Bacteriology Lab Final
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What technique is designed to keep the working environment as clean as possible by sterilizing equipment in contact with microorganisms?
Aseptic technique
What is the loop used for?
Transferring cultures to other mediums
Prepare bacterial smears
Streak plates
What is the straight wire used for?
Stab cultures
Pick single colonies from plate
What is the order of the stains in the gram staining technique?
Primary stain
Decolorizing agent
Counterstain
What is the primary stain in gram staining?
Crystal violet
What is the mordant, and what is it used for?
Gram’s iodine
Intensifies the colour of the stain
What is the decolorizing agent in gram staining and how does it differ in gram negative and gram positive organisms?
50% ethanol 50% acetone
Protein stain difficult to remove in gram-positive. Lipid concentration in outer layers of gram-negative easily dissolved by alcohol.
What is the counterstain in gram stain?
Safranin
Stains decolorized cells red.
What’s an example of a gram-negative bacteria?
E. coli
What is an example of a gram-positive bacteria?
Staphylococcus
What is Acid-Fast stain (Ziehl-Neelsen Method) used for?
Mycobacterium and Nocaridia
Why is the acid-fast stain useful for staining mycobacterium?
The thick waxy wall makes it difficult to remove the penetrated stain
What is the primary stain in acid-fast stain?
Carbol fuchsin (red)
How is penetration of Carbol fuchsin enhanced?
Application of heat
What is counterstain in acid-fast stain?
Methylene Blue
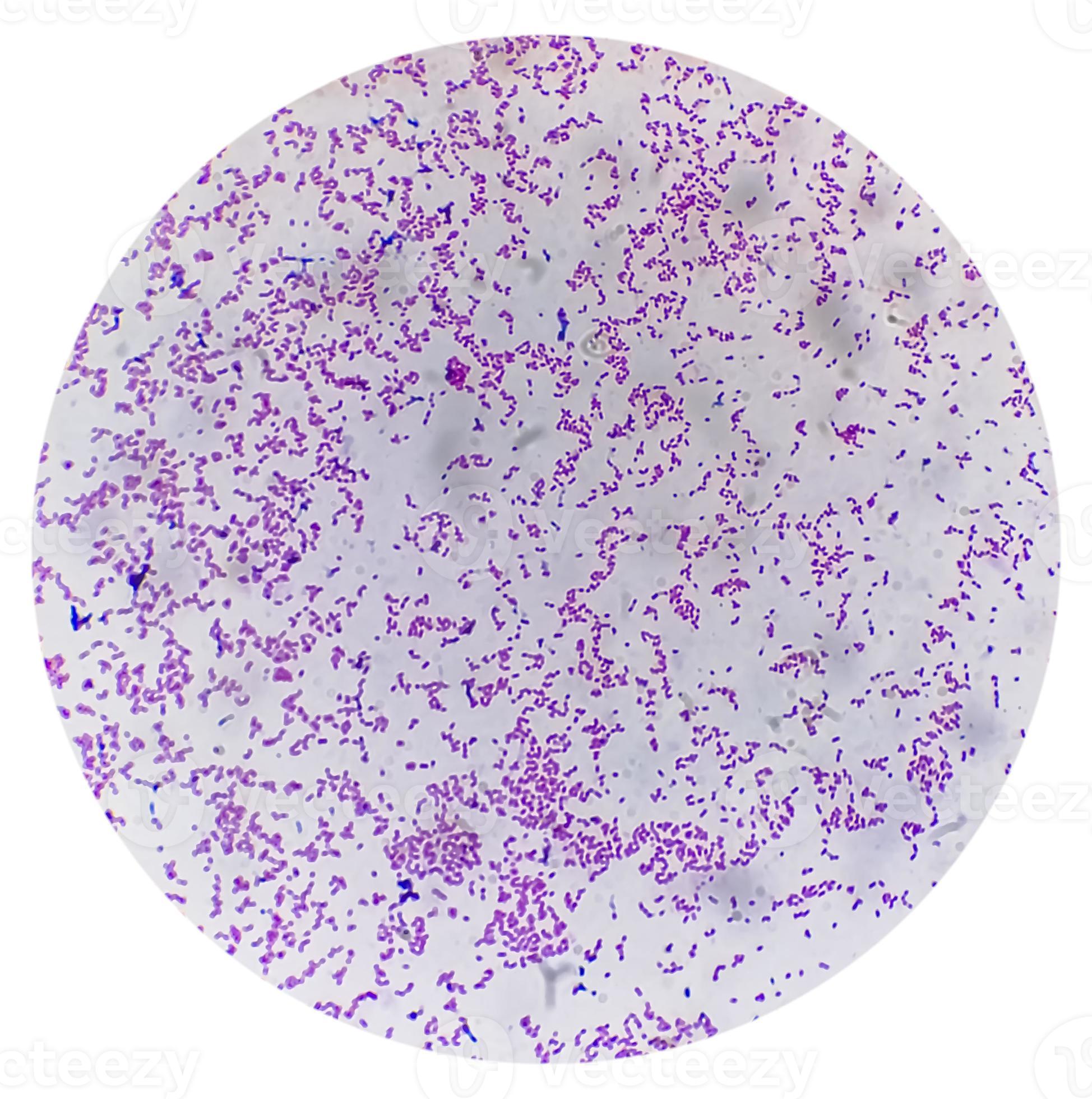
What stain is this?
Gram stain
What stain is this?
Acid-fast Stain
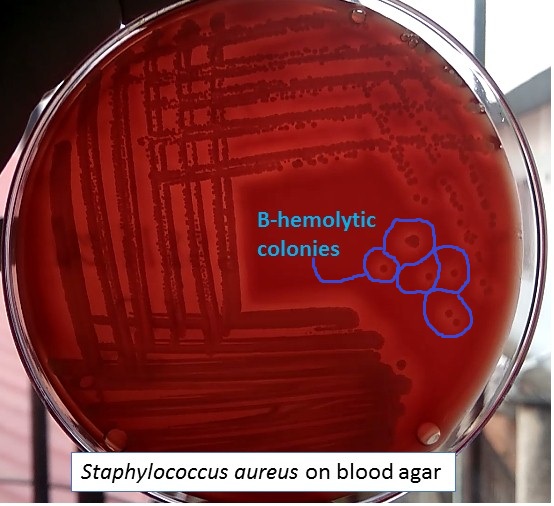
What hemolysis does Staphylococcus aureus display on blood agar?
Beta-hemolytic
Also forms a yellow film around colonies
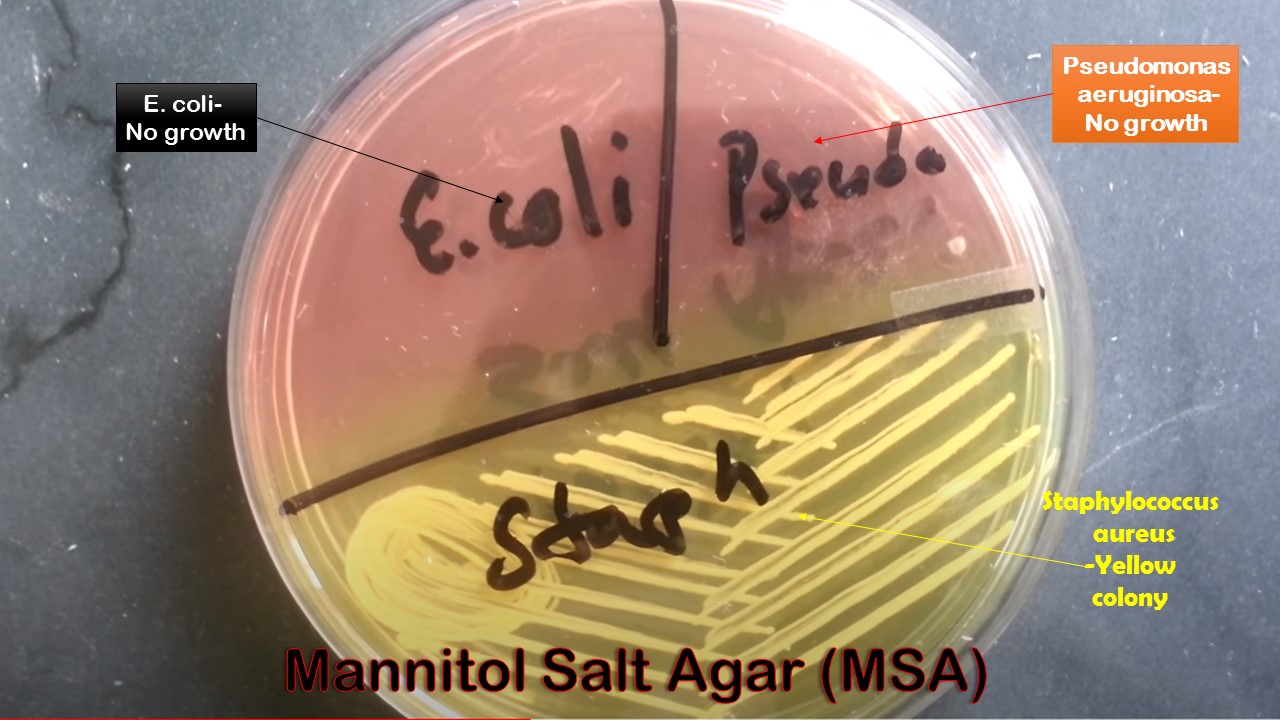
What does staph aureus do to MSA?
Color change from red to yellow
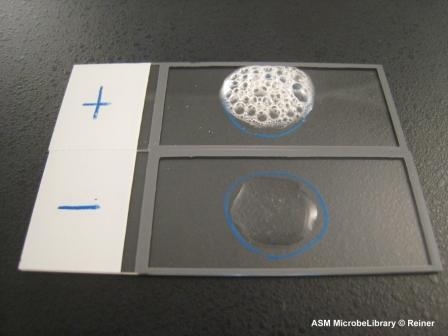
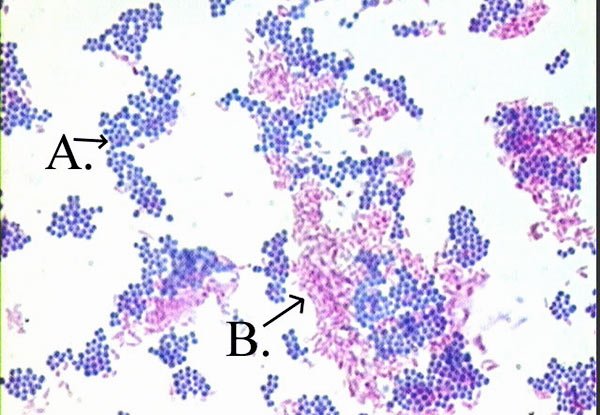
What result does streptococcus produce in the catalase test?
Negative
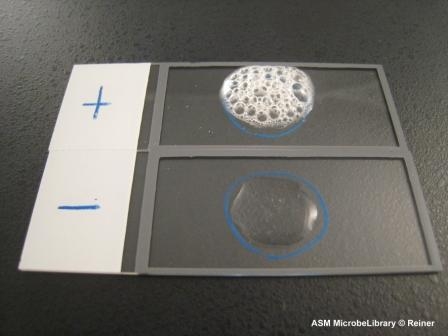
What result does staphylococcus aureus produce in the catalase test?
Positive
What is the principle behind the catalase test?
The bacterium contains catalase that will break down H2O2 into H2O and O2
What is the coagulase test used for?
To differentiate between Staph aureus (positive) from coagulase negative staphylococcus

What test is seen here, and what organism could it be?
Tube coagulase test
Positive: Staph aureus
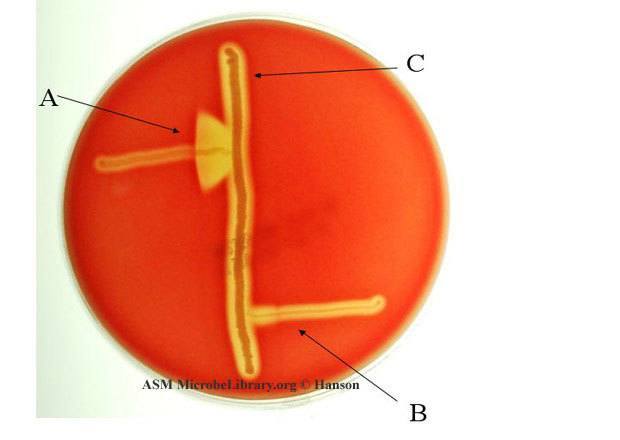
what test is seen here?
what organism is the middle streak
what organism gives a positive result? (arrow head)
CAMP test
Staph aureus
Streptococcus agalactiae
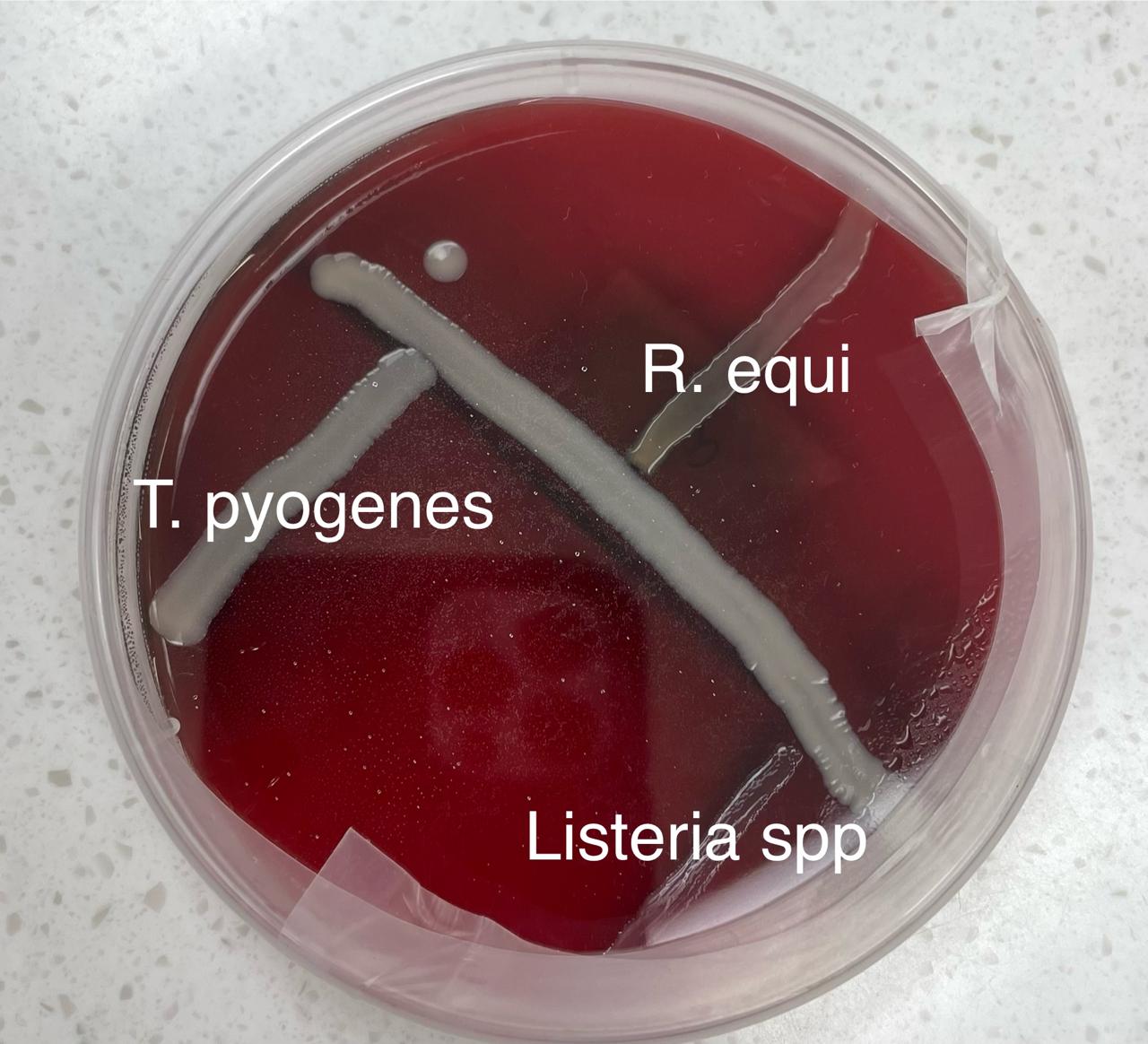
Which organisms are CAMP positive?
Listeria spp and Rhodococcus equi
How does the CAMP test work?
Interaction of the beta-hemolysin from staph aureus with a protein produced by group B streptococci causes synergistic hemolysis
Which organisms are catalase positive?
Nocardia asteroids
Rhodococcus equi
Listeria monocytogenes
Bacillus spp
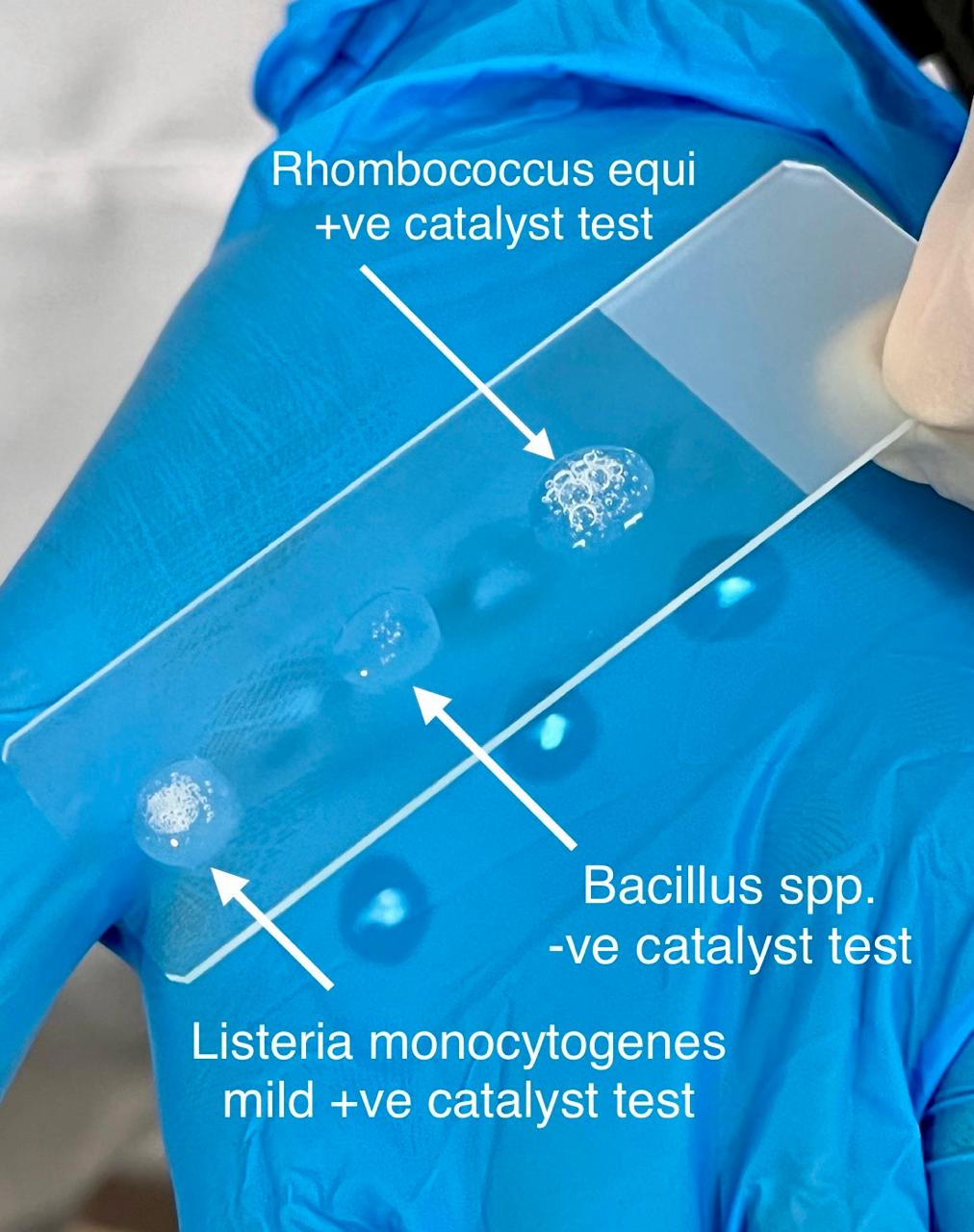
What’s an example of a catalase negative organism?
Trueperella pyogenes

What is the media and what organism is present?
Listeria monocytogenes in motility media
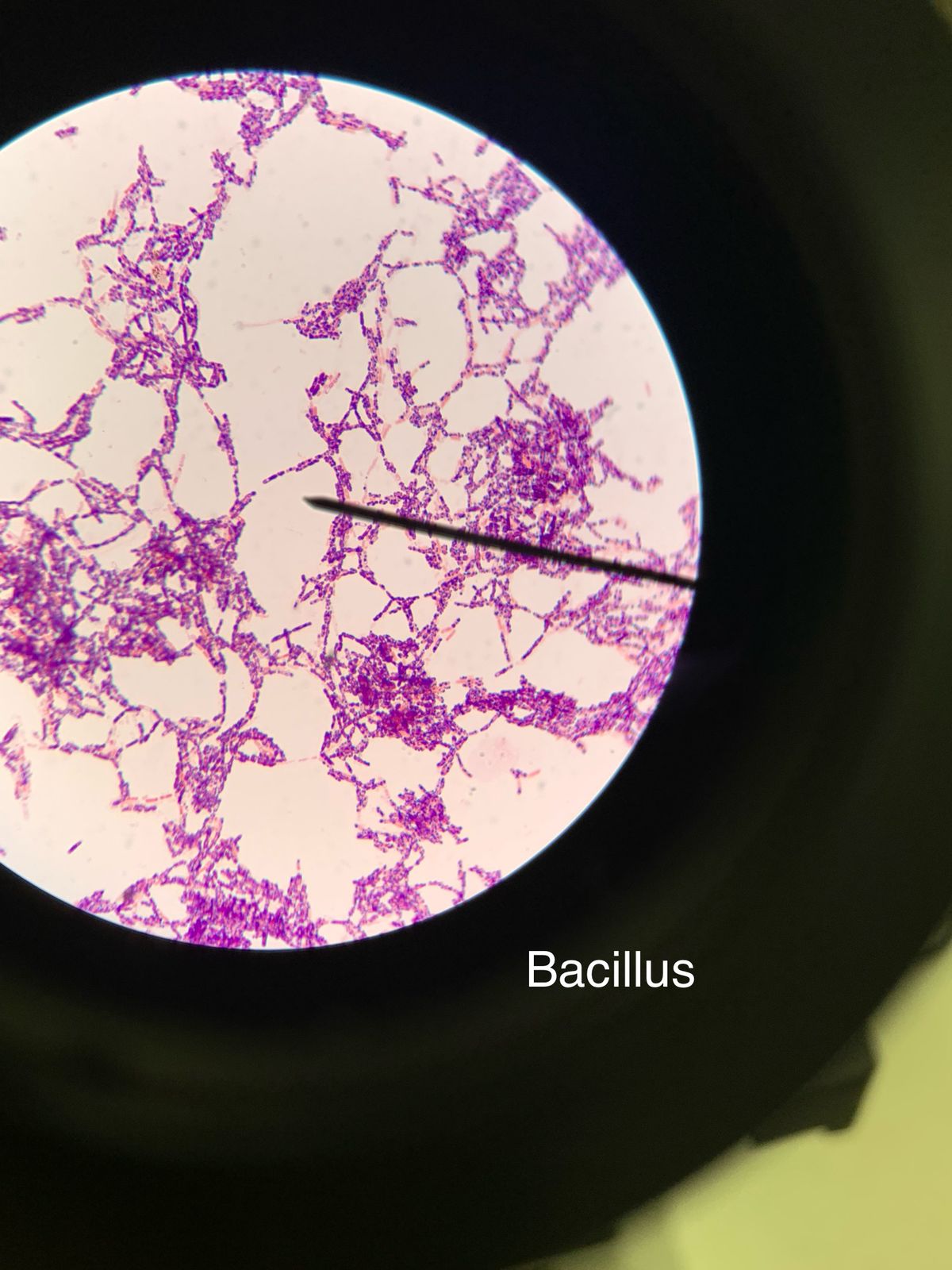
What species is this?
Is it gram positive or gram negative
Bacillus spp.
gram positive
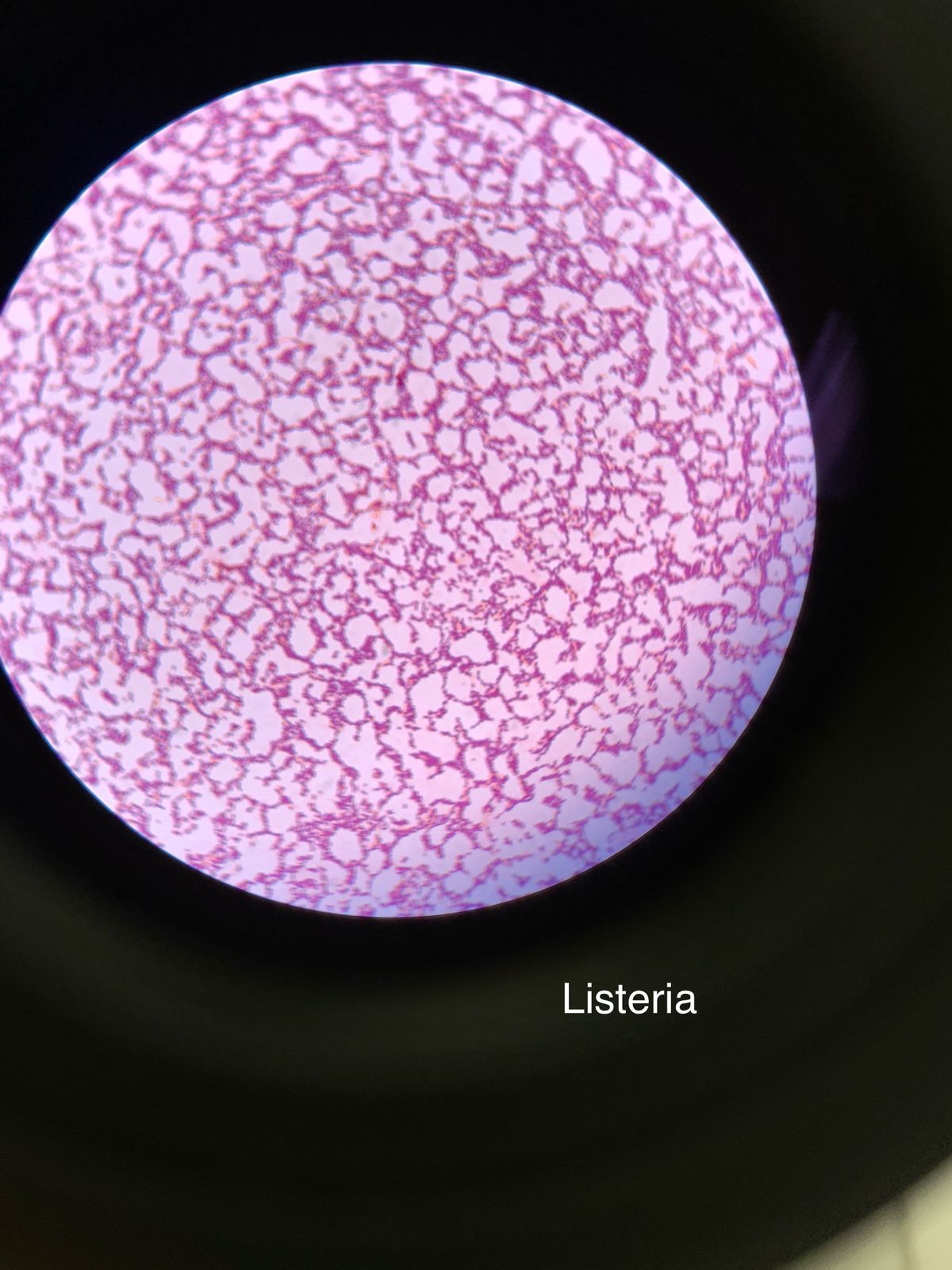
what organism is seen here?
Is it gram-positive or gram negative?
What is it’s shape?
Listeria monocytogenes
gram positive
rod-shaped
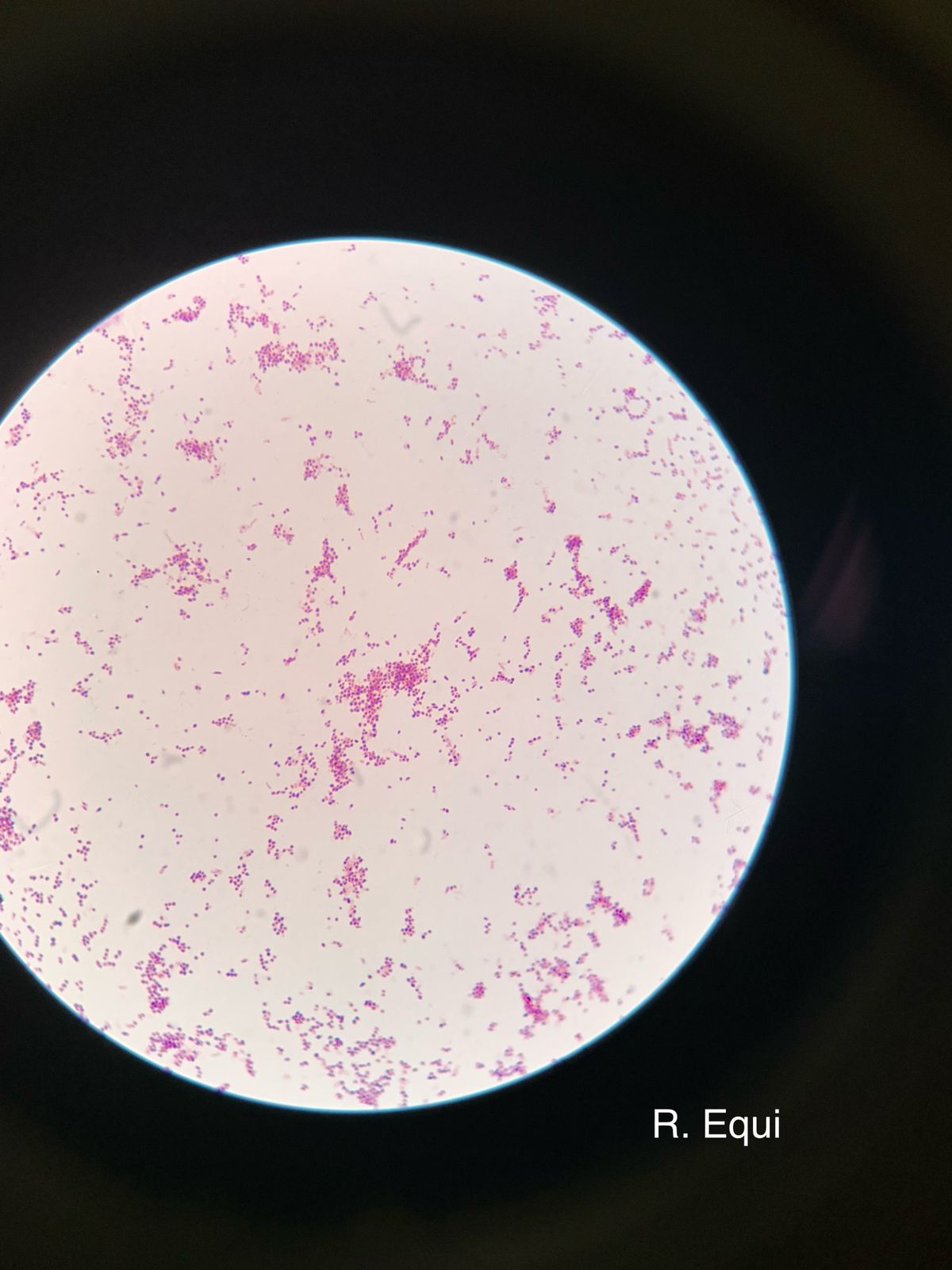
What organism is seen?
Is it gram-negative or positive?
What is the shape?
Rhodococcus equi
gram-positive
Coccobacilli
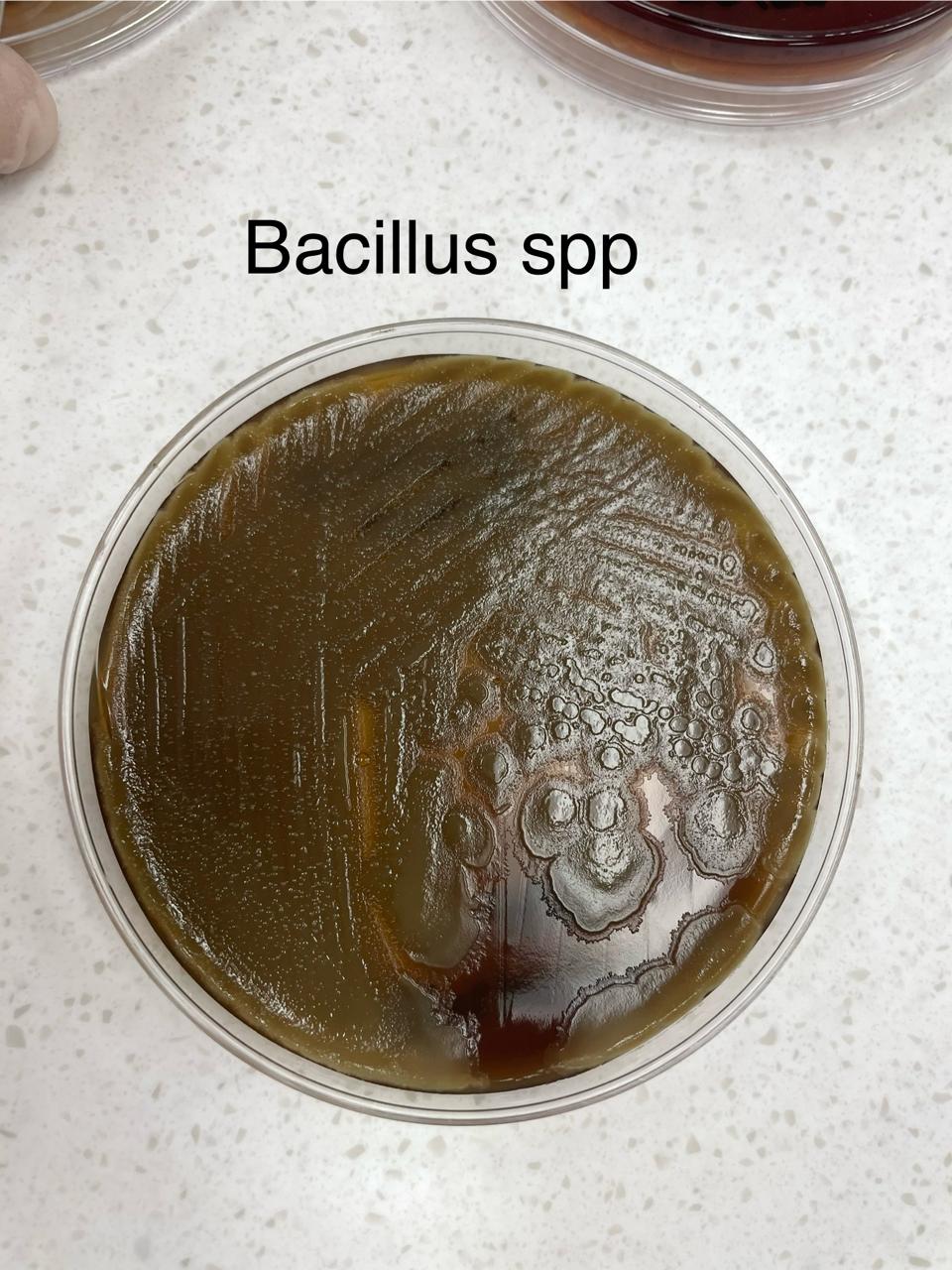
What organism is displayed on this plate?
Bacillus spp.
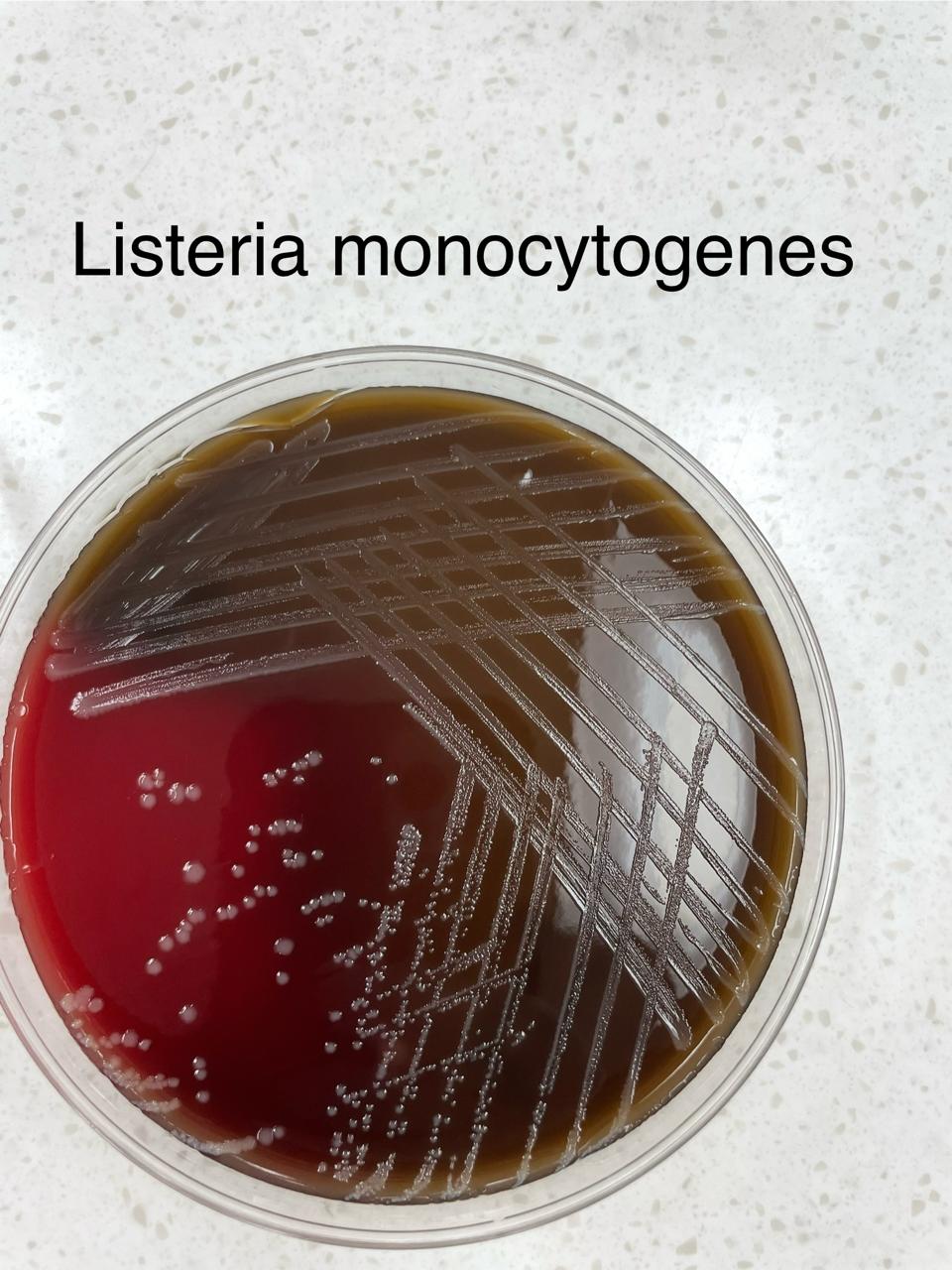
What organism is displayed on this plate?
Listeria monocytogenes
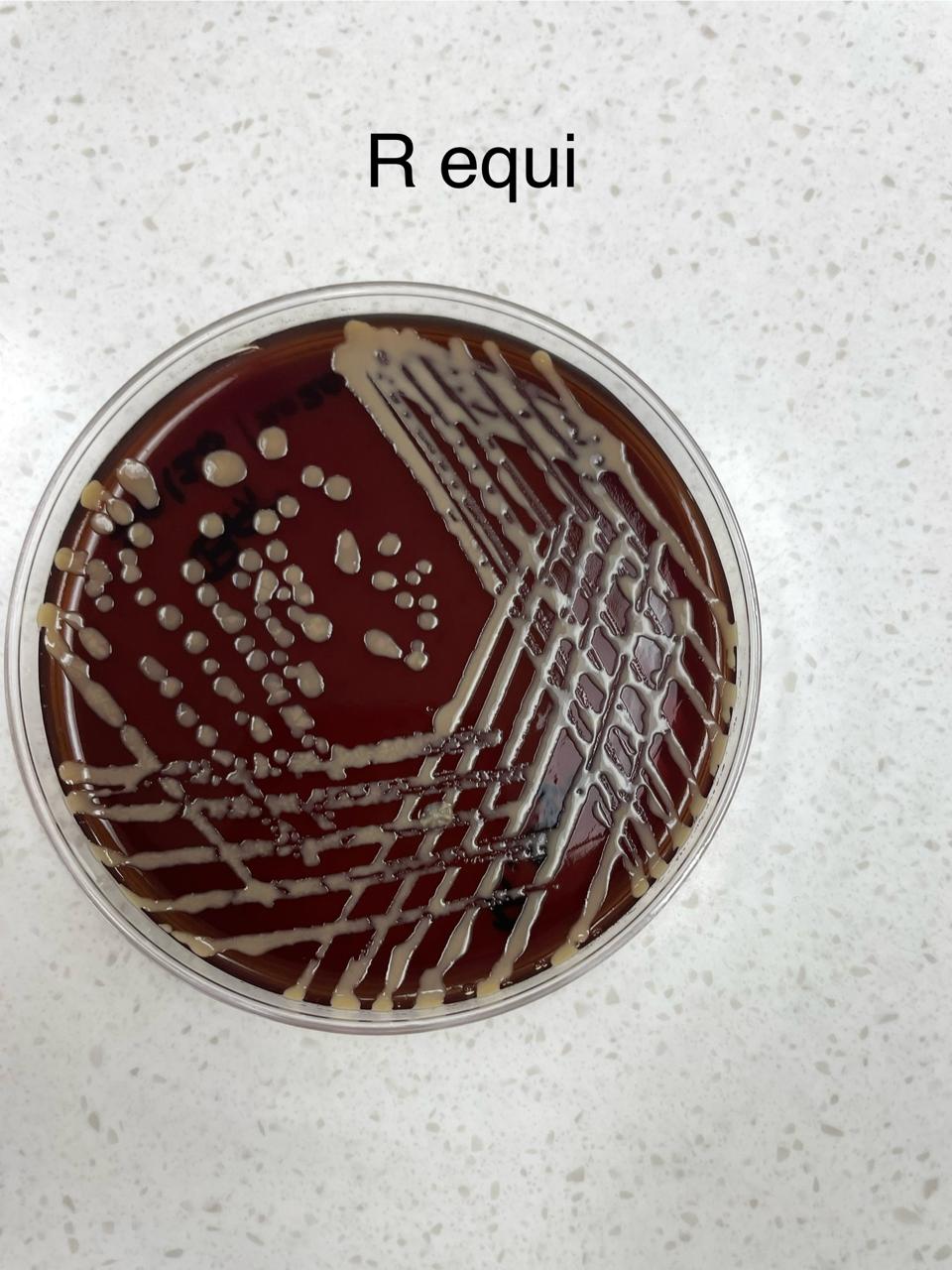
What organism is displayed on this plate?
Rhodococcus equi
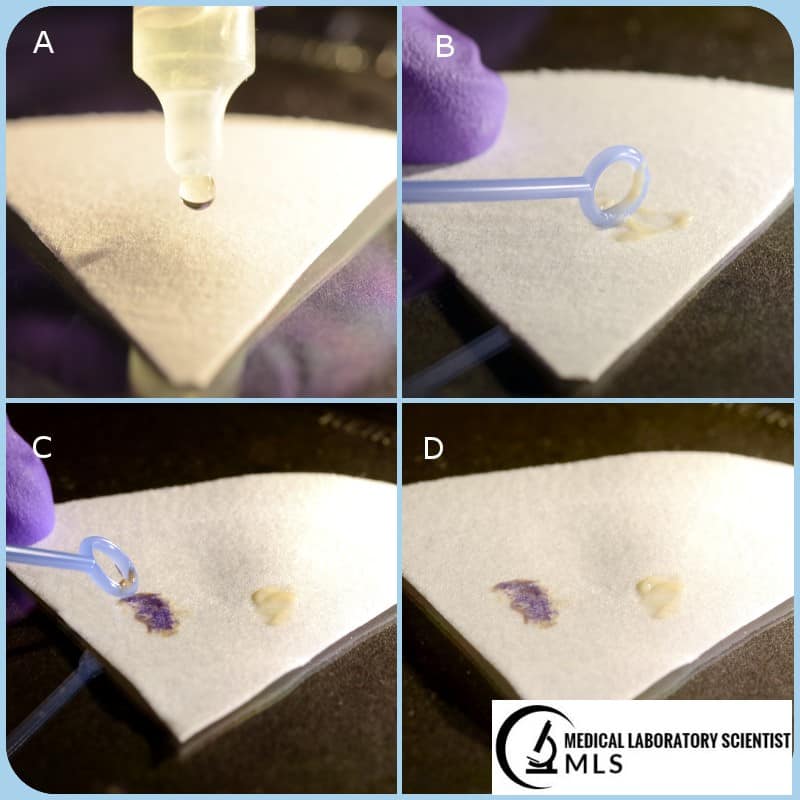
What is the principle of the oxidase test?
What is an organism that is oxidase positive?
Cytochrome oxidase enzyme oxidizes the reagent to a purple end product
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
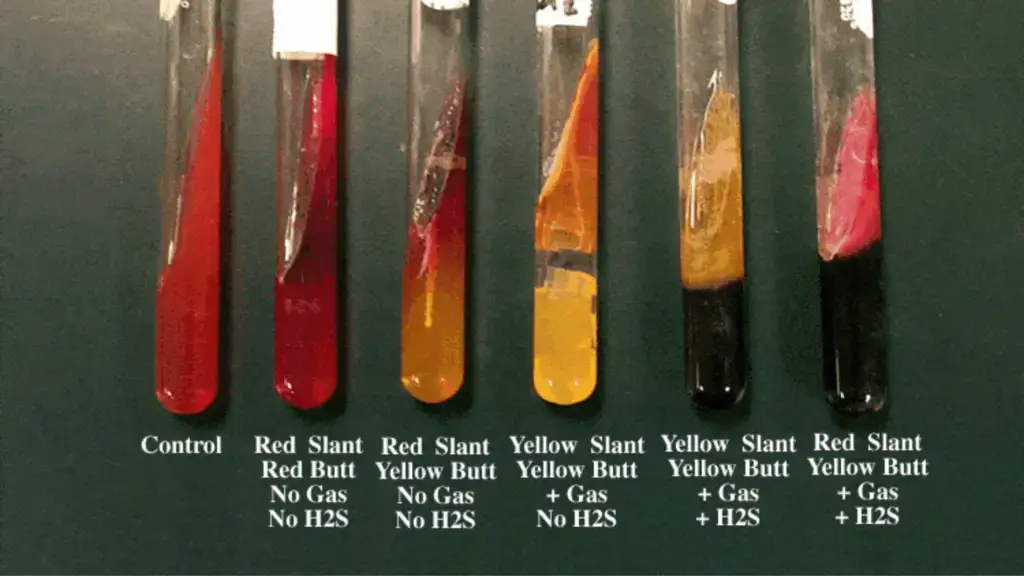

What occurs when the phenol indicator has a red slant and a red butt?
What organisms would cause this?
glucose and lactose non-fermentor
pseudomonas
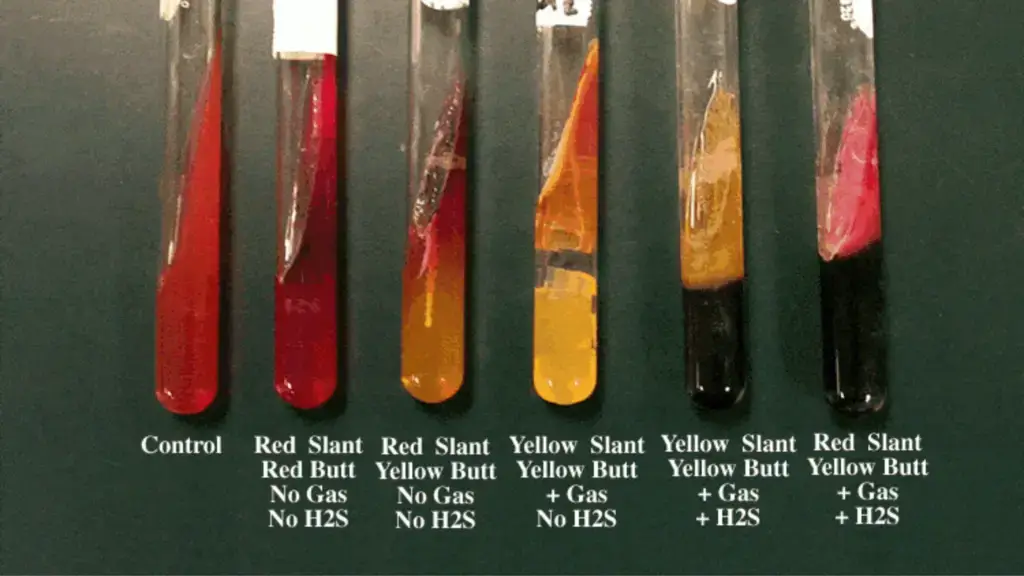

What occurs when there is a red slant and yellow butt?
What organism/s could cause this?
glucose fermentation only
Shigella, Serratia
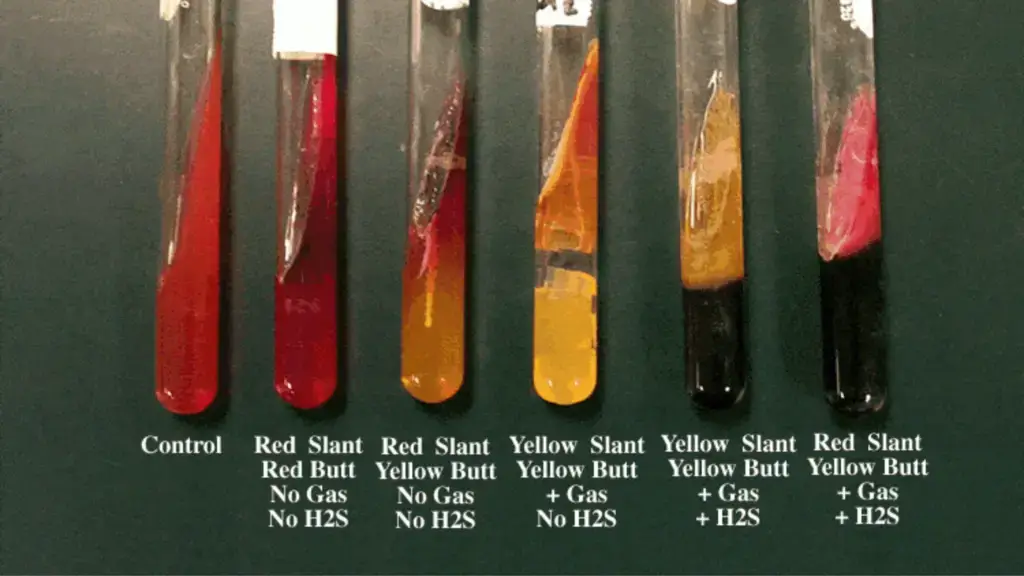

What occurs when there is a yellow slant, yellow butt and gas?
What organism/s can cause this?
glucose and lactose fermentation, and gas production
Escherichia, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
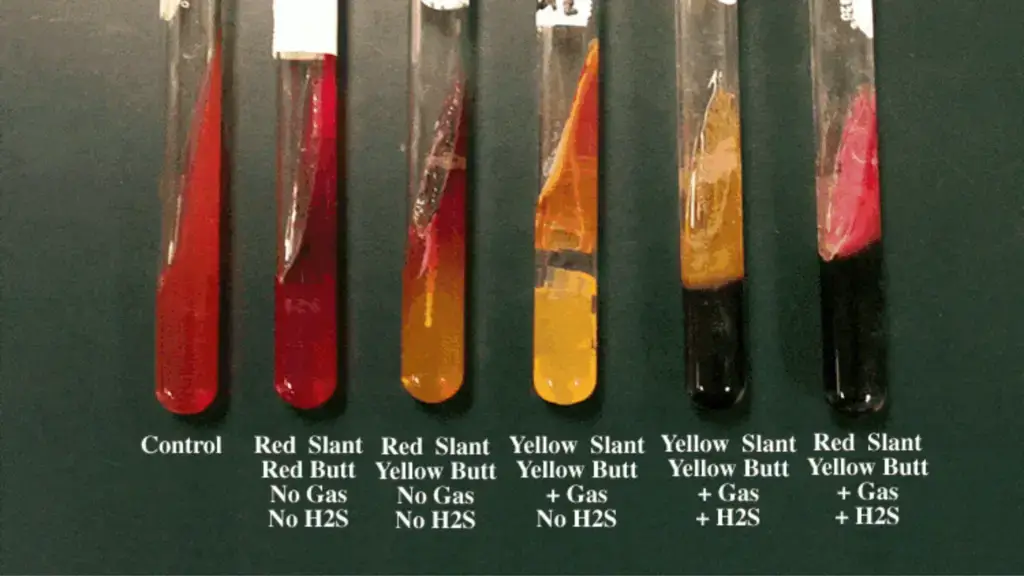

what occurs when there is a yellow slant and butt, gas, and a black colour?
What organism/s can cause this?
glucose + lactose fermentation, gas production, H2S production
?
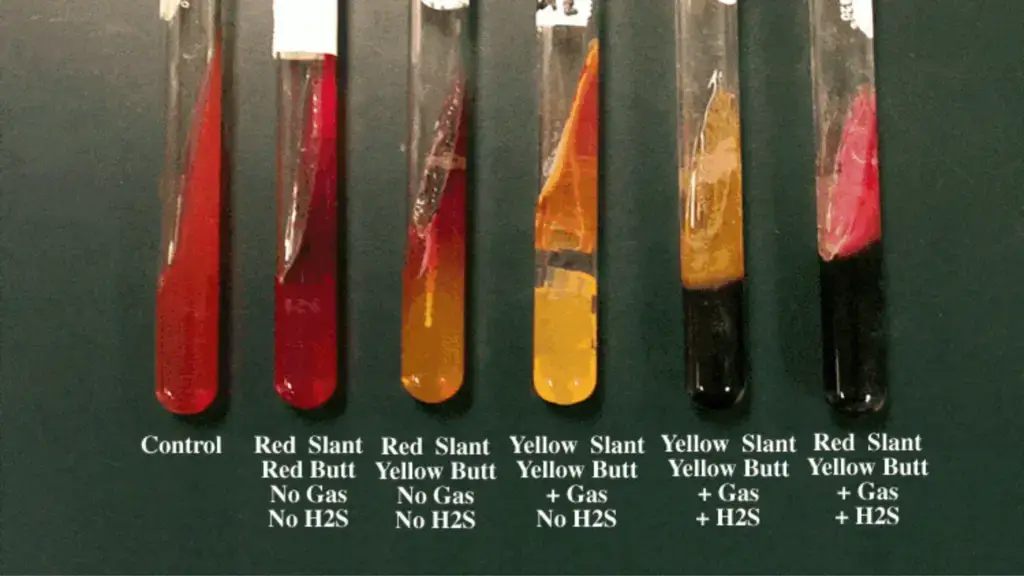

What occurs when there is a red slant, yellow but, gas and black coloration
What organism/s can cause this?
Glucose fermenter, gas producing, H2S producing
Salmonella, Proteus

What does a positive urease test look like?
What is the principal behind it?
What organism produces a positive result?
What organism produces a delayed-positive result? (weak pink coloration)
Production of a bright pink color on the slant that may extent to butt
Reaction from interaction of metabolic waste indicating the presence of enzyme (urease) required to break down carbohydrate.
Proteus spp.
Klebsiella pneumoniae

What organism produces a urease negative result?
Escherichia coli

What is the SIM medium used for?
Differentiation of microorganisms on the bases of hydrogen sulfide production, indole production and motility

What is motility indicated by?
What organism displays positive motility?
turbidity of the medium or growth extending from inoculating stab line
Salmonella spp
(also produces H2S)

What is the positive test for Indole production?
What organism produces this result
Red color after the addition of Kovac’s reagent
Shigella spp.

What test medium is this?
What’s the principle behind it
Simmons citrate agar
organisms that can utilize citrate contain permeases which results in the formation of CO2 reacting with the medium to produce sodium carbonate, which raises the pH

What is the positive citrate test?
What organism causes this?
increase pH causes green colour to change to blue
Klebsiella pneumoniae, Citrobacter spp, Enterobacter aerogenes
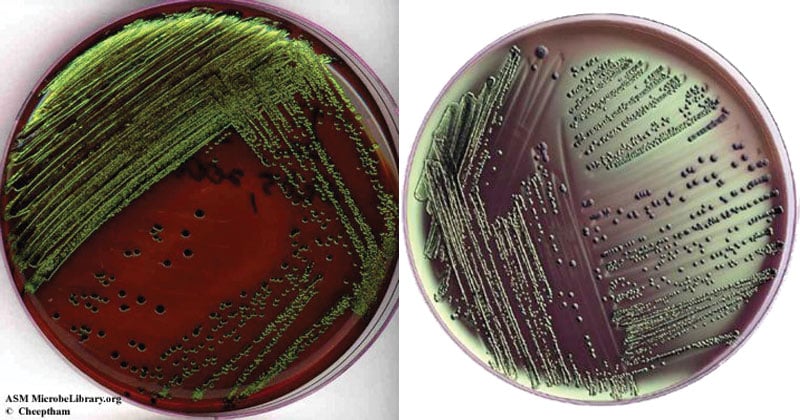
What is EMB used for?
What is the result of lactose fermenters?
What is the result of non-lactose fermenters?
Isolation and differentiation of gram-negative bacilli
Blue-black with or without a green metallic sheen (E. coli)
Colourless and translucent
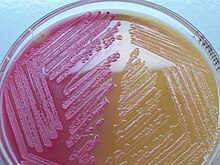
What is MacConkey Agar used for?
What is a positive test?
What organism gives a positive test?
Differentiation of lactose fermenting and non-lactose fermenting
Pink colonies
E. coli, Klebsiella