Cardiac Cycle, Blood Vessels, Blood, Partial Pressures EXAM #3
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
The majority of plasma is made from what?
Water (90-92%)
How do red blood cells carry oxygen? How many molecules of oxygen can each red blood cell carry?
- Red blood cells carry oxygen bound to hemoglobin
- Each hemoglobin molecule can carry up to 4 molecules of Oxygen
Abundance Of WBC in Normal Blood Smear
Neutrophils : 50-70%
Lymphocytes: 20-40%
Monocytes: 2- 8%
Eosinophils: 1- 4%
Basophils: 0.5-1%
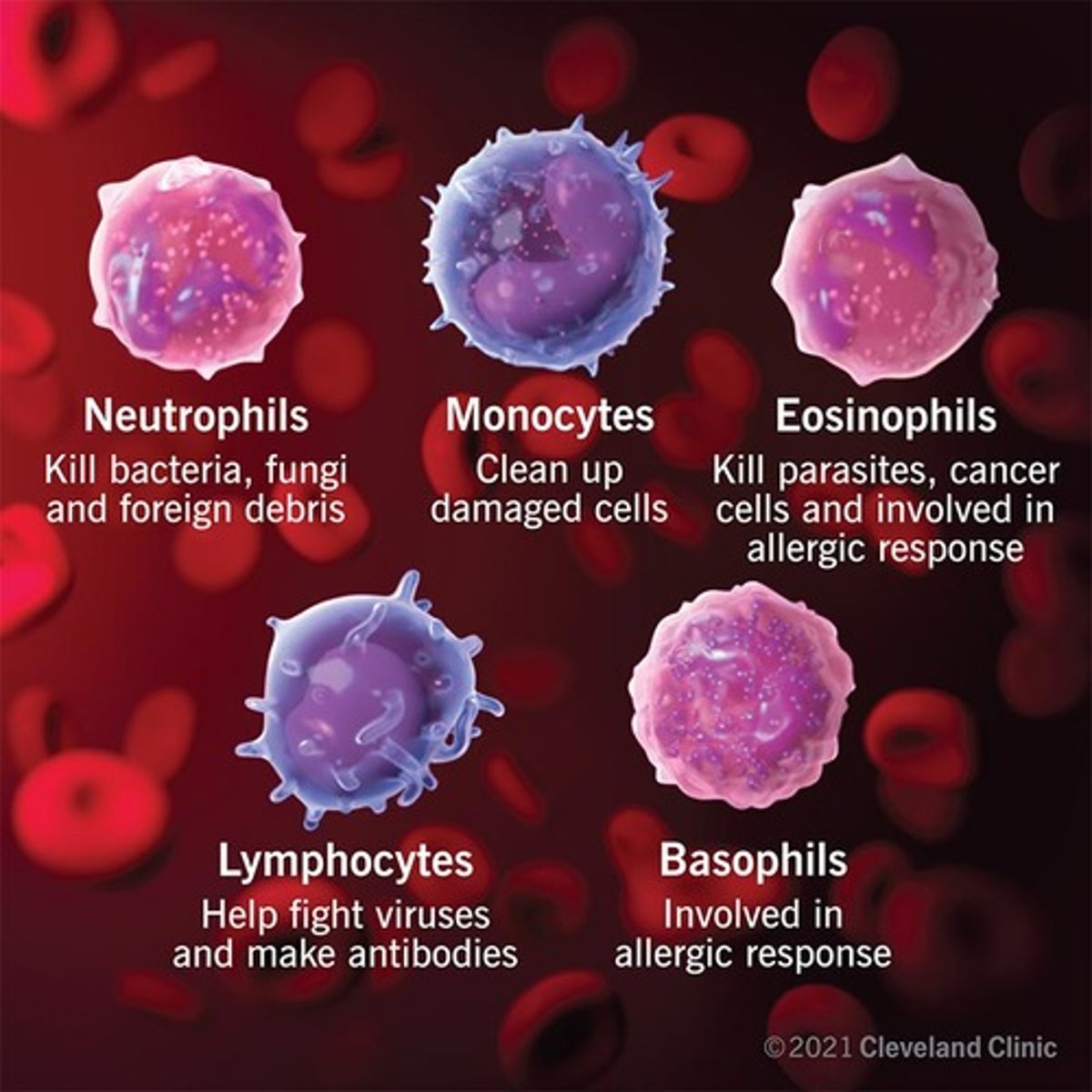
Granulocytes
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
Agranulocytes
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
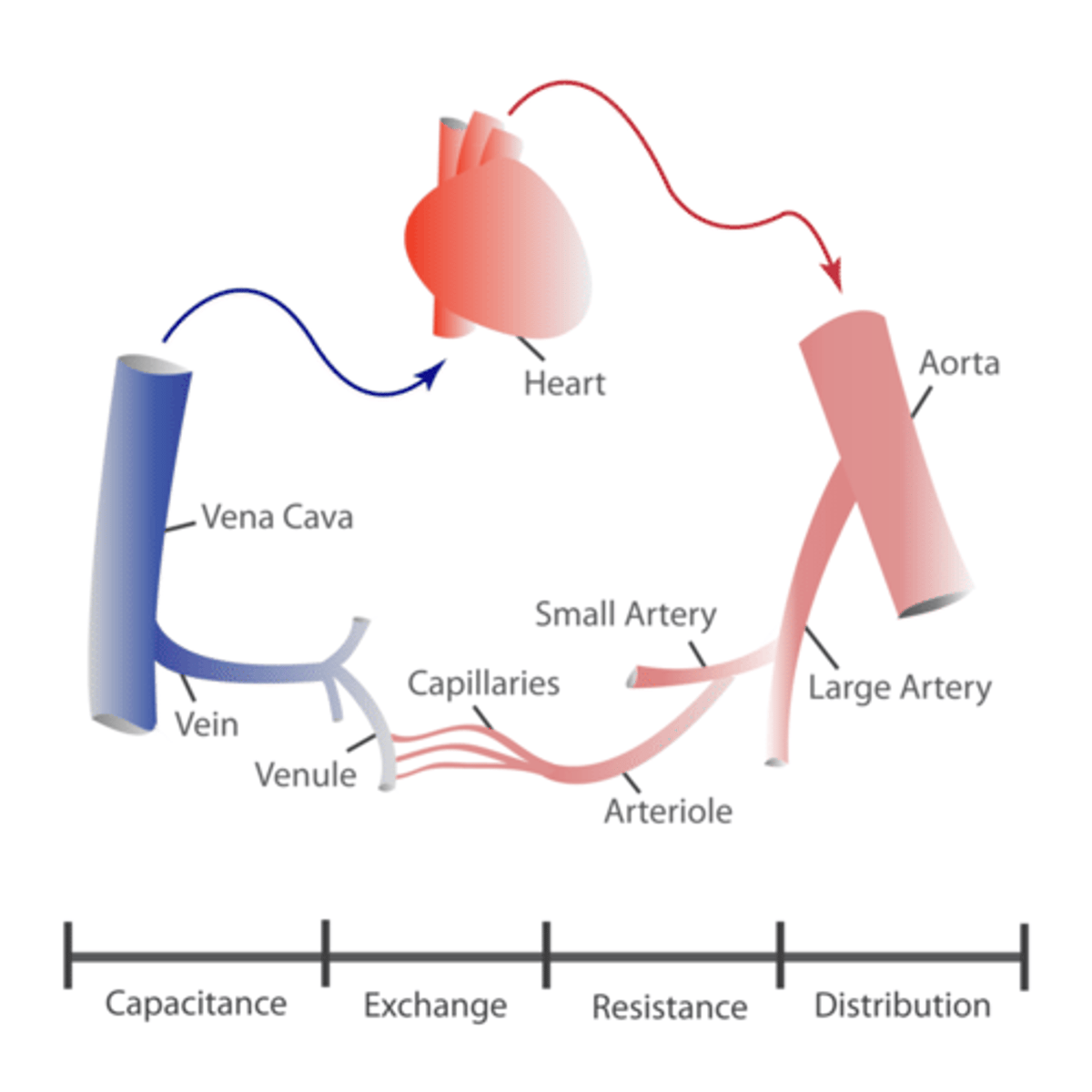
What happens to the diameter of arteries as you get farther away from the heart?
Arteries branch into smaller arterioles and then capillaries, their diameters decrease, by branching and narrowing of arteries it helps regulate blood flow and distribute blood to various tissues throughout the body.
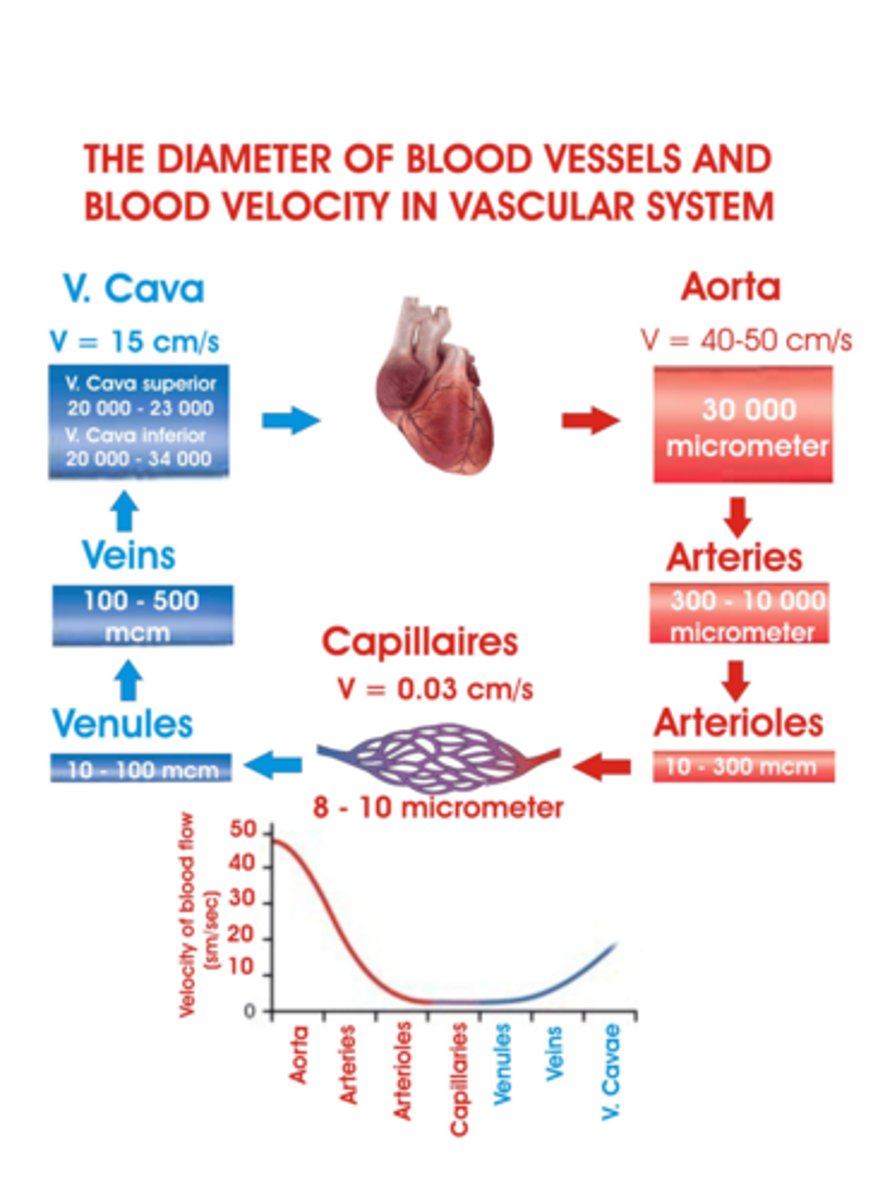
What happens to the diameter of veins from the Venules to the Vena Cava?
Veins gradually increase in diameter as they merge from venules to larger veins and eventually into the Vena Cava. This gradual increase in diameter helps veins accommodate increasing blood volume and lower pressure as blood returns to the heart
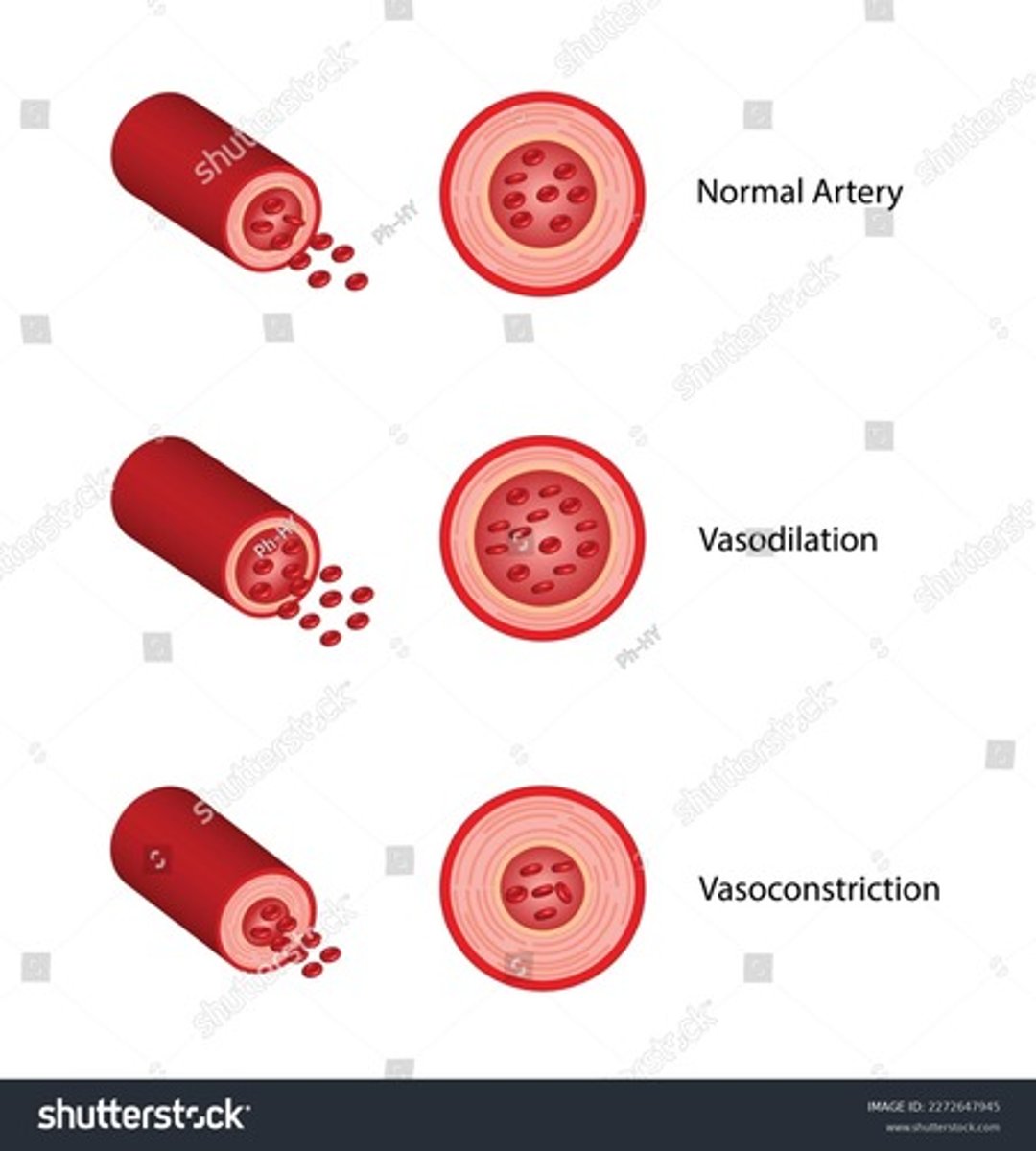
If the Arterioles are under Vasodilation, what happens to the amount of blood flow to the capillaries?
Vasodilation of Arterioles increases blood flow to the Capillaries
What is the purpose of valves in Veins?
- Prevent back flow of blood
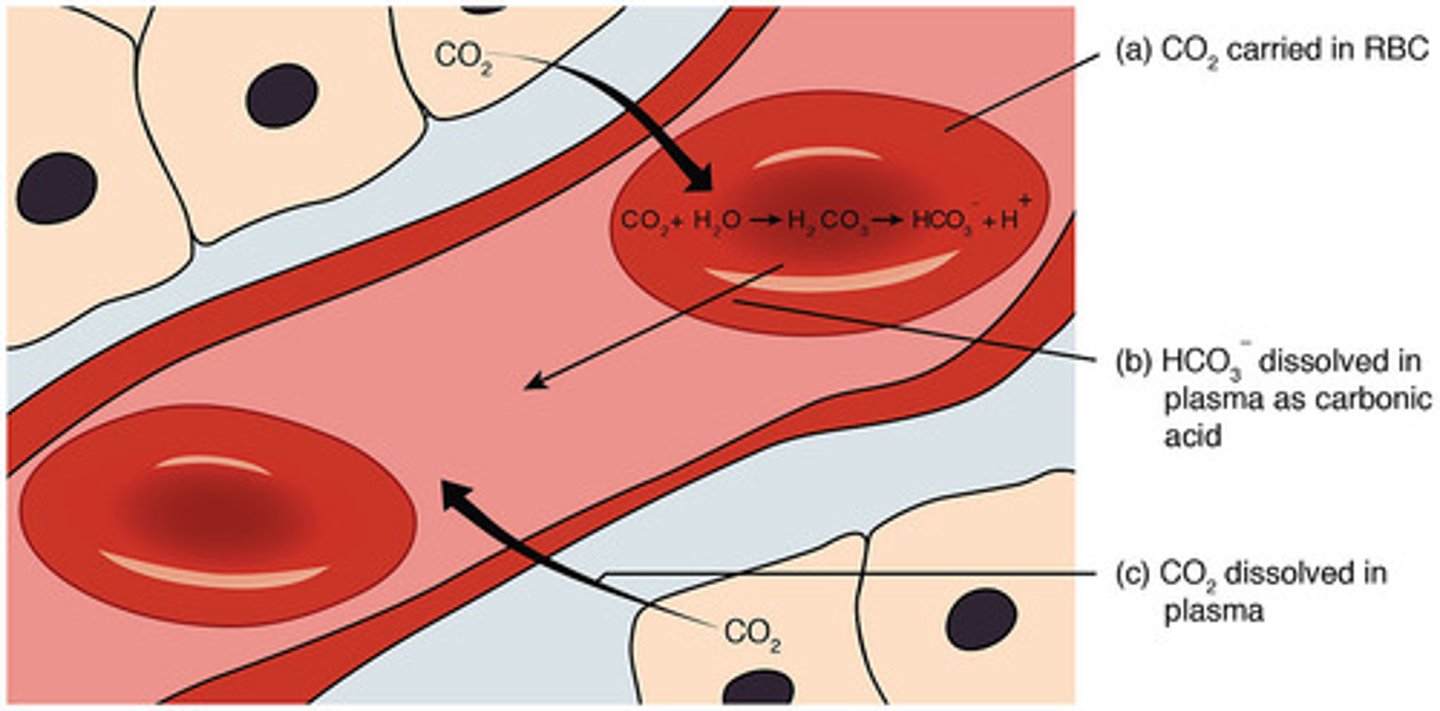
What is the percentage of how we carry CO2 as Bicarbonate (HCO3-) ? What is the function of Bicarbonate?
- Approximately 70%
- Function of Bicarbonate: acts as a buffer in the blood, helping to maintain the pH of blood within a normal range (7.35-7.45)
- Crucial for maintaining acid-base balance in body
What happens to the pressure of an artery during Vasoconstriction?
The diameter of the artery decreases, which increases resistance to blood flow, and a result pressure within the artery increases
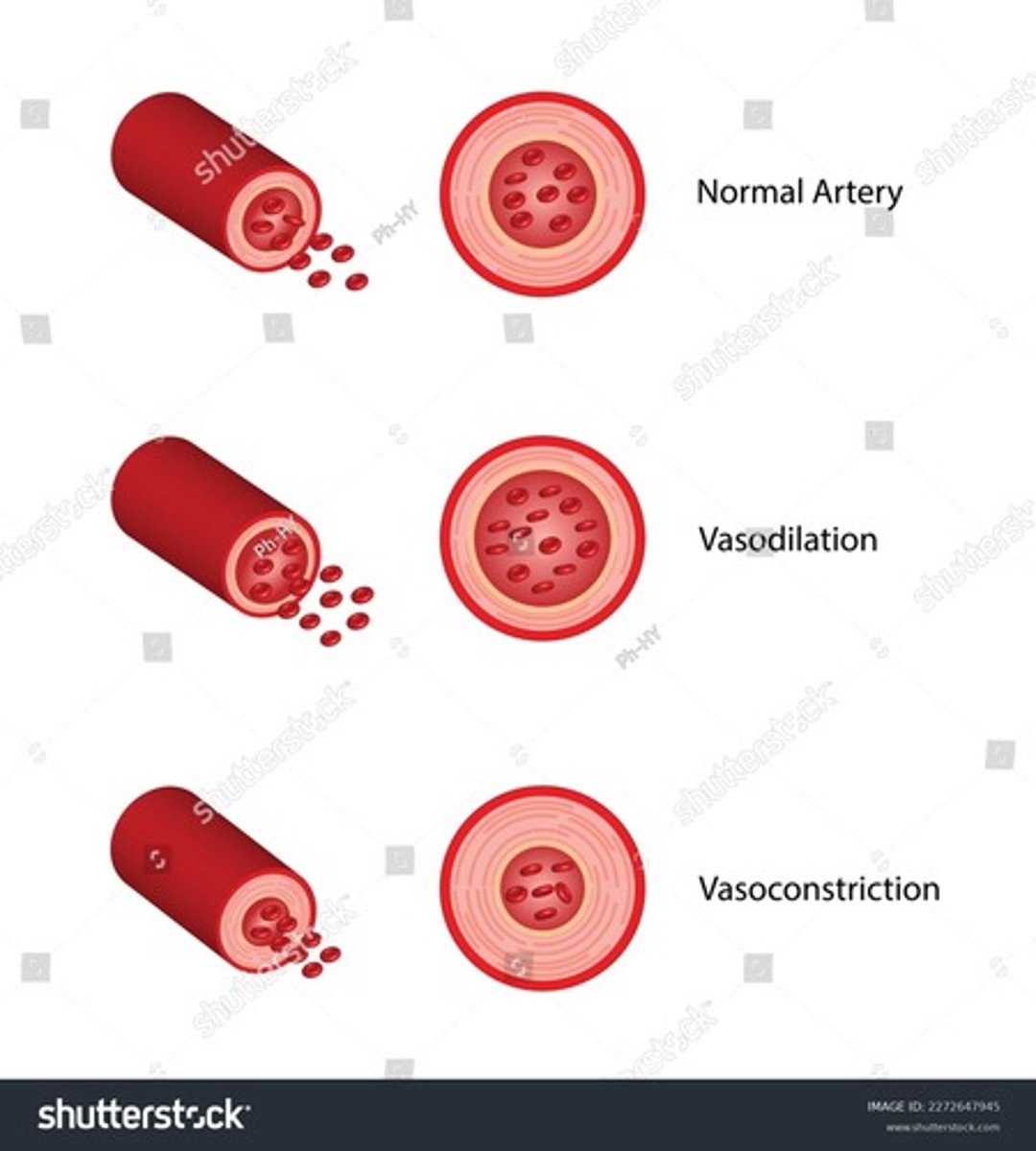
What effect does Vasoconstriction have on overall blood pressure?
Increases overall blood pressure- because the narrowing of the blood vessels increase resistance throughout the circulatory system, causing the heart to exert more force to maintain blood flow, thereby raising blood pressure
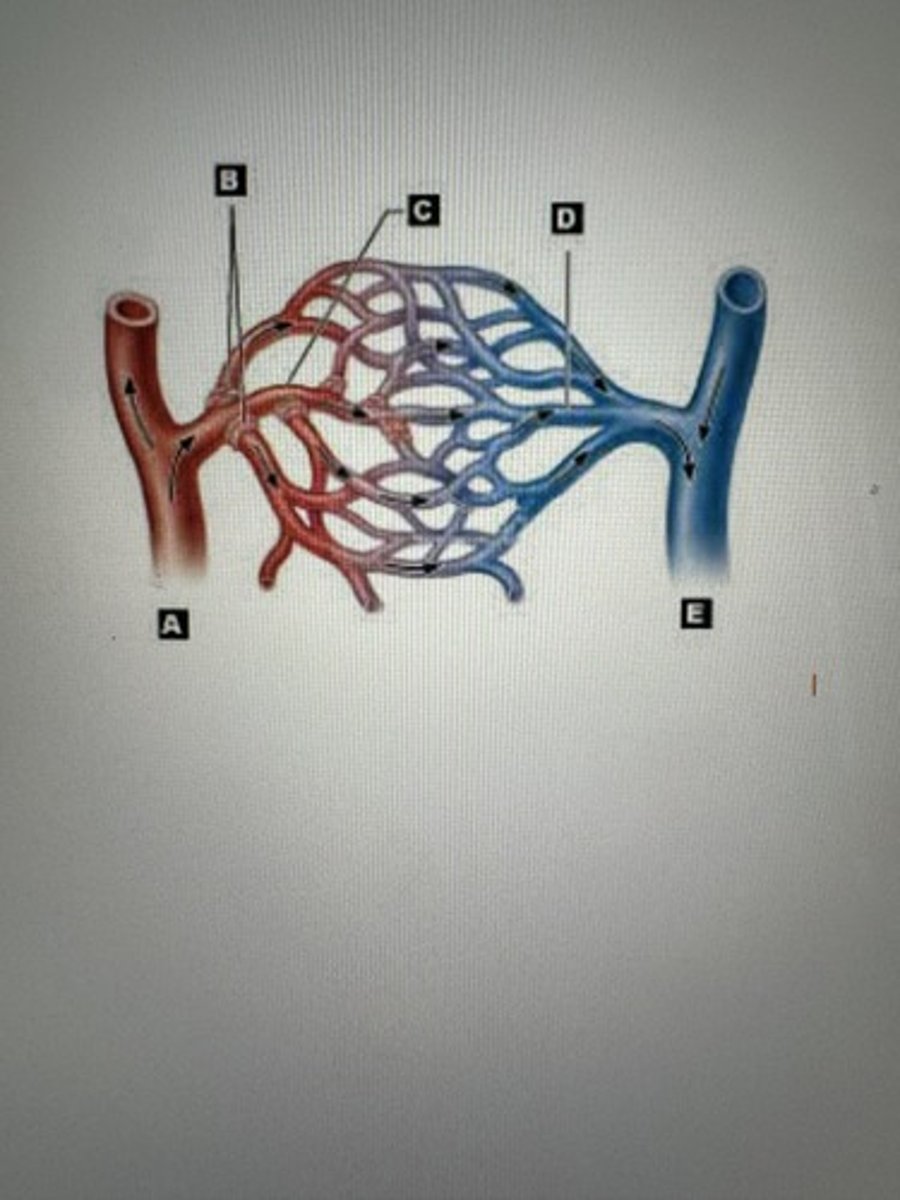
Artery
A
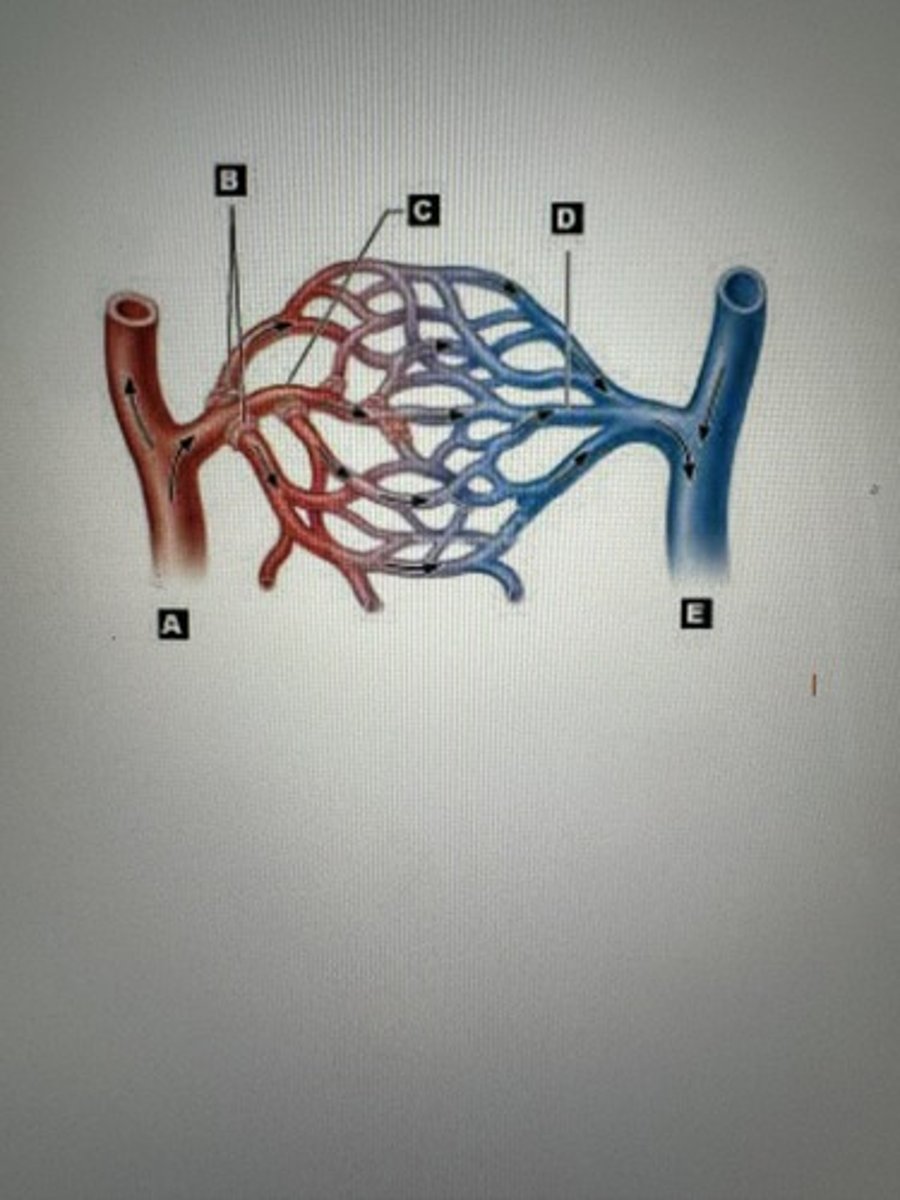
Arteriiole
B
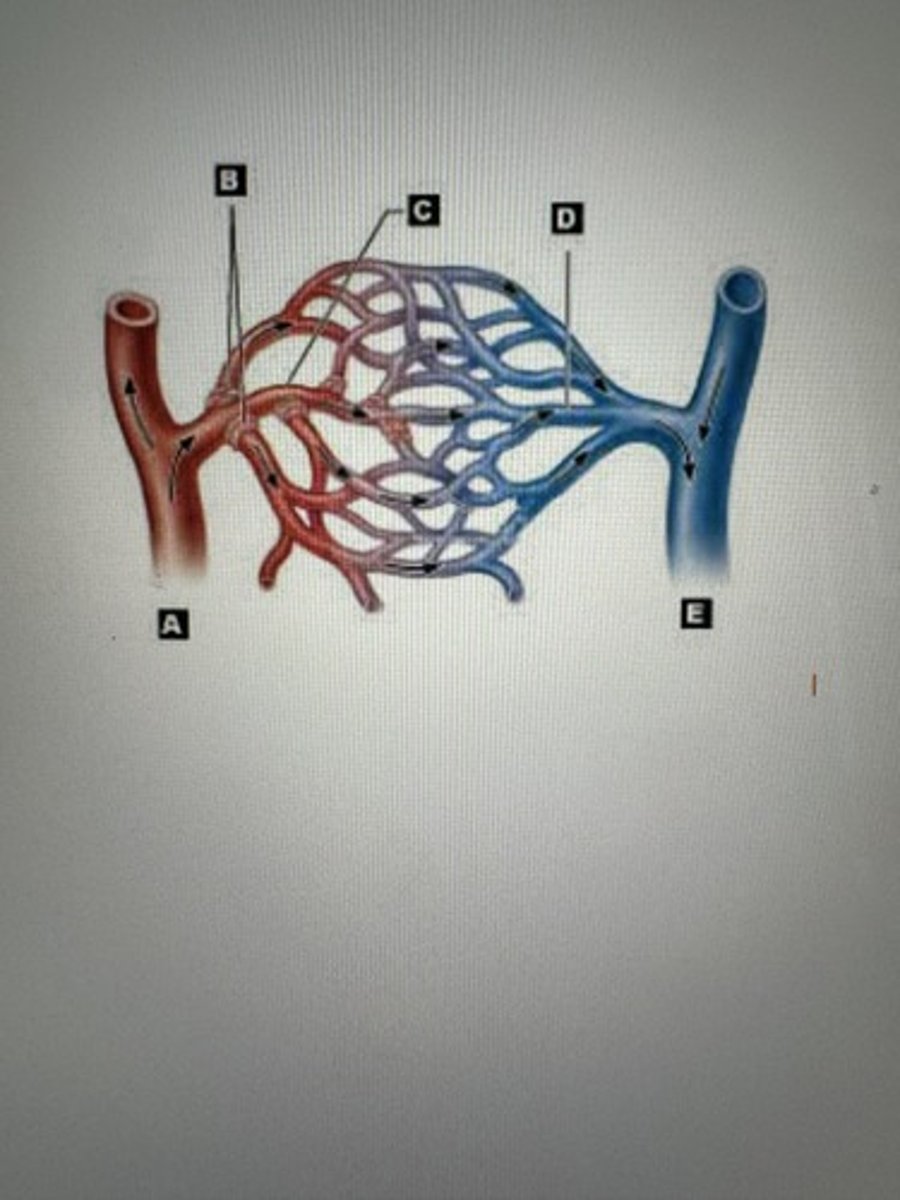
Capillaries
C
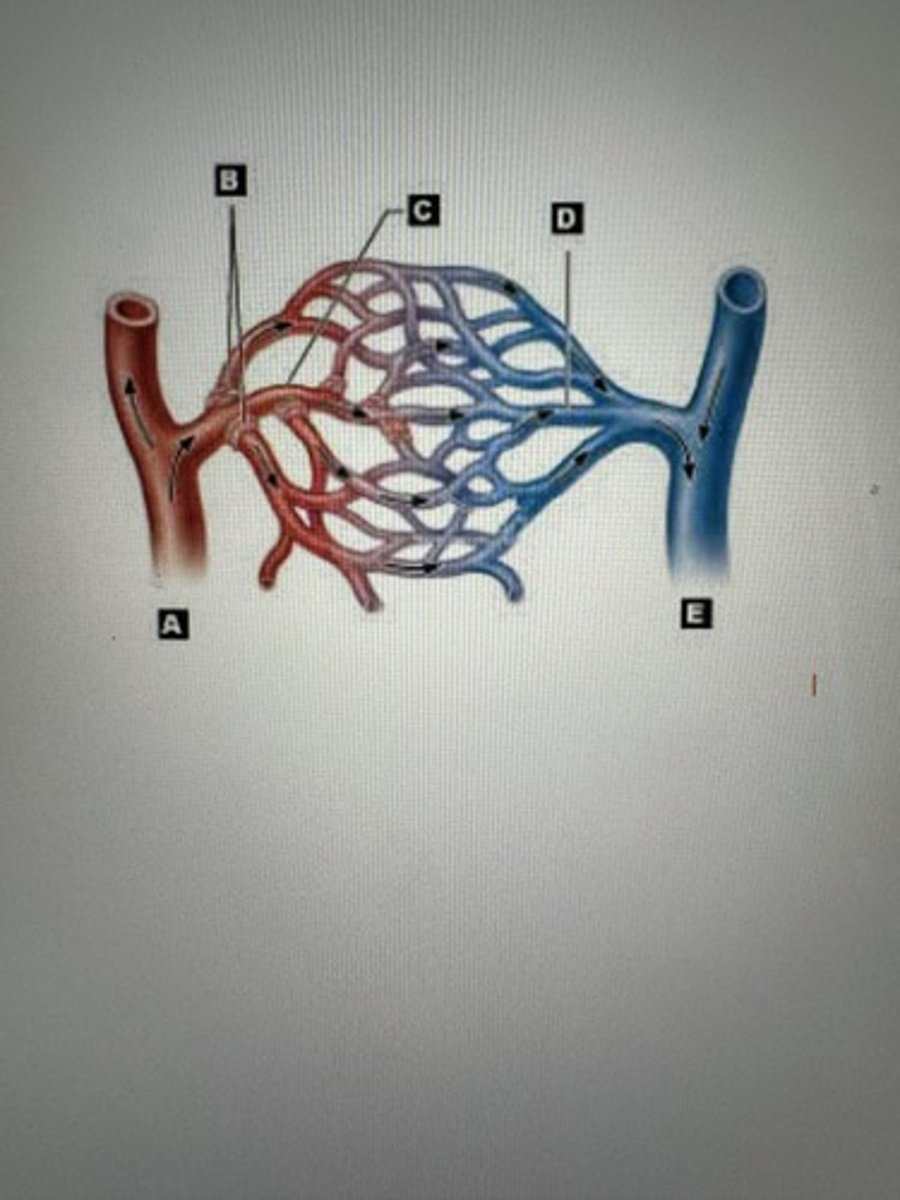
Venule
D
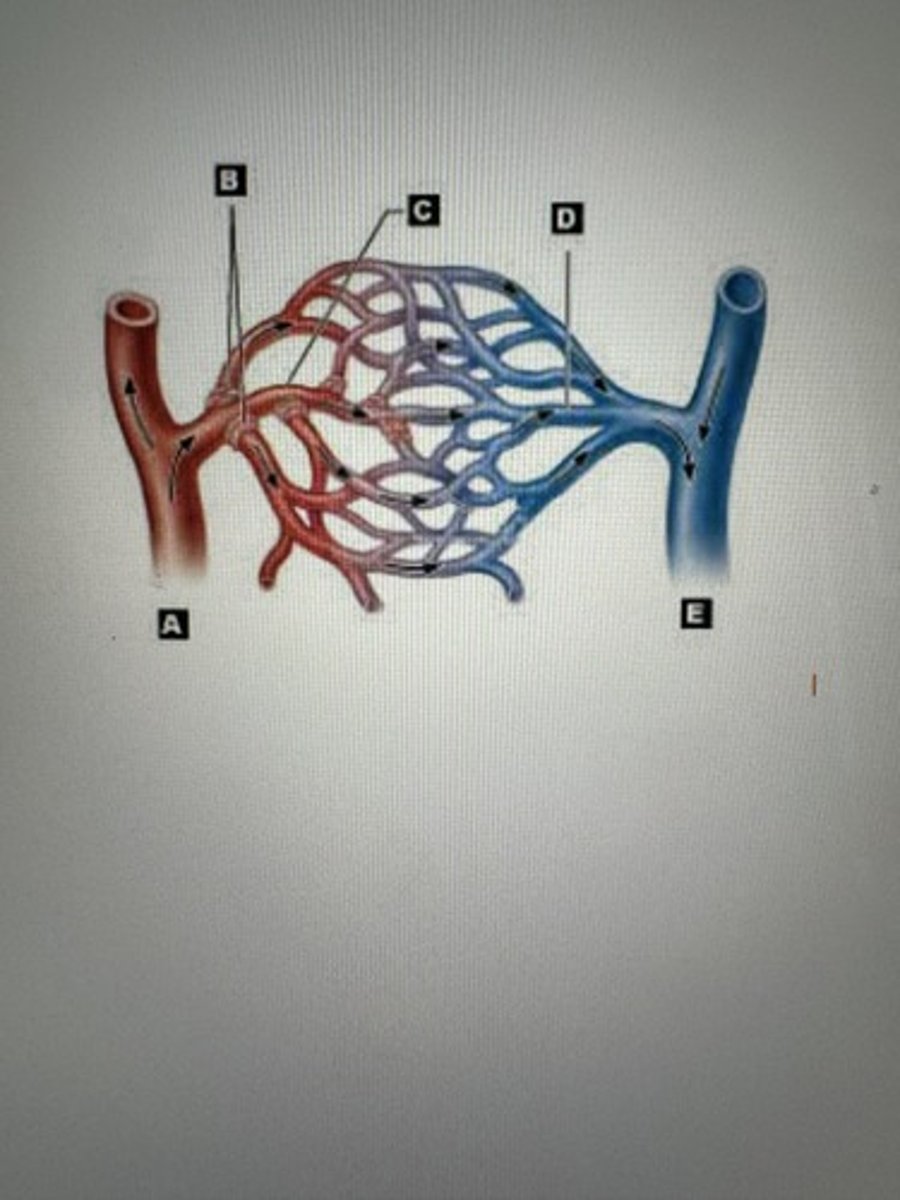
Veins
E
Which blood vessel would have a higher pressure, Venules or the Superior Vena Cava?
Venules
Which Leukocyte can become a Macrophage?
Monocytes- they migrate from the bloodstream into tissues they differentiate into macrophages, which are crucial for phagocytosing pathogens and cellular debris
Partial Pressure of O2 in a Systemic Artery
Around 95-100 mm/Hg
Which neurotransmitter is released from the Sympathetic Nervous System at the SA node to increase heart rate?
Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
What is the normal pH of blood?
7.35-7.45 (slightly basic)
What is the partial pressure of CO2 in the systemic veins returning blood into the Right Atrium?
Around 45 mm/Hg
Which two white blood cells can achieve phagocytosis?
Neutrophils and Monocytes
Which neurotransmitter from the Parasympathetic Nervous System is released at the SA node to decrease Heart Rate?
Acetylcholine
What percentage of CO2 is carried in the plasma?
About 7-10% of CO2 is carried dissolved in the plasma
What are the first blood vessels that branch off the Ascending Aorta?
L + R Coronary Arteries
3 Layers of Veins (Systemic Circuit)
- Tunica Intima
- Tunica Media
- Tunica Externa (Adventitia)
contains DEOXYGENATED BLOOD
Pressure Level : Low Pressure
Carrying blood from where? Away from heart
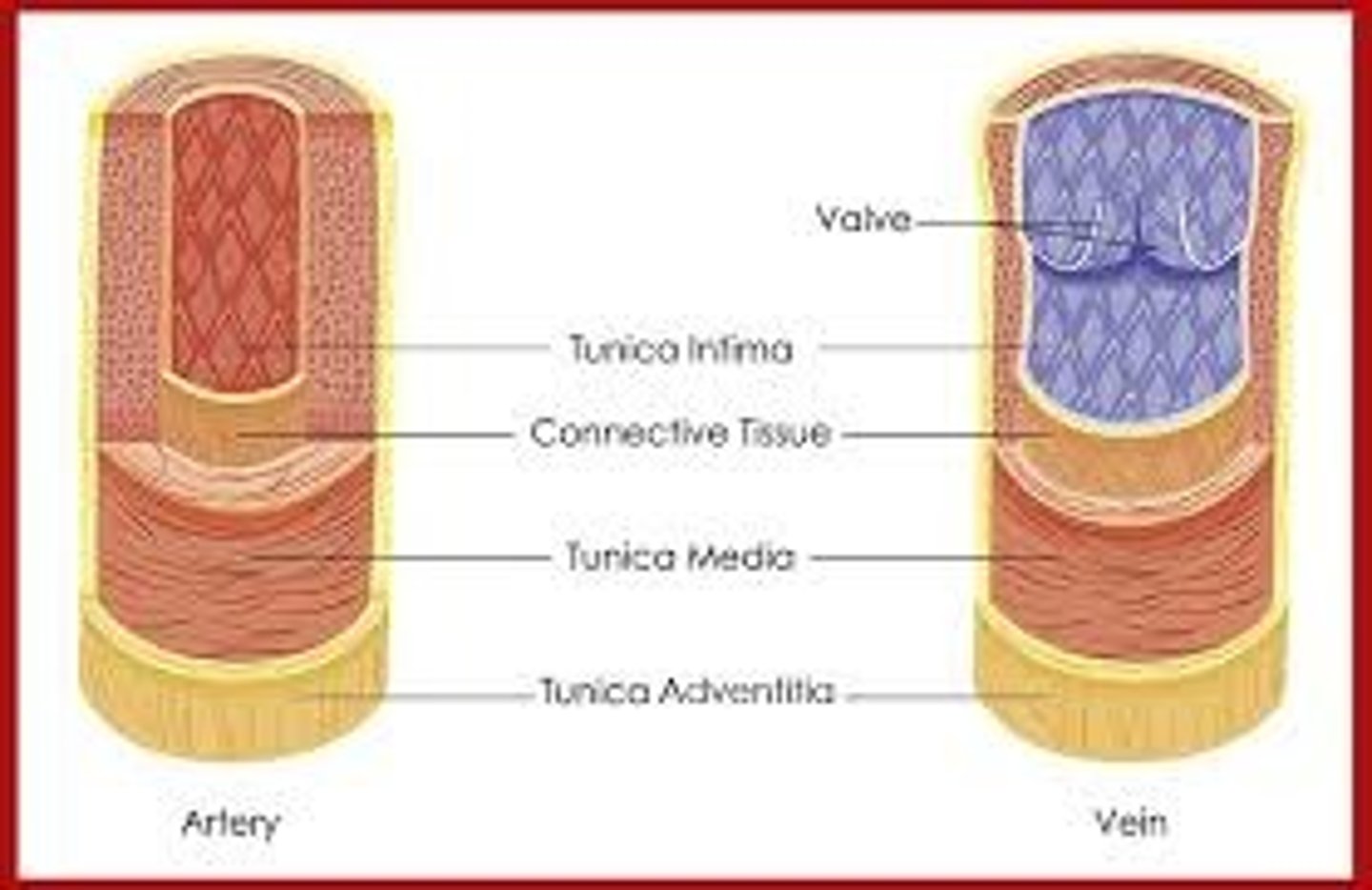
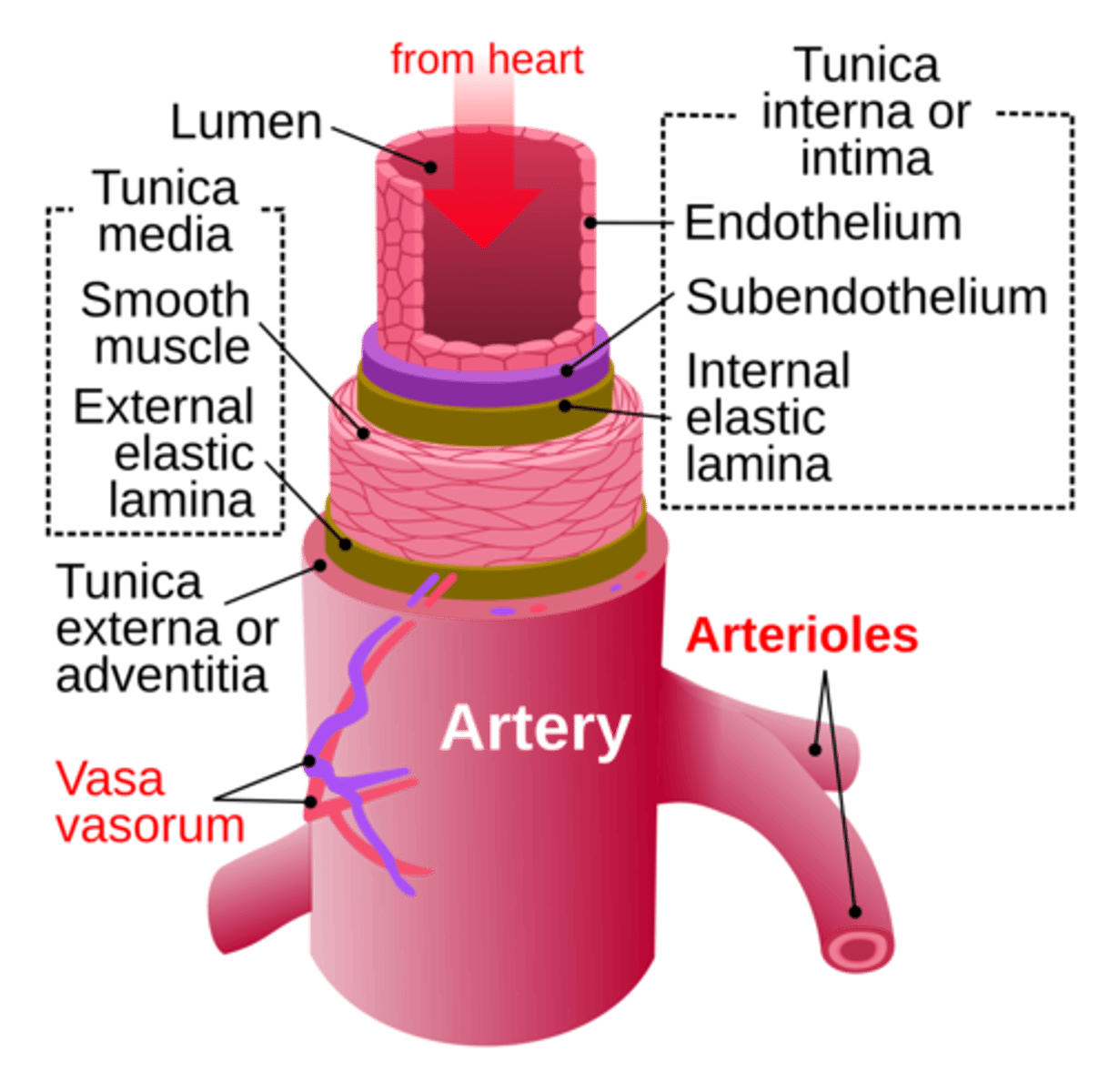
3 Layers of Arteries (Systemic Circuit)
- Tunica Intima
- Tunica Media
- Tunica Externa (Adventitia)
contains OXGENATED BLOOD
Pressure Level: High Pressure
Carrying blood from where? Toward the heart
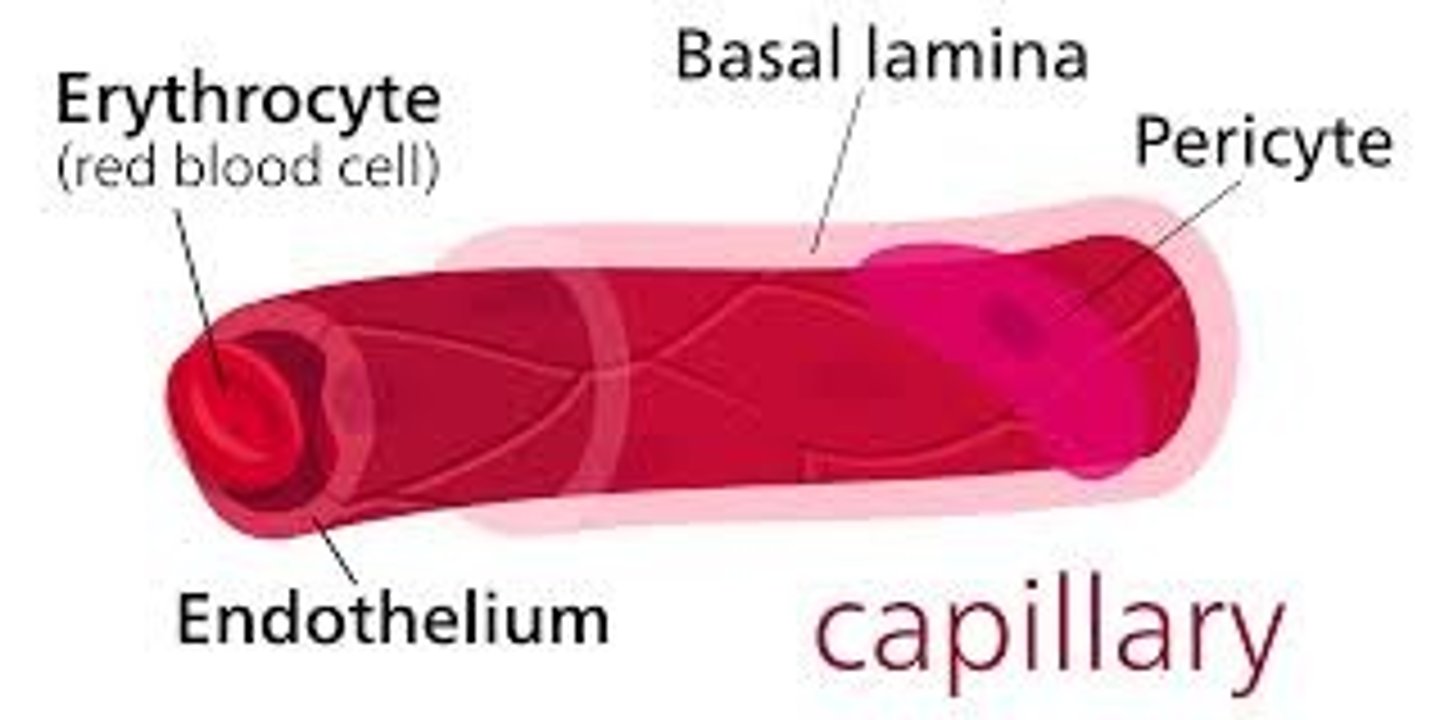
1 Layer of Capillaries (Systemic Circuit)
Endothelium
What is happening in the Capillaries?
Gas Exchange O2-> CO2 between blood and tissues
Nutrient Delivery: to tissues
Waste Removal: from tissues
Fluid Exchange: between blood and Interstitial fluid
Carrying blood from where? Arterial System to the Venous System, facilitating the exchange of O2, CO2, Nutrients, waste products between the blood and surrounding tissues. They connect arterioles (small arteries) to venules (small veins)
ORDER OF VESSELS THAT BLOOD TRAVELS IN ANY CIRCUIT
ARTERIES --> ARTERIOLES--> CAPILLARIES--> VENULES--> VEINS
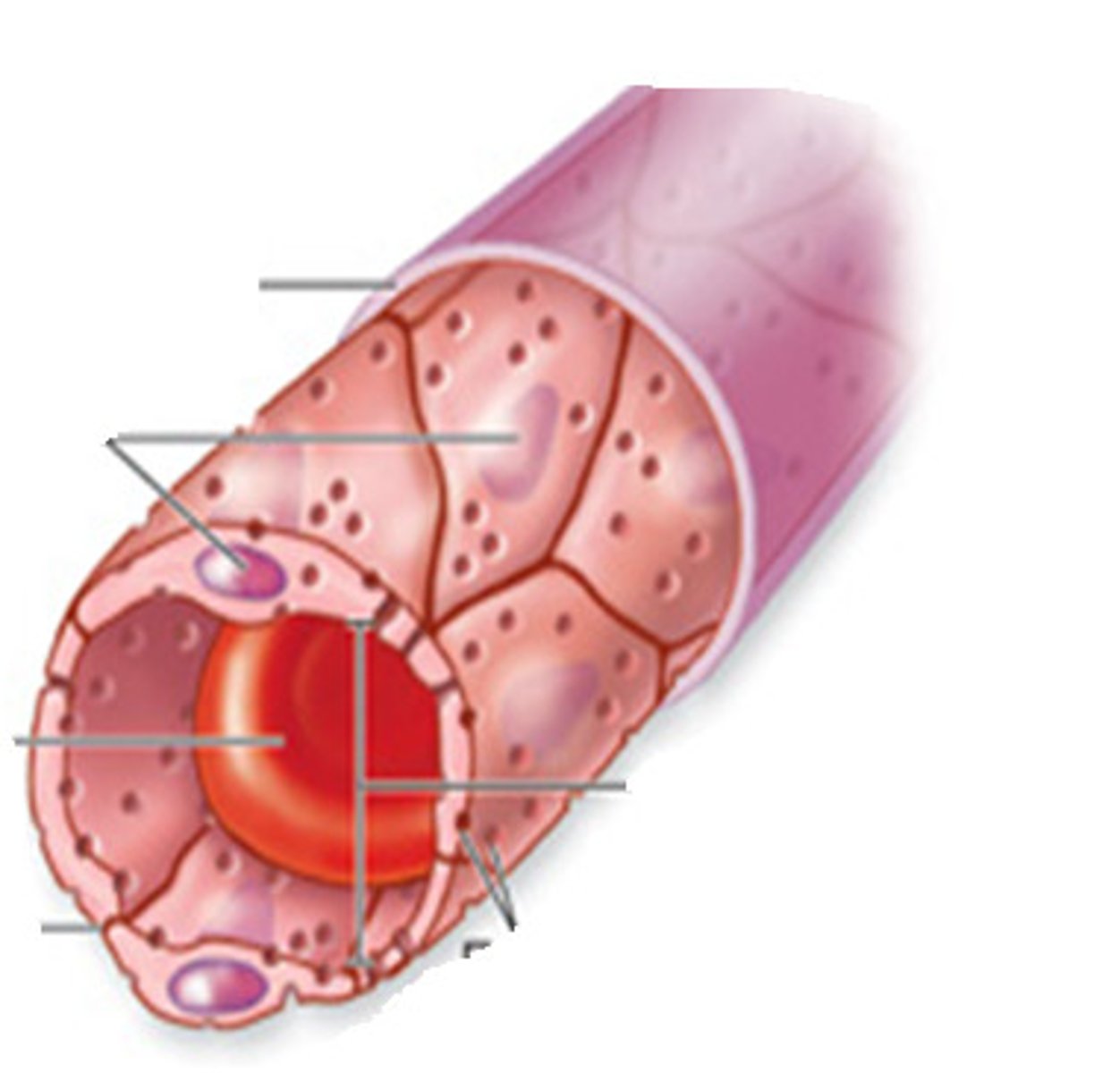
FENESTRATED CAPILLARIES
"Leaky" capillaries- have pores (fenestrations) in their endothelial lining that allow for increased permeability. These pores enable rapid exchange of small molecules and fluids between
What is Oxygen bound to in a red blood cell?
Hemoglobin- can carry up to 4 O2 molecules
Name this white blood cell:
What is the abundance in a normal blood smear?
What is its function?
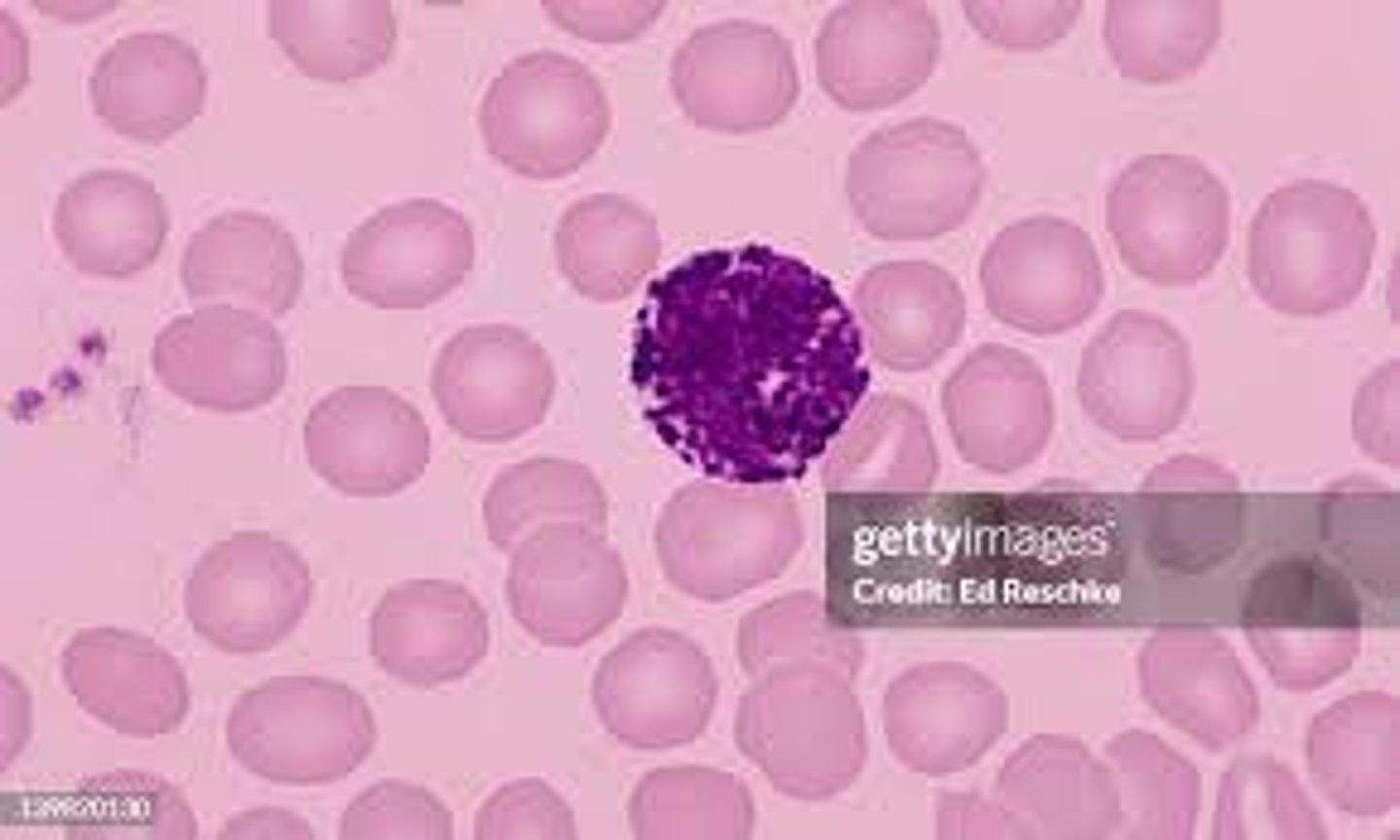
Monocyte
Abundance: 2-8%
Function: Phagocytosis, Differentiation into Macrophages, Antigen Presentation, Cytokine Production
Systemic Arteries Partial Pressure of Oxygen
Systemic Arteries Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide
PO2--> 95-100 mm/Hg
PCO2--> 40 mm/Hg
Systemic Tissues Partial Pressure of Oxygen
Systemic Tissues Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide
PO2--> 40 mm/Hg
PCO2--> 45 mm/Hg
Systemic Veins Partial Pressure of Oxygen
Systemic Veins Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide
PO2--> 40 mm/Hg
PCO2--> 45 mm/Hg
Which way will oxygen diffuse at the systemic tissues? From the tissues into the blood or blood into tissues?
From the blood into the tissues (O2 diffuses from areas of higher partial pressure to areas of low partial pressures)
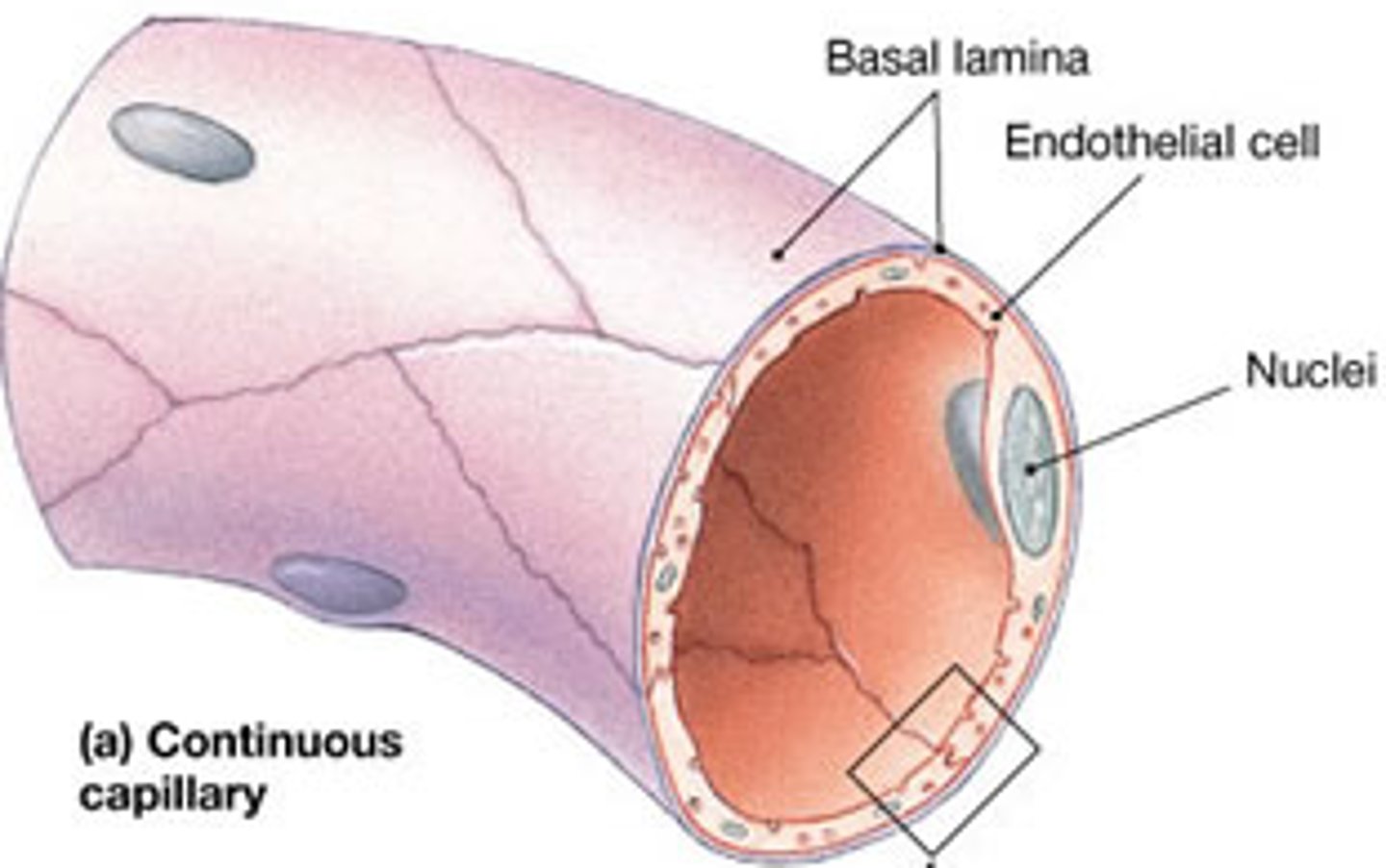
Describe a Continuous Capillary
- most common + least permeable type of capillary
- found in lungs, skin, nervous system, connective tissue + blood brain barrier
- has intact endothelial lining that forms a tube, only interrupted by intercellular clefts + joined by tight junctions
- rich in transport vesicles ➜ endocytosis or exocytosis
How much Oxygen is carried in the plasma?
1.5% is carried to dissolve in plasma
How many molecules of oxygen can one hemoglobin molecule bind with?
4
What is the skeletal muscle pump and how does it help with blood return?
Skeletal Muscle Pump- (Venous Return) refers to the mechanism by which contracting muscles compress veins, pushing blood back towards the heart
Why is it important for large arteries to be elastic?
- Absorbs the pressure
- Maintains blood flow
- Reduces workload on the heart
Basophil
Abundance: Less than 1% in a normal blood smear
Function: Releases Histamine to promote inflammation and helps in allergic reactions and defense against parasites
What two vessels bring blood into the Superior Vena Cava?
R + L Brachiocephalic Vein
Phase 4 of Cardiac Cycle (Systemic Circuit): ISOVOLUMETRIC VENTRICULAR DIASTOLE
Valves Open : None
Valves Closed : Atrioventricular Valves (Mitral & Tricuspid), Semilunar Valves (Aortic & Pulmonary)
Phase 5 of Cardiac Cycle (Systemic Circuit): PASSIVE VENTRICULAR FILLING
Valves Open: Atrioventricular Valves (Mitral & Tricuspid),
Valves Closed: Semilunar Valves (Aortic & Pulmonary)
SYMPATHETIC EFFECTS ON HEART RATE:
Increases heart rate by releasing Noradrenaline at the SA node, which increases the rate of depolarization and enhances contractility of the heart
PARASYMPATHETIC EFFECTS ON HEART RATE:
Decreases heart rate by releasing Acetylcholine at the SA node, which decreases the rate of depolarization and slows down the heart rate
What is Atherosclerosis?
Condition which fatty deposits (plaques) build up on the inner walls of arteries, leading to hardening and narrowing of the arteries. Can restrict blood flow and lead to Cardiovascular complications such as Heart Attacks and Strokes
Causes of Atherosclerosis
- Lifestyle
- Hypertension
- High Cholesterol
- Genetic Factors
- Obesity
- Diabetes
T/F: Capillaries work in groups called "beds"
True- networks called capillary beds
Which Leukocyte is responsible for making antibodies?
B- Lymphocytes (B cells)
If the arterioles are under vasoconstriction , what happens to the blood flow to the capillaries?
Arterioles decreases their diameter, which increases resistance to blood flow. As a result, blood flow to the capillaries decreases
What percentage of Oxygen is carried in a red blood cell?
98.5%
What are the formed elements of blood?
Red Blood Cells- Erythrocytes
White Blood Cells- Leukocytes
Platelets- Thrombocytes
T/F: The plasma proteins make up about 70% of Plasma
False- Plasma proteins make up about 7-9% of plasma volume
Which way would CO2 diffuse between the systemic capillaries and tissues: would it diffuse from the capillaries into the tissues, or from the tissues into the capillaries
CO2 would diffuse from the tissues into the capillaries
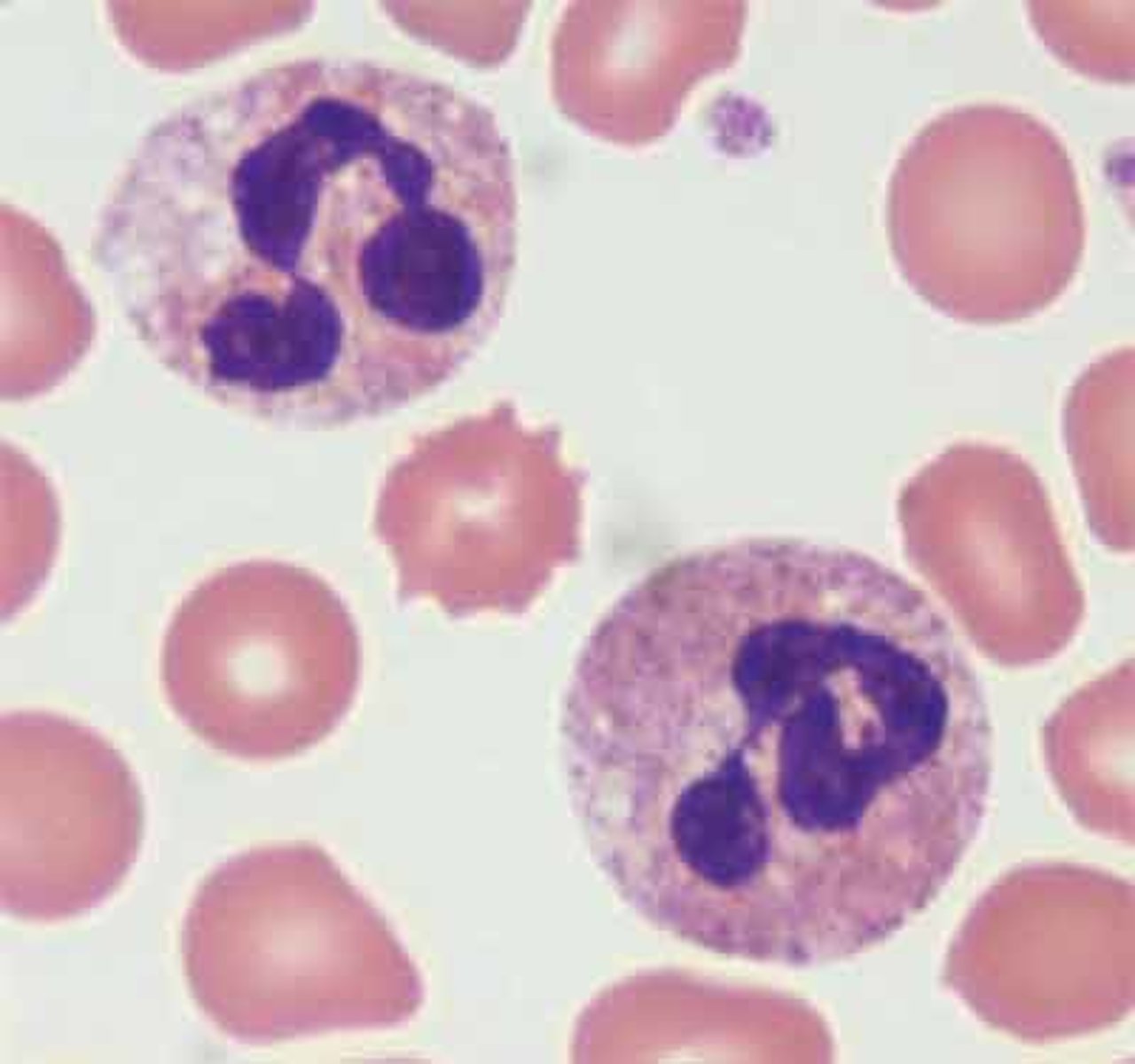
Neutrophil
Abundance: Approximately 50-70% in a normal blood smear (most abundant)
Function: Primary role is phagocytisis--engulfing and digesting bacteria, fungi and other pathogens.
(1st responders to infections and play a crucial role in immunity
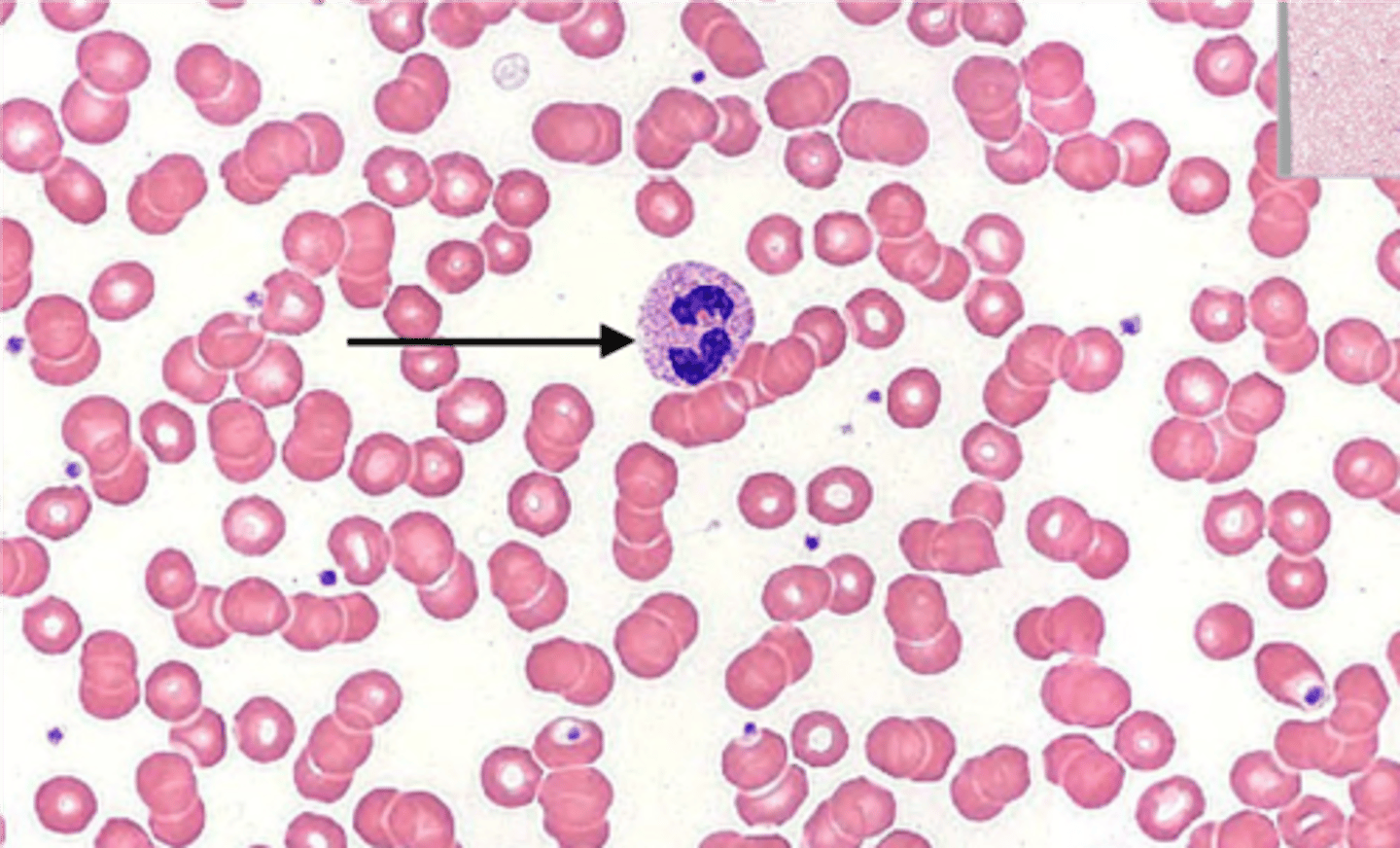
Eosinophil
Abundance: Typically 1-4% in a normal blood smear
Function: Involved in combating parasitic infections and modulating allergic reactions by releasing enzymes that target parasites and chemicals that reduce inflammation
Granulocyte
T/F : Capillaries consist of three layers
False- Single layer
3 Different ways CO2 is carried in the blood
1) Dissolved in plasma - (7-10%)
2) As Bicarbonate ions- (70%)
3) Bound to Hemoglobin- (23%)
If Sympathetic stimulation increased to the arterioles , what happens to the diameter of the Vessel?
Sympathetic stimulation causes Vasoconstriction of arterioles , leading a decrease in their diameter
Which blood vessel would you expect to be under the highest amount of pressure?
Subclavian Artery
What is the partial pressure of oxygen in a systemic circuit vein returning blood to the heart
PO2--> 40 mm/Hg
Phase 1 of Cardiac Cycle (Systemic Circuit): ATRIAL CONTRACTION
Valves Open: AV valves (Mitral, Tricuspid)
Valves Closed: Semilunar Valves (Aortic, Pulmonary)
Phase 2 of Cardiac Cycle (Systemic Circuit): ISOVOLUMETRIC VENTRICULAR CONTRACTION
Valves Open: NONE
Valves Closed: AV valves (Mitral, Tricuspid), Semilunar (Aortic, Pumonary)
Phase 3 of Cardiac Cycle (Systemic Circuit): VENTRICULAR EJECTION
Valves Open: Semilunar valves (Aortic, Pulmonary)
Valves Closed: AV valves (Mitral, Tricuspid)