39 & 40 - Plant Reproduction & Vegetative propagation
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
DIAGRAMS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Give a brief biological explanation for fruit formation by plants
To aid seed dispersal
What is meant by the term vegetative propagation?
Asexual reproduction in plants
Give two methods of vegetative propagation and an example of each
Stem: strawberry (runners)
Root: dahlia
Give three methods horticulturists use to artificially propagate plants
Cutting (e.g. Busy Lizzy)
Grafting (e.g. rosebush)
Micropropagation (e.g. orchids)
Layering (e.g. blackberries)
Which part of the embryo in the seed gives rise to
the root
the shoot
Radicle
Plumule
What is meant by seed dispersal?
The scattering or spreading of seeds away from the parent plant
Give two methods of seed dispersal
Wind
Water
Animal
Self
Give one advantage of seed dispersal
To minimise competition for the parent plant /
To colonise new habitats
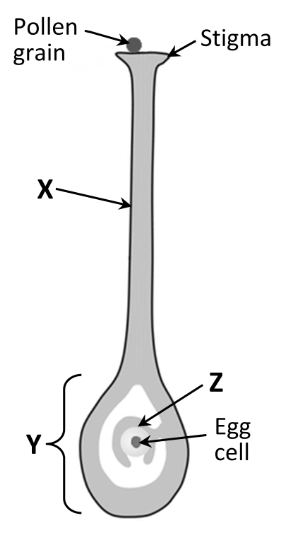
Name X, Y and Z
X: style
Y: Ovary
Z: Ovule
Give one way other than animals that the pollen grain can be carried to the stigma
Wind
Draw in a pollen tube to show the path taken by the male gametes
Describe how the generative nucleus becomes the male gametes
Generative nucleus divides by mitosis to produce two sperm nuclei
Give an account of the development of the egg cell
Diploid / megaspore mother cell / divides by meiosis / produces four haploid cells / three degenerate / divides by mitosis three times / embryo sack has eight nuclei / one becomes egg cell / two polar nuclei
Describe what happens in double fertilisation
Egg cell fuses with one sperm nucleus to form a diploid zygote
Two polar nuclei fuse with one sperm nucleus to form triploid endosperm
State the collective term used to describe the anther and the filament of the flower
Stamen
Outline the development of the pollen grains in the anther
Diploid / mother cell / divides by meiosis / to produce four haploid cells / divides by mitosis / pollen grain with two nuclei / generative nucleus / tube nucleus
What is pollination?
The transfer of pollen from the anther to the stigma
Give two methods of pollination
Animal
Wind
State the location where food is normally stored in a:
monocotyledonous seed
dicotyledonous seed
Endosperm
Cotyledon
Describe how seeds contribute to the formation of fruit
The seed produces growth regulator
Name the part of the flower that becomes the fruit
Ovary
Outline one role of genetics in fruit production
Seedless fruit or more advantageous traits
Describe the role of each of the following in germination:
Digestion
Respiration
Makes nutrients available
Release of energy from food in the form of ATP
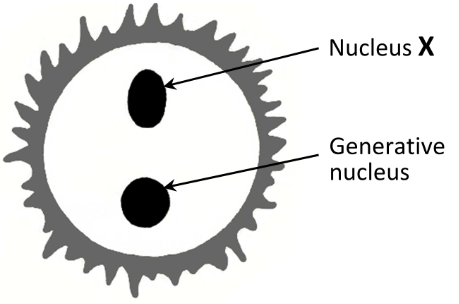
State the function of the nucleus X
Forms the pollen tube
Describe what happens to the generative nucleus following pollination
Divides by mitosis
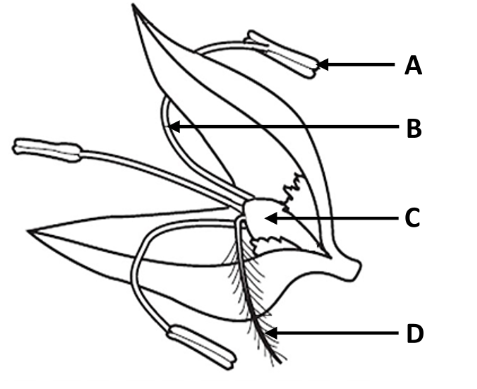
Label the structures A, B, C and D
A: Anther
B: filament
C: Ovary
D: Stigma
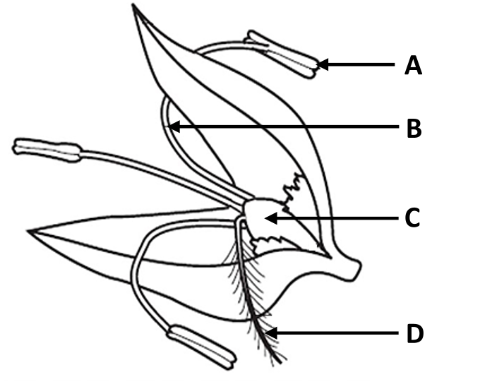
Is this plant insect or wind pollinated?
Give two reasons for your answer
Wind
Large stigma (or anther)/ feathery stigma / stigma (or anther) outside the flower / long style (filament)
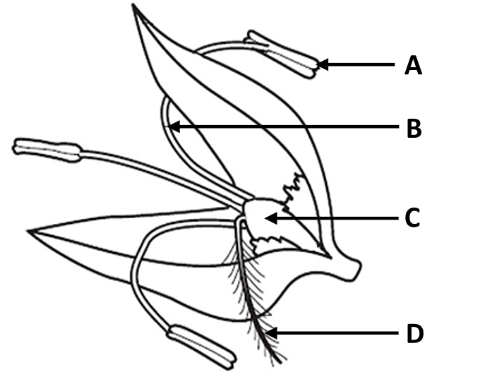
What is the role of parts A and D?
A: produce pollen
D: trap pollen
Give one disadvantage of self pollination
Less variation or offspring more susceptible to disease
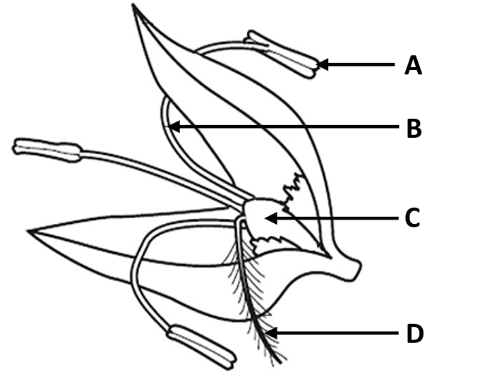
Which labelled part develops into the fruit?
C - ovary
How are seedless fruits developed?
Sprayed with growth regulators or auxins
State two advantages of sexual reproduction versus asexual reproduction in plants
Variation / seed dispersal / less competition / less disease
Describe in detail the development of the embryo sac from a megaspore mother-cell
Embryo sac mother-cell (diploid) divides by meiosis
Four haploid cells produced
Three degenerate, haploid embryo sac remaining
Undergoes mitosis x3 giving eight nuclei
Embryo sac swells with food from nucellus
Five nuclei degenerate
Two polar nuclei and one egg cell remain. These are the female gametes
Give two features of vegetative propagation
One parent / no gametes (or no seeds) / no variation
Give one example of natural vegetative propagation from and leaf and one example from a bud
Leaf: plantlets (cactus)
Bud: Bulb (Daffodil / onion)
Suggest a benefit of artificial vegetative propagation
Rapid / desirable characteristics maintained
What structure leads to the formation of the seed’s testa?
Integumens
Name two biomolecules stored in endosperm or cotyledon tissue
Lipids / carbohydrates / protein / vitamins
Give one way knowledge of seed dormancy has been useful to humans
How to store seeds or maximise the growing season
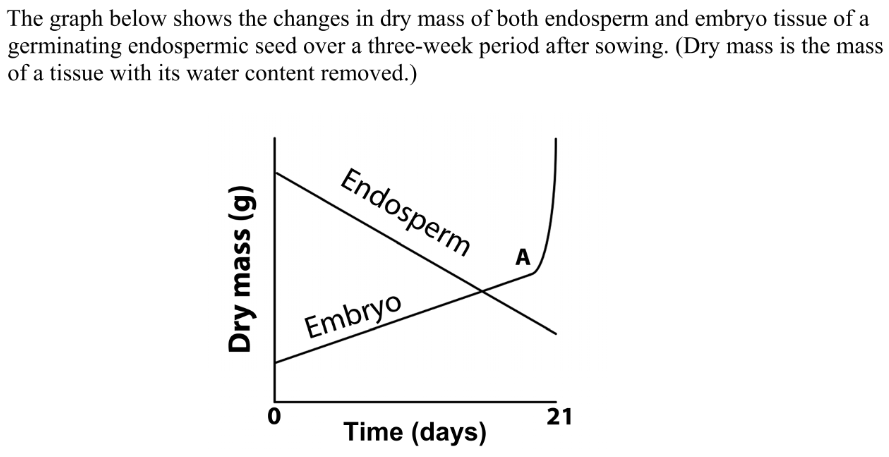
Suggest why the measurement of dry mass is preferred in investigations
Water content can vary between seeds
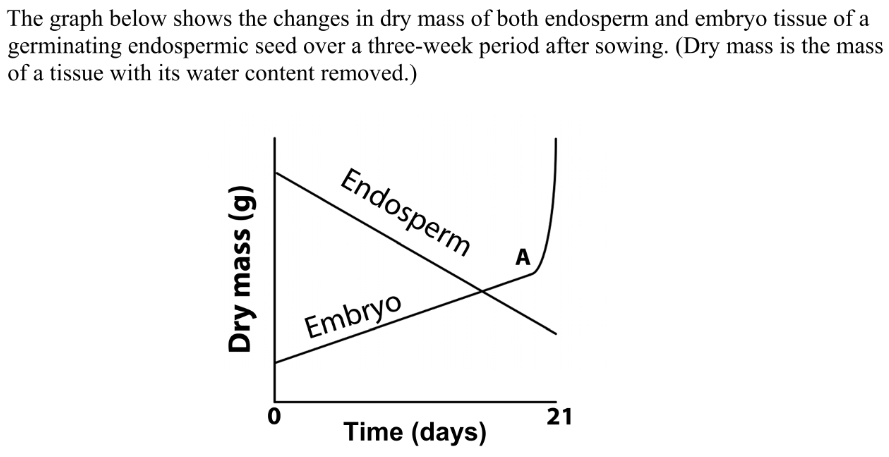
Explain why the dry mass of the endosperm tissue decreases over the three weeks
Food is transferred to the embryo or respiration is occurring for energy or loss of CO2
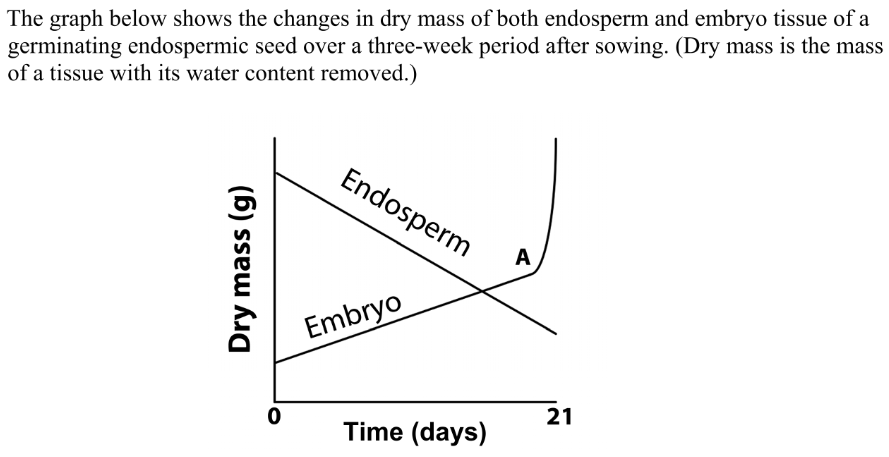
What process begins at A?
Photosynthesis
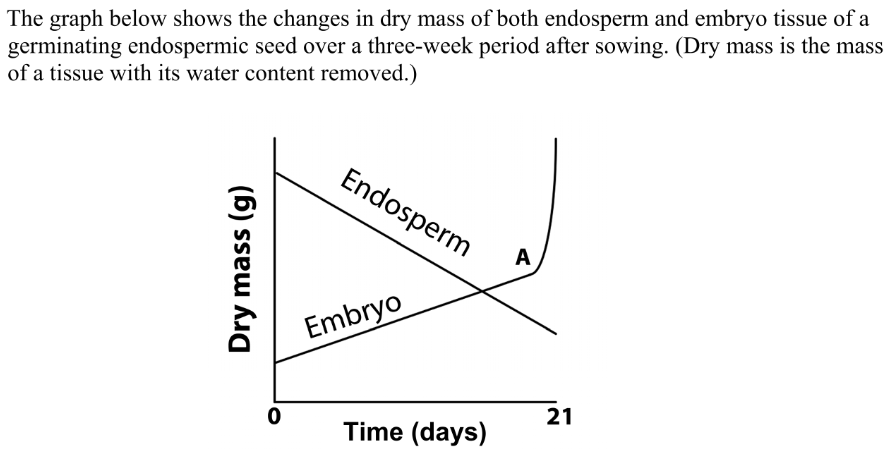
Would you expect the total dry mass of the seed (embryo + endosperm) to have remained the same up to A
No
it will lose mass due to respiration / loss of CO2