Physics A-Level AQA particles practise exam Q's
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is the number of neutrons in a polonium-210 nucleus?
84, 126, 210, or 294 The number of neutrons in a polonium-210 nucleus is 126, calculated by subtracting the atomic number (84) from the mass number (210).
Why do bismuth-210 and polonium-210 have different proton numbers?
Bismuth-210 undergoes beta-minus decay, emitting a beta particle and increasing the proton number, changing into polonium-210.
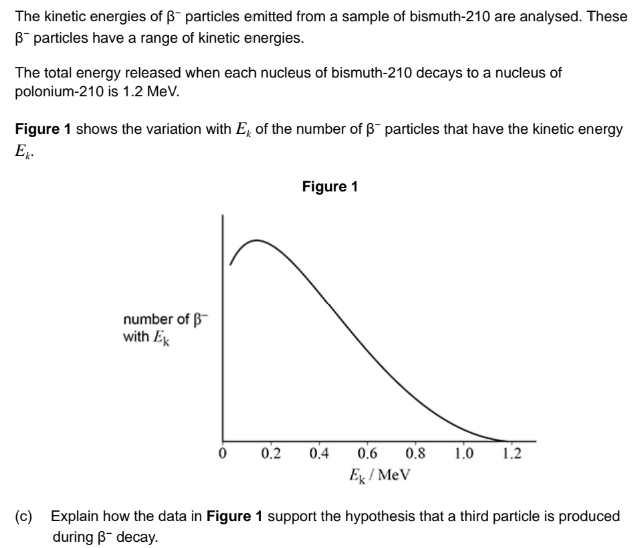
Explain how the data supports the hypothesis that a third particle is produced during β− decay.
The kinetic energy distribution of β− particles shows a range indicating the presence of an undetected particle, likely the electron antineutrino.
Why is an electron antineutrino produced during β− decay instead of an electron neutrino?
An electron antineutrino is emitted to conserve lepton number during the decay when a neutron converts into a proton.
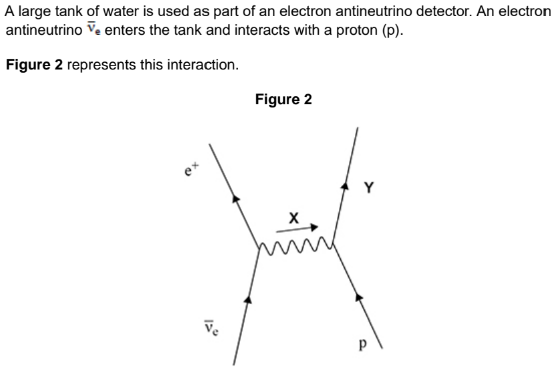
Identify X and Y in the interaction of an electron antineutrino with a proton.
X represents a neutron and Y represents a positron.
The positron produced in the interaction in Figure 2 slows down and collides with a lepton in a molecule of water.
Describe the process that occurs when the positron collides with this lepton. In your answer you should identify the lepton in the molecule of water.
When the positron collides with an electron (the lepton in the molecule of water), they annihilate each other, producing two gamma-ray photons. This process conserves energy and momentum, resulting in the emission of high-energy electromagnetic radiation.

Which particle is likely to travel a shorter distance in water before interacting: positron or electron antineutrino?
The positron is likely to travel a shorter distance due to its strong interaction range compared to the weak interaction range of the electron antineutrino.
What is the specific charge of an ion formed from oxygen-15 after gaining two electrons?
The specific charge options are: A −1.3 × 107 C kg−1, B −2.4 × 107 C kg−1, C −5.1 × 107 C kg−1, D −6.4 × 107 C kg−1.
The specific charge of the ion formed from oxygen-15 after gaining two electrons is A −1.3 × 107 C kg−1.
Which particle is an exchange particle for the weak interaction?
The exchange particle for the weak interaction is W+.
What are the possible decay products for a baryon structured as dss?
Decay products can include n + π− or Λ0 + π-.
What is the maximum wavelength of photons produced when a muon and an antimuon annihilate?
5.9 × 10−15 m
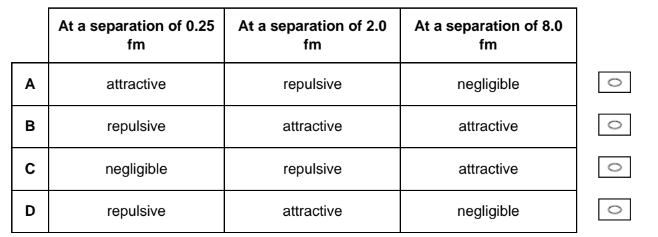
Describe the nature of strong and weak nuclear forces between two nucleons at varying separations.
At 0.25 fm the force is repulsive, at 2.0 fm it is attractive, at 8.0 fm it is negligible.
What are the products when a free neutron decays?
A free neutron decays into: p + e− + ve.
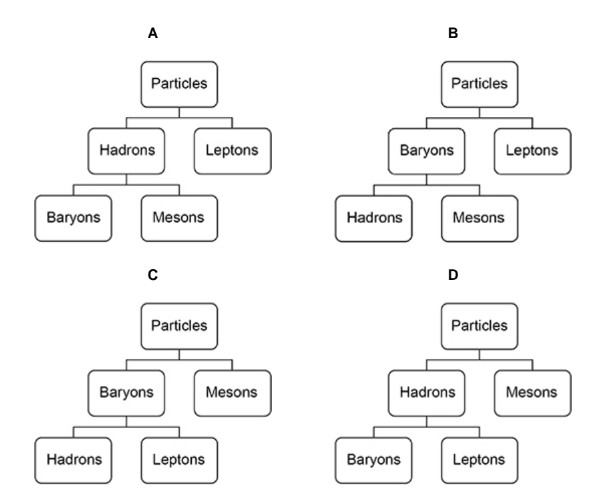
Which shows the classification of particles?
B
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles that come from space. Most of these particles are protons.
There are other particles in cosmic rays, including atomic nuclei.
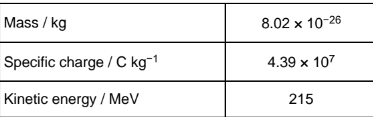
The table gives the data for one particular nucleus X.
Determine the number of neutrons in nucleus X.
26 neutrons
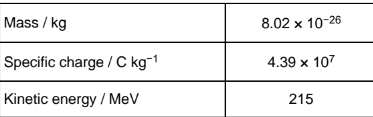
Calculate the speed of X.
Ignore realistic effects.
2.9 × 107 m/s-1.
A pion (π+) and a kaon (K+) are produced when cosmic rays interact with the upper atmosphere.
The π+ decays to produce a positron and an electron neutrino
Show how the conservation laws apply to this decay.
In this decay, both charge and lepton number are conserved. The initial charge of the pion is +1, and the final products (positron with charge +1 and neutrino with charge 0) also sum to +1, maintaining charge conservation. Additionally, the lepton number is conserved as the positron contributes +1 and the neutrino contributes +1, while the pion has a lepton number of 0.
The K+ decays to produce an anti-muon and a muon neutrino.
Explain how strangeness applies in this decay.
In this decay, strangeness is conserved. The K+ meson has a strangeness of +1, while the anti-muon has a strangeness of 0 and the muon neutrino also has a strangeness of 0, resulting in a total strangeness of +1, which matches the initial strangeness of the K+.
Write an equation for a K+ decay that involves only hadrons
K+ → π+ + π0
What interactions does a muon experience?
A muon is subject to the weak interaction.
What is the lepton number, strangeness, and charge of particle X in the reaction p + p → p + π+ + π− + X?
Lepton number: 0, strangeness: 0, charge: +1.
State the specific charge of the fluoride ion produced by the addition of an electron to fluorine.
The specific charge options are: A 3.2 × 10−26 C kg−1, B 8.4 × 10−21 C kg−1, C 5.0 × 106 C kg−1, D 4.5 × 107 C kg−1.
What is the quark structure of the positive kaon (K+)?
The quark structure of K+ is us̄.
How is lepton number conserved in the decay K+ → μ + + vμ?
The sum of lepton numbers on both sides remains equal in this decay.
What happens to excess energy when photon energy exceeds minimum threshold for electron-positron creation?
Excess energy is converted into kinetic energy of the produced particles.
What is the frequency associated with a photon energy of 1.0 MeV?
Calculate the frequency using the energy equation E=hf, with energy E = 1.0 MeV.
What is the potential decay of a neutral pion π0?
The decay π0 → e− + μ+ + e is not possible due to conservation laws.
Determine the quark structures of a π0 configuration.
The quark configurations of a π0 are: u u̅ or d d̅.
What is the quark composition of X in π+ + n → ∑0 + X?
X has a quark composition of us̅.
Identify the interaction type in a decay represented by a W− particle.
The interaction type is a weak interaction.
How are charge and baryon number conserved when a W− particle decays?
The sum of charges and baryon numbers of initial and final states must remain equal in the decay.