DDS MODULE 6
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Tablets
Cheapest type
prepared with the aid of suitable pharmaceutical excipients
vary in size, shape, weight, hardness, thickness, disintegration and dissolution
most widely used dosage form
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF A TABLET
strong and hard to withstand mechanical shock during manufacturing, packing. shipping, dispensing and use.
must be bioavailable, must be able to release its content in a predictable and reproducible manner
must be chemicallt and physically stable, during manufacturing, storage, and use
Should have an elegant product identity, free form any tablet defect.
must be uniform in weight and in drug content
Advantages (PLESMT)
Precision and low content variability
Low manufacturing cost
Ease of packaging and shipping
Simple to identify
Most-stable of all dosage forms
Tamper proof
Disadvantages
Resis compressions, requires encapsulation prior to compression
TABLETS FOR ORAL INGESTION
by mouth
COMPRESSED TABLETS
provide rapid disintegration in the gastric fluid following ingestion hence, allowing rapid release of the drug and, ultimately, systemic absorption of the dosage form.
pumcher & dier
Diluents or fillers
necessary bulk to a formulation to prepare tablets of the desired size
Binders or adhesives
promote adhesion of the particles, allowing granulation
Disintegrants or disintegrating agents
promote breakup of the tablets after administration to smaller particles
Antiadherents, glidants, lubricants, or lubricating agents
flow of the material, produce tablets with a sheen.
Miscellaneous adjuncts
colorants and flavorants.
MULTIPLE COMPRESSED TABLETS
more than a single compression, multiple-layer tablet, the inner tablet being the core and the outer portion being the shell. TRI-LAYER / PI-LAYER
Layered tablet
initial compaction of a position of ill material in a die followed by additional fill material & compression, two-layered or three layered tablets, EX: Neozep
Physical or chemical incompatibility
Staged drug release
Simply for the unique appearance of the layered tablet
Compression coated tablets
completely surrounded by the coat, coats prevent drug release, from the core, like sugar-coated or film-coated tablets in, may cover a bitter substance
SUGAR COATED TABLETS
coated with concentrated sugar, improve patient’s compliance, mask objectionable tastes or odours, Ex: Poten-cee
Disadvantages:
Expertise is required in the coating process .
Increase in size, weight and shipping costs
FILM-COATED TABLETS
coated with a thin layer of a polymer capable of forming a skin-like film. The coating is designed to rupture, durable, less bulky and less time consuming to apply.
GELATIN COATED TABLETS
capsule-shaped compressed tablet, about one-third smaller than a capsule filled with an equivalent amount of powder.
facilitates swallowing, and gelatin-coated tablets are more tamper evident than unsealed capsules.
ENTERIC-COATED TABLETS
delayed-release properties, coated with polymeric substances, drug dissolution and absorption in the intestine. Ex: Buscopan
TABLETS USED IN ORAL CAVITY
BUCCAL & SUBLINGUAL TABLETS
CHEWABLE TABLETS
IMMEDIATE RELEASE TABLETS
INSTANTLY DISINTEGRATING TABLETS
BUCCAL & SUBLINGUAL TABLETS
flat, oval tablets intended to be dissolved in the buccal pouch (buccal tablets) or beneath the tongue (sublingual tablets), oral mucosa.
pouch (buccal) 1 - 2 hours sublingual - 3 - 5 minutes
CHEWABLE TABLETS
intended to be chewed and then swallowed by the patient rather than swallowed whole. palatable and be easily chewed and swalloed, children and adults who have dificulty swallowing solid dosage forms
Ex: Ceelin, Meclizine(Bonamine)
IMMEDIATE RELEASE TABLETS
designed to disintegrate and release their medication with no special rate-controlling features, 75% of the labeled amount dissolves in 45 minutes.
INSTANTLY DISINTEGRATING TABLETS
Rapid-release tablets (rapidly dissolving tablets or RDTs), dissolving in the mouth within 1 minute, some within 10 seconds.
mourh within approximately 15-30seconds, Anything slower would not be categorized as rapidly dissolving
TABLETS USED TO PREPARE SOLUTIONS
EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
MOLDED TABLETS
TABLET TRITURATES
HYPODERMIC TABLETS
DISPENSING TABLETS
EFFERVESCENT TABLETS
uncoated tablets, organic acids (such as tartaric or citric acid) and sodium bicarbonate, react rapidly in the presence of water by releasing carbon dioxide, disintegrator
MOLDED TABLETS
such as tablet triturates, molding rather than by compression, are very soft, designed for rapid dissolution. Ex: Flumucil
TABLET TRITURATES
small, usually cylindrical, molded, or compressed tablets containing small amounts of usually potent drugs, provide accurate amounts of potent drug substances. similar w/ molded
HYPODERMIC TABLETS
no longer available, originally used by physicians in extemporaneous preparation of parenteral solutions.
DISPENSING TABLETS
AKA. compounding tablets,
no longer in use
used them to compound prescriptions; they were not dispensed as such to the patient
contained large amounts of highly potent drug substances
dangerous potential of being inadvertently dispensed as such to, patients.
can caure overdorage of toxicity
Ex: Hgcl-antiseptic, neomycin sulfate - ophtalmic drug, Basitracin - Antibiotic
MISCELLANEOUS
EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS
VAGINAL TABLETS
EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS
controlled-release tablets, release their medication in a predetermined manner over an extended period.
Ex: drugs that once a day to be taken
VAGINAL TABLETS
also called vaginal inserts, are uncoated, bullet-shaped, or ovoid tablets inserted into the vagina for local effects.
nonspecific vaginitis caused by Haemophilus vaginalis or antifungals for the treatment of vulvovaginitis candidiasis caused by Candida albicans and related species.
Ex: Canesten (1-day therapy or 6-day therapy)
QUALITY STANDARDS AND COMPENDIAL REQUIREMENTS FOR TABLETS
Tablet Weight & USP Weight Variation Test
Content Uniformity
Tablet Thickness
Tablet Hardness
Tablet Friability
Tablet Weight & USP Weight Variation Test
In the test, 10 tablets are weighed individually, and the average weight is calculated. The tablets are assayed, 10 tablets is calculated assuming homogeneous drug distribution. The tablet passed the U.S.P. test if no more than 2 tablets are outside the percentage limit and if no tablet differs by more than 2 times the percentage limit.
Content Uniformity
ensure content consistency of active drug substances within a narrow range around the label claim in dosage units. This test is crucial for tablets having a drug content of less than 2 mg or when the active ingredient comprises less than 2% of the total tablet weight.
10 dosage units are individually assayed
les within the range of 85% to 115% of the label claim and the standard deviation is less than 8%.
Tablet Thickness
determined by the diameter of the die
important in reproducing tablets identical in appearance and also it ensures that every production lot will be usable with selected packaging components.
determined with a caliper in milimeters, Using vermier caliper
Tablet Hardness
refers to the resistance to breakage under conditions of storage, transportation and handling.
A force of about A Kg
Importance of tablet hardness
Hardness (or more appropriately crushing strength) determination are made throughout the tablet runs to determine the need for pressure adjustments on the tableting machine.
Equipment used for hardness testing
Stokes or Monsanto Hardness Tester
Strong-cobb Hardness Tester
Pfizer Hardness Tester
Schleuniger Apparatus
Tablet Friability
tendency of tablet to powder, chip or fragment and can affect the elegance, appearance, consumer acceptance, property that is related to the hardness of the tablet.
how well a tablet resists chipping and crumbling, Compressed tablets that lose less than 0.5%-1% of their weight are usually considered acceptable
TYPES OF TABLET PRESS
Single Punch | Rotary Press
PARTS OF A TABLET PRESS
Hopper - For strong material for compression
Feed Shoe - For distribution of materials into the die
Punch - For compaction; determines the hardness of the tablet
Die - Determones the size and shape of the tablet
Cam Tracks - For guiding the movement of punches
TABLET COATING
Reasons for tablet coating:
To protect the medicinal agent against destructive exposure to air/humidity
To mask the taste of the drug
To provide special characteristics of drug release
To prevent contact with a drug which is irritating or potentially allergicTo separate reactive ingredients
To delay or prolong absorption of the drug component by retarding release of drug from the dosage form (sustained-action)
To provide aesthetics or distinction to the product
Compression Coating
Basic Processes used in the application of coating
Equipments
Uncoated Tablets should be
Friabilator
Basic Processes used in the application of coating
Compression Coating - special dosage forms
Pan Coating - both sugar & film-coating -makes use coating pans provided w/a hot & cold air
Air suspension coating - atomized & applied to tablets
Dip coating - dipped into containers of coating solutions - has not been widely accepted because of the difficulties encountered. during the coating procedure & lack of coat uniformity.
Equipments
Coating Pan (Ex. Accela Cota, Fellegrini)
Steam Jacketed Tanks
Drying Oven
Polishing Drum
Uncoated Tablets should be
Sufficiently hard
Optimum convexity
Minimal friability
Rapid disintegration
Friabilator
apparatus to be used in determining the tablet's friability. or tendency to crumble.
Tablet Disintegration
is a measure of the time required under a given set of conditions for a group of tablets to disintegrate to particles
Complete disintegration is defined as "that state in which any residue of the unit, except fragments of insoluble coating or capsule shell, remaining on the screen of the test apparatus is a soft mass having no palpably firm core"
usually 30 minutes, but varying from about 2 minutes for NTG tablets to up to 4 hours for buccal tablets.
Parts of Disintegration Apparatus
Basket-rack assembly - six open-ended transparent tubes, 10-mesh stainless steel wire screen
Mesh - Attached under the surface of the lower plate
Disks - permitted only where the specified in the monograph
Tablet Dissolution
process by which a substance forms a solution, measures the amount of time required for a given percentage of the drug substance in a tablet into solution under a specified set of conditions.
Reasons for conducting in-vitro dissolution testing for solid dosage forms: assurance program, It is a requirement for regulatory approval
Dissolution Apparatus
Variable-speed stirrer motor.
Dossolution Testing
37*C + 0.5*C
Most commonly used app
Apparatus 2

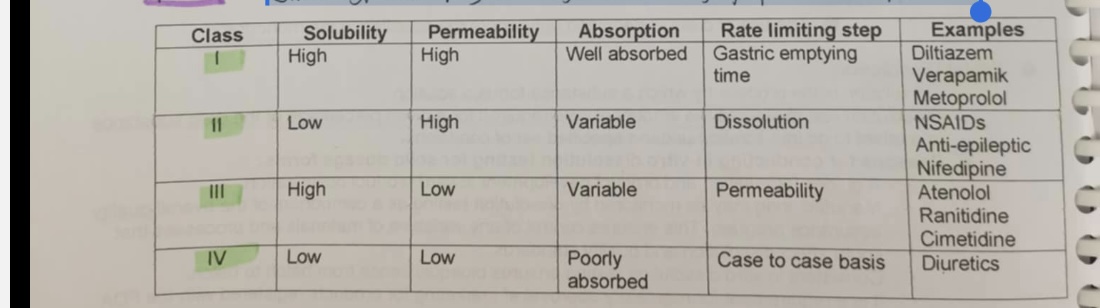
BIOPHARMACEUTICS CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM
is a system to differentiate the drugs on the basis of their solubility and permeability, restricts the prediction using the parameters solubility and intestinal permeability, based on a United States Pharmacopoeia (USP).
checking/ dassifying ē drugs that is highly permeable | soluble
METHODS OF PREPARATION OF COMPRESSED TABLETS
wet granulation, dry granulation, and direct compression.
WET GRANULATION
a widely employed method for the production of compressed tablets.

Dry Granulation
AKA. Double compreccion or pre- comprescion
compacted in large pieces and subsequently, broken down or sized into granules.
Slugging
Advantage: Used for moisture | heat cencitive material
the powder mixture is slugged
Roller compaction
powder compactors, increase the density of a powder by pressing it between rollers at 1 to 6 tons of pressure
The roller compaction method is often preferred to slugging.
Disadvantage: Dusty, may result uneven color
Ex: Multiv, aspirin
Direct Compression
like potassium chlorde, possess Mae-lowing and cohesive properties that enable them to be compressed directly in a tablet machine without any need of granulation.
EXCIPIENTS USED IN TABLET FORMULATION
Diluents/Fillers
Binders/Adhesives
Disintegrants
Glidants
Lubricants
Anti-adherents
Absorbents
Coloring Agents
Diluents/Fillers
Ex: Lactose, starch, cellulose derivatives, mannitol, sorbitol, sucrose
Binders/Adhesives
Ex: starch, gelatin, methylcellulose, polyvinylpyrrolidone,
Disintegrants
Ex: starch, gums, clays, cellulose, alginates, surfactants
Glidants
Ex: Talc, corn starch, colloidal silica, calcium silicate, calcium phosphate, Zn, Mg, and Ca stearates
Lubricants
Ex: talc, magnesium stearate, and calcium stearate
Anti-adherents
Ex: Colloidal silica, corn starch, sodium lauryl sulfate, stearates
Adsorbents
Ex: Magnesium oxide, magnesium carbonate, bentonite, silicon dioxide
Coloring agents
Ex: FD&C - food, drug & cosmetics, D&C - drug & cosmetics, external D&C - external use only
Sugar Coating Tablets
Sealing
Subcoating
Syruping
Finishing
Polishing
Sealing
AKA “Waterproofing”, protect the tablet core from water in subsequent
Ex: Shellac, phthalic anhydride
Subcoating
This improves the bond between, build up standard size for tablets
Ex: Gelatin, Acacia
Syruping
Finalize the rounding-off of the tablet.
Grossing
base color, a syrup solution w/ subcoating powder
Heavy sugar coating
to guild up a solid color
Regular syrup coating
desired color - dilute syrup solution
Finishing
desired color is attained and to attain final smoothness of the tablet
Polishing
done in a canvas polishing pan for sheen or gloss
Ex: beeswax, carnauba wax
Film-Coating
thin, skin-tight coating of plastic like material
Non-aqueous solutions contain the following types of materials:
Film-Former
Alloying Substance
Plasticizer
Surfactant
Opaquants
Glossant
Volatile Solvent
Film-Former
capable of producing smooth, thin films reproducible under conventional coating conditions and applicable to a variety of tablet shapes.
Ex: Shellac: CAP (Cellulose Acetate Phthalate)
Alloying Substance
imparts eater-solubility/ permeability
Ex: PEG (Polyethylene Glycol)
Plasticizer
imparts flexibility & elasticity
Ex: Castor Oil; Sorbitol
Surfactant
imparts spreadability
Ex: Spans, Tweens; Polyoxythylene sorbitan derivatives
Opaquants
to enhance appearance
Ex: Titanium Dioxide
Glossant
provide luster to the tablets w/out a seperate polishing operation
Ex: Beeswax
Volatile Solven
allow the spread of the other components over the tablets while allowing rapid evaporation to permit an effective yet speedy operation
Ex: Alcohol mixed with acetone
Aqueous Film-Coating Formulation contains
Film-forming Polymer (7% to 18%): Cellulose ether polymers
Plasticizer (0.5 to 2.0%): Glycerin
Colorant & Opacifier (2.5% to 8%)
Vehicle (water, to make 100%)
Enteric Coating Tablets
intended to pass through the stomach intact to disintegrate and release their drug content for absorption along the intestines.
Coatings used are: Shellac and HPMC
Types of tablet printing
Debossed, Embossed, Engraved
Debossed
imprinted w/ a mark below
Embossed
imprinted w/ a mark above
Engraved
imrpinted w/ a code
TABLET PROCESSING PROBLEMS
Picking
Peeling
Orange peel effect
Mottling
Bridging
Wrinkling
Sweating
Blistering
Picking
flaking from the tablet surface (punch); removal of material
Peeling
large amounts of film fragments flaking
Orange peel effect
roughness of the tablet surface
Mottling
uneven color distribution
Bridging
filling-in of the score line