Biochemistry: Proteins
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
protein
a naturally occurring, unbranched polymer consisting of amino acid monomers; forms many of the functional components of a biological organism; a peptide with at least 40 amino acid residues
amino acid
compound with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end and a side chain which provides uniqueness that is the building block of peptides and proteins; 20 common occurring varieties separated according to acidity, basicity, and polarity
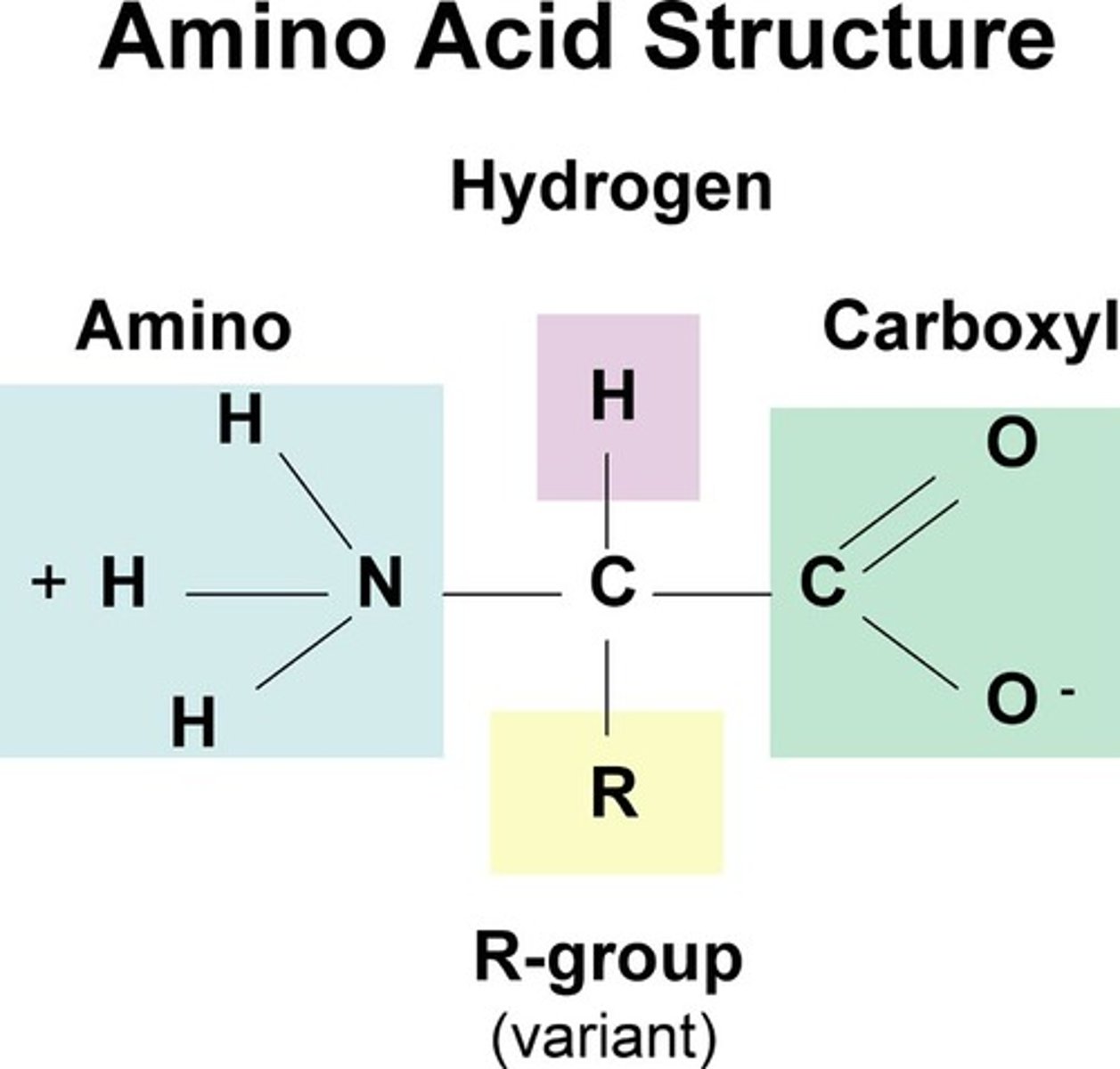
alpha amino acid
an amino acid in which the amino group is bonded to the carbon atom next to the -COOH group
standard amino acids
one of twenty amino acids coded by DNA; some amino acids (such as selenocysteine and hydroxyproline) are nonstandard amino acids, because they are not coded by DNA but instead are biosynthesized from standard amino acids
nonstandard amino acids
amino acids that are derivatives of amino acids coded by DNA; these amino acids are not themselves coded by any codon; examples include selenocysteine and hydroxyproline
nonpolar amino acids
amino acids that are composed mainly of carbon and hydrogen and do not possess any polar bonds; 8 amino acids; form hydrophobic interactions in secondary structure
polar neutral amino acids
amino acids that contain a polar bond as well as carbon and hydrogen atoms; can hydrogen bond with components of other amino acids; 6 amino acids
polar acidic amino acids
amino acids that contain a carboxylic acid on their side chain; can hydrogen bond with components of other amino acids; 2 amino acids
polar basic amino acids
amino acids that contain a basic nitrogen atom on their side chain; can hydrogen bond with components of other amino acids; 3 amino acids
essential amino acids
amino acids that are needed, but cannot be made by the body; they must be eaten in foods
complete dietary protein
protein that provides essential amino acids in the proportions needed to support protein synthesis
complementary dietary proteins
proteins in which two or more incomplete dietary proteins that, when combined, provide an adequate amount of all essential amino acids relative to the body's needs
limiting amino acid
the essential amino acid in lowest concentration in a food or diet relative to body needs
zwitterion
a molecule or ion having separate positively and negatively charged groups, like an amino acids
isoelectric point
the pH at which an amino acids exists primarily in its zwitterion form; more than 99% are in zwitterion form; calculated by taking the average of the pKa values of the amine and carboxyl group of non basic/acidic side chain amino acids; for amino acids that have a pKa for their side chain, pI is determined by taking the average pKa of either both acidic (COOH) or both basic sites (NH3+)
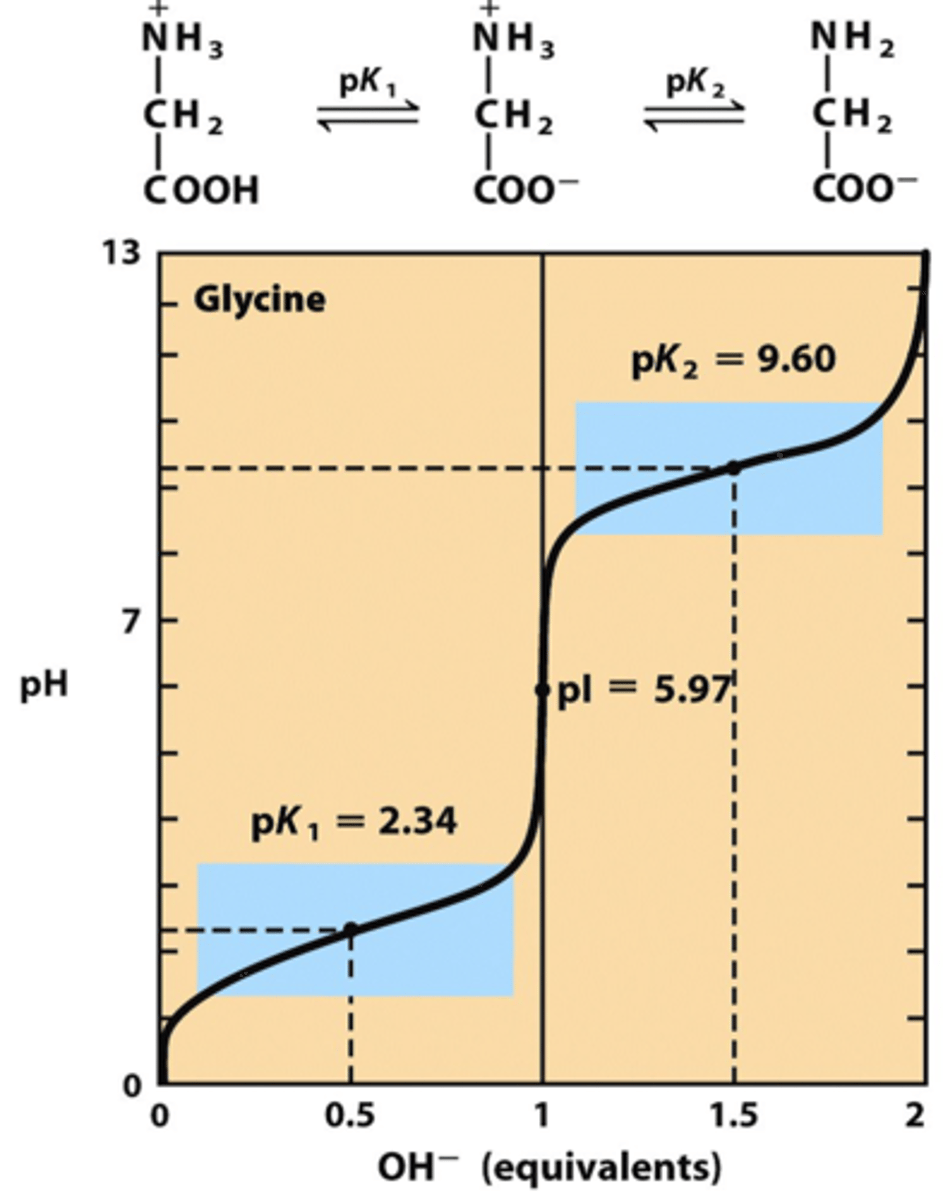
amphoteric
a substance that can act as both an acid and a base and can react with both acids and bases; for example, amino acids
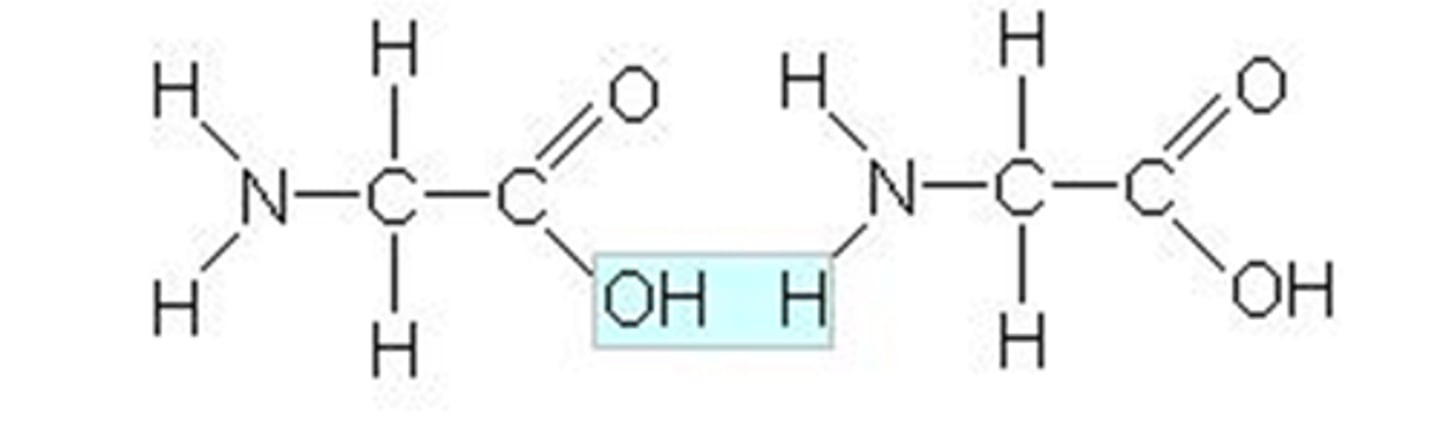
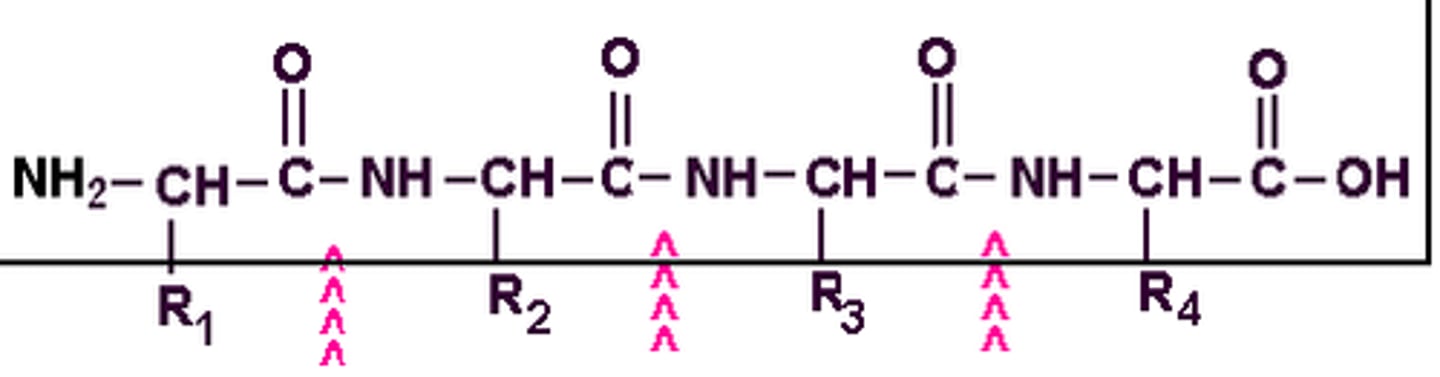
peptide
an unbranched chain of amino acids that can be further classified by length
polypeptide
a long unbranched chain of amino acids
peptide bond
a covalent bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid; amide linkage; forms via dehydration synthesis
N terminus
the end of a polypeptide or protein that has a free amino group
C terminus
the end of a polypeptide or protein that has a free carboxyl group
amino acid residue
the portion of an amino acid structure that remains, after the release of H2O, when an amino acid participates in peptide bond formation as it becomes part of a peptide chain
polypeptide backbone
repeating sequence of atoms (-N-C-C-) that forms the core of a protein molecule and to which the amino acid side chains are attached
peptide hormones
hormones composed of amino acids; examples include oxytocin and vasopressin or enkephalins, glutathione, etc
enkephalins
pentapeptide neurotransmitters produced by the brain itself that bind at receptor sites in the brain to reduce pain
small peptide hormones
hormones that are composed of short chains of amino acid
glutathione
reducing agent that can help reverse radical formation before damage is done to the cell; antioxidant
monomeric protein
a protein in which only one peptide chain is present
multimeric protein
a protein in which more than one peptide chain is present; may be identical or different
simple protein
a protein in which only amino acid residues are present
conjugated protein
a protein that has one or more non amino acid entities present in addition to one or more peptide chains; in other words, it has a prosthetic group
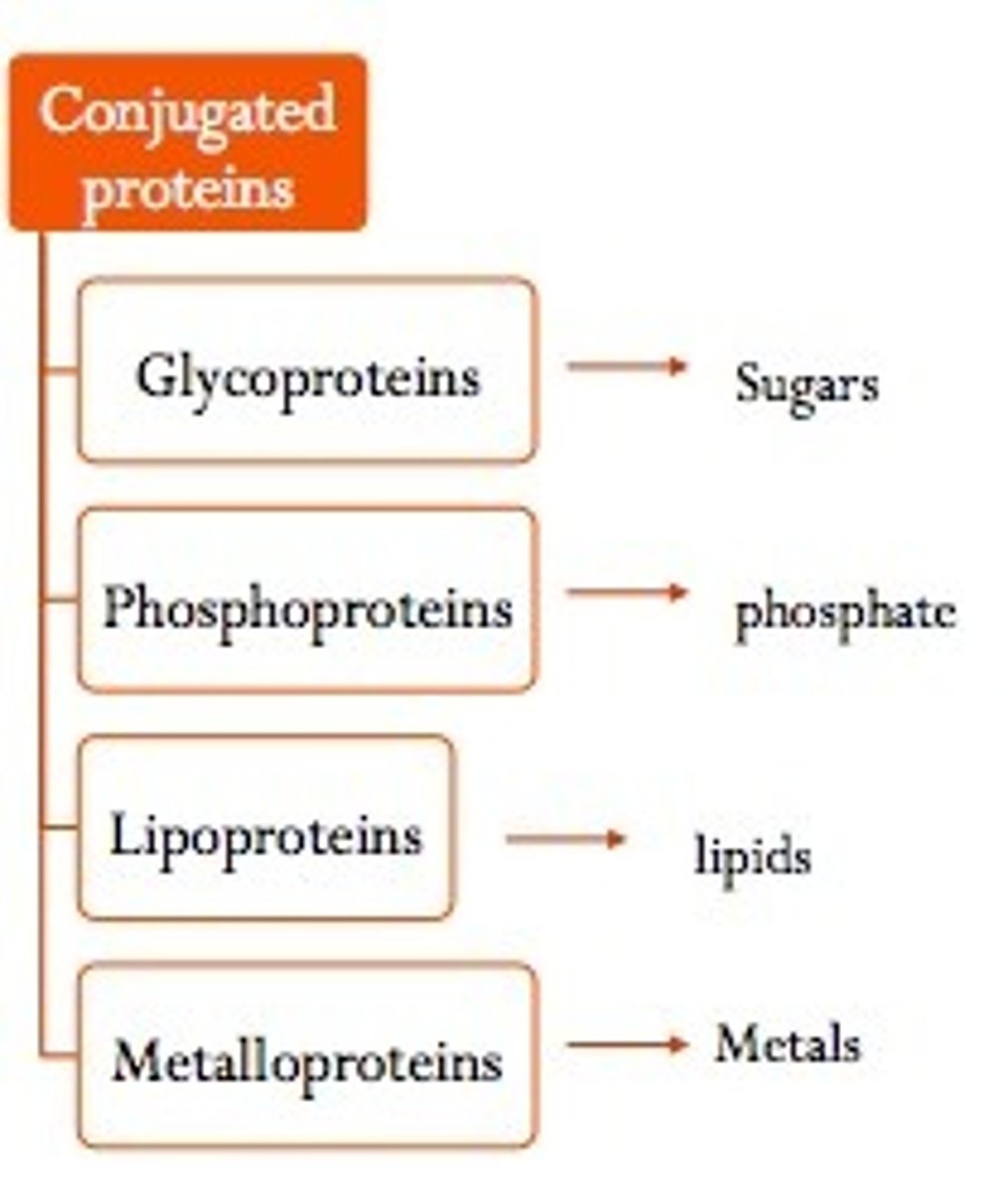
prosthetic group
a non-amino acid group present in a conjugated protein; examples include a fatty acid, saccharide, metal, etc;
primary protein structure
protein structure that details the order of amino acid residues from the N-terminus to the C-terminus; amino acids can be diastereoisomers if arranged differently; stereoisomers do not exist as amino acids are always in the L configuration
secondary protein structure
protein structure that details the folding and twisting patterns of the polypeptide backbone; the two most common types of this structure are the alpha helix and the beta pleated sheet; amino acids like to be trans, with respect to their side chain
tertiary protein structure
protein structure that details the overall 3D shape of a protein that results from interactions between amino acid side chains that are widely separated from each other within a peptide chain
quaternary protein structure
protein structure that details the organization among the various peptide subunits in a multimeric protein
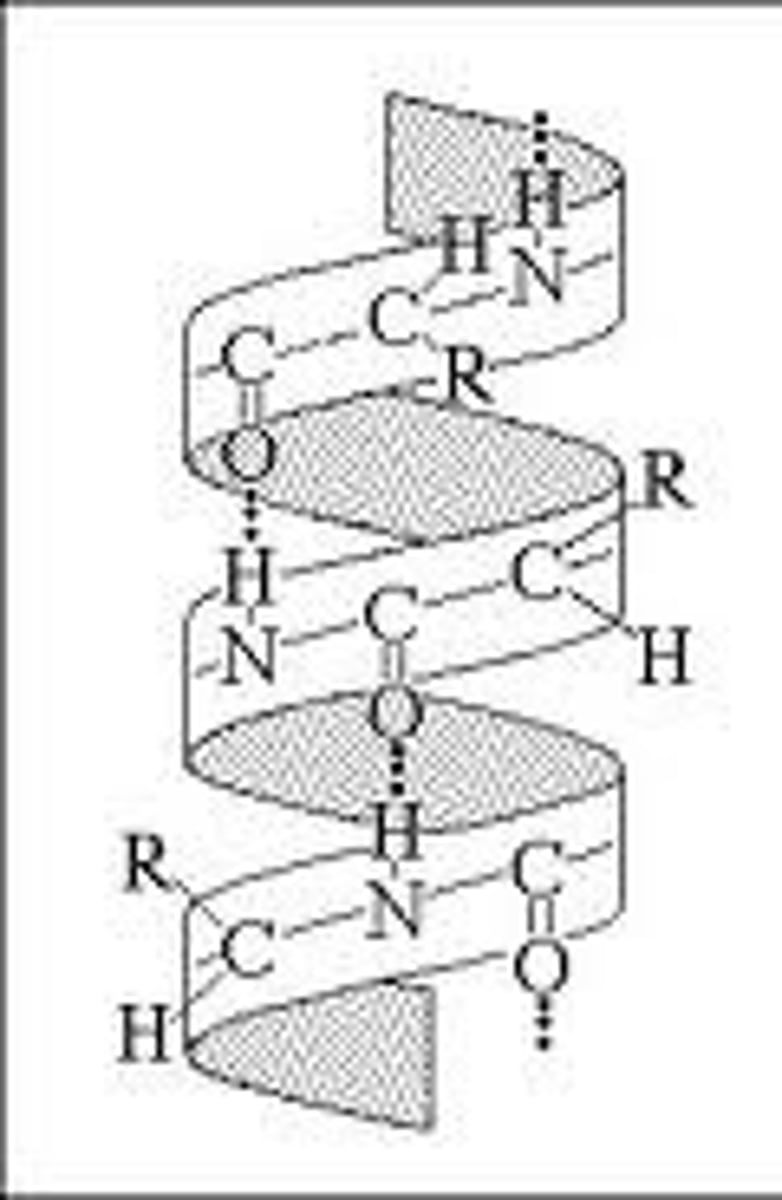
alpha helix structure
type of secondary structure of proteins formed by folding of the polypeptide into a helix shape with hydrogen bonds (from the amino group to the carboxyl group) stabilizing the structure; the twist is a clockwise spiral; the side chains extend outwards from the helix
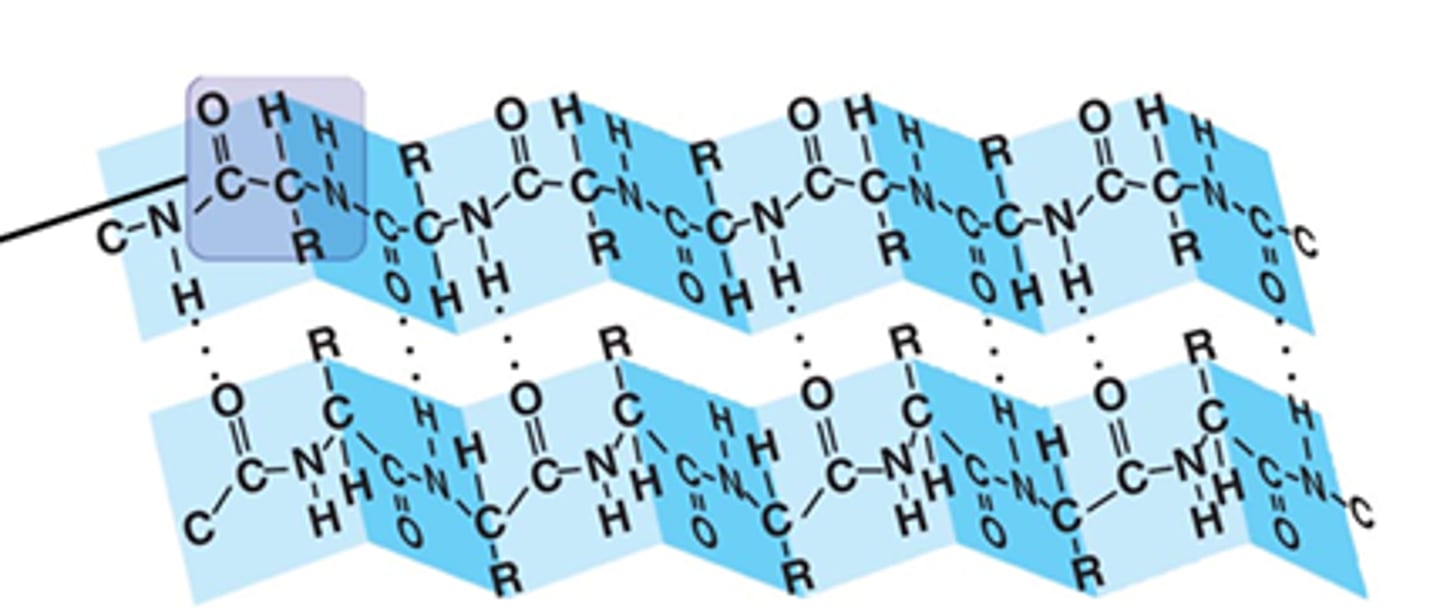
beta pleated sheet structure
type of secondary structure in which two fully extended protein chain segments in the same or different molecules are held together by hydrogen bonds; in molecules were the pleated sheet involves a single peptide, several U-turns in the protein chain arrangement are needed in order to form the structure; the side chains are found above or below the plane of the sheet, alternating between top and bottom (trans)
unstructured protein segment
the portions of a protein that have neither an alpha helix or a beta pleated sheet
intramolecular disulfide bond
a bond involving two oxidized cysteine residues that form a covalent bond and contribute to tertiary structure; can be between different polypeptides or the same one
electrostatic interactions
interactions between an acidic side chain and a basic side chain that occurs at an appropriate pH and causes two portions of a peptide (or two peptides) to be drawn towards each other, contributing to tertiary structure
hydrophobic interactions
interactions between non polar side groups in which London forces cause these groups to coalesce to exclude polar molecules; contributes to tertiary structure
hydrogen bonds
very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule; contributes to both secondary and tertiary structure
complete protein hydrolysis
when all of a protein's peptide bonds are cleaved and all amino acid residues are freed up
incomplete protein hydrolysis
when some, but not all, of a protein's peptides bonds are cleaved and amino acid residues are freed up
protein denaturation
when proteins are subject to heat, acid or other conditions that disturb their stability; protein uncoils, loses its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure, and loses its function
coagulation
the precipitation out of biochemical solution of denatured protein
fibrous protein
a protein that has only a secondary structure; generally insoluble; includes collagens, elastins, and keratins
globular protein
a protein that has peptide chains that are folded into spherical or glover shapes with most of the hydrophobic side chains pointing inwards
membrane protein
a protein that is found associated with a membrane system of a cell
alpha keratin
a fibrous protein that forms a dimer,is extremely stable and found in hair, horns and nails; acts as a protective coating in organisms; is the major constituent of hair, feathers, wool, fingernails, toenails, claws, scales, horns, shells, quills, and hooves;
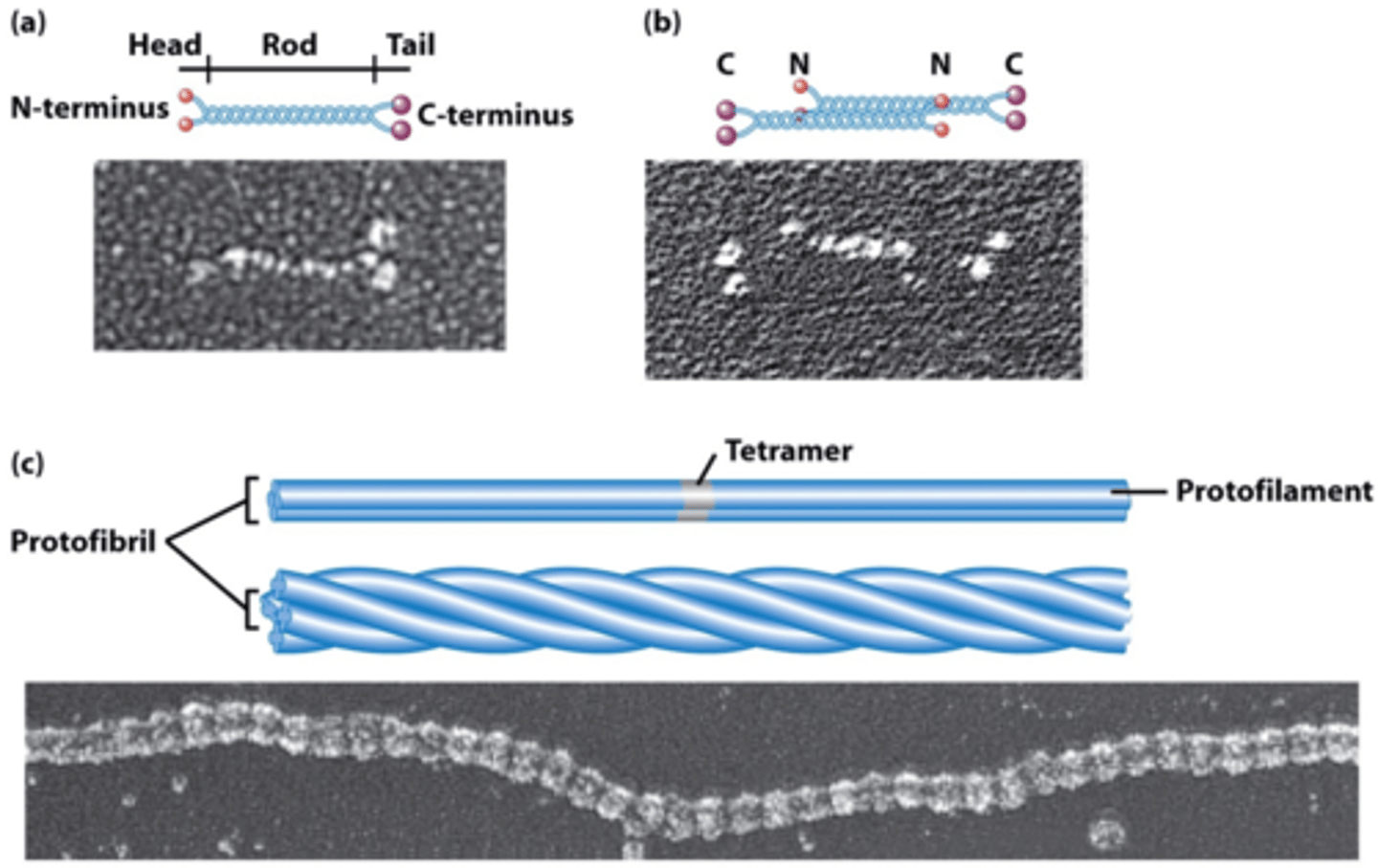
collagen
the most abundant of all proteins in humans (30%); a major constituent of structural material, including tendons, ligaments, blood vessels, and skin; also the organic component of bones and teeth; is composed of a triple helix; chains of collagen are very long, thin, and rigid
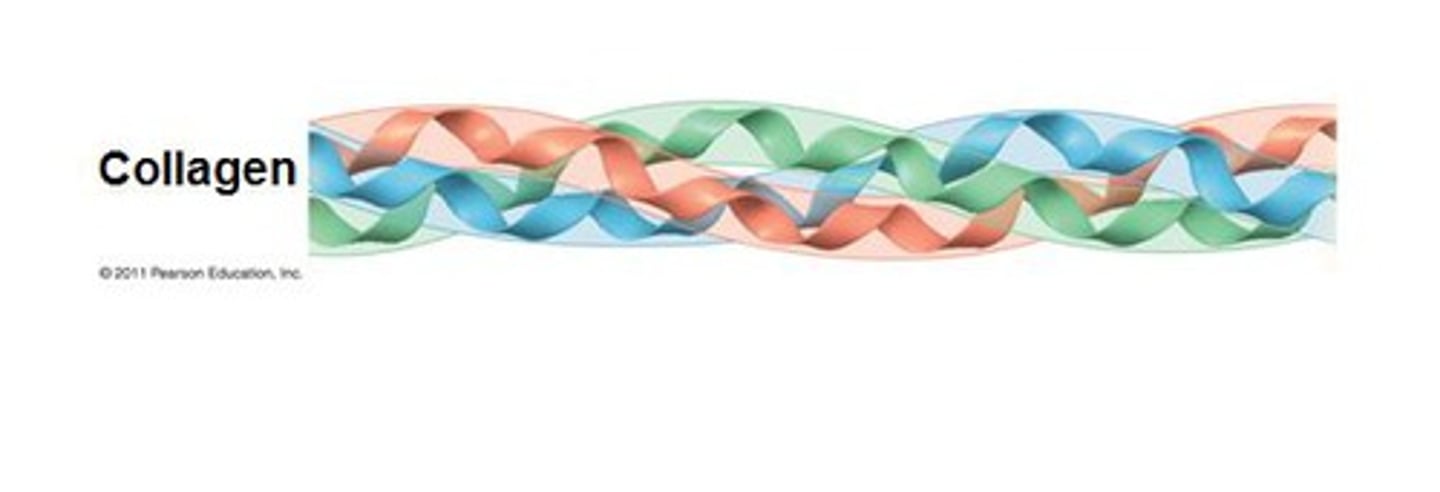
triple helix
the protein structure found in collagen, consisting of three polypeptide chains woven together like a braid
hemoglobin
a globular protein that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues; a tetramer with each subunit also containing a heme group that binds to oxygen
myoglobin
a globular protein that functions as an oxygen storage molecule in muscles; a monomer; only 1 O2 molecule can be carried; tertiary structure similar to hemoglobin;
immunoglobulin
a protein involved in the immune system's active immunity
antigen
a protein that, when introduced in the blood, triggers the production of an antibody
lipoprotein
a protein with a fatty acid prosthetic group that it transports to and from regions of the body
plasma lipoprotein
clusters of lipids associated with proteins that serve as transport vehicles for lipids in the lymph and blood
chylomicrons
the class of lipoproteins that transport lipids from the intestinal cells to the rest of the body
very low density lipoprotein
lipoproteins that function in transporting triacylglyerols synthesized in the liver to adipose tissue
low density lipoprotein
lipoproteins that function in the transport of cholesterol synthesized in the liver to cells throughout the body
high density lipoprotein
lipoproteins that function to collect excess cholesterol from the body tissues and transport it back to the liver for degradation to bile acids
info
protein are not very soluble in water, they are crystalline solids with high decomposition points
info
in acids, the carboxyl group of a protein is protonated and the amino acid/protein/peptide carries a net positive charge; in bases, the amino group is deprotonated and the amino acid/protein/peptide carries a net negative charge
info
we have L amino acids but D carbohydrates
info
cysteine dimerizes when mild oxidizing agent is present and is broken with reducing agents
info
proteins like to be trans, orienting their side groups to be on opposite sides
info
R groups need to be as small as possible to make an alpha helix as the secondary structure
info
the “U-turn” structure is a common secondary protein structure
info
amino acids can be separated by breaking the peptide bonds under acid/base + heat
info
all amino acids have an “S” configuration, except cysteine
info
To separate amino acids, a few drops of solution are added to a filter paper in a buffered solution between two electrodes. Amino acids then migrate by their net charge (negative to the cathode positive to the anode) and by their size (bigger are slower and smaller are faster to migrate). Then, the paper is treated with Ninhydrin to reveal the spots on the filter to which the amino acids migrate.
ninhydrin
a chemical reagent that reacts with amino acids to form compounds that have conjugated pi systems and have color
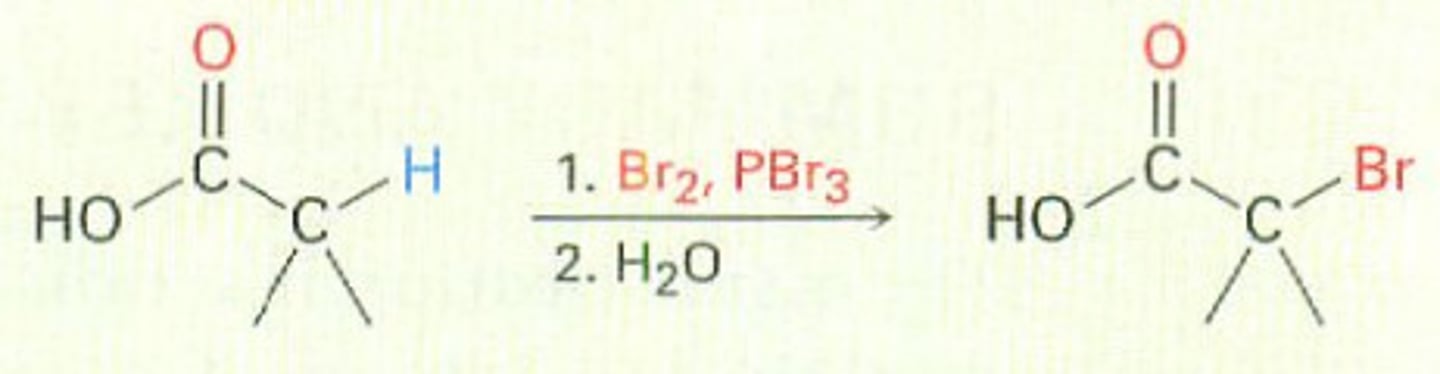
Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky halogenation
a chemical reaction in which bromine is installed at the alpha position of a carboxylic acid; this reaction can be used to form a racemic mixture of an amino acid after the bromine atom is reacted, via an SN2 reaction, with an amine
amidomalonate synthesis
a chemical synthesis of amino aicids that uses amidomalonate as a reactant to form amino acids on; the alpha carbon is alkylated with the side chain the specific amino acid and then with heating and acid catalysis, a racemic mixture of the amino acid can be formed after base workup
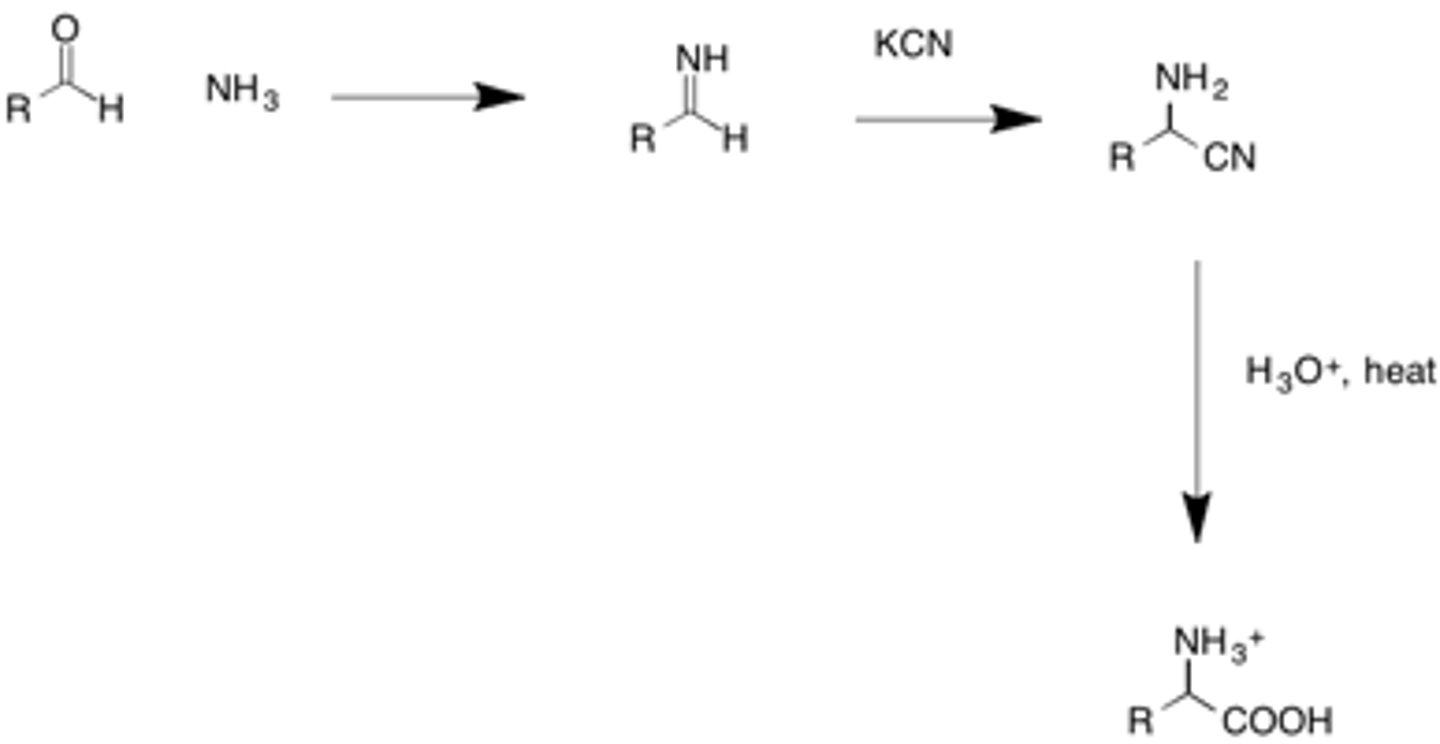
Strecker synthesis
a chemical synthesis of a racemic mixture of amino acids in which ammonia is added to an aldehyde, in which the R group is the side chain of the amino acid, and eventually forms an imine ion that is attacked by CN and then hydrolyzed to form he amino acid
enantioselective synthesis of L amino acids
a chemical synthesis of an optically active solution of L amino acids in which a chiral catalyst utilizing ruthenium (Ru) is complexed to a chiral ligand to form amino acids of only one configuration
BINAP
bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'binaphthyl; a chemical ligand that is complex to ruthenium that can be used to form a solution of optically active amino acids
info
amino acids are read from the N-term to the C-term
Edman degradation
a method of sequencing amino acids by removing an amino acid residue from the N-terminus by cleaving the peptide bond with phenylthiohydantoin; is only useful for small peptides
Phenylthiohydantoin
a reagent used in Edman degradation that cleaves a single amino acid from the N-terminus and forms a derivative that can be determined
enzymatic degradation
peptide sequencing of larger peptides in which small peptides are sequenced by Edman degradation and then stitched back together by determination of the primary structure; enzymes cleave only certain linkages
peptidases
enzymes that break down proteins into amino acids; can be used for peptide sequencing
trypsin
an enzyme from the pancreas that digests proteins in the small intestine; hydrolyzes the carboxyl end of the amino acids lysine and arginine
chymotrypsin
an enzyme that breaks down proteins in the small intestine; cleaves the carboxyl end of amino acids with aromatic side chains (tyrosine, phenylalanine, and tryptophan)
peptide bond formation
a type of bond that forms between a carboxyl group and an amine group; an amide linkage; a reagent that can be used to form it is DCC (dicyclohexylcarbodiimide)
dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)
a reagent used in laboratories that directs the formation of a peptide bond between a carboxyl and amine group
info
in order to make peptide bonds with DCC, you need to protect the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amine group of another amino acid to prevent unwanted side reactions; you can protect an amino group by converting it to a carbamate with (BoC)2O and protect a carboxyl group by converting it into a benzyl or methyl ester; cleavage of the protecting group with trifluoroacetic acid and acid catalysis, respectively
Merrifield synthesis
a peptide synthesis technique in which amino acids are added to a growing chain tethered to an insoluble polymer; unwanted side products are simply washed away while the desired growing amino acid chain remains tethered until released
exopeptidases
a type of protease which hydrolyses the peptide bonds on the terminal amino acids of the peptide molecules formed by endopeptidases; they progressively release dipeptides and single amino acids
endopeptidases
a type of protease which hydrolyses the peptide bonds between amino acids in the central region of a protein molecule forming a series of peptide molecules
ion pair
amino acid residues with opposite charges that stabilize each other in the core/surface
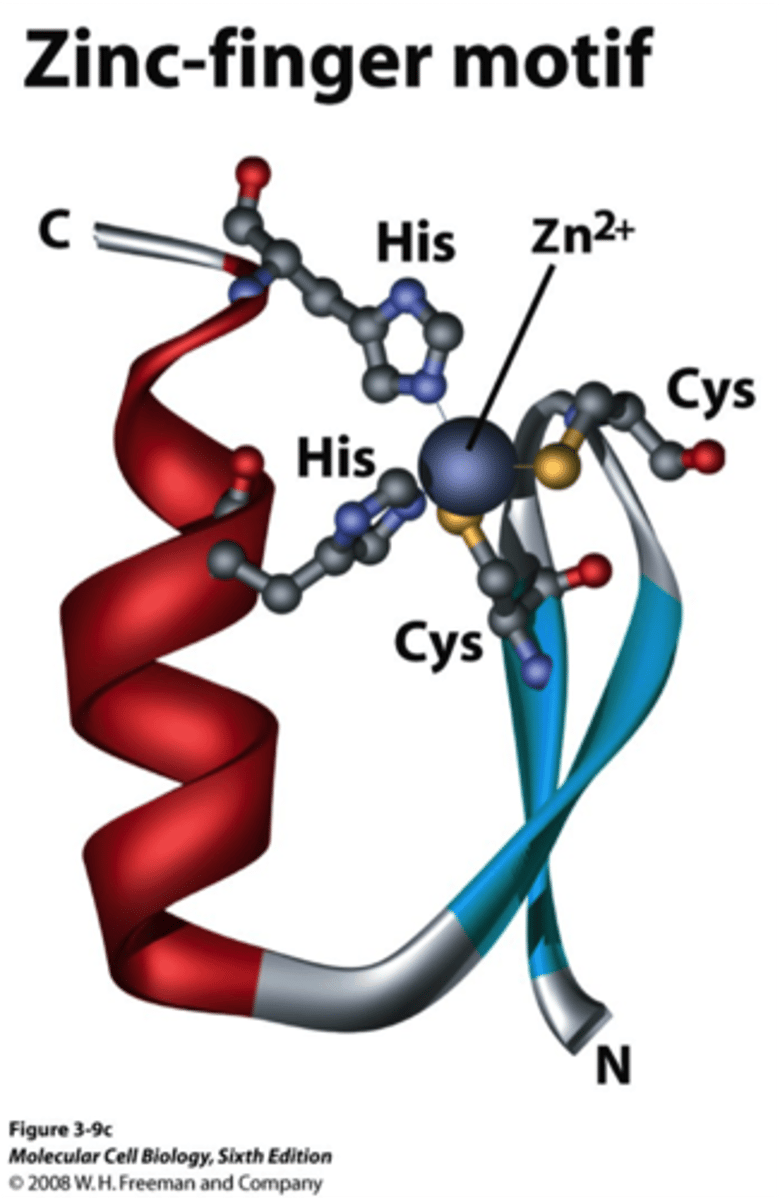
zinc fingers
a structure forming/stabilizing chemical feature in which a zinc atom binds to negative regions of chains of amino acids
molecular chaperones
a protein that helps other proteins fold or refold from a partially denatured state
post-translational processing
alteration in the structure of a protein such as phosphorylation, glycosylation, or proteolytic cleavage, that occurs after it is translated
intrinsically unstructured proteins
proteins or protein segments that lack a fixed structure and depend on other compounds and environments to form their tertiary structure
homodimer
protein composed of two identical subunits
homotrimer
protein composed of three identical subunits
homotetramer
protein composed of four identical subunits