Fragment-Based Drug discovery
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what is rational drug design
the aim is to increase selectivity of the drug for the target site and increase the activity of the drug
consequently this should lead to a lower dosage required and fewer side effects
strategies for rational drug design
vary alkyl, aryl and other substituents
chain extension and contraction
ring expansion, contraction and variation
bio - isosteric replacement
simplification
rigidification
advances in technoolgy
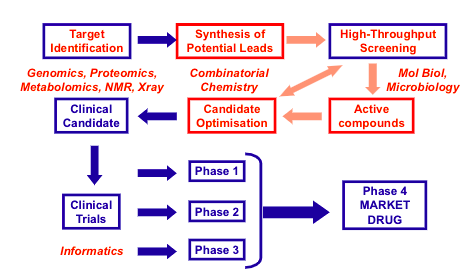
target identification
genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, NMR, Xray
Synthesis of potential leads
combinational chemistry
High - throughput screening
mol bol, microbiology
Active compounds
Candidate optimisation
Clinical candidate
clinical trials - informatics
market drug
what is high-throughput screening HTS
hit generation
lead generation and optimization
candidate
tells you whether a molecule has biological activity via different screens
need a lot of compounds
automated
fragment- based drug discovery
small fragments that may fit into our receptors
screening
confirmation methods - seeing key interactions before going on to develop the finished drug molecule
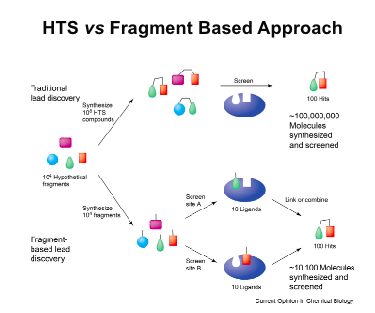
HTS vs Fragment based approach
traditional method
10000 compounds
react together to create more compounds
then screen
find some compounds that have activity
100,000,000 finish so not very useful
newer method
synthesise 1000 frgaments
screen individually against the receptor we want
then link or combine successful ones
then your left with 10100 molecules so much more narrowed down
low quality hit from HTS
high molecular weight compounds that occupy a large volume in the target
high potential for low quality hits and false +ve and -ve responses
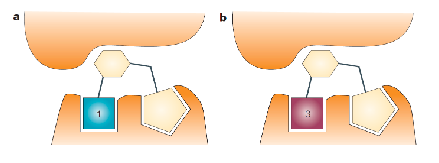
what is fragment evolution/ growing
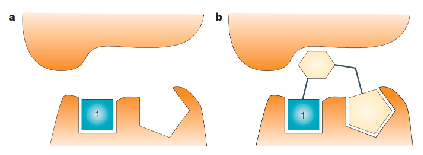
An initial fragment is optimised to
bind to adjacent regions of the desired target site
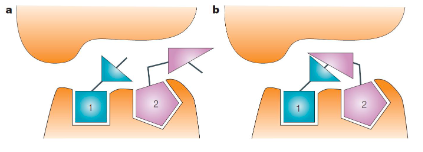
what is fragment linking
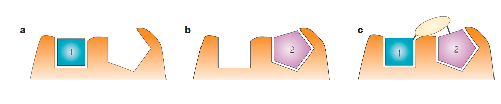
Two (or more) fragments, which bind to
proximal parts of the target site, are joined together to give a
larger molecule with higher affinity for the target
what is fragment self-assembly
Fragments with complementary
functional groups are allowed to react together in the presence of
the protein target and the most potent larger molecule is chosen
what is fragment optimisation
Rational approaches which are used to
optimise drug-like properties of a lead, other than just receptor
binding affinity
NMR techniques in drug discovery
when bound the ligand L will no longer be free in solution and will take on the characteristics of the target protein R
Various phenomena such as change in chemical shift and polarisation transfer, enable the accurate measurements of distances and the 3-d shape of the ligand-protein complex, complementary to x rays