Classifying Chemical Reactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
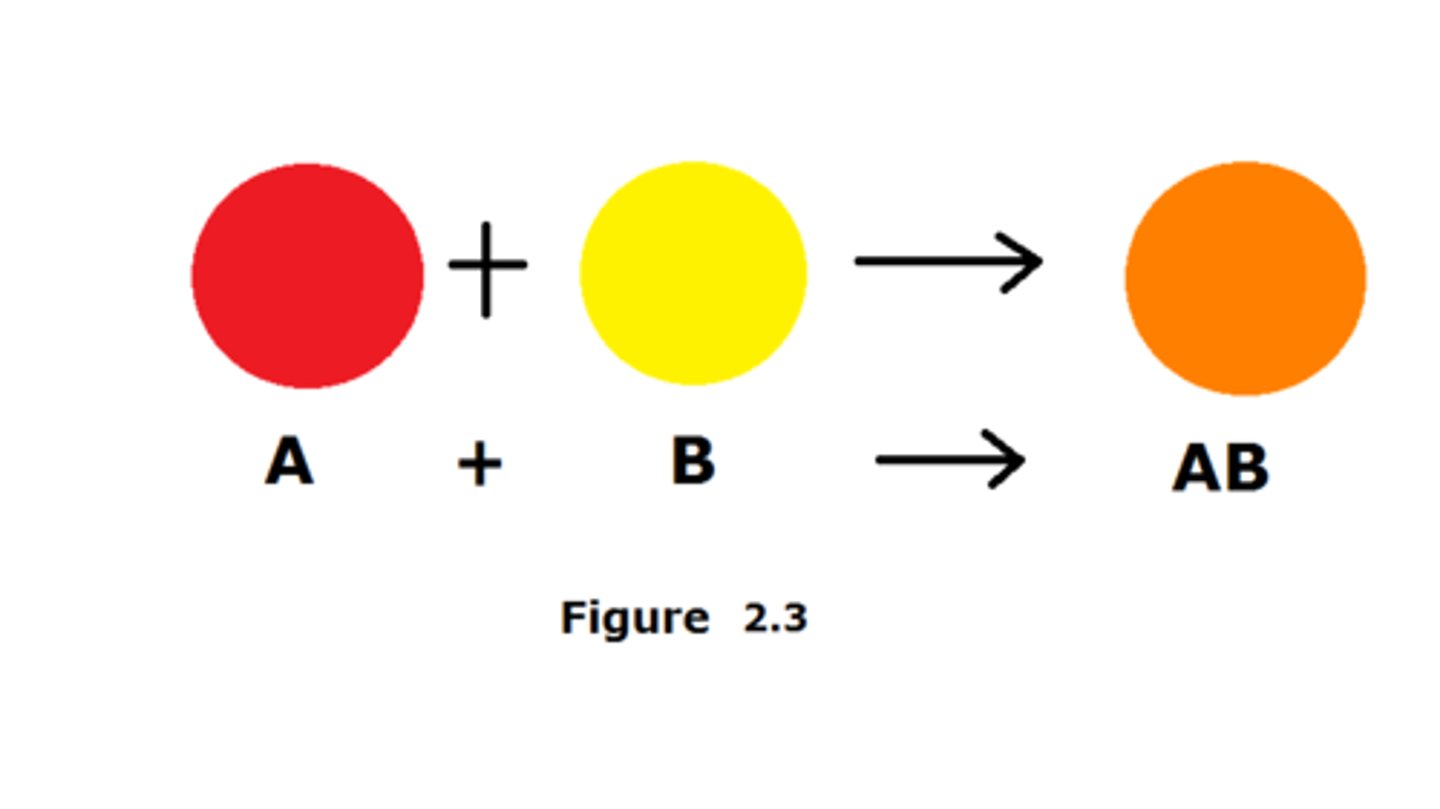
synthesis reactions
two or more reactants combine to form one new product. Chemists often use the following generic equation to represent a synthesis reaction:
A + B → AB
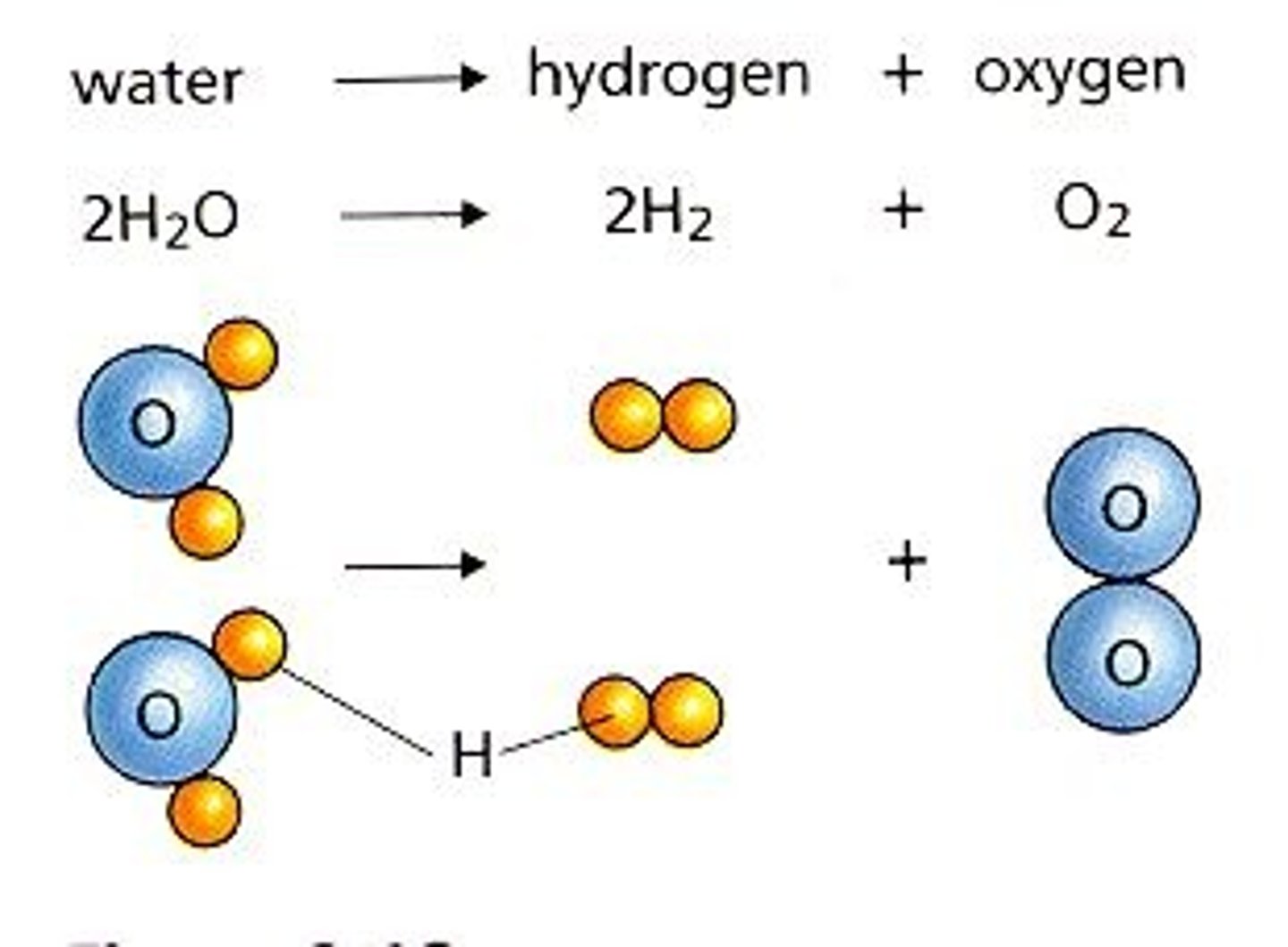
decomposition reactions
one reactant breaks down to form two or more products. The general form for a decomposition reaction is shown below.
AB → A + B
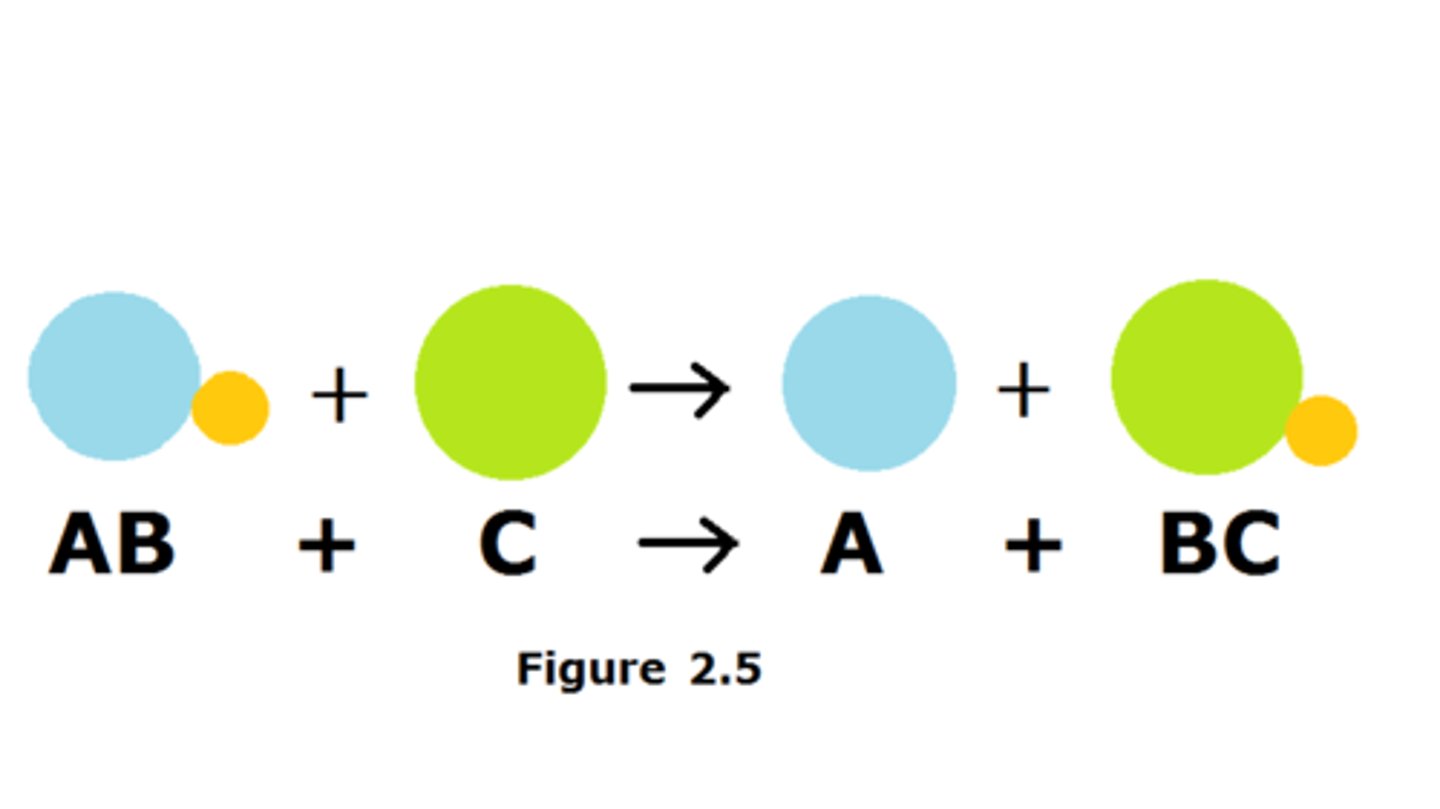
single replacement reactions
one element replaces another element in a compound to form a new substance. Single-replacement reactions have the same number of reactants as products. Replacement reactions are also called displacement reactions. The general form for a single-replacement reaction is shown below.
A + BC → AC + B
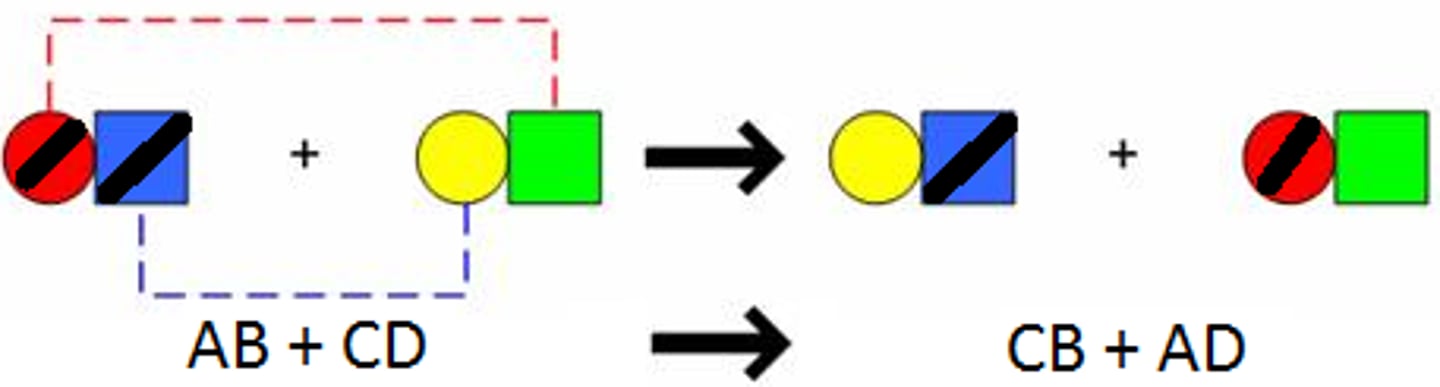
double replacement reactions
he ions of two different compounds in an aqueous solution exchange places to form two new compounds. One of the products formed is typically a solid (or precipitate), a gas (bubbles), or water. The other product usually remains dissolved in the solution. The general form for a double-replacement reaction is shown below.
AC + BD → AD + BC
acid-base reactions (neutralization reaction)
an acid and a base react to form salt and water. An acid-base reaction is also called a neutralization reaction
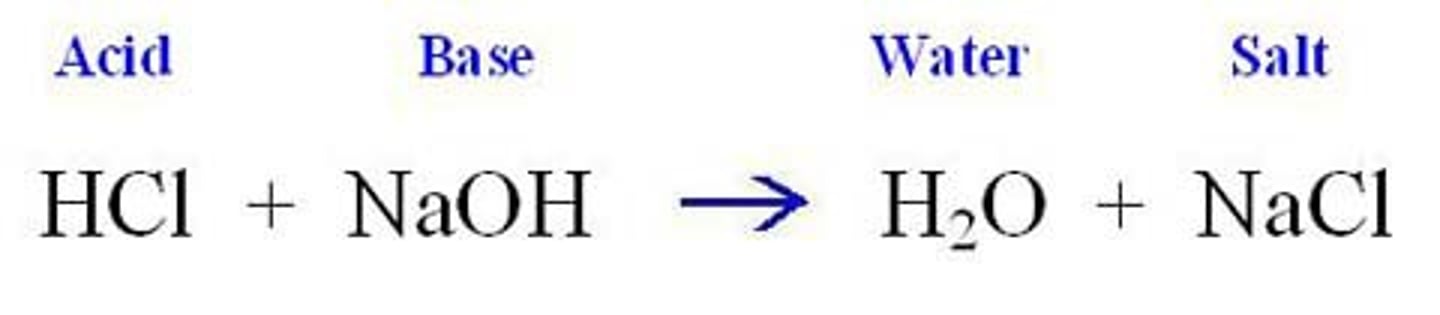
exothermic
release energy
Endothermic
Energy needed to break chemical bonds
Products
The end result of a chemical reaction
Reactants
The beginning ingredients of a chemical reaction
Ca(OH)₂ + H₃PO₄ →
Ca₃(PO₄)₂ + H₂O
HCl + Mg(OH)₂ →
MgCl₂ + H₂O
HCl + NaOH →
NaCl + H₂O