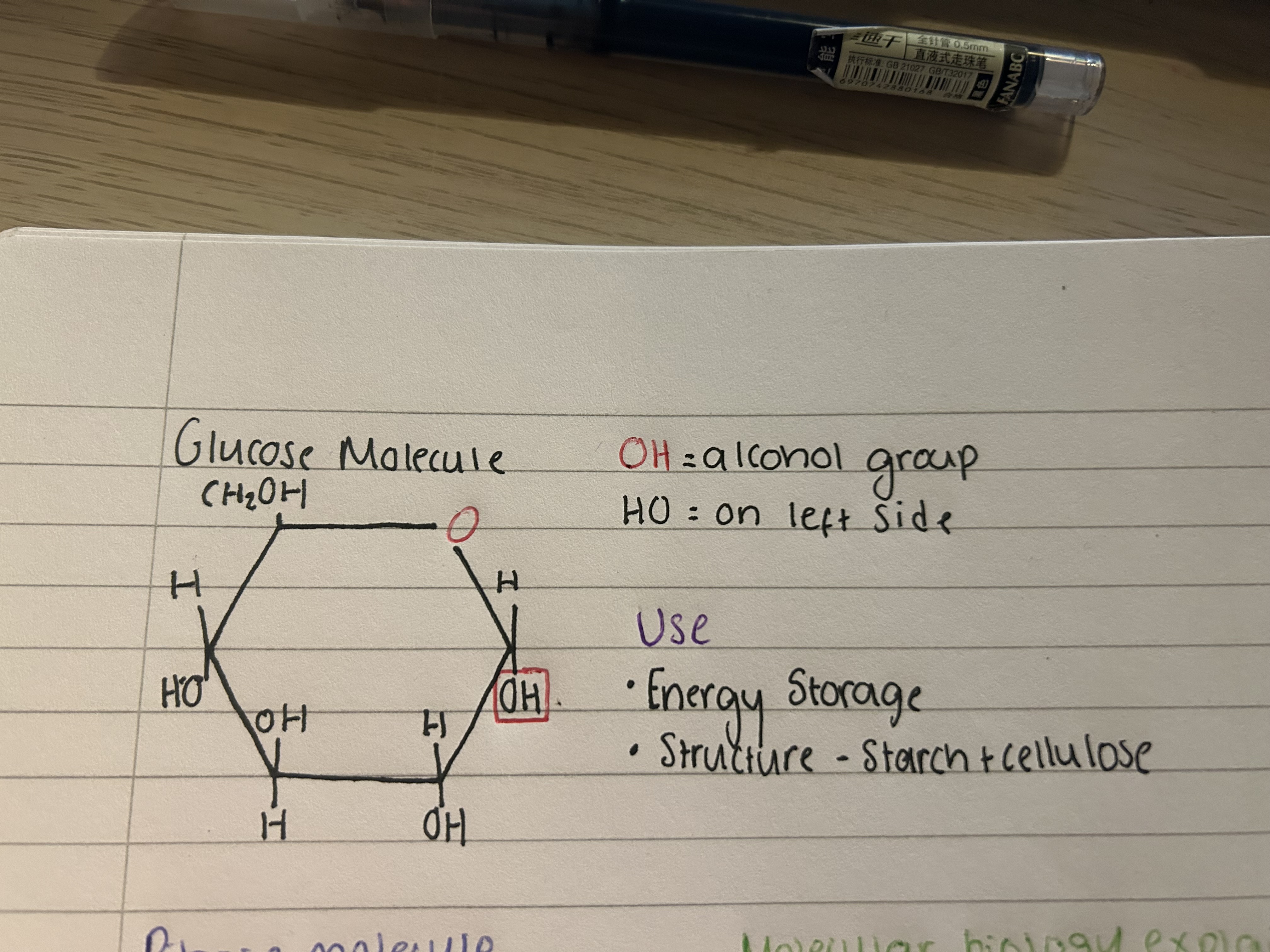
What does a glucose molecule look like? (+uses)
Uses
Energy storage
Structure- starch and cellulose
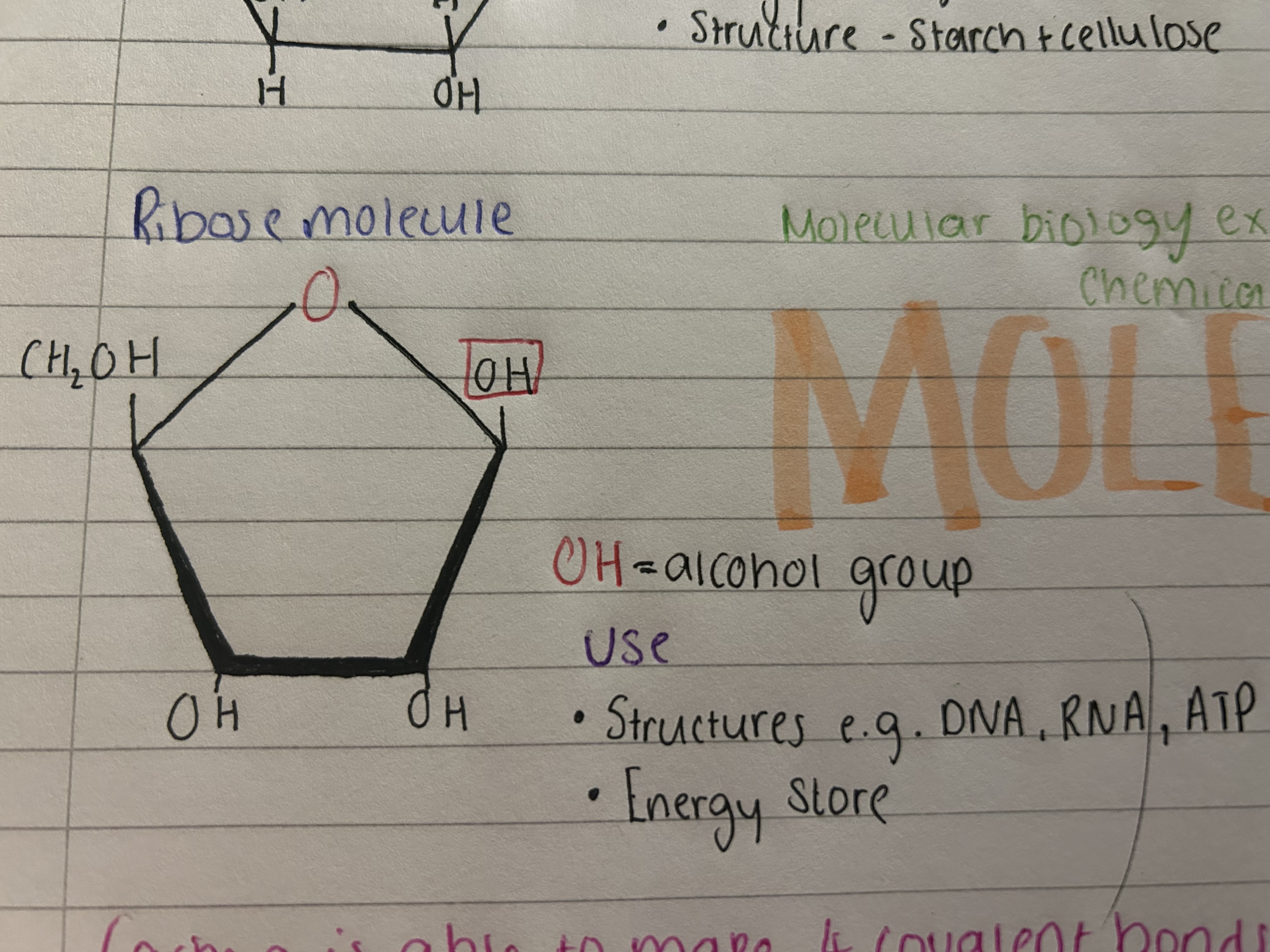
What does ribose look like? (+uses)
Uses
Structures- DNA, RNA, ATP
energy storage
How many covalent bonds can carbon make?
Four
What type of structures can carbon make?
Branched
Unbranched
Multiring
Ring
What is a monosaccharide?
A single carbon ring structure
E.g glucose, galactose, fructose
Function of monosaccharides
Monosaccharides serve as the primary energy source for cells and are the building blocks for more complex carbohydrates.
What is a disaccharide?
Two carbon ring structure
Eg. Maltose, lactose and sucrose
Function of disaccharide
Disaccharides serve as a source of energy and can be broken down into monosaccharides for easier absorption by the body.
what is a polysaccharide?
Many carbon rings bonded together structure
Eg.starch, glycogen and cellulose
Function of polysaccharide
Polysaccharides serve as long-term energy storage and provide structural support in plants and some animals.
Function + structure of cellulose
Cellulose is composed of long chains of β-glucose molecules linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds, forming tightly packed microfibrils that provide rigidity and strength to plant cell walls.
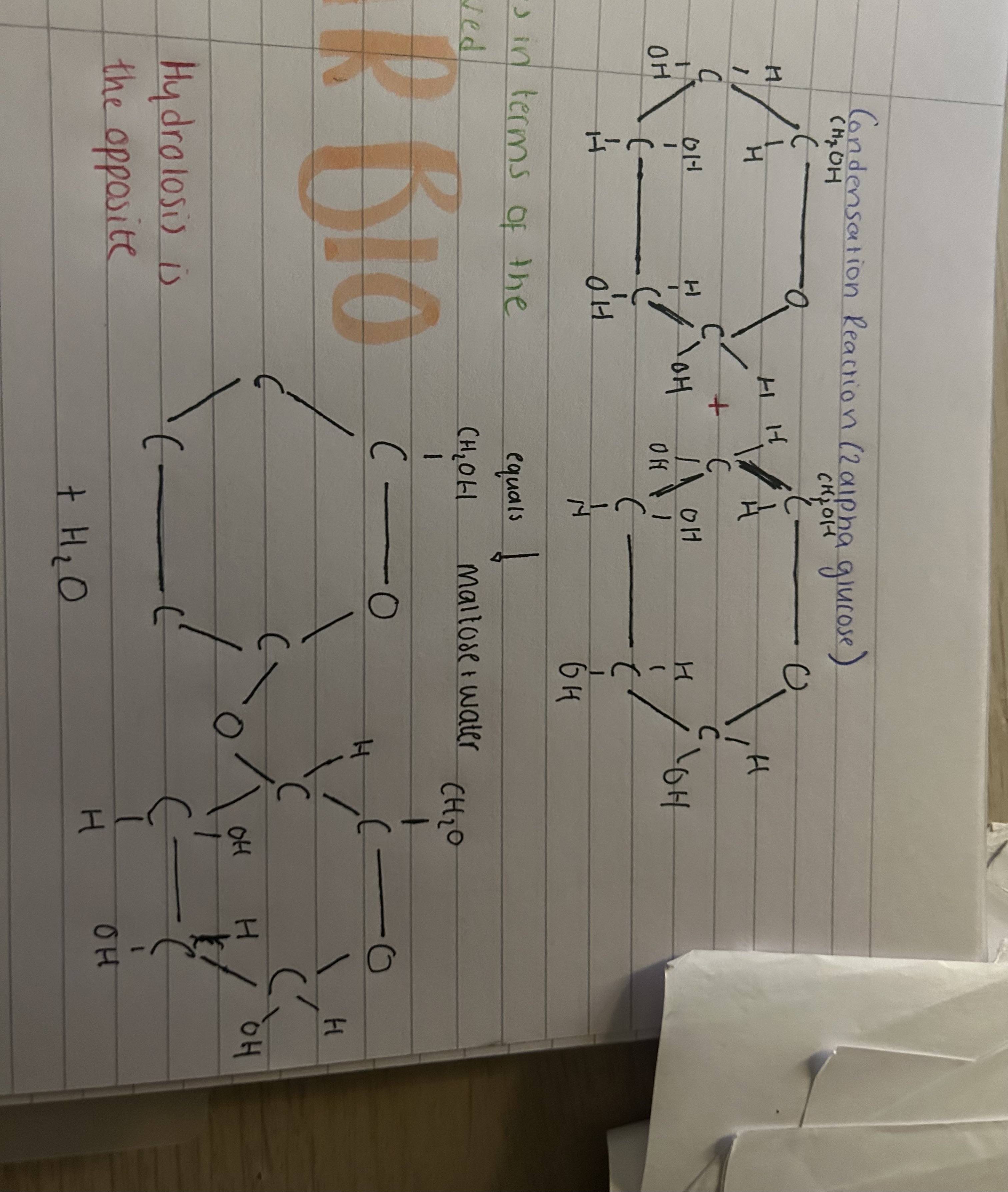
What does an condensation reaction (2 alpha glucose) look like + make?
Maltose + water
What is the role of glycoproteins in cell-cell recognition?
Glycoproteins act as markers on cell surfaces
allowing cells to identify and interact with each other,
which is crucial for immune responses and tissue formation.
ABO antigens are an example of glycoproteins that determine blood type.
What does a hydrolysis reaction make?
Opposite of condensation reaction
What is a condensation reaction?
A condensation reaction is a chemical reaction where two molecules combine to form a larger molecule, releasing a small molecule, often water, as a byproduct.
What is hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis is a chemical reaction where water is used to break down a compound, typically splitting it into smaller molecules.
What does a beta glucose look like?
On the right side OH at top and H on the bottom
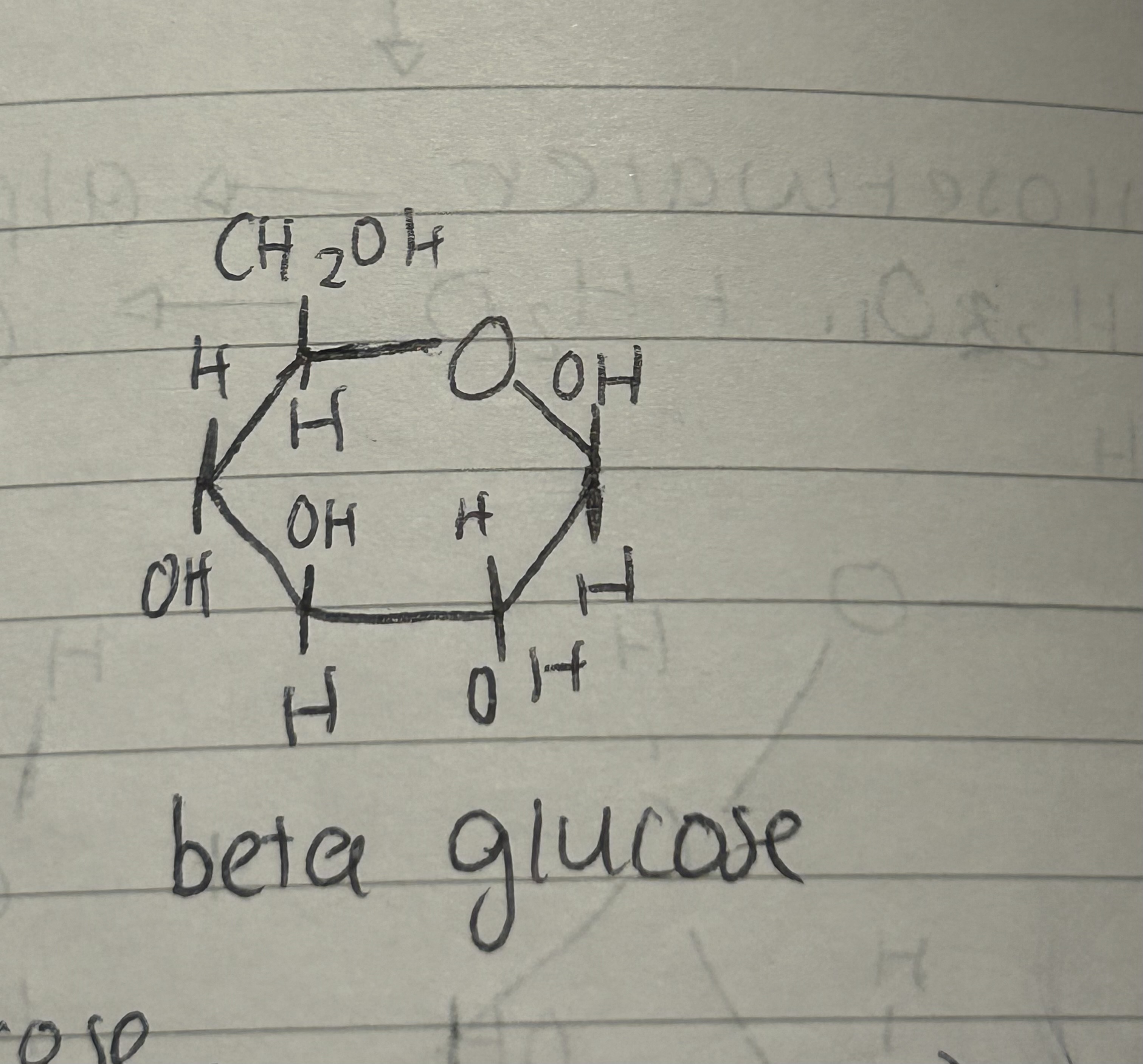
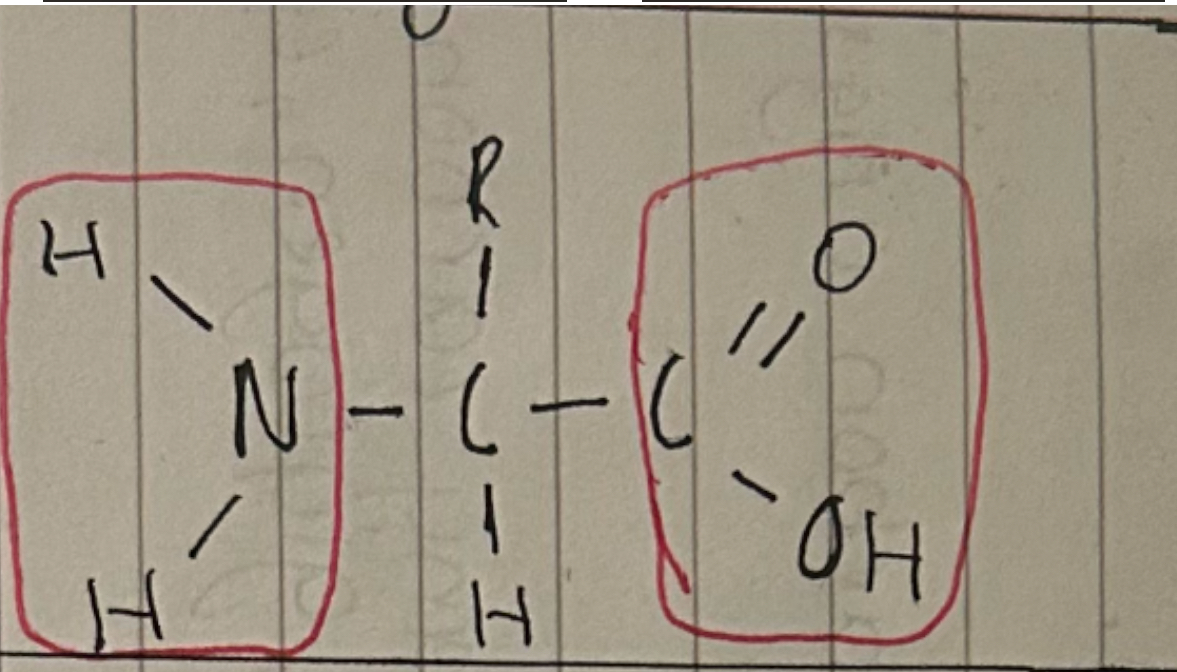
Amino acid + functional groups
Amine
Carboxyl
Saturated fatty acid + functional groups
Carboxyl
No double bond cause saturated with hydrogen

Unsaturated fatty acid + functional groups
Carboxyl
1 Double bond between two carbons
What is an organic molecule?
Molecule with carbon-hydrogen bond
What is an inorganic molecule?
No carbon-hydrogen bond
What can lipids be divided into?
Fats
Oils
Waxes
Steroids
Lipids contain many areas of __________.
hydrocarbons.
The C-H covalent bond is __________.
non-polar.
Lipid solubility in water
Do not dissolve well. Hydrophobic
Lipid solubility in non polar solvents
Dissolves
What is a polar substance?
A polar substance is a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one side and a partial negative charge on the other, resulting in an uneven distribution of electron density.
What is a non-polar substance?
A non-polar substance is a molecule that does not have distinct positive or negative regions, resulting in an even distribution of electron density.
What does a cis monounsaturated look like?
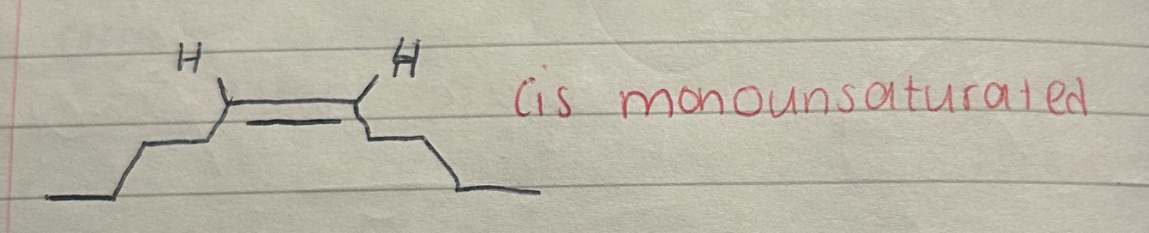
What is a cis monounsaturated fatty acid
a fatty acid with one double bond between carbon atoms
where the hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double bond are on the same side of the carbon chain
causing a bend in the molecule.
Transmonounsaturated
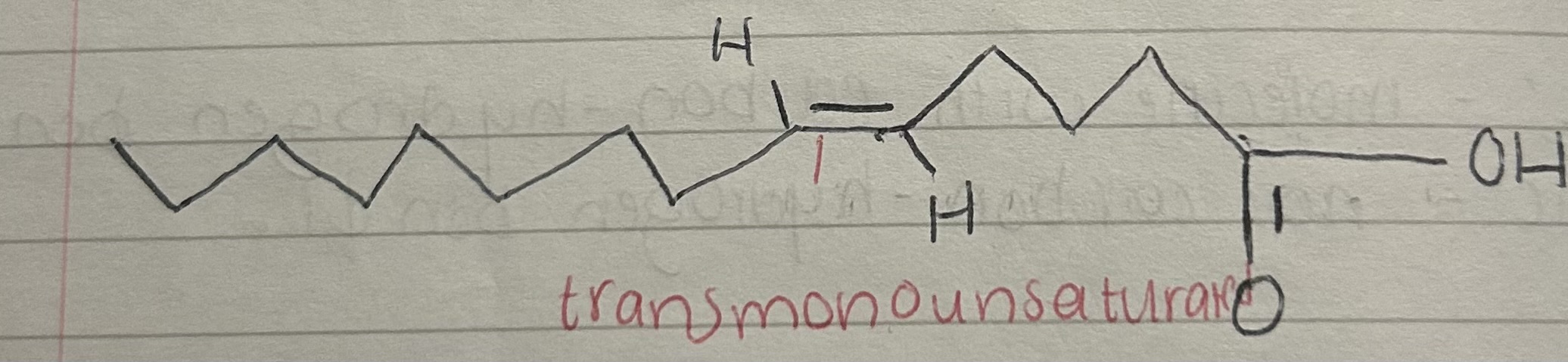
What is a trans monounsaturated fatty acid?
A fatty acid with one double bond between carbon atoms
where the hydrogen atoms adjacent to the double bond are on opposite sides of the carbon chain,
causing a straighter shape compared to cis fats.
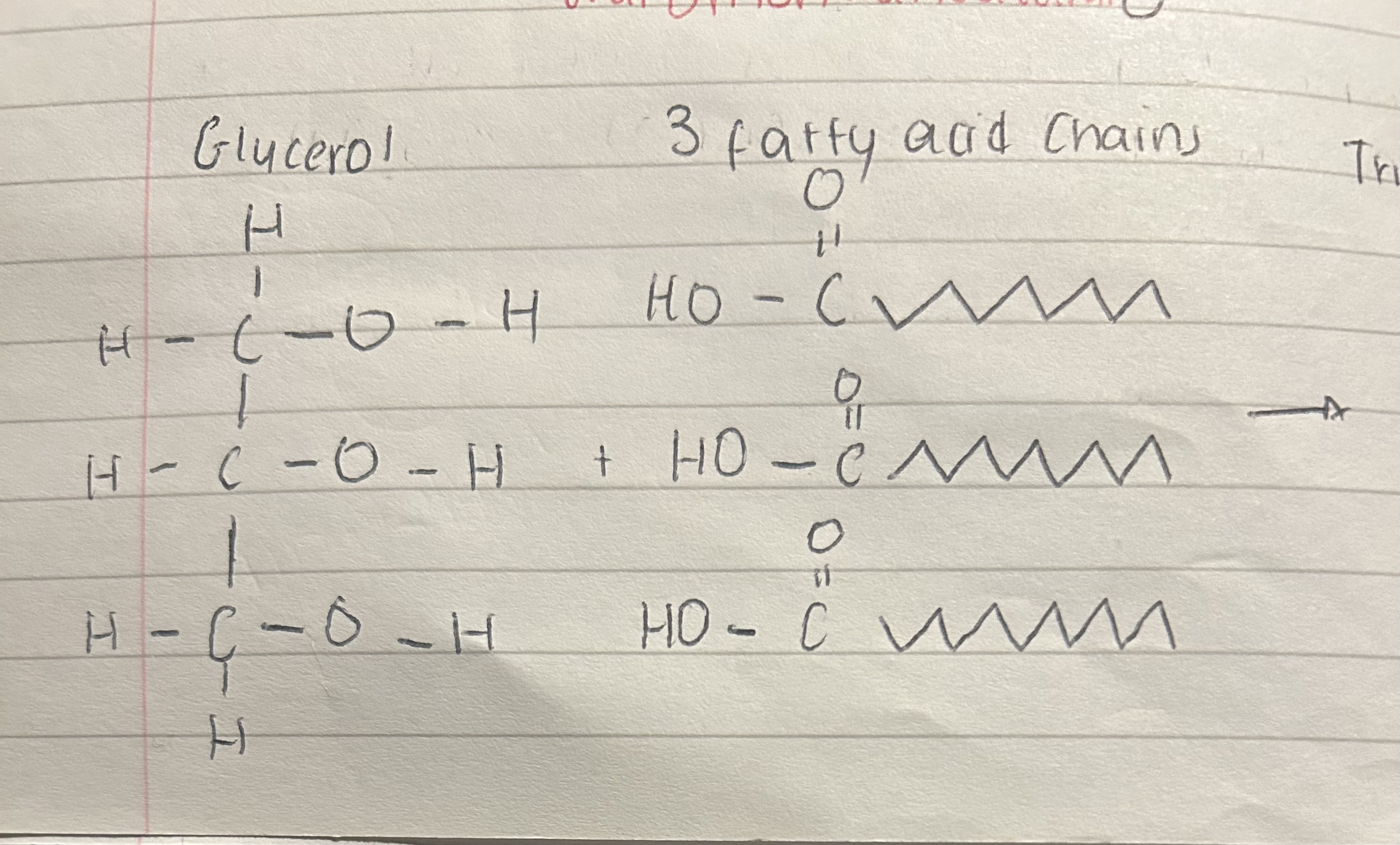
Glycerol + 3 fatty acid chains
Triglyceride/ natural fats
What is a polyunsaturated fatty acid?
a fatty acid that contains two or more double bonds in its carbon chain,
which affects its shape and properties,
commonly found in fish oils and plant oils.
Glycerol + two fatty acids + phosphate group
What does R mean when drawing lipid?
Something that can change
Unsaturated fats tend to be __________ at room temperature.
liquid
Saturated fats tend to be __________ at room temperature.
solid.
Why do unsaturated fats have their state at room temperature?
Because molecules can’t pack together closely, due to their bent shape.
Why do saturated fats have their state at room temperature?
Because the straight molecules can pack together pack together closely
What are ectotherms and endotherms?
Cold and warm blooded animals
Where do humans store triglyceride fats?
Adipose tissue to insulate us so we don’t lose thermal energy
Properties of triglycerides that suit them for long term storage
Triglycerides are hydrophobic,
allowing for compact storage without attracting water.
energy-dense, providing more energy per gram compared to carbohydrates.
Their structure enables slow digestion and release,
making them efficient for sustained energy.
Movement of steroid hormones
Enter cell/ can pass through cell membrane
Then bind to receptor in cytoplasm
Receptor- hormone complex interacts directly with genes / regulates gene expression.
Relation of triglyceride use to body temperature and habitat
Triglycerides provide insulation in adipose tissue, helping to maintain body temperature, especially in cold habitats. They also store energy efficiently, which is vital for survival in variable environmental conditions.
Comparison of lipids and carbs
Lipids = long term energy store, insoluble in h2o, takes longer to digest, hard to transport, has no effect on osmosis, more energy per gram
Carbs= Short term energy store, soluble in h2o, quick digested, easy to move, effects osmosis, less energy per gram.
Ability of non polar steroids do pass through the phospholipid bilayer
Can diffuse through
Eg. Oestradiol and testosterone
All steroids are arranged in … + bonded to … hydrogen atoms
4 rings (hexagonal)
28