Energy requirements models
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy can’t be created or destroyed only transferred
Numbers must be added up in calculations
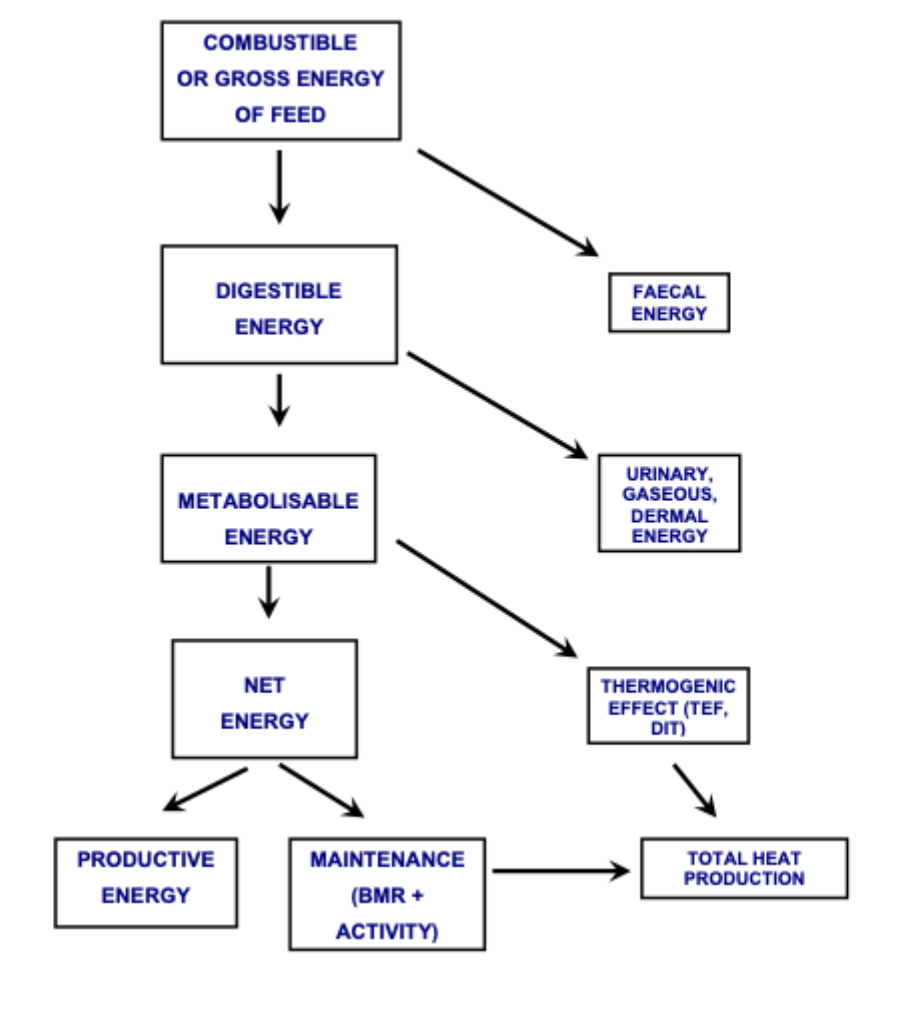
Nutritional energetics
TEF- thermogenic effect of food
DIT- diet induced thermogenesis
FED/ DIT = total heat production
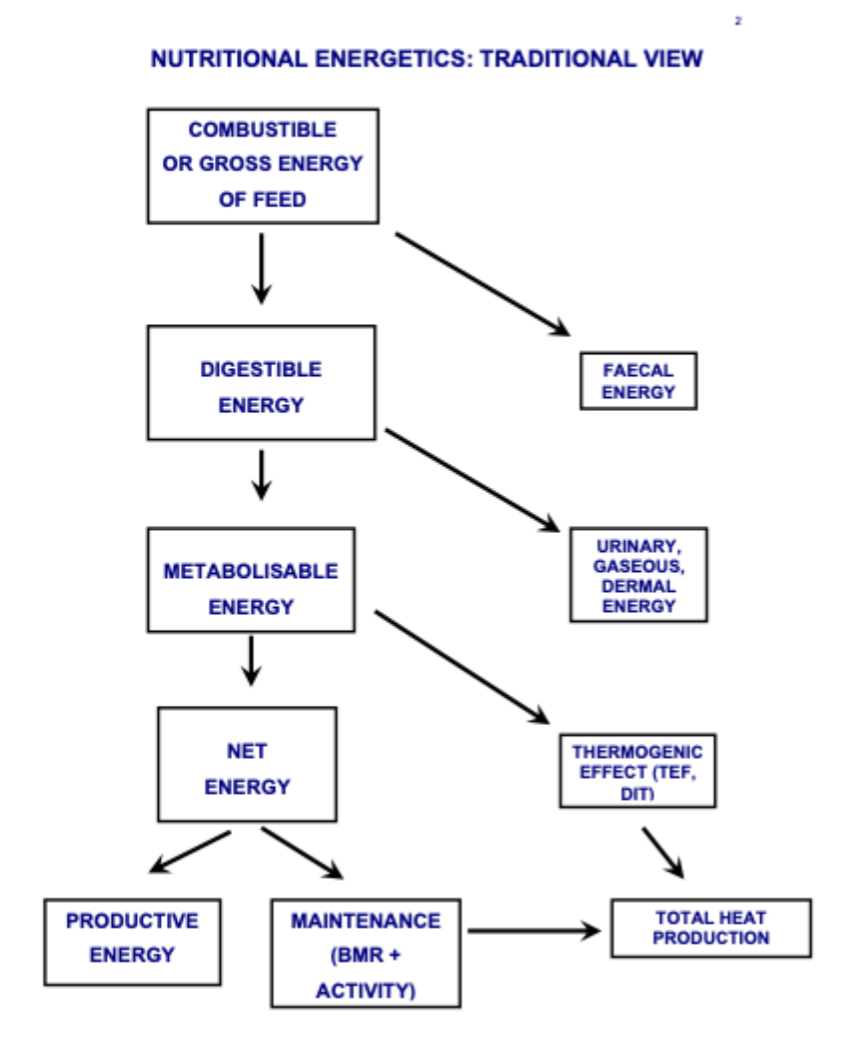
How do you measure the energy content of any feed or ingredient?
Using bomb calorimetry
What are the 2 approaches to determining nutrient requirements:
Empirical or ‘practical’
Factorial or ‘theoretical’
Empirical
Based on simple observations (no assumptions involved)
Method: dose- response
Difficulties
response measure?
quality of data (biological variation)
interpretation of data:
linear/ curvilinear?, inflection point?
limited applicability (animals, diets/ feeds)
Advantages:
accessibility, ‘near- market’
Factorial
Based on theory, summation of ‘facrtors’
e.g. R = M + P + …..
R: requirement, M: maintenance, P: production
‘M’ and ‘P’ are factors, there may be others
Measurement of factors
Maintenance requirement: ‘the amount of dietary energy required to maintain the body in a constant state (mass and composition)’
It may be calculated from the intercept with the X- axis or by observation of dietary energy required to maintain body weight/ condition
Production requirement: ‘the amount of dietary energy required to support to product formation’ It may be calculated from dietary energy required to form product or measured via product energy content (PE) and formation rate
Difficulties:
Available of data
Efficiency of conversion- where FHP/ PE approach used
Food intake
Advantages:
General statement- can accommodate different animals/ production rates
Flexible- reduces animal experimentation, can be up- dated
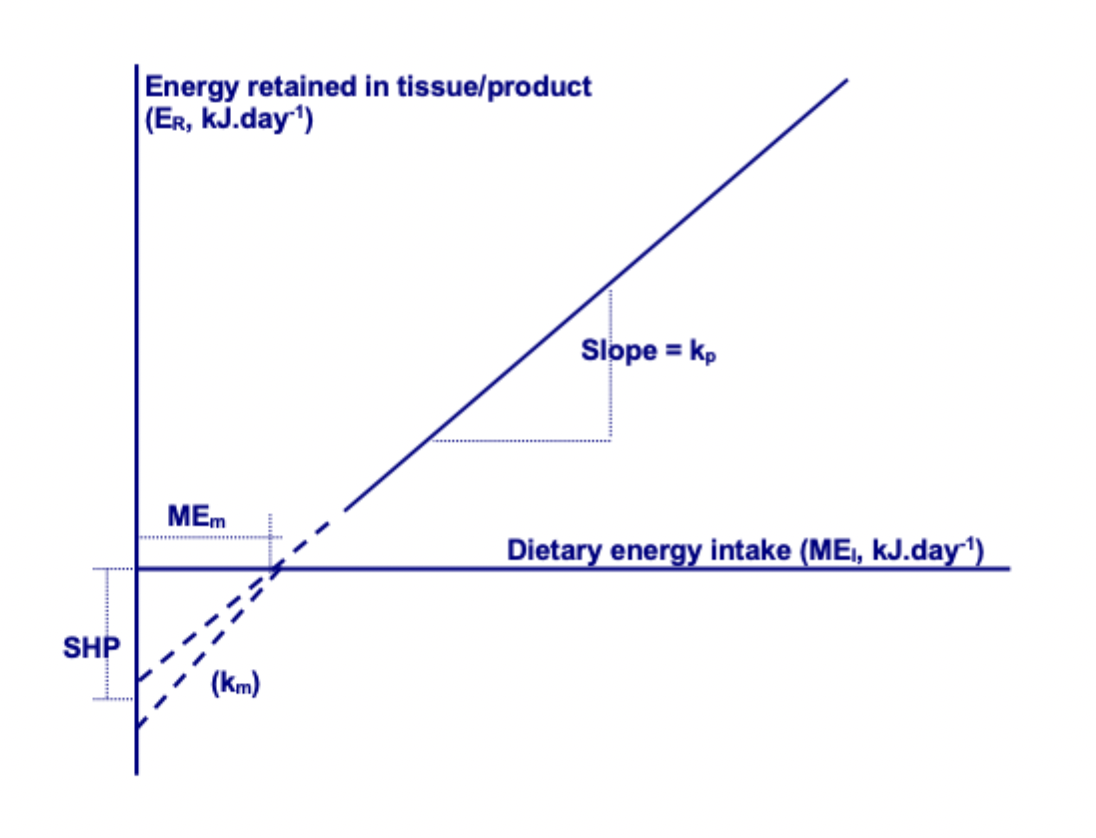
What is SHP?
Starving heat production
SHP is the loss of heat at 0 energy intake (ordinate intercept). In a normally- active animal, SHP is the hear production associated with maintenance (note: NOT the dietary energy required for maintenance)
What is MEm?
Dietary energy required for maintenance
MEm is the energy intake required for zero gain, or to prevent weight loss (abscissa intercept).
What is delta Er?
The change in energy retention (delta Er) as a function of the change in energy intake (delta MEl), i.e. delta Er/ delta El, is known as ‘energetic efficiency’ (k).
The k values for tissue gain or product formation (Kp) and maintenance (Km) may differ. Values for k are slopes of the lines.
Response in tissue energy to dietary energy
The line may be represented as: Er = Kp. MEl - SHP
The relationship between SHP and MEm = SHP/ Km
Similarly, the relationship between the energy retained in product or tissue (Er or PE) or MEp (dietary energy required for product) is:
MEp = Er/ Kp (MEp îs MEl - MEm)
NE
NE = k x ME
Net energy = efficiency factor x metabolisable energy
Nutritional energetics