Geriatrics-Week 1
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
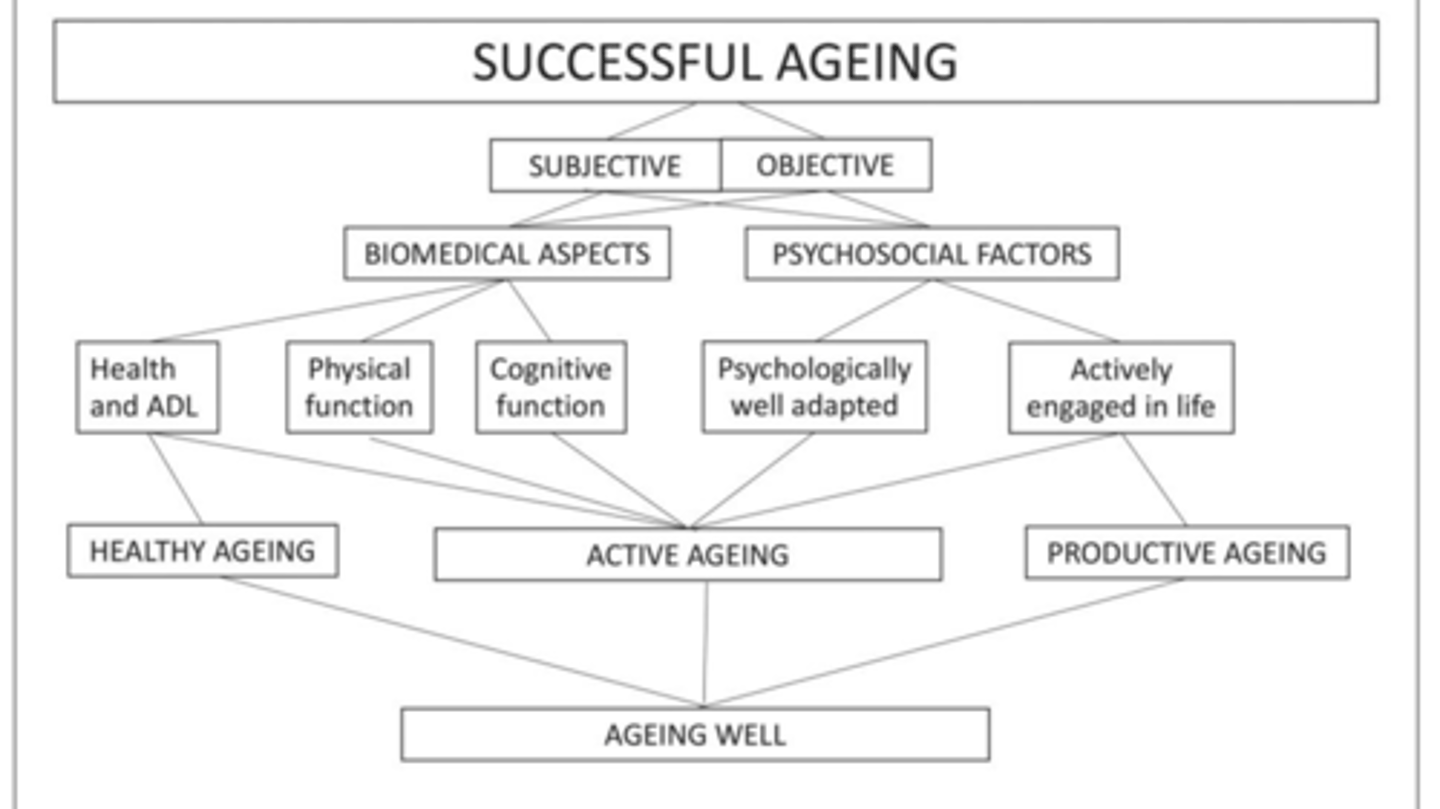
successful aging involves both subjective and ______________ factors
objective
successful aging involves ___________ aspects and ________________ factors
biomedical, psychosocial
successful aging biomedical aspects (3)
1. health and ADL
2. Physical function
3. cognitive function
successful aging psychosocial factors (2)
psychologically well adapted, actively engaged in life
true or false: healthy aging, active aging, and productive aging are all factors in aging well
true
true or false: between 2014 and 2060 the number of americans 65 years and older is increasing from 15% to 24% of population
true
Hayflick limit theory
limited cell population doubling, average being 50 per life cycle
evoluntionary theory
each successive generation is more resistant to mutations
stress theory
resistance to stress by the genes
neuroendocrine and hormonal theory
neurons and associated hormones central to aging
theory of intrinsic mutagenesis
specific characteristics of genes that regulate rate of errors
immunological theory
immune system declines w age
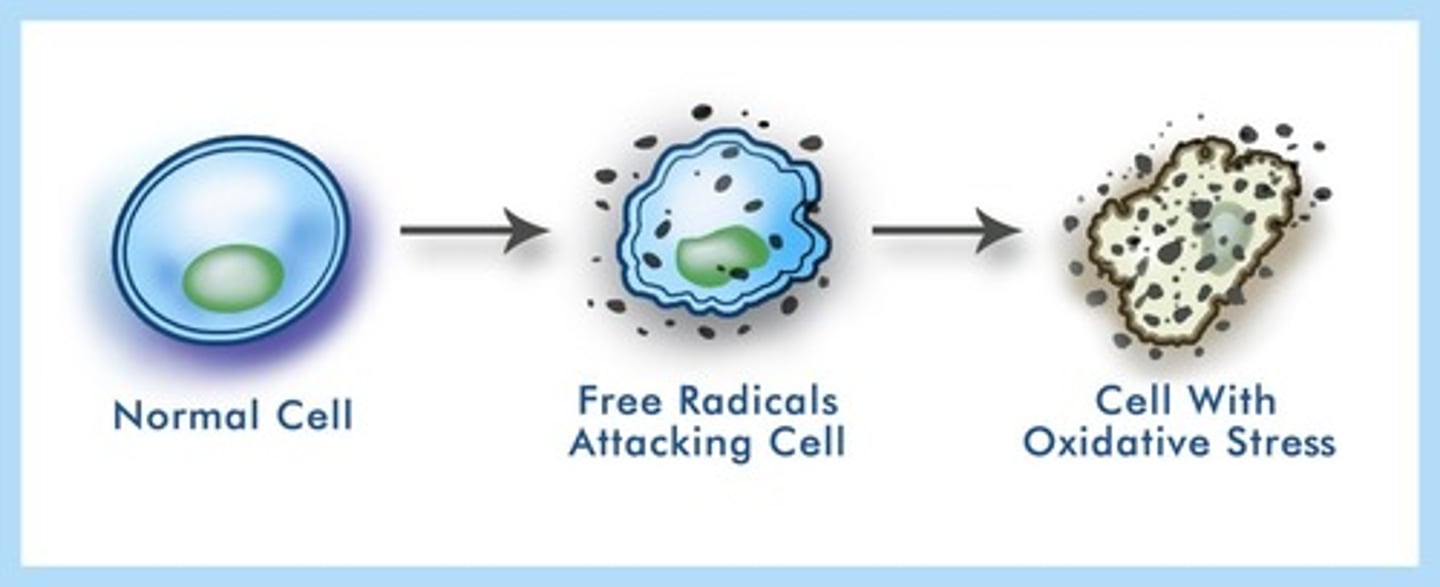
free radical theory
damage caused by free radicals
caloric restriction theory
high-nutrient and low-calorie diet is beneficial

error theory
error in making proteins causes multiple effects
redundant DNA theory
errors accumulating in genes
somatic mutation theory
mutations or genetic damage from RADIATION

transcription theory
aging exists in nuclear chromatin theory
cross-linkage theory
large reaction proteins, cross link, responsible for aging
stochastic theories
view aging as the result of random cellular damage that occurs over time (error theory, transcription theory etc. )
sleep and aging theory
prolonged sleep loss affects homeostasis

growth hormone theory
too much GH and not enough insulin
dehydroepiandrosterone theory
failure at adrenal gland exacerbates aging associated loss of neuronal synapses and plasticity
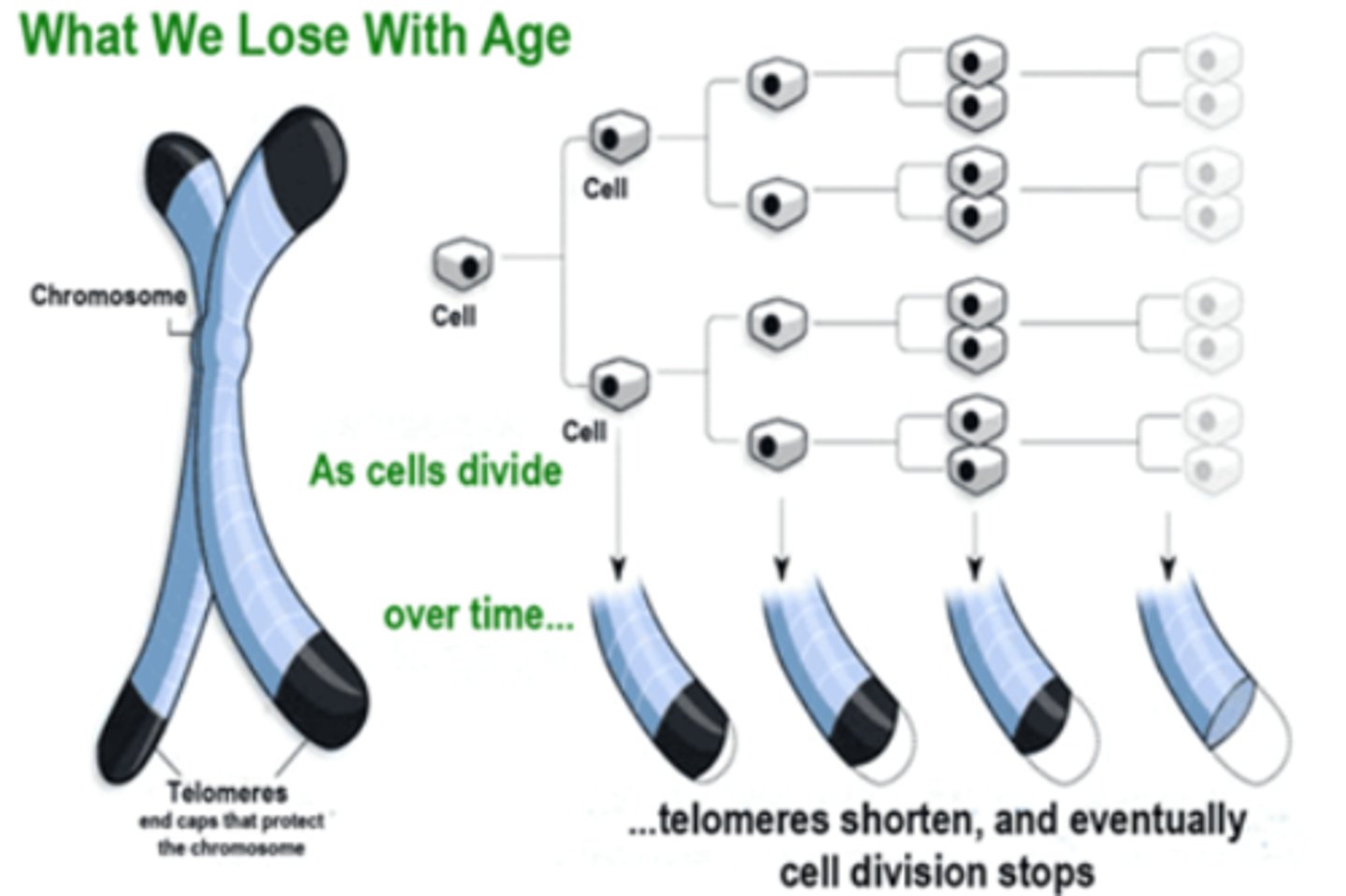
telomere theory
length of telomere is predictive of life span
progress of cell culture theory
dysregulation of nontraumatic and noninflammatory cell death more prevalent in older persons
the genome project
strong relationship between genetic influences and longevity

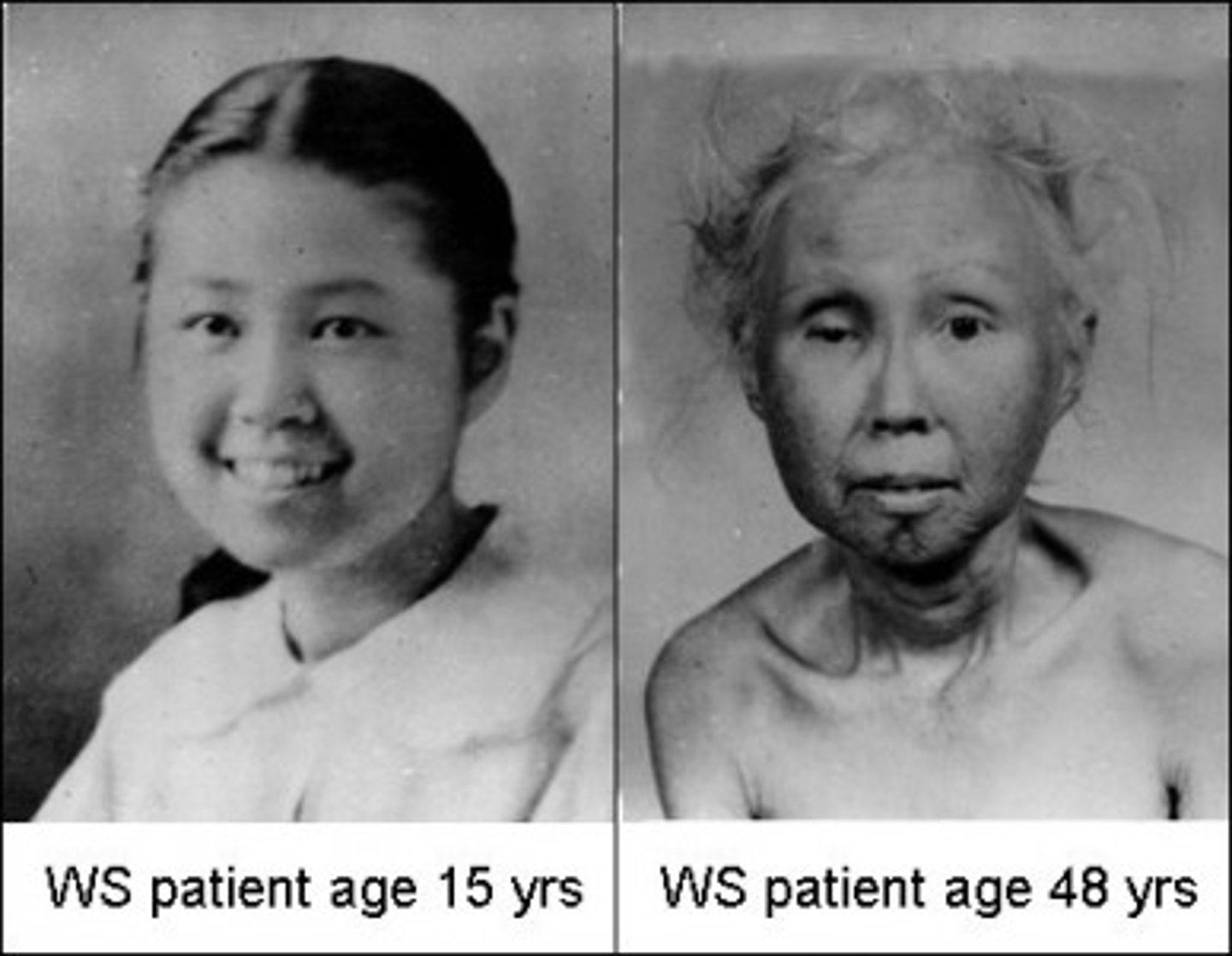
Werner syndrome
this syndrome causes premature aging, variants of gene influence life span
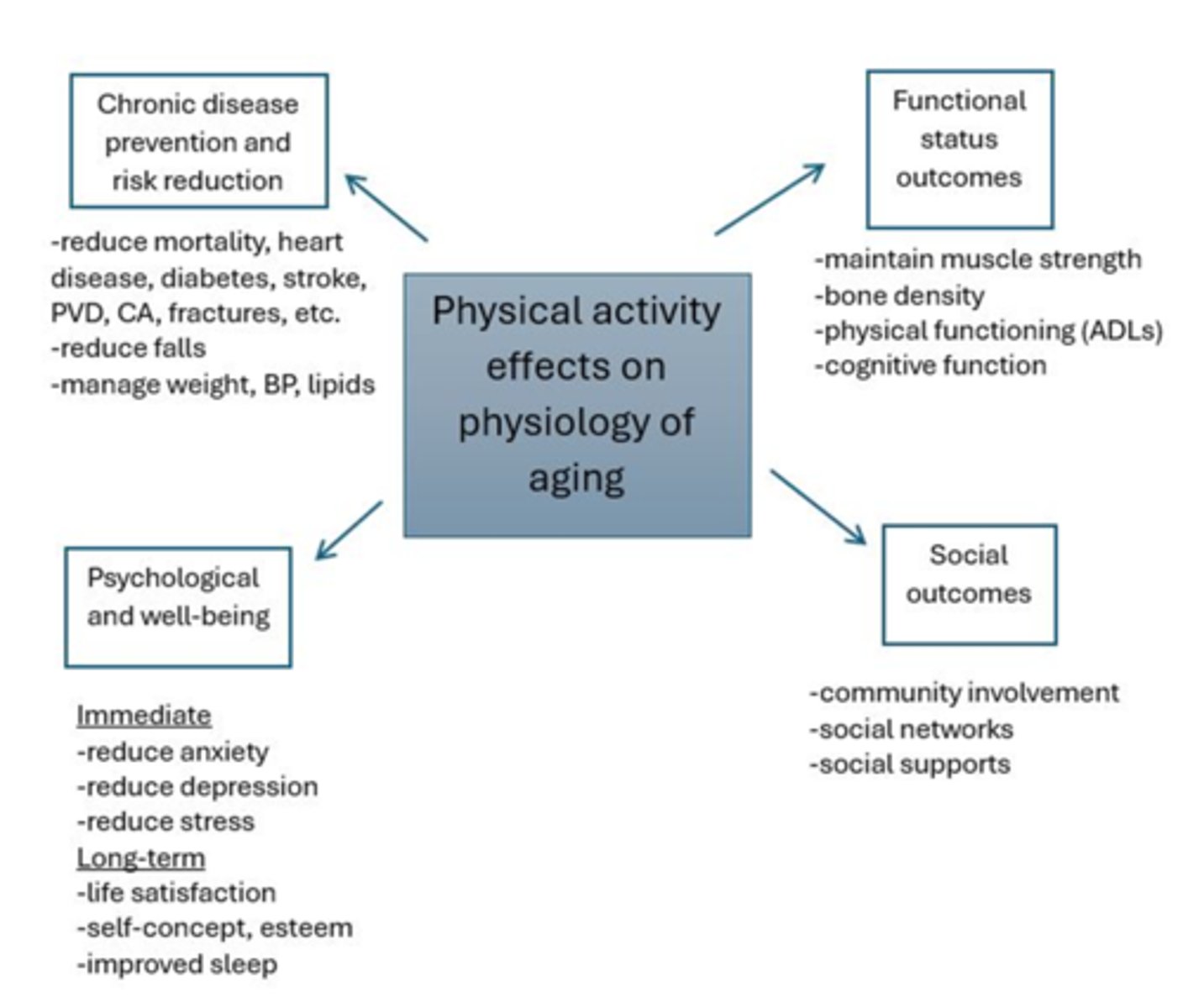
what are the effects on aging from physical activity
chronic disease prevention, functional status improvement, social outcomes, psychological well being
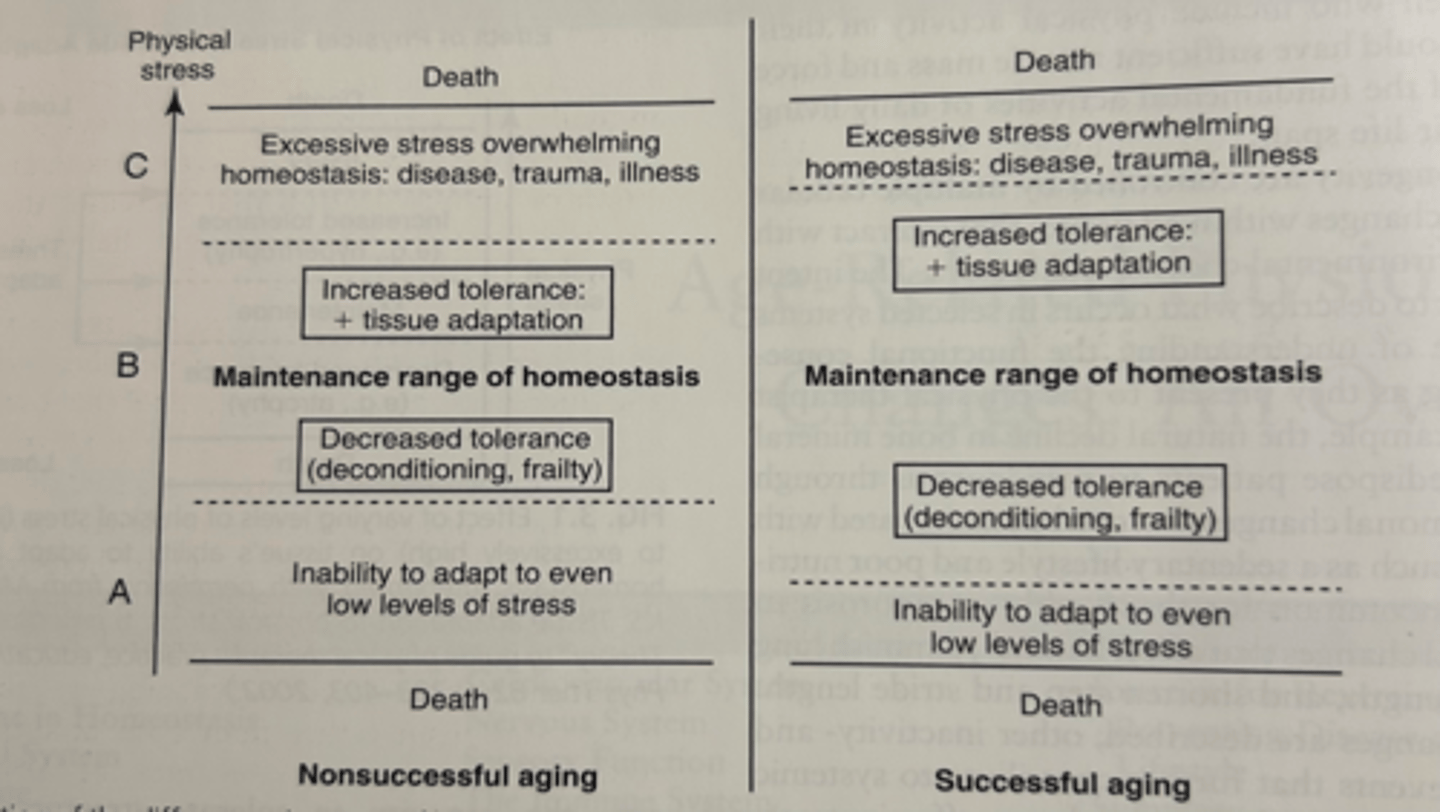
true or false: our ability to adapt to physiological stressors influence illness and injury
true
physical stress theory (Mueller and Maluf)
changes in the relative level of physical stress cause a predictable adaptive response in biological tissue
CV changes with age what decreases?
decrease max HR, decrease diastolic filling rate, decreased ventricular compliance
CV changes with age what increases?
peripheral resistance
pulmonary changes with age what decreases?
chest wall compliance, elastic recoil, muscle strength, VC, max voluntary ventilation, RV
lung cilia with age
less strong (weaker if you will)
pulmonary changes with age what increases?
calcification of ribs and kyphosis

cartilage with age
deteriorates, decreases hydration, reduced elasticity, increased fibrous growth around bony prominences
muscle changes with age
atrophy of fibers (type 2 especially), decline in alpha motor neurons, decreased max strength, decreased muscle mass

bones: decreased _____________, decreased circulating levels of vitamin ____, decreased bone _____________, and decreased reserve to accelerate production of RBC
calcium, D, strength

true or false: brain mass decreases w age
true
CNS: decline in number/efficiency of ______________, slower ______________ ______________, decreased _____________
neurons, conduction velocity, neurotransmitters
PNS: decreased __________ cells, decreased __________ to nerves
nerve, blood
intersystem homeostasis: hypothalamic thermostat
declines

intersystem homeostasis: BMR
decreases
intersystem homeostasis: reactivity of _________________ system declines
autonomic NS
intersystem homeostasis: vasomotor system less responsive to ______________ and _______________
warming and cooling
intersystem homeostasis: decreased _________________ balance and decreased blood flow to brain
hormonal
true or false: touch receptors and nerve fibers decline w age
true
skin changes with aging (3)
1. dermal thinning
2. decreased elasticity
3. vascularity
sweat glands with age?
number and size of these glands diminish

vision changes with aging
pupil smaller, increase density of lens, diminished tear production, loss of receptors, decrease in muscle tone
hearing: sclerotic changes in ______________ membrane
tympanic
hearing: cochlear _______________
osteosclerosis
hearing: decrease receptors in the _______________
Corti
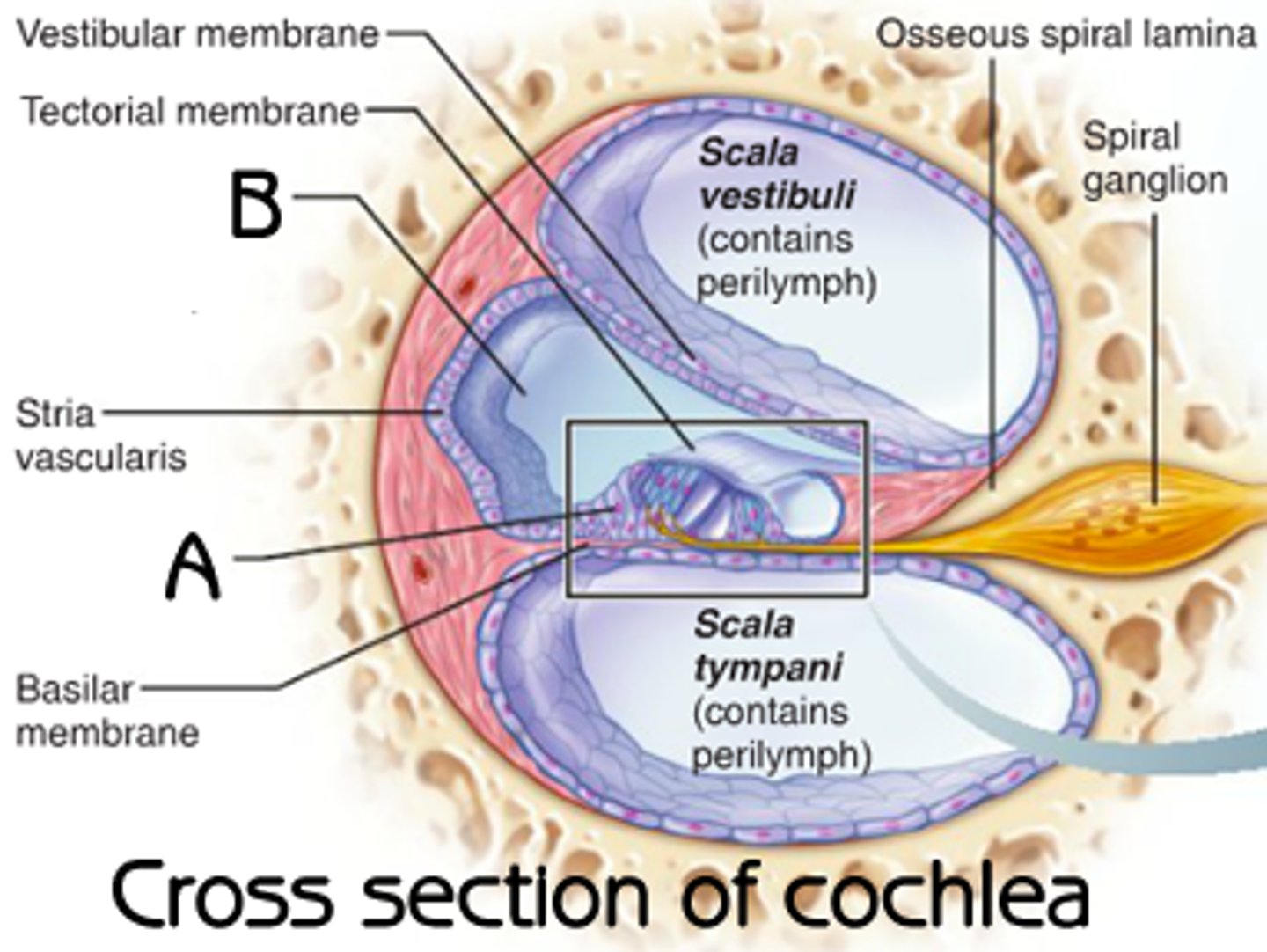
hearing: degeneration of the _______________ nerve
auditory

true or false: proprioception and kinesthesia are enhanced with age, so Berg will just keeping getting better and better
false

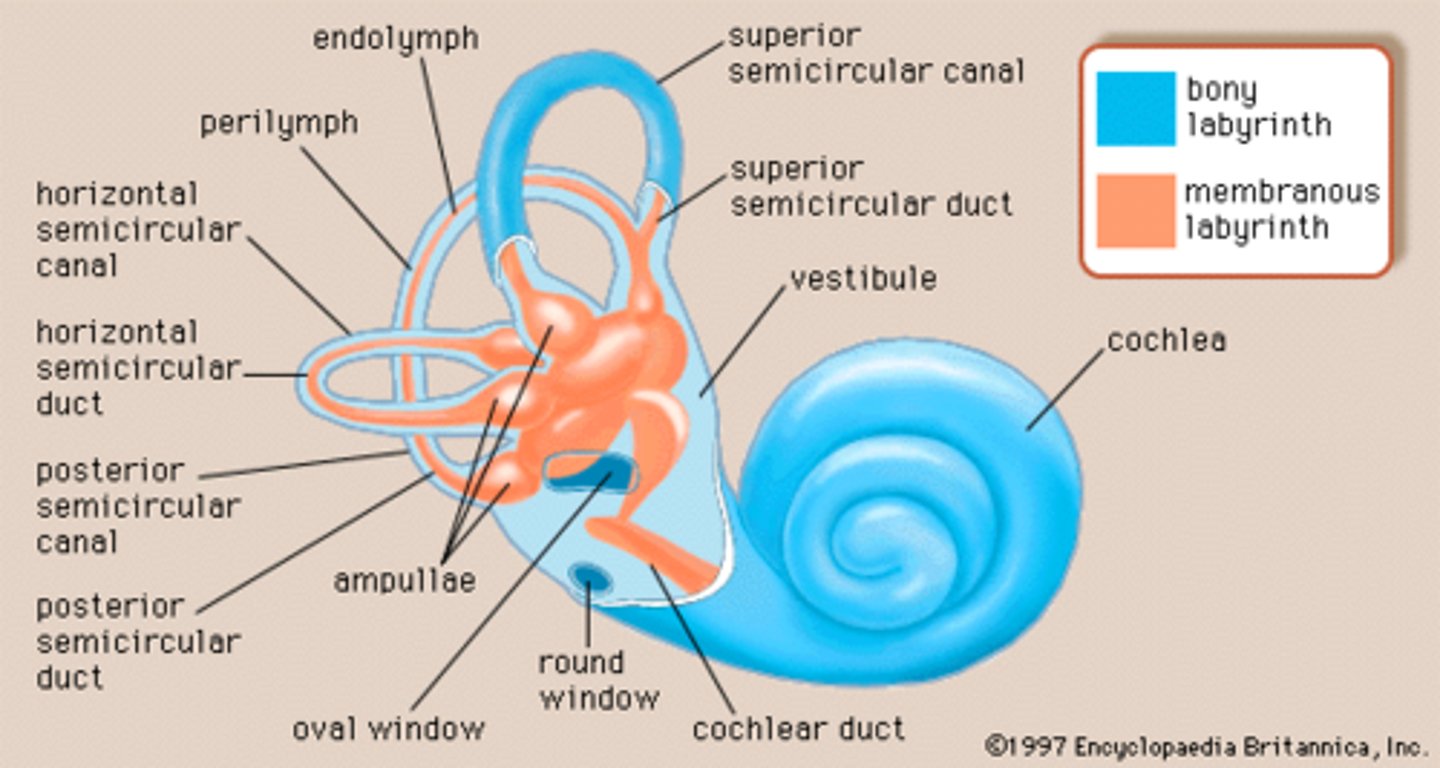
vestibular system: degeneration in the sensory receptors in the _____________ and ______________
otoliths, SCC
______% of taste bud atrophy
80
decreased ______________ production (harder to digest food and taste)
saliva
true or false: decreased cells in olfactory bulb may be a reason behind older adults not knowing if food has gone bad
true
motility of esophagus with age?
decreases
motility in stomach and intestines
decreases
blood supply to the gut?
decreased w age
renal changes with age
decrease mass and weight, protein binding of medications is decreased

true or false: there are prolonged drug effects in the older adult
true
hepatic changes with age
liver mass and perfusion decline, decreases urine-concentrating abilities, decline in extretory/reabsoprtive capacities
urinary changes w age
increase in residual urine, increased reflux into ureters
5 Ms of Geriatrics
1. mind/mentation
2. mobility
3. medication
4. multicomplexity
5. matters most
Mind
communication strategies, seek input from care partners, respect, motivational interviewing, assess barriers to learning
what patient education techniques should you use?
teach back, show me
Mobility
use EBP, fall risk, mental health, geriatric syndromes, appropriate dosing, prevention strategies, screening, annual wellness visits
Medications
consider effects of pharm profile, fall risk, adverse drug reactions
Multicomplexity
osteoporosis, fracture risk, consider effects of organ system changes with age, home body systems influence function, CPGs
Multicomplexity: screen older adults for
cognitive change, functional decline, fall risk, depression, frailty, delirium, polypharmacy, elder abuse
matters most: restraints?
promote restraint-free environment, find alternatives
matters most:
advocate during care transitions, referrals, resources, recommendations, community resources
community resources/programs for:
nutrition, food security, care partner support, social needs
matters most: explain how ageism can negatively affect what 4 things?
mental health, physical health, emotional health, lifespan
Terms central to psychology of patient care
motivation, compliance, engagement, empowerment
visual field accomodation
lower height
visual acuity accomodation
visual aids
vision: glare accomodation
lamp shades, curtains, blinds, non-glare wax, carpeting
vision: dark adaptation
nightlights, pocket flashlight, light switches
vision: color accomodations
bright, warm colors

vision: contrast accomodations
bright detail on dark background

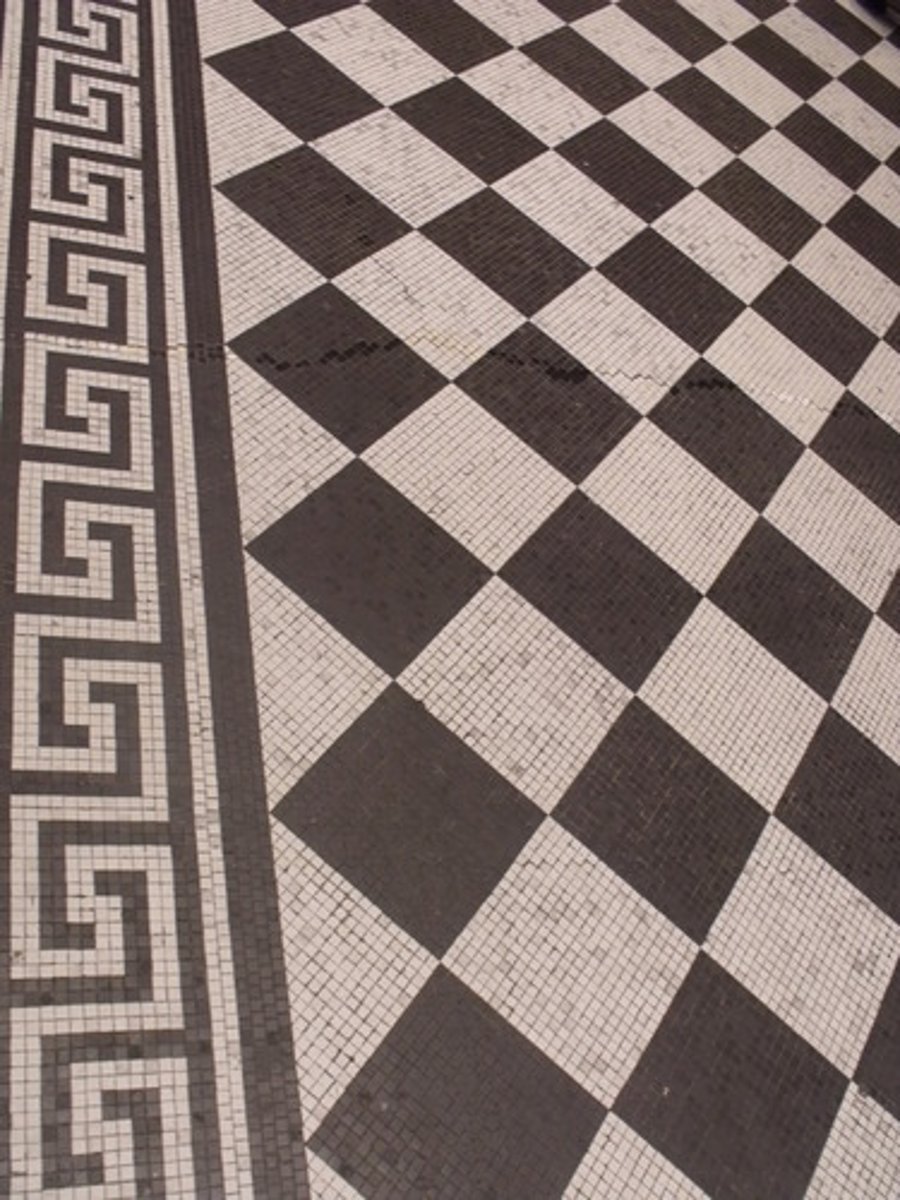
vision: depth perception accomodations
contrasting colors, avoid patterned floors

hearing accomodations
hearing aids, pocket amplifiers, acoustically absorbent window sheers

taste and smell accomodations
spices, check dates on food, adapt smoke detectors, safety spring caps
true or false: when communicating with your patient you should face them, make eye contact, start with name, talk clearly, normal pace, project voice, use visual aids, avoid chewing gum or covering mouth
true!
