5.1 Homeostasis and 5.2 the human nervous system
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Define homeostasis
It is the regulation of the internal conditions of a cell or organism to maintain optimum conditions for function, in response to internal + external changes.
why does the core body temperature need to be controlled by homeostasis?
To maintain the optimum temperature for enzymes
(they can denature when temp is too high and can work too slowly when temp is low)
why do PH levels need to be controlled by homeostasis?
Enzymes denature if PH increases or decreases too far away from the optimum PH
why does the blood glucose concentration need to be controlled by homeostasis?
Glucose needed as it is the main substrate for respiration to provide energy for metabolic processes
why do the water levels of blood need to be controlled by homeostasis?
Needed to prevent water movement into or out of the cells by osmosis
(too high- water moves into the cell causing them to lyse (burst). Too low- water moves out of cells causing them to plasmolyse (shrivel))
why does the ion concentration of blood need to be controlled by homeostasis?
water will move into or out the cells by osmosis if this is incorrect
(Too high- plasmolyse. Too low- lyse)
why does the concentration of waste material need to be controlled by homeostasis?
These are usually poisonous + need to be removed from the body before they build up to toxic levels + cause damage to cells
What do receptors do?
They detect changes in the internal/external environment (called stimuli)
What do coordination centres do?
They receive and process the information from the receptors + then coordinate the response (where it needs to go)
What are the effectors?
Muscles or glands, which bring about a response when it receives a message from the brain
State 3 ways in which your external environment may vary:
Temperature
PH levels
Lack of food
What is a stimulus and a response?
A change that can be detected
What happens as a result of the stimulus
What is a sensory neurone?
It sends electrical impulses from the receptors in the sense organs, to the brain
What is a motor neurone?
Sends electrical impulses from the brain to the muscles and glands (effectors)
What is a coordinator?
The brain and the spinal column, also known as the CNS. This processes the information from the sensory neurones.
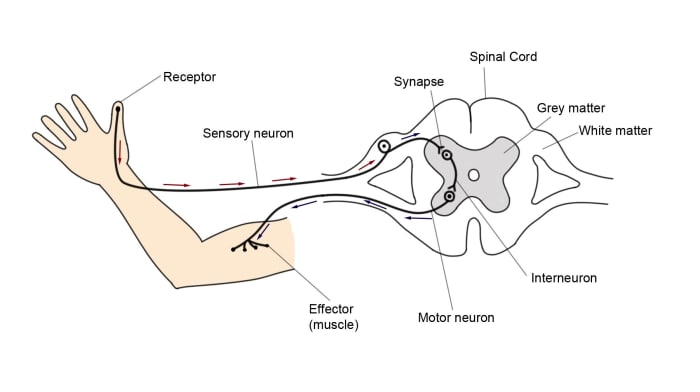
What is the path of a nerve impulse?
Stimulus detected by receptor
Nerve impulse passed along sensory neurone
Synapse between neurones
Central nervous system (CNS) processes the information
Nerve impulse passes along the motor neurone
Message reaches the effector (a muscle or gland) causing a response
What is a neurone?
Nerve cells which send + receive signals from the brain
What is a nerve impulse?
Electrical charge that travels along the membrane of a neurone
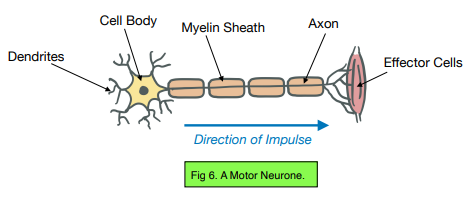
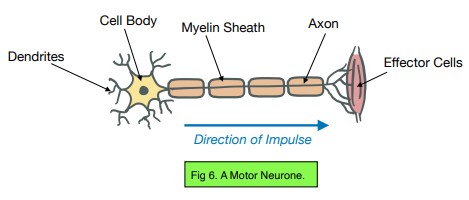
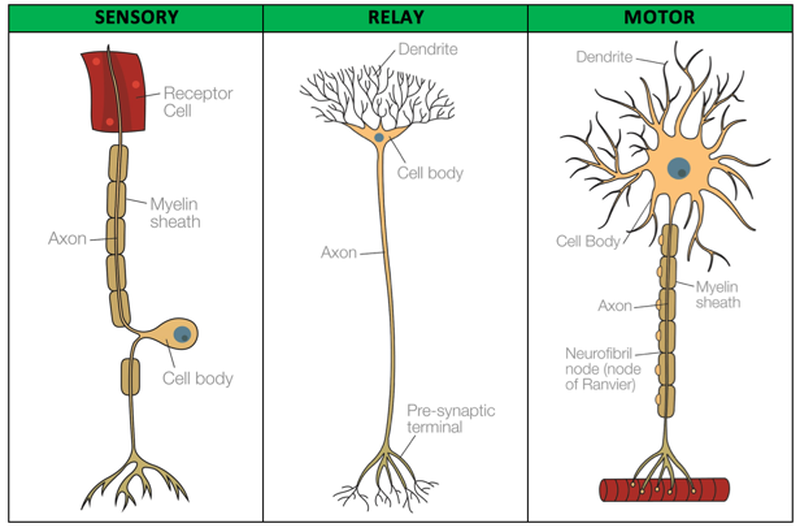
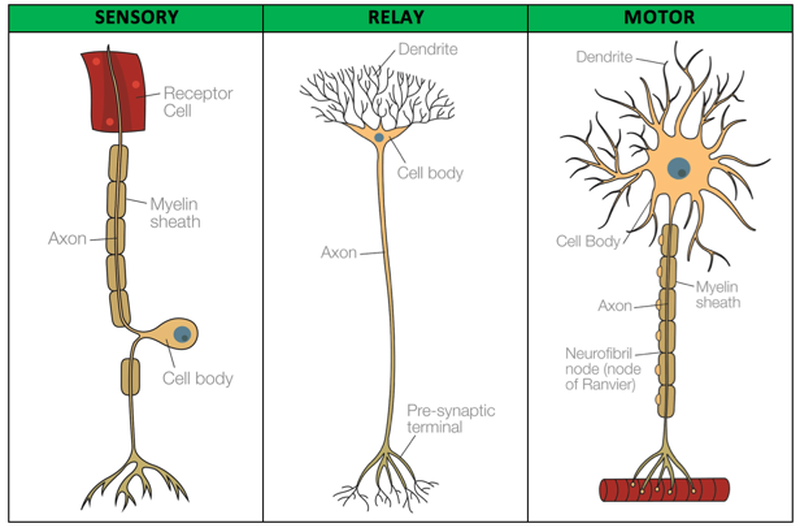
What is the synapse?
A junction between 2 nerve cells consisting of a minute gap across which impulses pass by diffusion of a neurotransmitter
The electrical nerve impulses can’t cross the synapse
Chemicals called neurotransmitters are released which diffuses across the synapse
The neurotransmitter binds to receptors on the membrane of the next neurone causing a new nerve impulse
Suggest how drugs could affect the transmission of information at synapses:
Blocking the neurotransmitter from binding to the receptor and stopping the impulse in the next nerve
Binding to the receptor + causing a new impulse, even when there’s no neurotransmitter
Define a reflex action:
Automatic responses that don’t involve the conscious part of your brain
Examples of reflex actions:
Breathing
Sneezing
When you touch something hot or sharp you pull your hand back
If something comes near your face you blink
Moving food through your digestive system

Why are reflexes important?
They are faster than conscious actions therefore….
Protect the body from damage/ injury
Increase chances of survival (for animals)
Why are reflexes faster than conscious actions? (IMPORTANT)
There is only one relay neurone (either in the spinal column or the brain) in a reflex, where conscious actions will have many relay neurones
Therefore reflex actions involve fewer synapses
Diffusion of neurotransmitters across
Factors affecting reaction time:
Drugs (e.g. cocaine)
Alcohol
Lack of sleep
Stress
Adrenaline
Energy (how much you have eaten)
REQUIRED PRACTICAL 9
STRUCTURES IN THE BRAIN ON PHYSICAL REVISION CARDS
Main function of the meninges:
To protect and support the central nervous system
Main function of the cerebral cortex:
It is responsible for higher level processes of the human brain (e.g. language, memory and learning)
Main function of the medulla:
It controls breathing, heart rate + peristalsis
Main function of cerebellum:
It controls movement, balance and co-ordination
Main function of hypothalamus:
Detects changes in blood temperature + water concentration
Main function of the pituitary gland:
Secretes several hormones into the blood in response to the bodies conditions
Name different ways in which scientists can study the brain:
MRI scans
Scanning the living brain
Post mortem examinations
FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
Explain some of the difficulties of investigating brain functions and treating brain damage and disease: