Coulomb's Law and Electric Field - ch 21-22
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Superconductors:
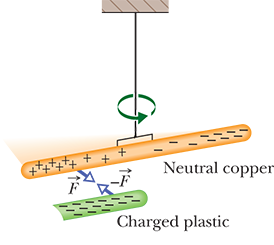
materials that are perfect conductors, allowing charge to move without ANY hinderance
induced charge
some of its positive and negative charge have been separated due to the presence of a nearby charge
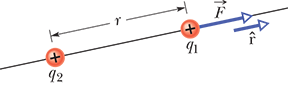
Couloumb’s Law of Electrostatic:
particles with the same sign of electrical charge repel each other and particles with opposite signs attract each other
equation: F = k ((q1/q2) /r²) r
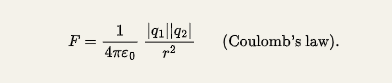 E0 (permittivity constant) = 8.85 × 10^-12 C² /N * m²
E0 (permittivity constant) = 8.85 × 10^-12 C² /N * m²
Shell Theory 1
a charged particle outside a shell with charge uniformly distributed on its surface is attracted or repelled as if the shell’s charge were concentrated as a particle at its center
Shell Theory 2:
a charged particule inside a shell with charge uniformly distributed on its surface has no net force acting on it due to the shell
elementary charge
= 1.602 × 10^-19
quantized
when a physical quantity such as charge can have only discrete values rather than any values
annihilation process
if two charged particles undergo an annihilation process, they have opposite signs of charge
annihilation process: electron + positron e → 2 gamma rays
pair production
gamma ray → electron and positron
if two charged particles appear as a result of a pair production process, they have opposite signs of charge
electric field
force / positive charge q0
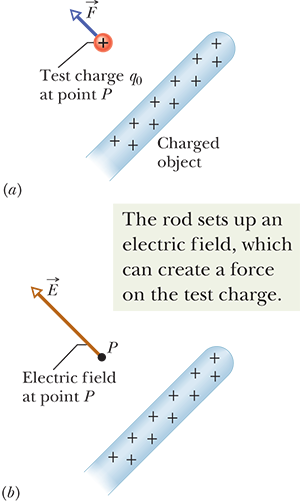
electric field line
helps us visualze the direction and magnitude of electric fields
closer field lines = stronger field
originate on positive charge and terminate on negative charge
magnitude of electric field
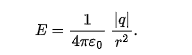
electric dipole
2 particles with charges of equal magnitude q but opposite signs separated by distance d
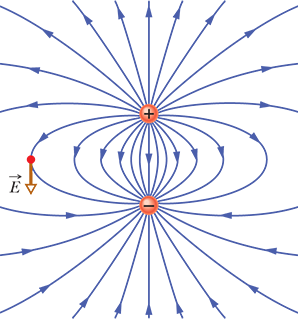
lectric dipole moment p
magnitude qd
points from negative charge to positive charge
mangitude of the electric field set up by an electric dipole at a distant point on the dipole axis
z: distance between the point and the center of the dipole
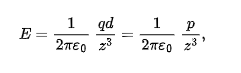
electric field of an extended object
electric field set up by particle does not apply to an extended object with charge
how to find it:
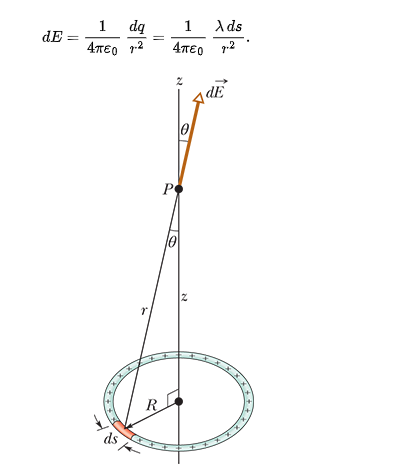
electric field due to a charged disk
o = surface charge density
z =distance along the axis from the center of the disk
R = radius of the disk
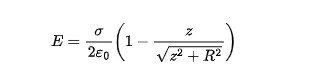
f particle with charge q is placed in an ecternal electric field E, electricstatic force =
q: if +: force vector goes in same direction as field vecotr
if -, goes in opposite direction
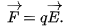
torque on an electric dipole
p = dipole moment
e = external electric field
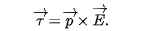
potential energy U
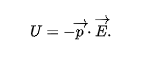
work done by electric field
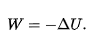
potential energy is ____ when electric dipole of dipole moment is _____ to electric field
zero, perpendicular
potential energy is greatest when
p is opposite e
if source charge is positive
e vector points away
if source charge is negative
e vector points towards
E in terms of src and test charge
e = 1/4piE0 x q / r² (direction)