9 - ANS Pharm and Cholinergic Agents
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Muscarinic ACh System Includes
Symp is T1-L3
Skin
Parasymp is CNs and S2-S4
Stimulation with ACh causes rest and digest
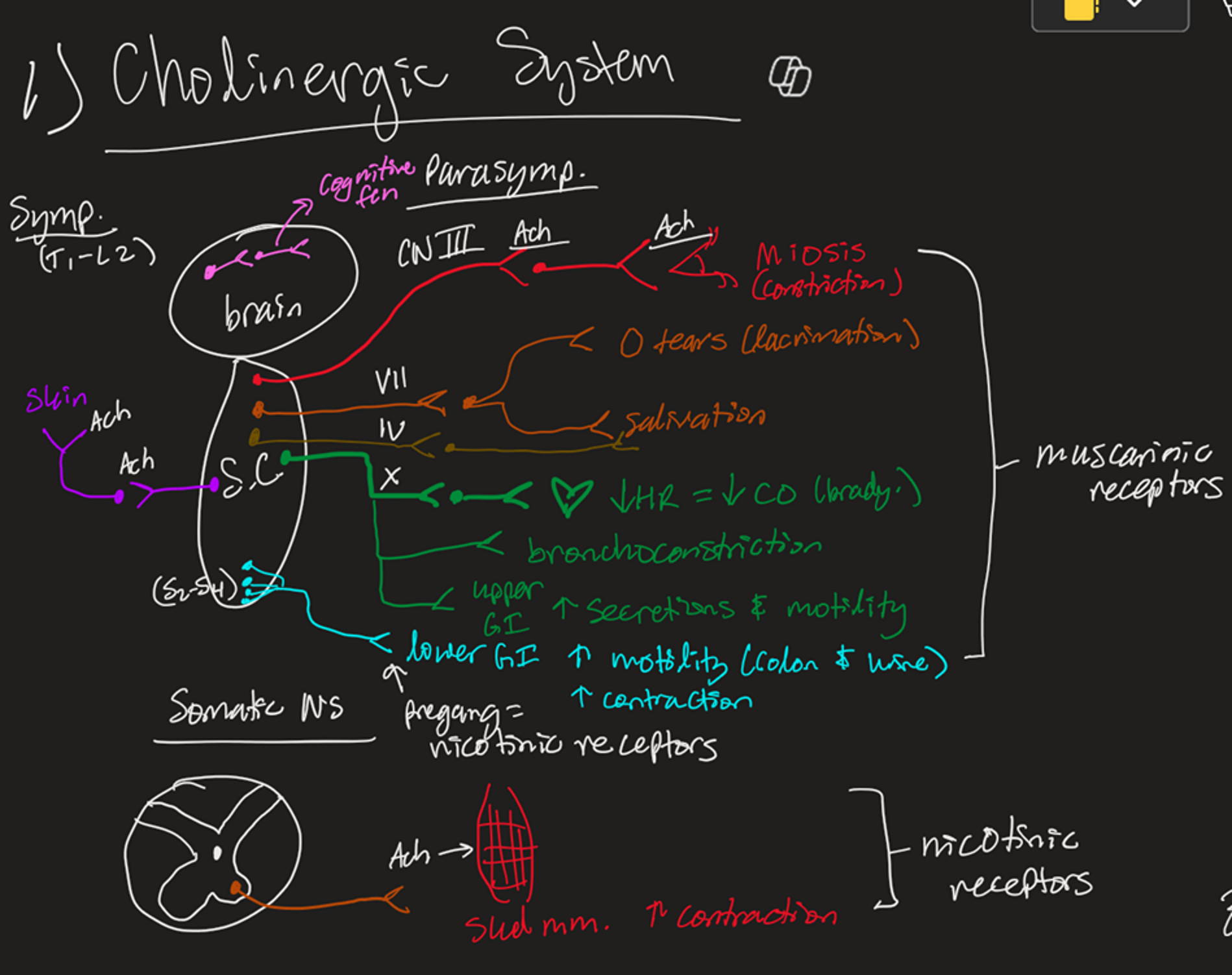
Nicotinic ACh System Includes
Somatic NS
Nicotinic receptor
ACh → skeletal muscle contraction
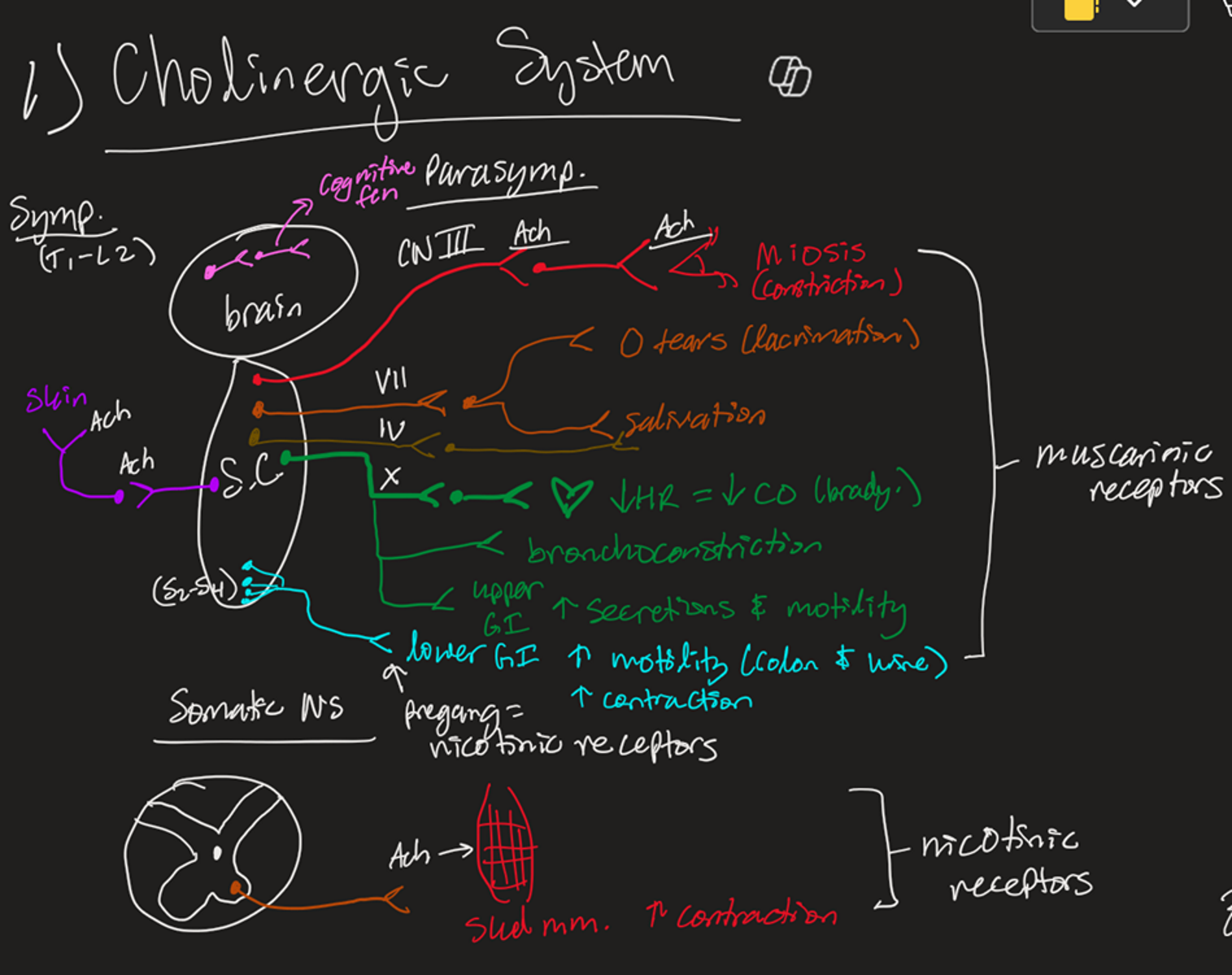
Steps for ACh Release to Cells
Choline combines with Acetyl-CoA (via Cholineacetyltransferase) → ACh
Action potential causes Ca2+ influx → ACh vesicles fuse and endocytose
ACh binds receptors:
Nicotinic for skeletal muscle (let's Na+ inside)
Muscarinic
Gi (inhibitory)
Gi takes a GTP → GDP
Adenyl Cyclase is inhibited, so it can’t make ATP → cAMP → PKA (K+ leaves, hyperpol.)
Gq (stimulatory)
Gq takes GTP → GDP
Phospholipase C is stimulated to create PIP2 → (DAG → PKC) & (IP3 → Ca2+ depol.)
ACh is taken up by Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) → Becomes Choline → Cycle Repeats
List Cholinergic Agonists (direct)
Muscarinic agonists
Acetylcholine
Bethanechol
Cevimeline
Methacholine
Pilocarpine
Nicotinic agonist
Varenicline
List Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors (indirect)
Edrophonium
Neostigmine
Pyridostigmine
Physostigmine*
Donepezil*
*= tertiary amine (lipophilic, crosses BBB)
List Cholinergic Antagonists (direct)
(AKA anticholinergics)
(AKA muscarinic antagonists)
Atropine
Benztropine
Darifenacin
Diphenhydramine
Glycopyrrolate**
Ipratropium**
Oxybutynin
Scopolamine
Tiotropium**
Tropicamide
List Ganglion Blocker (Nicotinic Antagonist) (direct)
Mecamylamine
List Acetylcholinesterase (AChe) Regenerator (indirect)
Pralidoxime
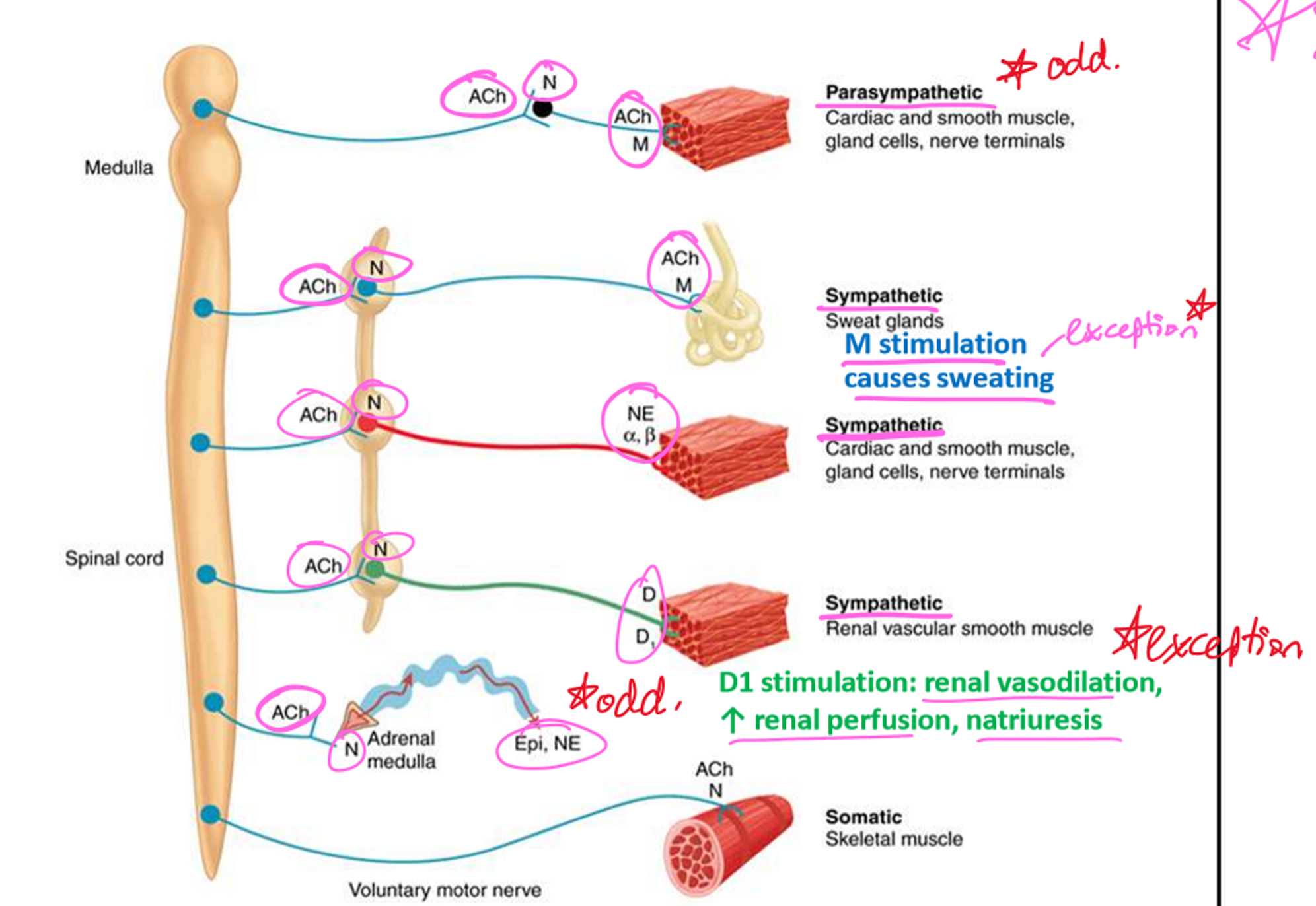
Parasympathetic Pre/Postganglionic Transmitters and Receptors
Pre: ACh → Nn receptors (ganglia)
Post: ACh → M
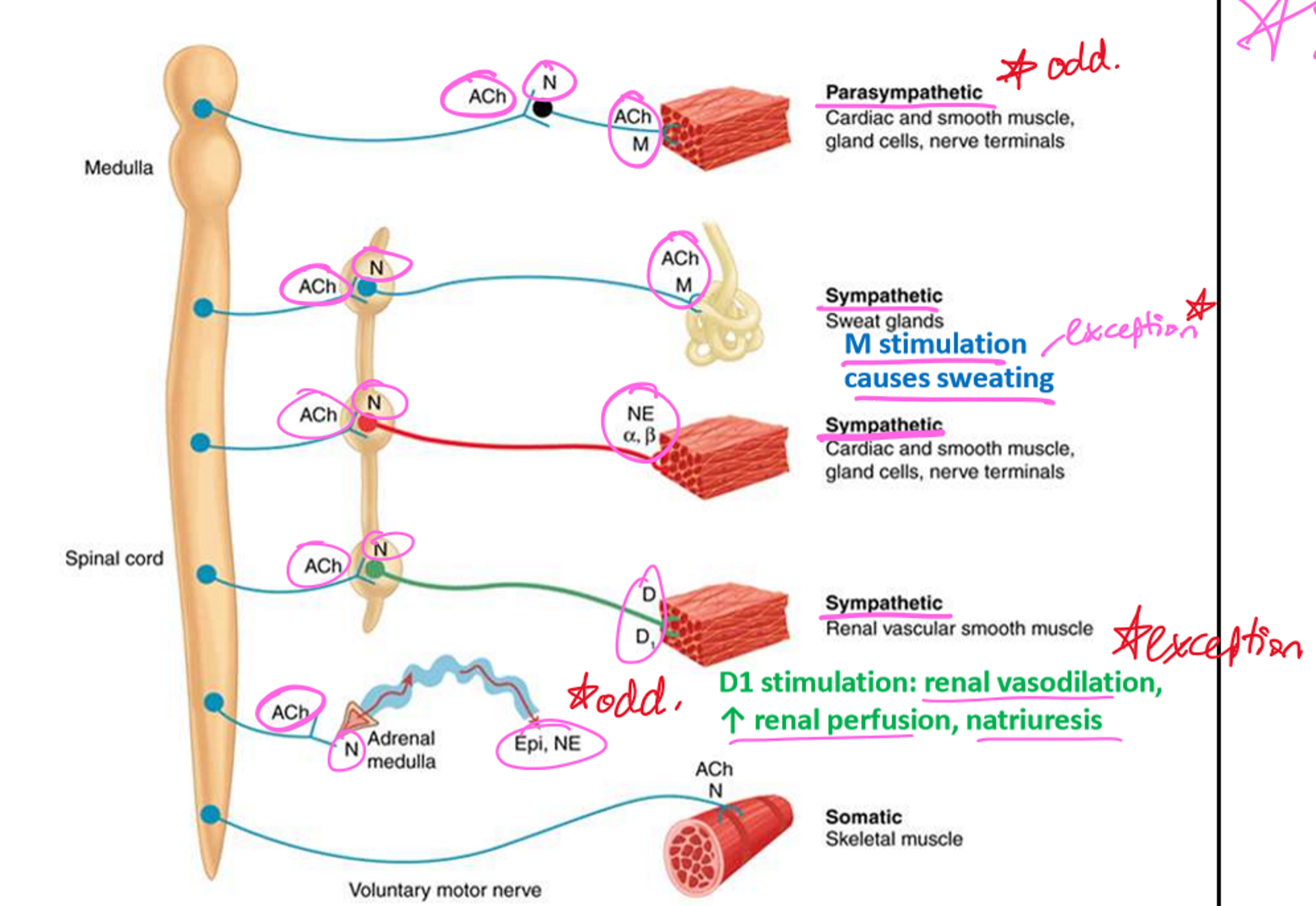
Sympathetic Pre/Postganglionic Transmitters and Receptors
Pre:
Ach → Nn receptors (ganglia)
Post:
NE → Alpha or Beta receptors
ACh → M (sweat on skin)
DA → Dopamine D1 (renal vasodilation/perfusion)
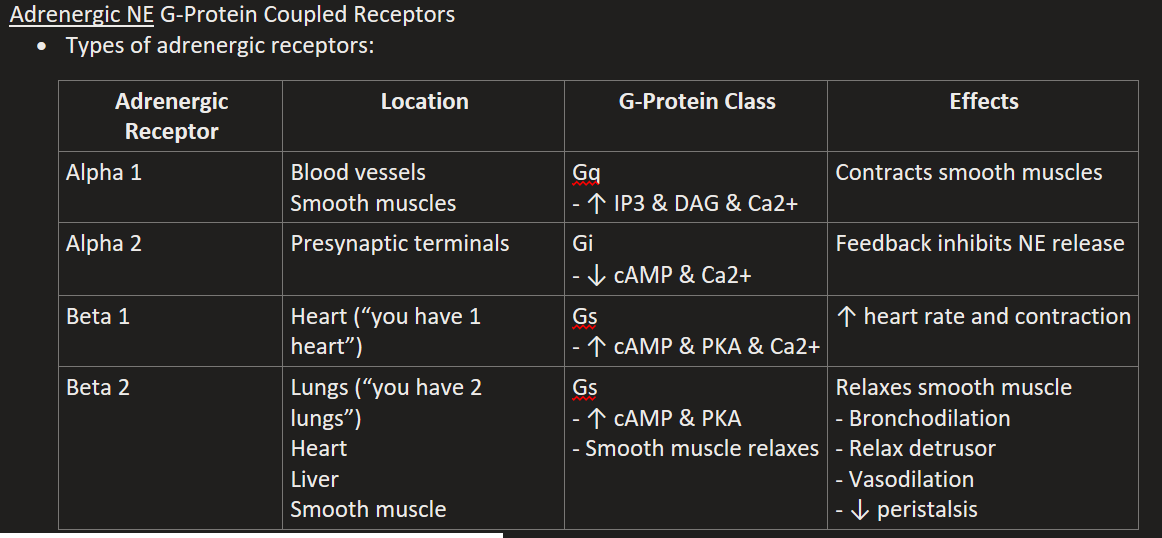
List the Metabotropic Adrenergic (NE) Receptors
Alpha 1
Alpha 2
Beta 1
Beta 2
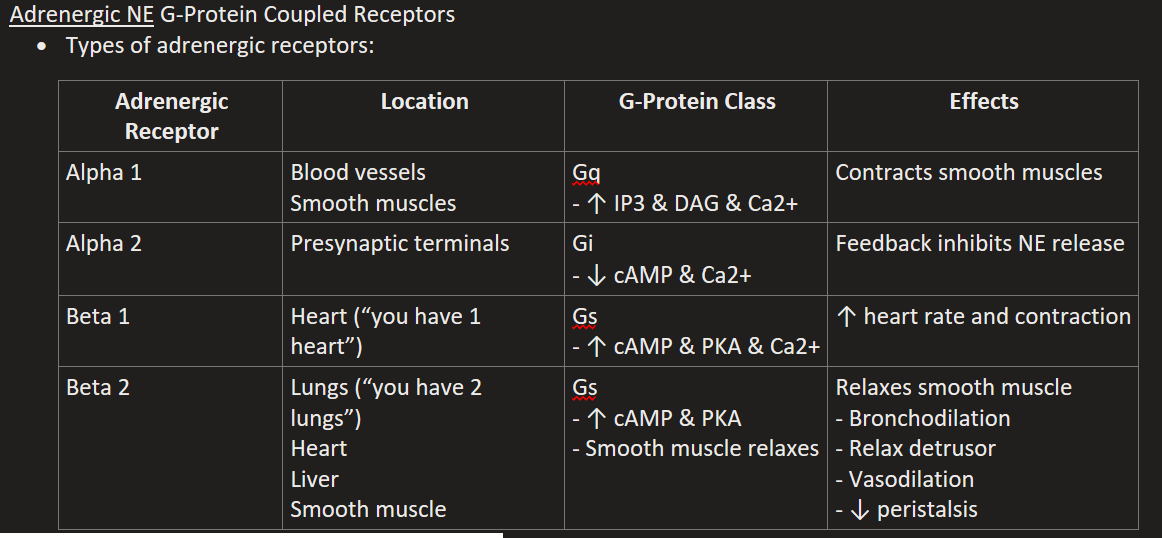
Alpha 1 Location, G-Protein, & Effects
“1 squeeze vessels and smooth muscle”
Blood vessels & Smooth muscles
Gq (↑ IP3 & DAG & Ca2+)
Contracts smooth muscles and vessels (increases BP)
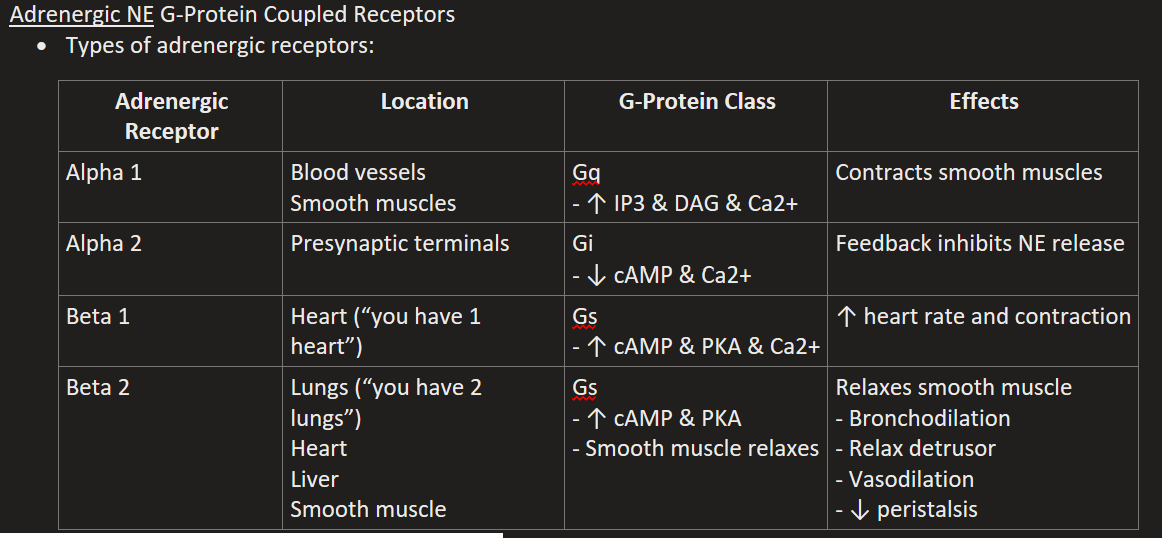
Alpha 2 Location, G-Protein, & Effects
Presynaptic terminals
Gi (↓ cAMP & Ca2+)
Feedback inhibits NE release
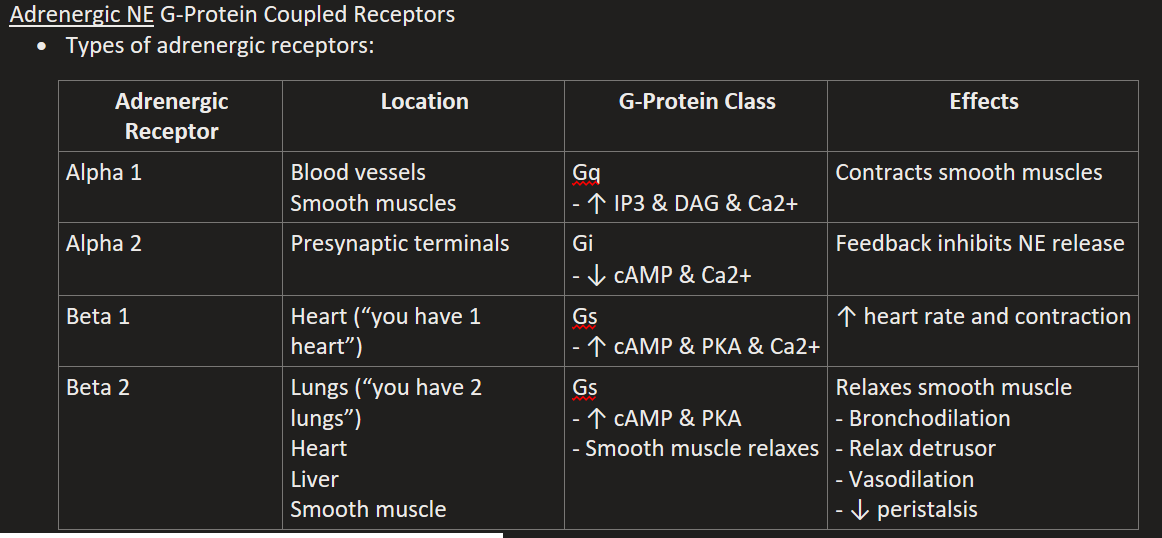
Beta 1 Location, G-Protein, & Effects
“1 heart beats harder”
Gs (↑ cAMP & PKA & Ca2+)
↑ heart rate and contraction
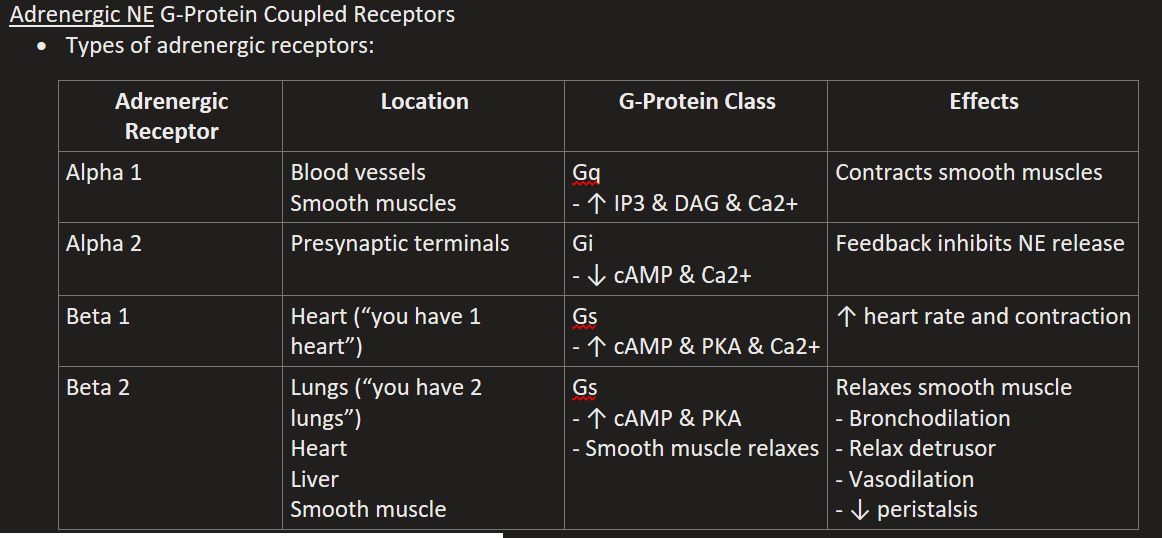
Beta 2 Location, G-Protein, & Effects
Lungs (“2 lungs & smooth muscle relax”), Heart, Liver, Smooth muscle (uterus, bladder).
Gs (↑ cAMP & PKA)
Relaxes smooth muscle, Bronchodilation, Relax detrusor, Vasodilation, ↓ peristalsis
List the Metabotropic Muscarinic (ACh) Receptors
M2
M3
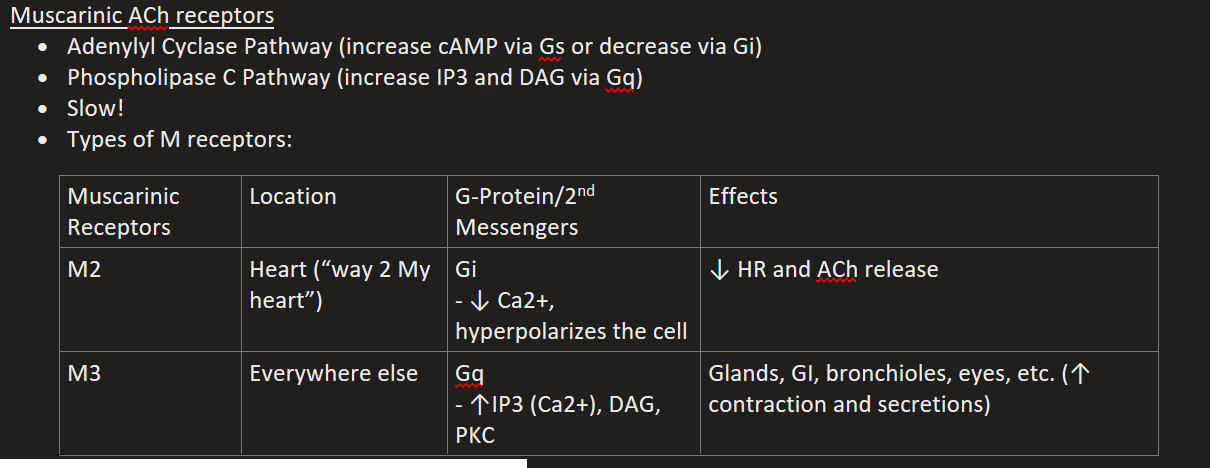
M2 Location, G-Protein, & Effects
Heart (“way 2 My heart”)
Gi (↓ Ca2+, hyperpolarizes the cell)
↓ HR and ACh release
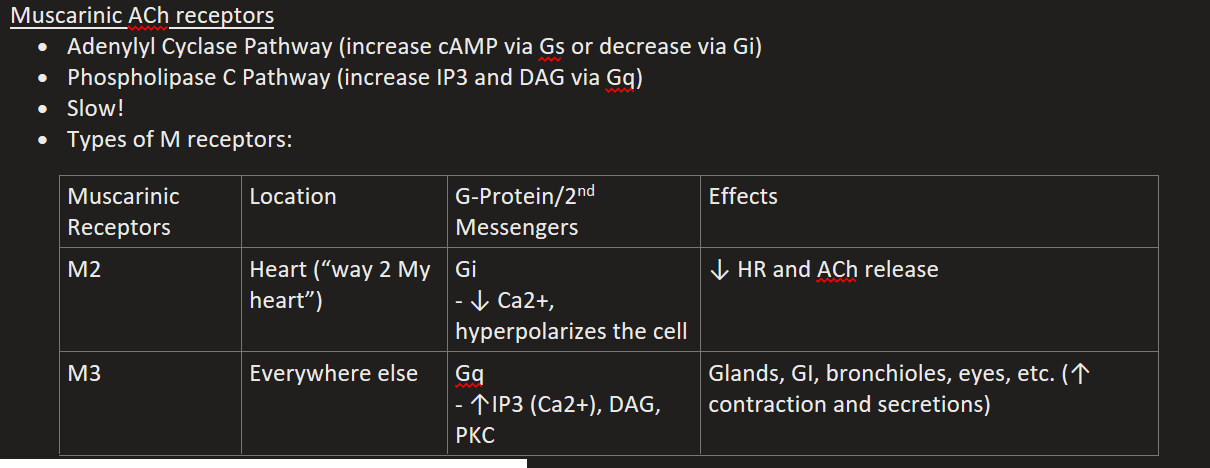
M3 Location, G-Protein, & Effects
Everywhere else
Gq (↑IP3 (Ca2+), DAG, PKC)
Glands, GI, bronchioles, eyes, etc. (↑ contraction and secretions)
Ionotropic Nicotinic (ACh) Receptors
Nn for brain
Nm for NMJ (skeletal)
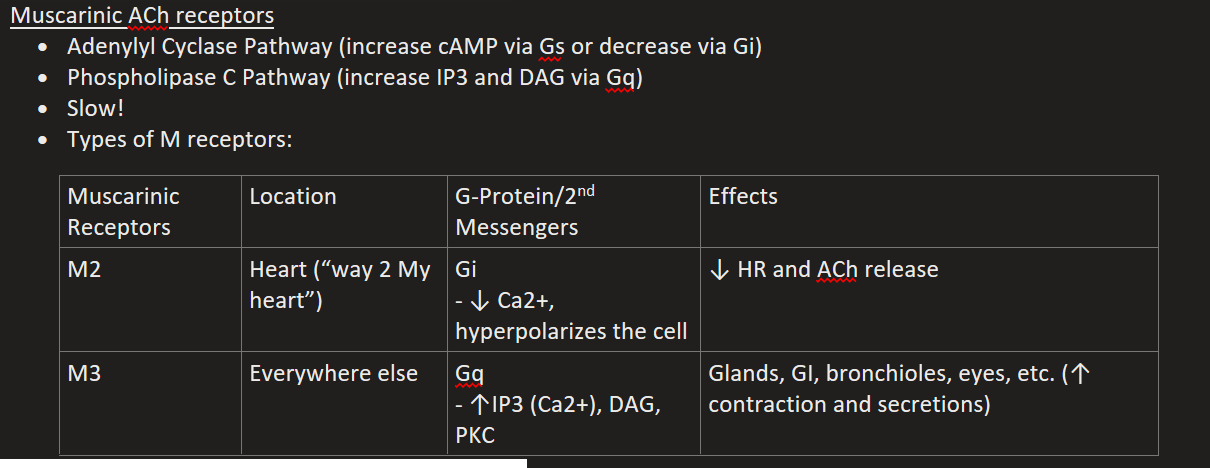
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
Autoimmune disease, autoantibodies attack nicotinic receptors and block nicotinic binding sites
Causes weakness
Tx = meds that inhibit AChE (ACh build-up to kick out blockers)
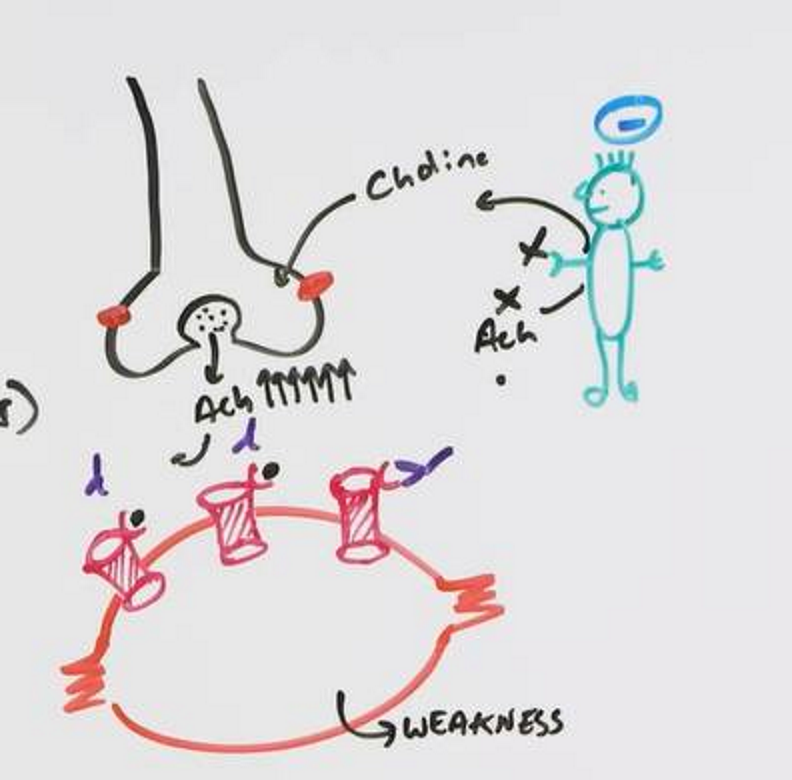
Botulinum Toxin
Inhibits ACh release from terminal
Causes paralysis
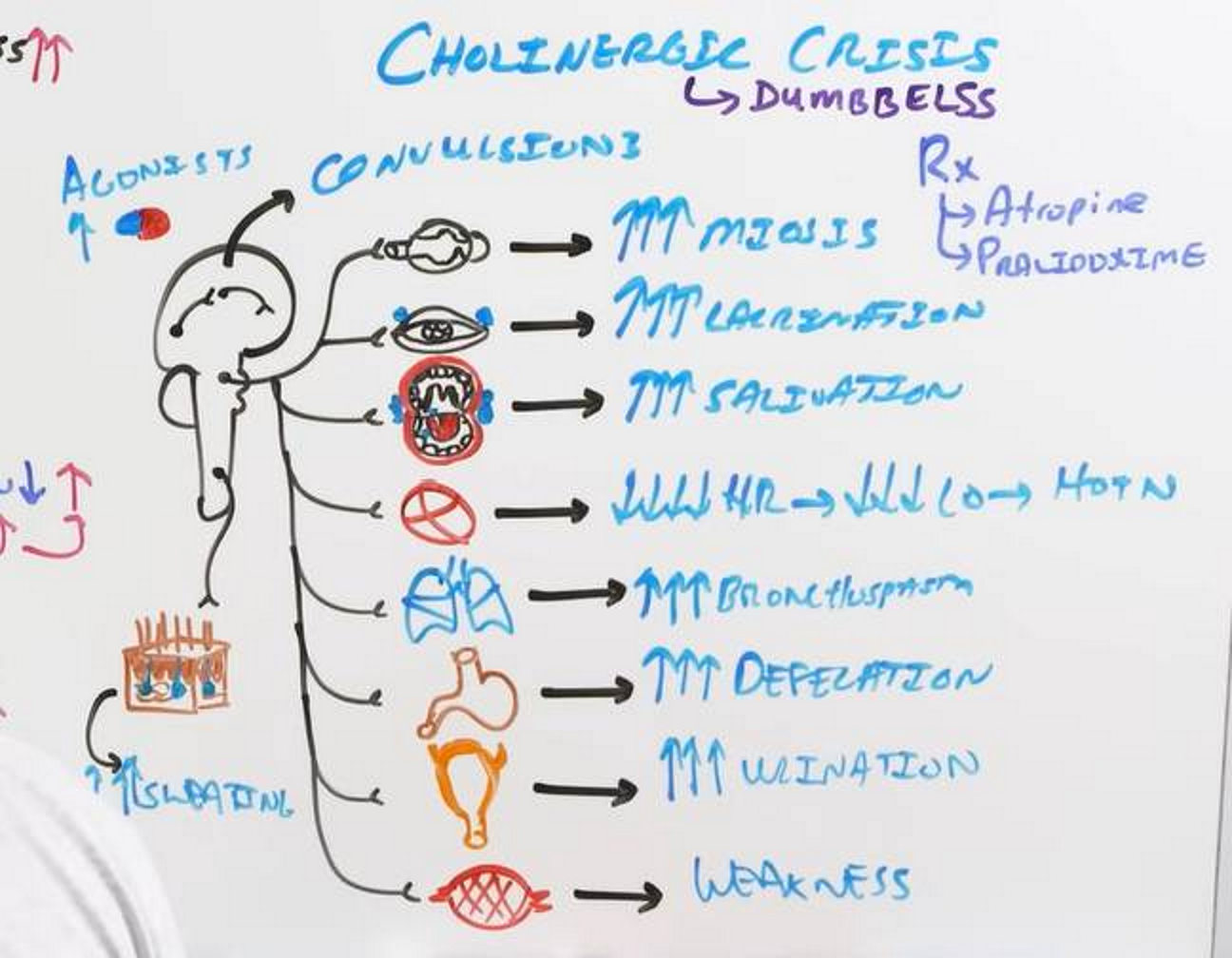
Cholinesterase Inhibitor Toxicity (Cholinergic Crisis)
(causes, symptoms, tx)
Caused by:
Neostigmine or Pyridostigmine
Too much ACh because AChE is overly inhibited!
DUMBBELSS
Digestion/Diarrhea
Urination
Miosis
Bradycardia
Bronchoconstriction
Emesis
Lacrimation
Salivation
Sweating
Tx:
Atropine (muscarinic antagonist, prevents ACh overload)
Pralidoxime (AChE regenerator, restores nicotinic function)
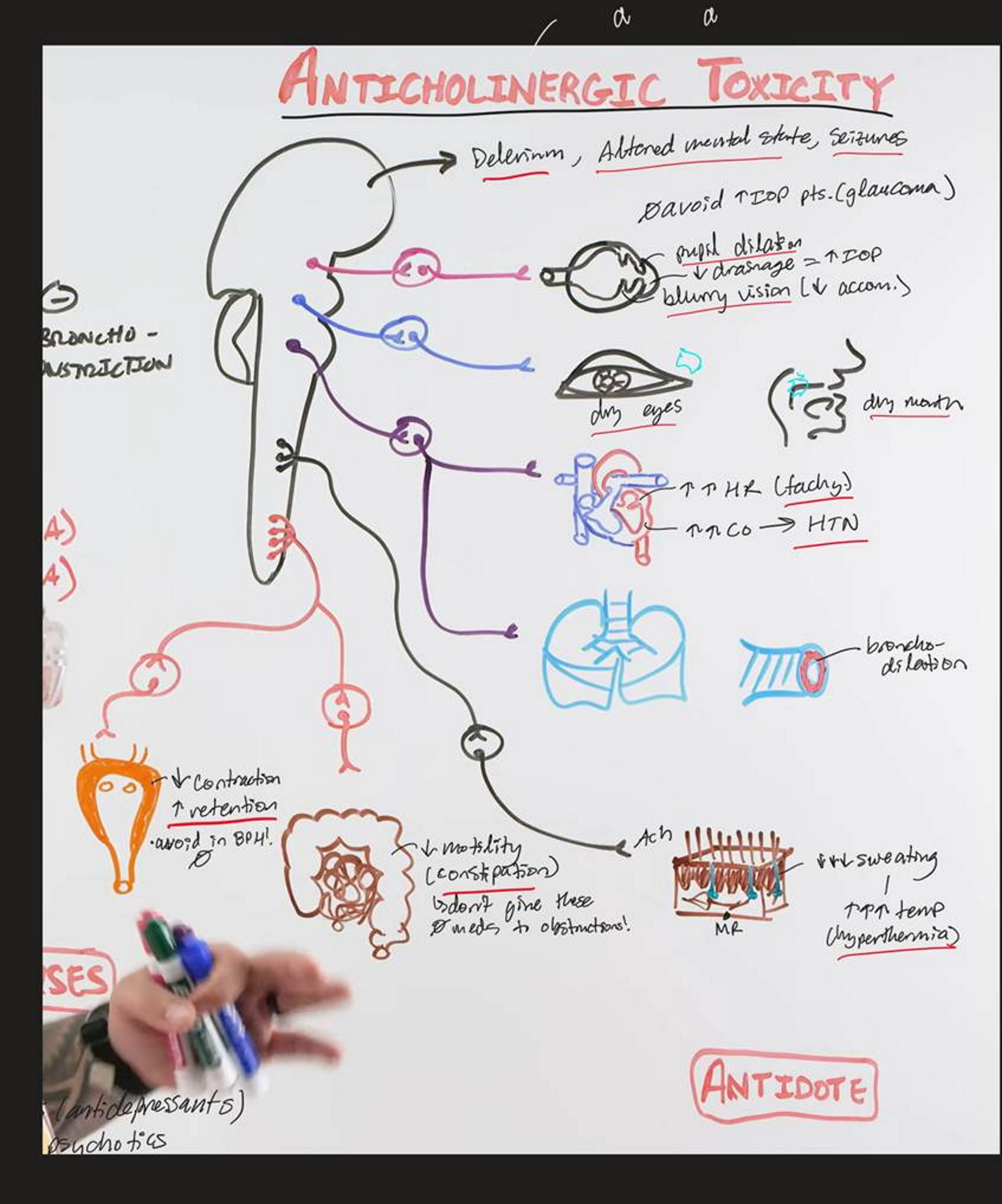
Anticholinergic Toxidrome (toxicity)
(causes, symptoms, tx)
Caused by:
Too little ACh means no CNS stimulation, you can’t sweat (so your temp rises), you turn red, your mucous membranes can’t secrete anything
“Mad as a hatter
Red as a beet
Hot has a hare
Dry as a bone”
Tx:
Cholinesterase inhibitors (physostigmine!)
Increased Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
Muscarinic antagonists (anticholinergics) can all cause THIS.
(dilate the pupil via relaxing iris sphincter)
This blocks the canal of Schlemm and causes increased intraocular pressure
Secretions
These function to decrease risk of infection
Halitosis
Bad breath, improves with salivation
Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
N receptors are blocked, need a bunch of Ach to knock it off via AChE inhibitors!
Edrophonium diagnoses it
Neostigmine treats it short term
Pyridostigmine treats it long term
NET vs AChE
NE uses THIS reuptake
ACh is broken down by THIS
Vasodilation
THIS involves sympathetic only, no parasymp.
Indirect Agent
“No vascular effect” implies THIS
Cycloplegia
No accommodation
Diarrhea
THIS is a result of increased bowel activity
Atropine
Belladonna plant has THIS
Pilocarpine and Physostigmine
2 things that can fix atropine toxicity are:
Muscarinic agonist or Indirect Antagonist (that can cross the BBB)
THIS is agonist
THIS is indirect antagonist (uncharged so it can cross the BBB)
COPD
You need antimuscarinic drugs to treat THIS
Tropicamide
Antimusc. For eye only
Oxybutynin
Antimusc. For bladder
Muscarinic blockers
THESE reverse bradycardia (Bradycardia comes from too much ACh)
Postural Hypotension
THIS is due to the sympathetic blockade (not part of parasymp.)
Due to nicotinic