Microscope Parts and Functions: A Detailed Study Guide
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Ocular Lens
To magnify the image which is produced by the microscope's objective lens
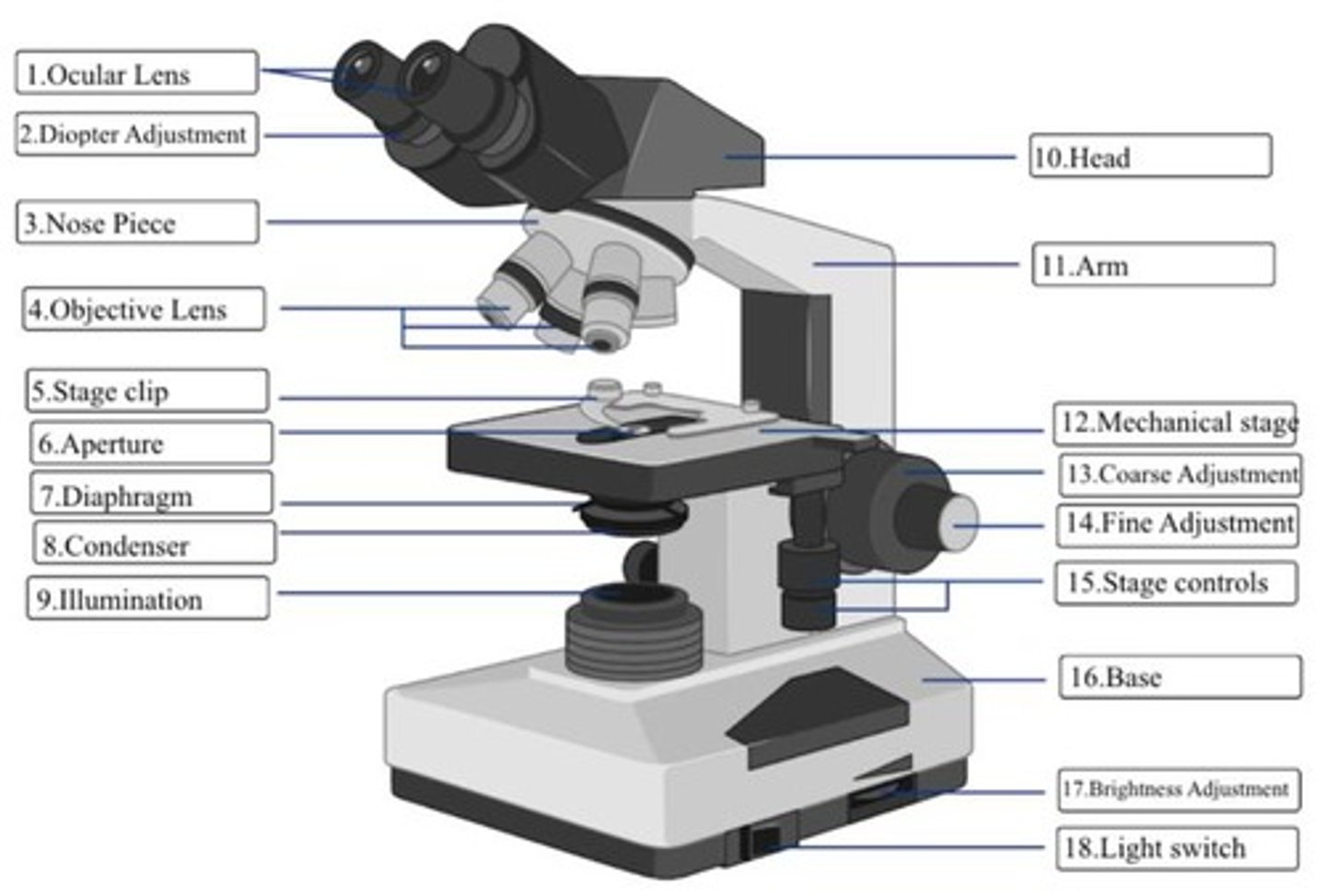
Diopter Adjustment
Localizes the focus on each eyepiece in order to compensate for the difference in vision between the eyes
Nose Piece
Connects the objective lenses to the microscope head
Objective Lens
Provides different objective magnifications in order to view the specimen.
Stage Clip
Hold the slide with the specimen in place.
Objective Aperture
Crucial role in controlling the resolution and depth of field in the microscope's optical system.
Diaphragm
An adjustable circular aperture located within or just above the condenser.
Condenser
Critical role in focusing and directing light onto the specimen being observed
Illumination
Serves to make the specimen visible by directing light through it, allowing the microscope's optical system to create a magnified image that can be observed through the eyepieces.
Head
A fundamental component of a microscope that contains the optical system and serves as the main support structure for the eyepieces and objective lenses.
Arm
A structural component that connects the main body of the microscope with the base.
Mechanical Stage
A movable platform or holder that is designed to securely hold and precisely position the specimen slide for observation.
Coarse Adjustment
Control knob or wheel that is used to make rapid and large changes to the focus of the specimen being observed
Fine Adjustment
Control knob or wheel that is used to make slight and precise changes to the focus of the specimen being observed.
Stage Controls
Used to move the specimen slide of the microscope's stage, which is the platform where the specimen is placed for observation.
Base
Serves as the stable and supportive foundation of the entire instrument. It is the lowermost part of the microscope that rests on the surface, providing stability and balance to the entire setup.
Brightness Adjustment
Used to control the intensity of the light illuminating the specimen being observed.
Light Switch
Allows you to turn the light on or off, which is essential for viewing the specimen clearly. When the light is turned on, it passes through the condenser lens and then through the specimen on the slide.