nucleophilic substitution (SN1 and SN2)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is SN2 short for

what is SN2 and what are the species
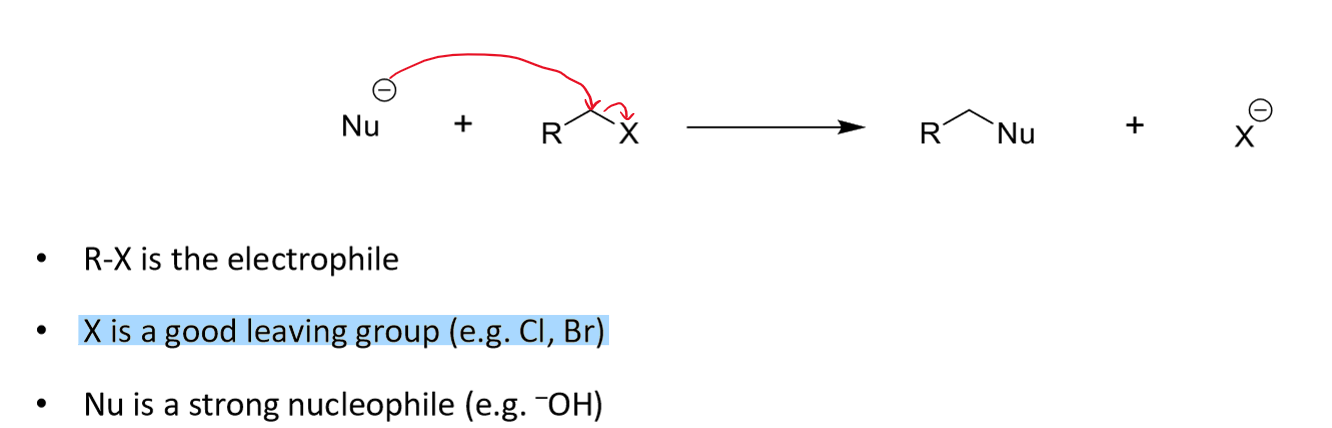
steps in SN2
it is a concerted reaction so happens in one step
Nu-C forms and C-X breaks in same step
rate determining step for SN2
both Nu and E are in the RDS as the reaction is only one step - there is evidence for them both being in the RDS which supports the SN2 mechanism
as they are both in the RDS the properties of both species are significant
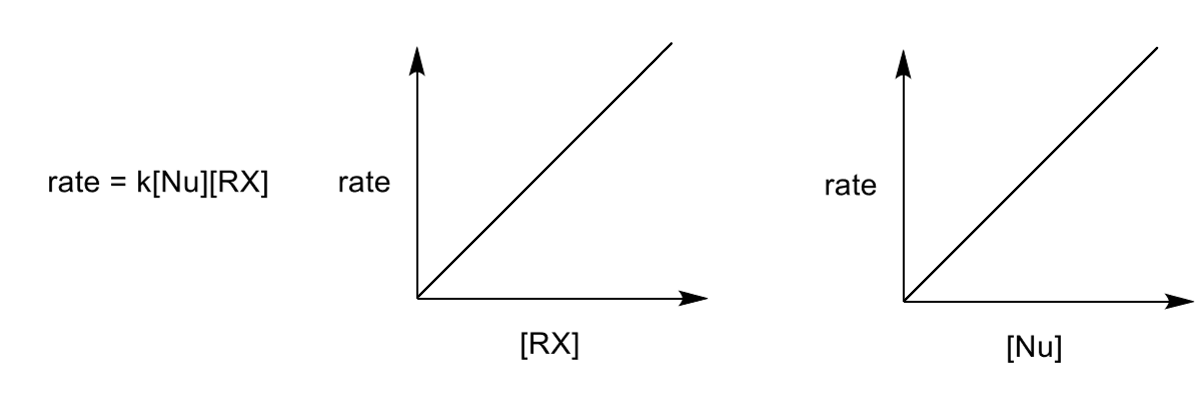
rate profile and transition state properties for SN2
high energy transition state which gives high energy maximum in rate profile. it cannot be isolated.
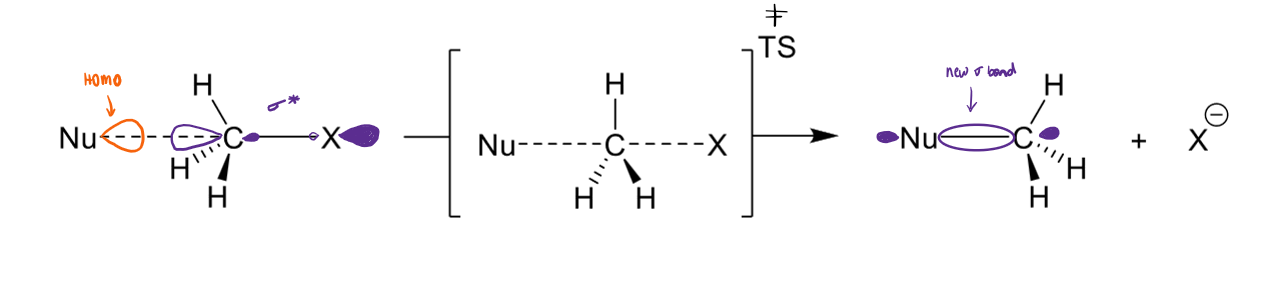
orbitals of SN2
Nu attacks σ* (LUMO) of C-X bond
Nu has to attack at 180° to have good orbital overlap
the transition state forms when the new bond is forming and the old bond is breaking at the same time
make sure have flipped the Hs properly
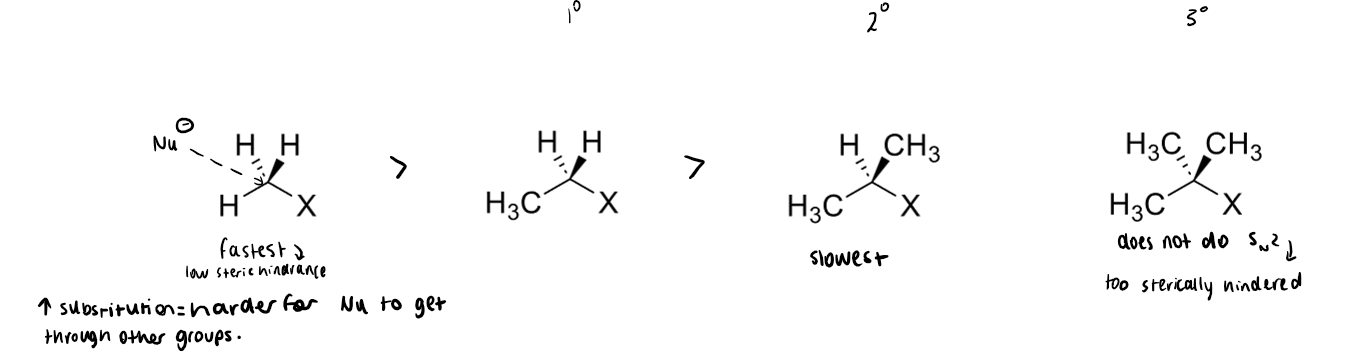
sterics of SN2
SN2 works well when there is little steric hindrance to prevent the nucleophile from attacking behind the C-X bond. increasing substitution makes it harder for Nu to get through the groups.
CH3X is fastest. primary slower, secondary slowest. tertiary too sterically hindered so does not do SN2.
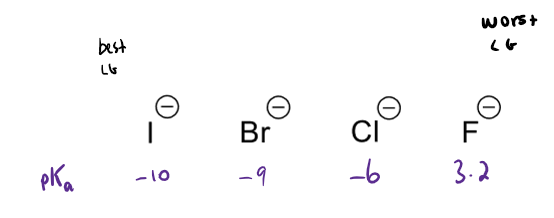
properties of good leaving groups (SN2)
need to be stable
low pKa = stable conjugate base = good leaving groups (LG)
good SN2 LGs
alkyl halides
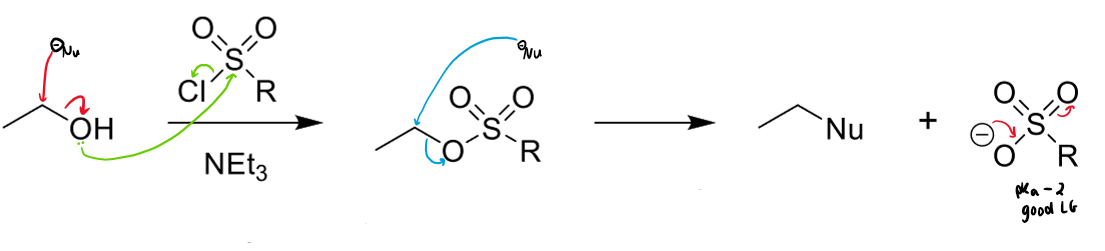
how can alcohols/ethers be made into better LGs
can be turned into more stable tosylate/mesylate groups
conversion of alcohols to better leaving groups using MsCl or TsCl
other reagent needed?
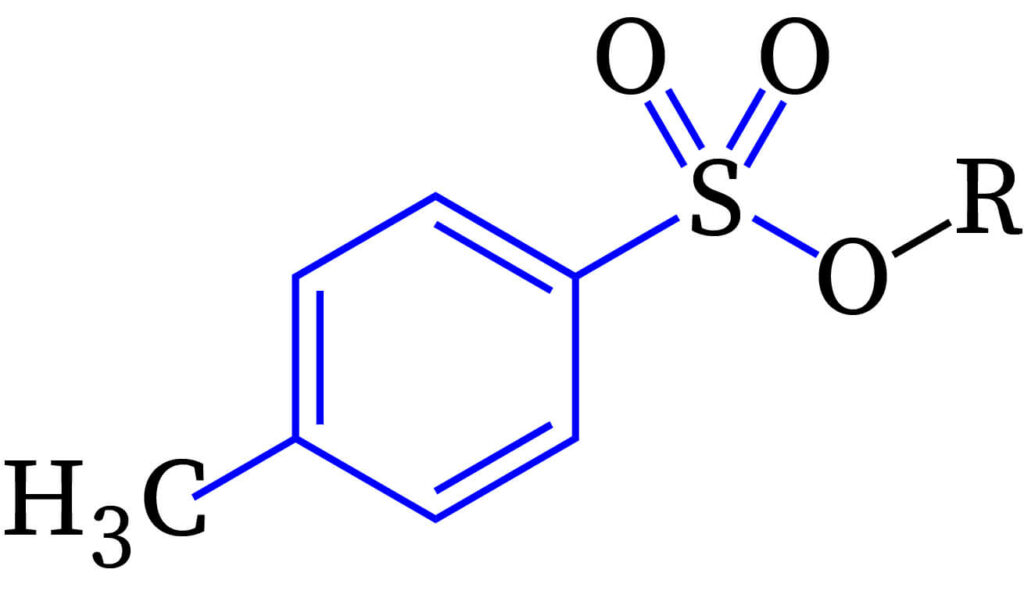
mesylate group and short name
Ms

tosylate group and short name
Ts
properties of good nucleophiles (SN2)
high energy HOMO to overlap with the LUMO of the electrophile
negative charge best, lone pair next best
higher pKa tends to be better Nu - anions less stable to they want to react making them stronger nucleophiles
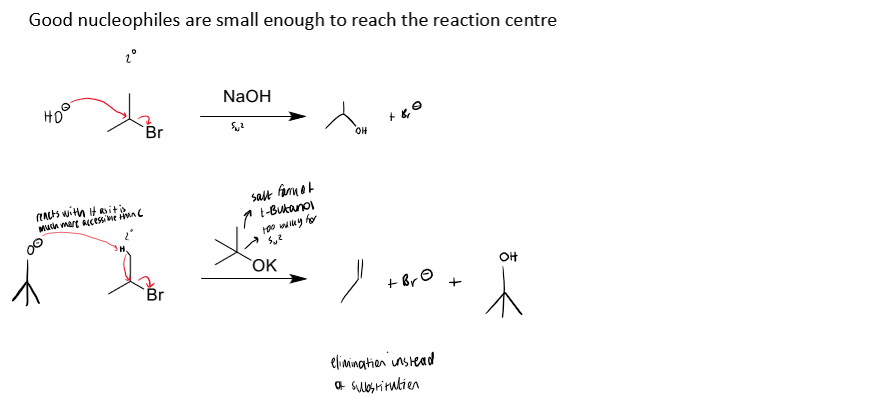
small nucleophiles are better able to reach the reaction centre
examples of good SN2 nucleophiles
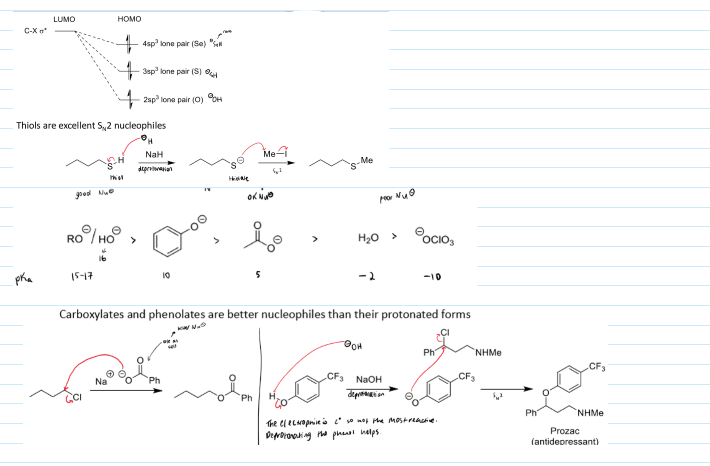
example of size of nucleophile impacting SN2
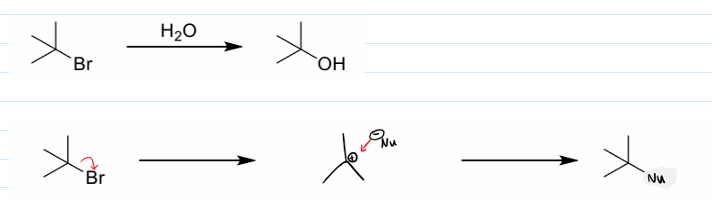
what is SN1 short for

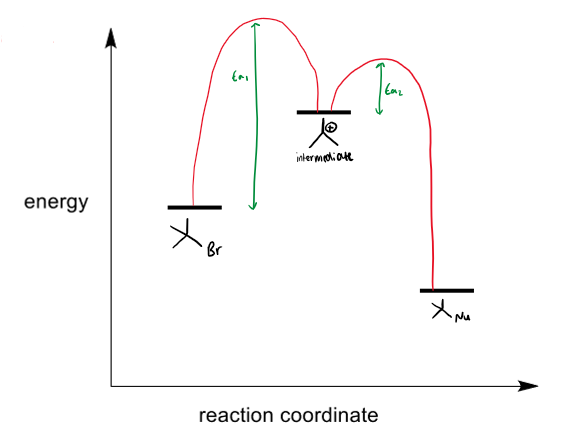
what is SN1 and its steps
substitution of a nucleophile on an unsaturated (sp3) carbon over 2 steps in the first step, the leaving group leaves and in the second step the nucleophile attacks
reaction kinetics of SN1
only the electrophile is involved in the RDS, which confirms the mechanism
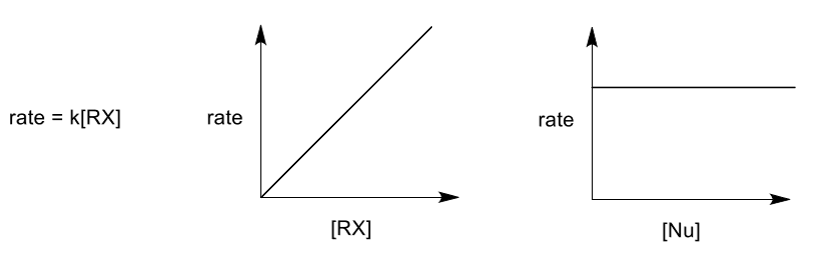
SN1 rate profile
reaction proceeds through a carbocation intermediate which is isolatable. the carbocation must be stable.
the EA of step 1 is greater than the EA of step 2 (as 1 is the RDS)
nucleophiles for SN1
can use any strength including weak unlike SN2
electrophile properties for SN1
stable carbocation can be formed from having more substitution
the carbocation has an empty p-orbital. adjacent methyl groups (eg) can stabilise it via hyperconjugation.
unsubstituted electrophiles don’t do SN1 without some other kind of effect to stabilise the carbocation
carbocation could also be stabilised by +M instead