Lecture 6: Nasal Cavity and Pterygopalatine Fossa
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Nasal Cavity Development
Nasal pit without communication to oral cavity
Barrier between nasal and oral cavities breaks down
Nasal and oral cavities continuous, olfactory system develops, palate forming
Nasal and oral cavities separated by palate, olfactory system established, conchae developing, sinuses initiate later (term)
Nose Cartilage
CARTILAGE (hyaline)
Septal cartilage with broad lateral processes
Nares bounded by the U-shaped alar cartilage
Alar fibrofatty tissue
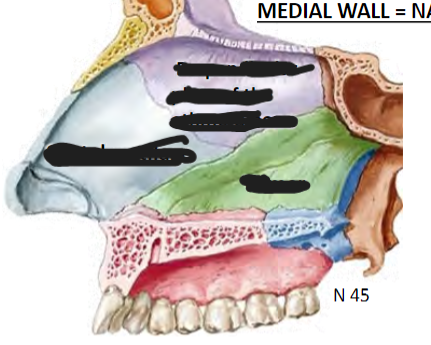
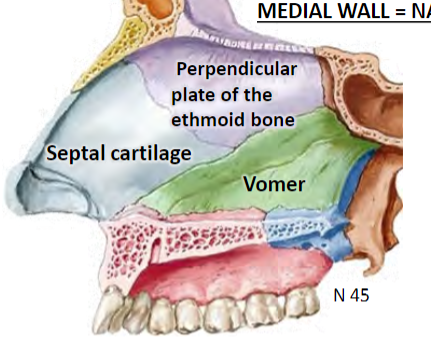
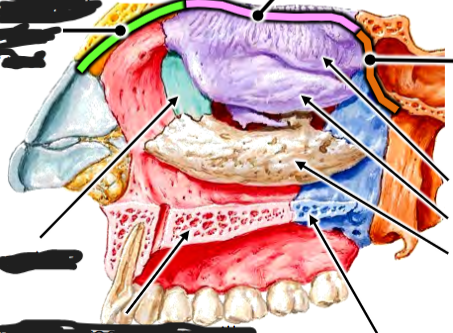
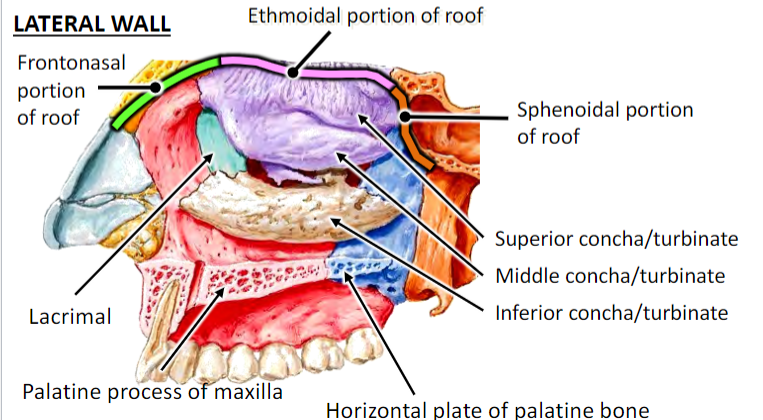
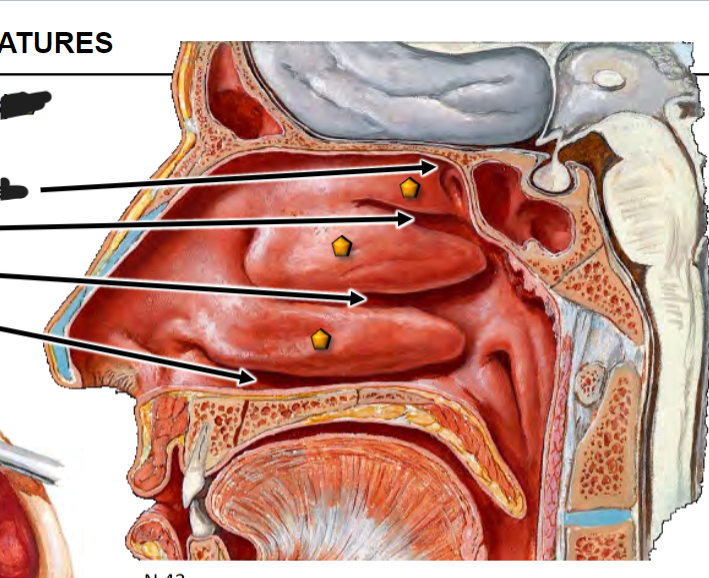
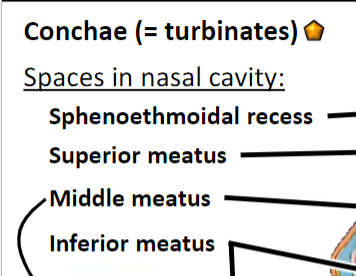
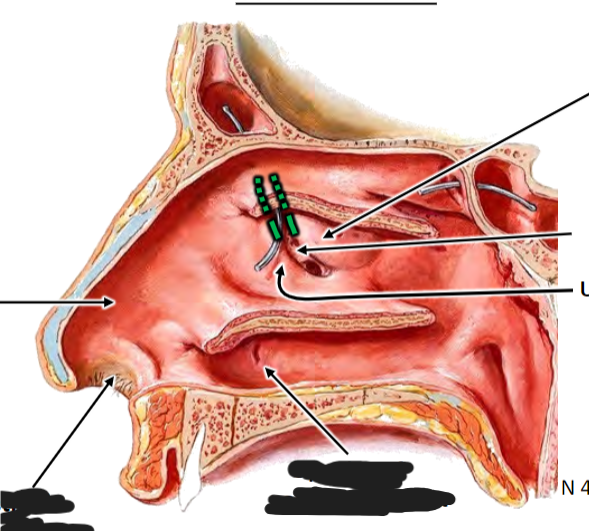
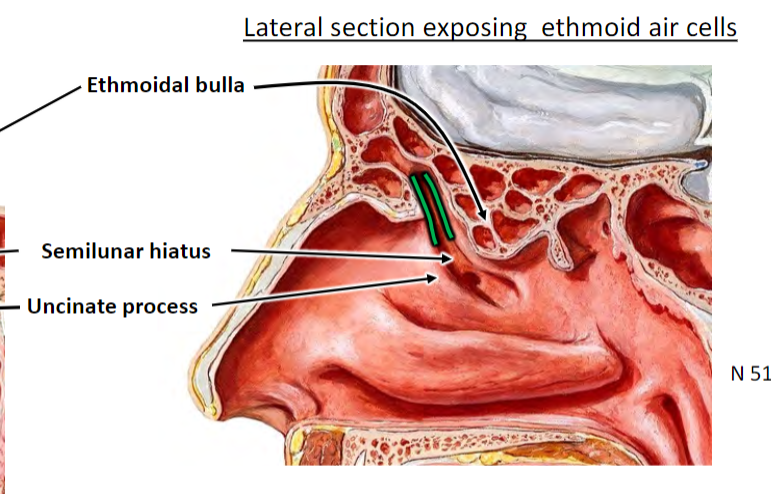
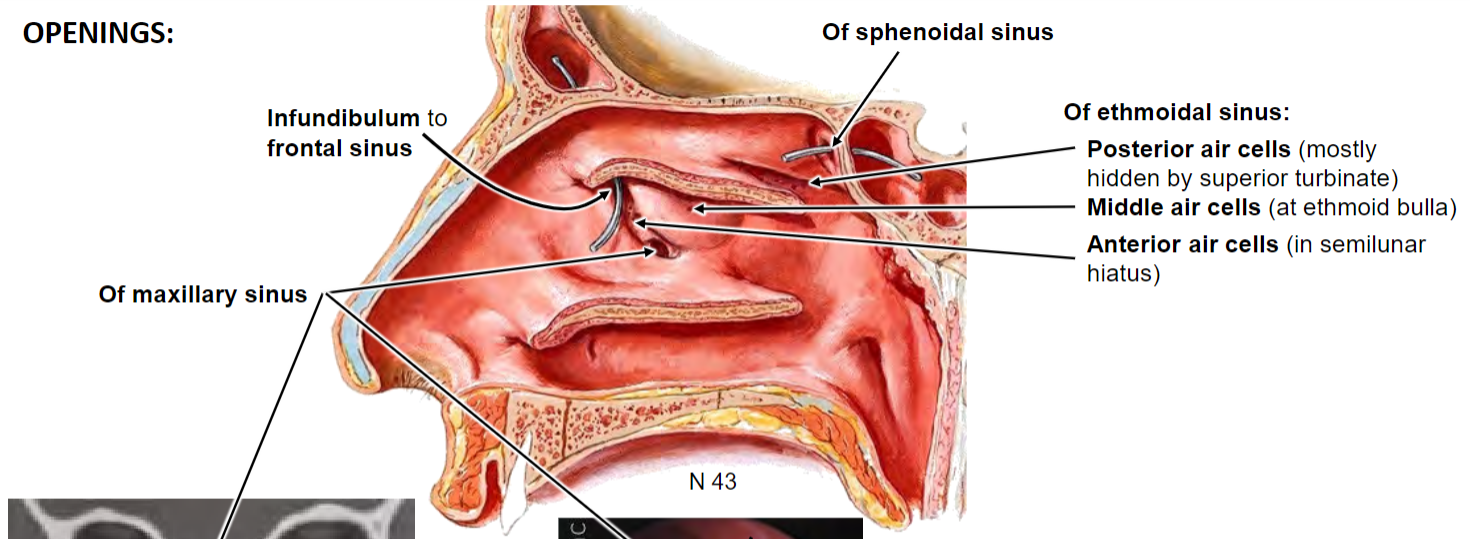
Infundibulum is opening of frontal sinus; concern for frontal sinus infection
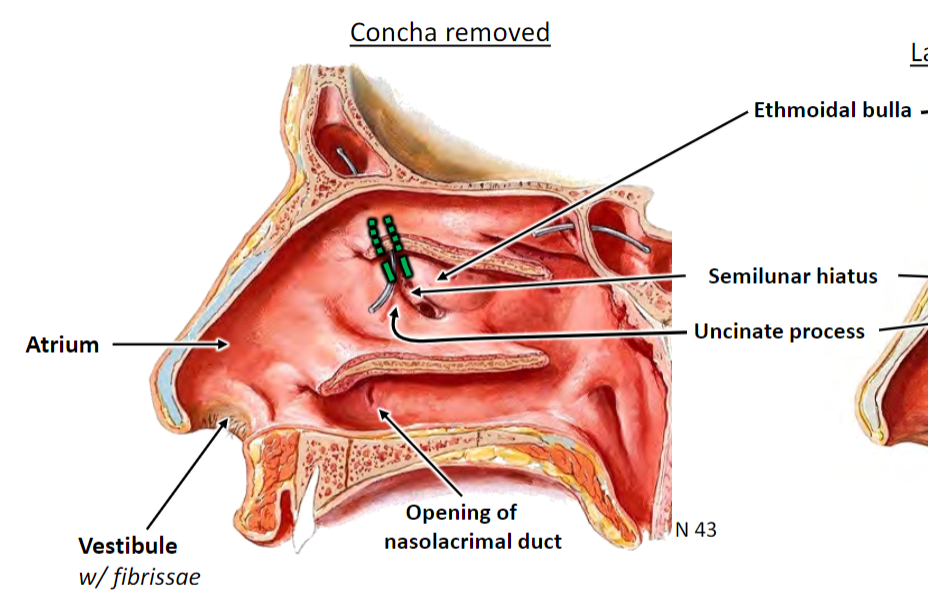
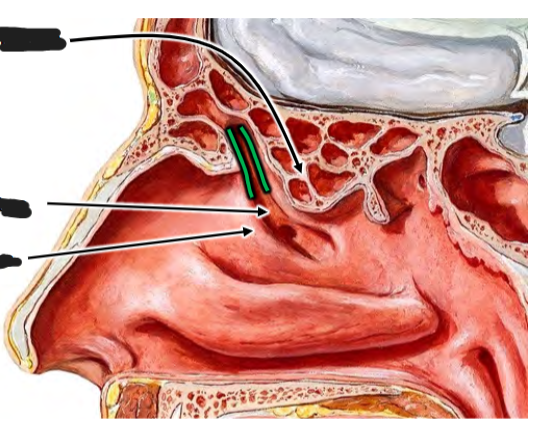
Infundibulum is opening of frontal sinus; concern for frontal sinus infection
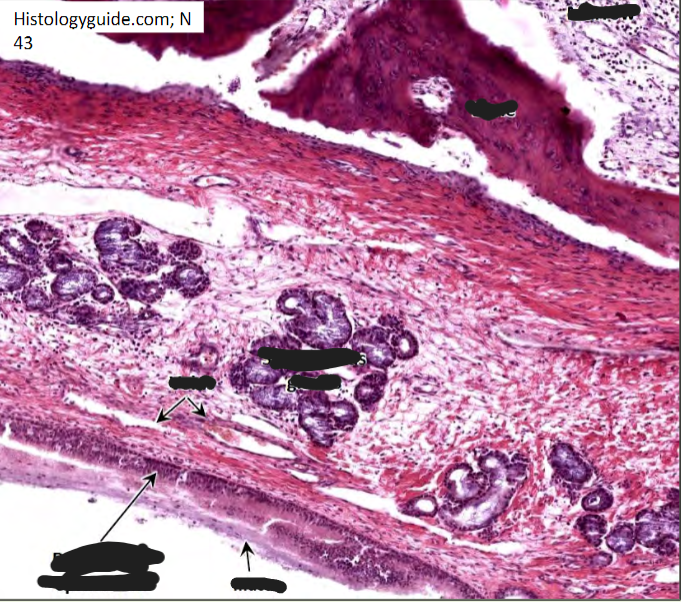
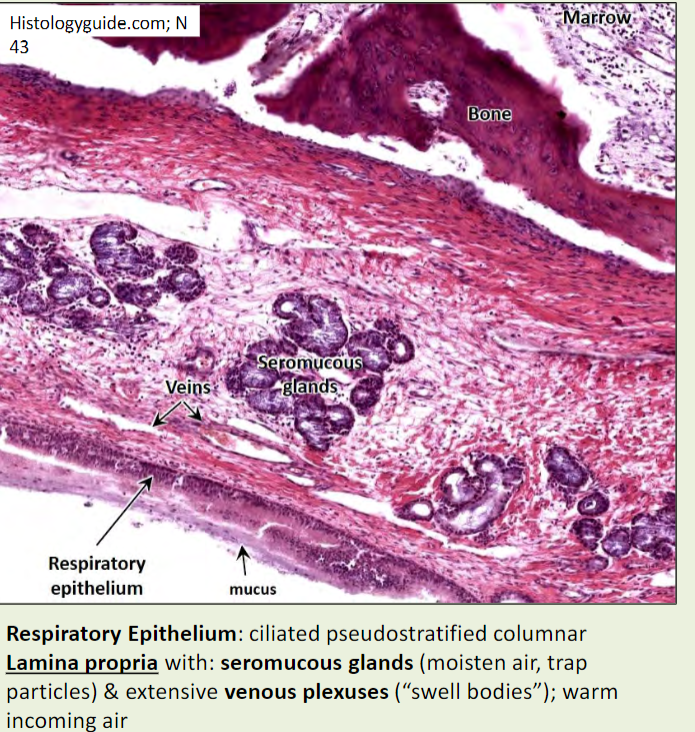
Nasal mucosa
Bound tightly to periosteum: Mucoperiosteum
Parasympathetic visceral motor (VE) of mucus glands: CN VII via pterygopalatine ganglion
Extends into the paranasal air sinuses
Aids in olfaction, humidification, cleansing, thermoregulation
Swells/shrinks to control caliber of nasal cavity (activity related)
Swells rapidly with rhinitis (infection), can prevent sinus
drainage or spread to sinuses

Rhinorrhea
Discharge from mucous membrane: “runny nose”
Rhinitis
Inflammation of nasal mucosa, may spread to:
1. Anterior cranial fossa via cribriform plate
2. Nasopharynx/retropharyngeal soft tissues via choanae
3. Middle ear via pharyngotympanic (eustachian) tube
4. Paranasal sinuses via openings
5. Lacrimal apparatus/conjunctiva via nasolacrimal duct
CSF Rhinorrhea
CSF discharge through nose
Fracture of cribriform plate
May result in Meningitis
Serious injury
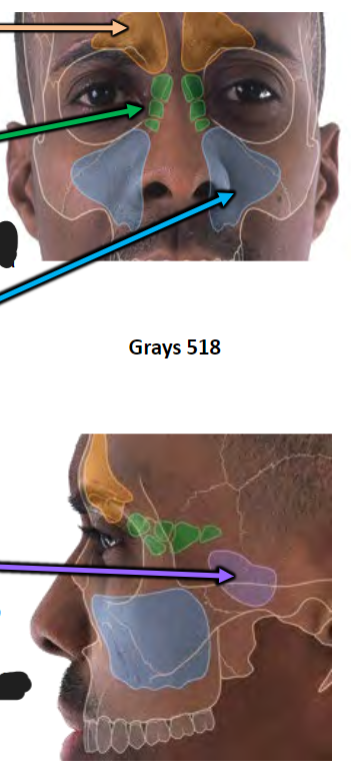
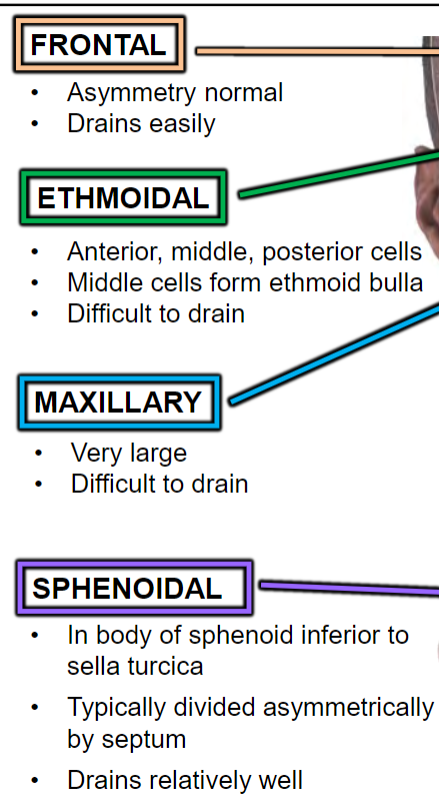
Paranasal Air Sinuses
Grow from nasal cavity
Continuous mucosa
Lighten skull
Add resonance to voice
Born with small ethmoidal, rudimentary maxillary, sphenoidal sinuses
Sinusitis
Maxillary sinusitis-most common:
Maxillary sinus is difficult to drain
Teeth and sinus share sensory innervation
Ethmoid/sphenoid sinusitis:
Proximity to optic nerve (CN II) can put pressure on optic nerve or lead to optic neuritis
Transillumination of sinuses
Healthy is warm, red glow
Lack of glow—congestion/infection likely
Blow out fracture and the maxillary sinus
Inability to look up due to entrapped inferior rectus muscle
Mechanical concern
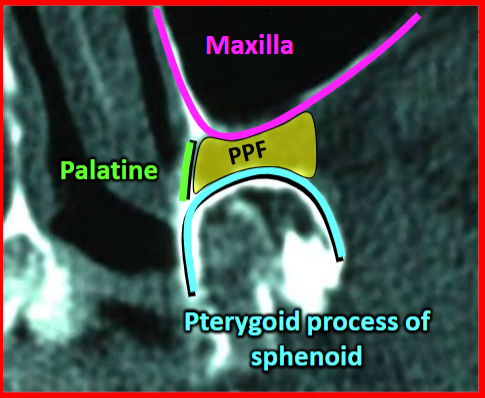
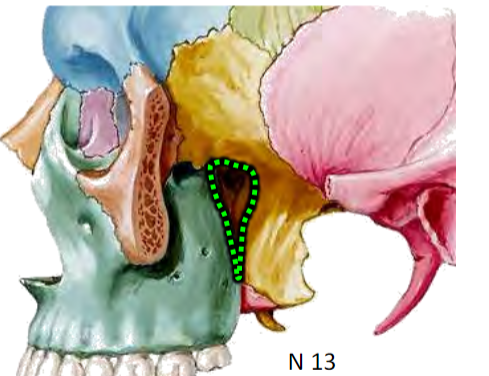
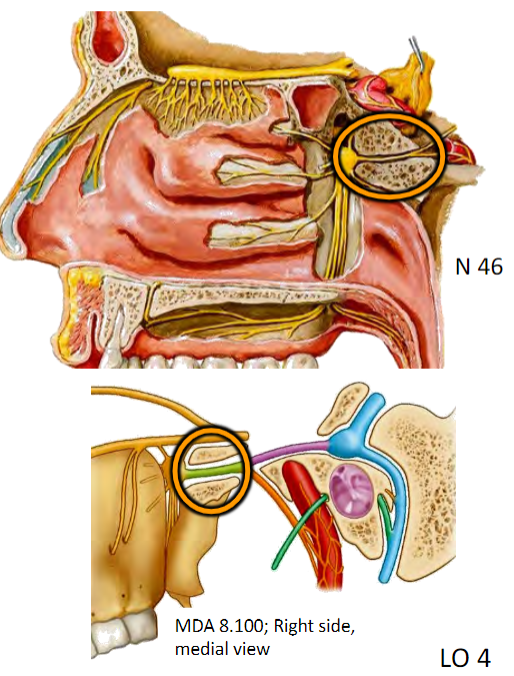
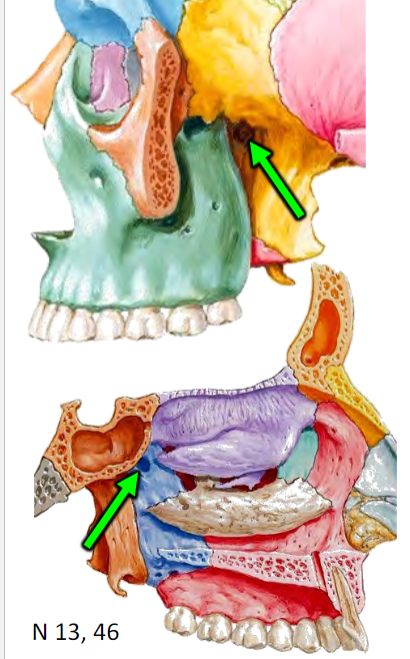
Pterygopalatine fossa
Between the neurocraniun and viscerocranium
Distribution hub for maxillary artery and maxillary nerve branches
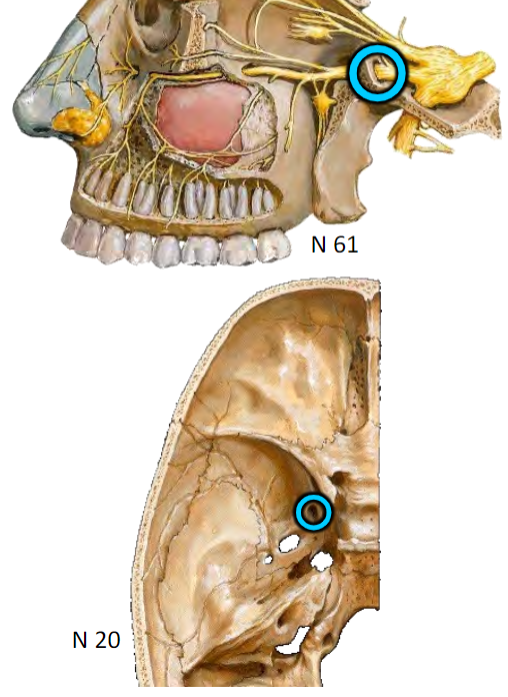



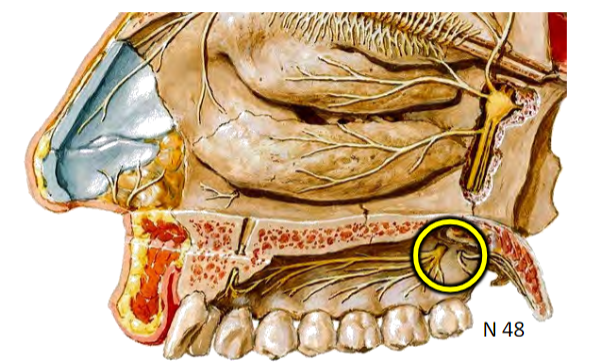


All are branches of the Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
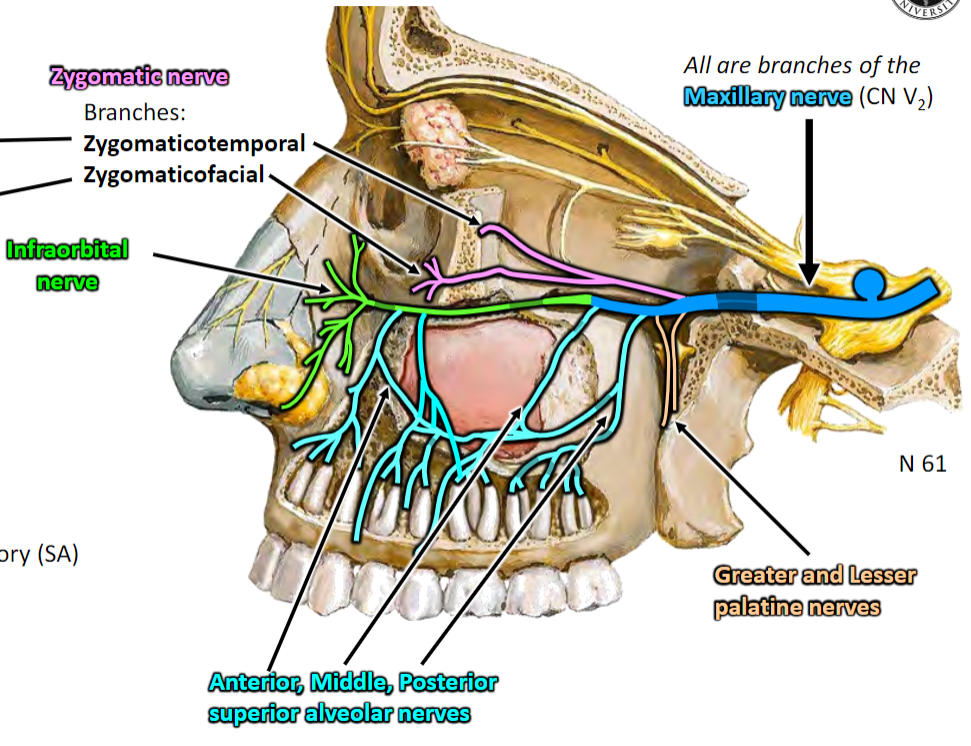
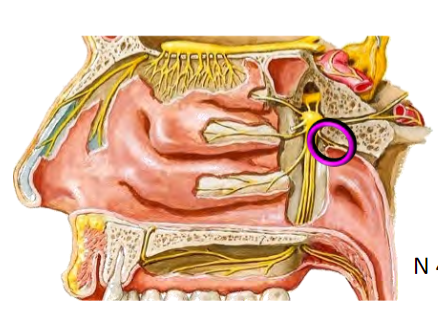
Somatic sensory (SA) branches of Maxillary nerve (CN V2) to NASAL CAVITY via Sphenopalatine foramen
Nasopalatine nerve: To nasal septum, anterior hard palate (via incisive canal)
Posterior lateral nasal branches: To lateral nasal wall
Somatic sensory (SA) branches of Maxillary nerve (CN V2) to PALATE via Lesser and Greater palatine foramina
Lesser and Greater palatine nerves
Hard and soft palate, respectively
Somatic sensory (SA) branches of Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
Brs. of superior labial nerve branch of Infraorbital nerve (CN V2) To vestibule
Somatic sensory (SA) branches of CN V1
Anterior ethmoidal n. Branches
From orbit to anterosuperior nasal cavity
Olfaction
Olfactory nerve (CN I) fibers
Visceral (chemical) sensory (VA)
Cell bodies in olfactory epithelium
Fibers arise in olfactory mucosa (lateral wall &
septum)
Fibers pass through the olfactory foramina of
cribriform plate
Synapse in the olfactory bulb
Pterygopalatine (= sphenopalatine) ganglion
Distribution hub for PARASYMPATHETICS to nasal cavity, palate, nasopharynx
Suspended by pterygopalatine nerves of CN V2
Composed of postganglionic parasympathetic cell bodies
Secretomotor (VE) to palatal, nasal, nasopharynx mucosal mucus glands & lacrimal gland
Overstimulation results in hay fever-like symptoms: watery eyes, runny nose, excessive palatal and pharyngeal mucous
Preganglionic Parasympathetic Fibers
Cell bodies in brainstem
Fibers course within CN VII
Then onto greater petrosal nerve [near geniculate ganglion]
Joins with deep petrosal n. to become nerve of the pterygoid canal
Synapse in pterygopalatine ganglion
Postganglionic fibers “hitchhike” on somatic sensory branches of CN V2 to target mucosa/glands
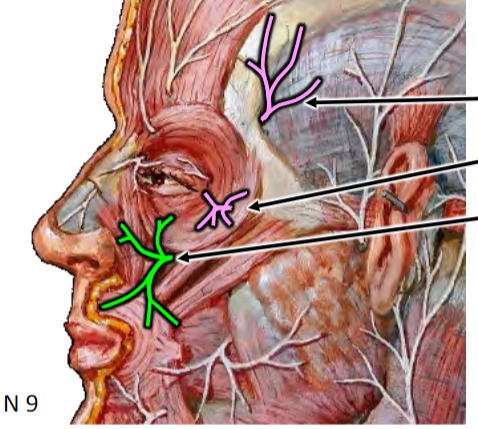
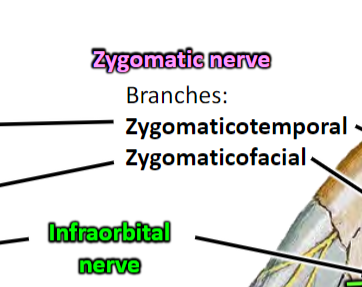
Innervation to Lacrimal Gland
INDIRECT: Pterygopalatine ganglion → Maxillary n. → Zygomatic branch → communicating branch → Lacrimal n. (CN V1)
DIRECT: Communicating branch direct to lacrimal gland
Postganglionic Sympathetic Fibers
Arise from superior cervical ganglion
Course on periarterial plexus of Internal Carotid artery
Fibers become Deep petrosal n.
Joins with Greater petrosal n. to become nerve of pterygoid canal
Fibers pass through pterygopalatine ganglion without synapsing
Primarily function for vasoconstriction
Pterygopalatine fossa—distribution hub for Maxillary artery
TO FACIAL-MAXILLARY REGION:
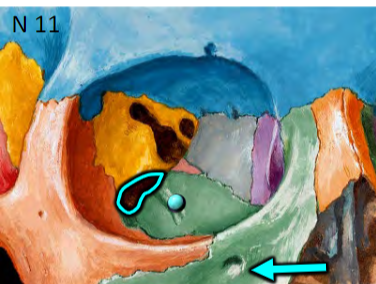
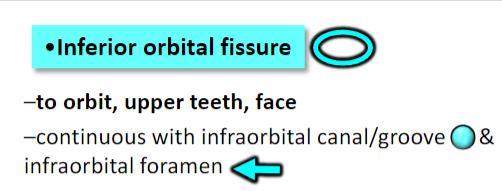
Infraorbital artery (via inferior orbital fissure/infraorbital
canal)
Superior alveolar arteries to maxillary teeth
TO NASAL CAVITY:
Sphenopalatine artery to nasal cavity
TO PALATE:
Descending palatine artery
Greater palatine artery to hard palate via greater palatine foramen
Lesser palatine artery to soft palate via lesser palatine foramen
INTERAL CAROTID ARTERY SUPPLY
From ophthalmic artery (branch of internal carotid artery)
Septal and lateral branches of anterior & posterior ethmoidal arteries
EXTERNAL CAROTID ARTERY SUPPLY
Maxillary artery (branch of external carotid artery)
To nasal cavity:
Septal branch of sphenopalatine artery: to septum and anterior hard palate (via incisive canal) with anastomosis with Greater palatine artery
Sphenopalatine artery to nasal cavity
Posterolateral branches of sphenopalatine artery: to lateral wall
Epistaxis
Nose bleed
KIESSELBACH’S PLEXUS (= LITTLE’S AREA):
Dense arterial anastomoses
Area of ~90% of all epistaxis
“G-A-S-S”
1. Greater palatine a.
2. Anterior & posterior ethmoidal aa.
3. Sphenopalatine a.
4. Superior labial a.
DRIPPING—typically venous (thin-walled, more superficial)
SPURTING—typically arterial
Nasal Venous Drainage
Plexus of veins in mucosa drain blood via:
Veins in nasal cavity play major role in thermoregulatory system of body
Veins tend to be superficial to arteries in mucosa and are thin-walled: bleed first
Danger triangle—infection can spread to cavernous sinus/dural sinuses via facial/nasal veins
Facial vein via superior labial
Sphenopalatine vein to maxillary vein/pterygoid venous plexus
Inferior ophthalmic vein (to cavernous sinus)
Nasal Lymphatics
Most of nasal cavity drains to deep superior cervical nodes, particularly jugulodigastric (pharynx pattern)
Vestibule area drains to submandibular nodes (facial pattern)
Anosmia
Loss of smell
Test unilaterally
Complaint typically is a “loss of taste” (is actually diminished “flavor”)
May be caused by injury to the olfactory nerves at or near the cribriform plate
Clue to skull fracture; May be associated with CSF rhinorrhea