PSIO107 FINAL
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/173
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:54 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
1
New cards
Nervous System
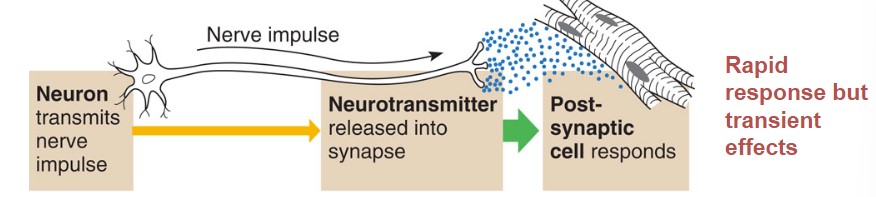
* Neuron transmits nerve down the axon to the neurotransmitter
* neurotransmitter releases the impulse into the synapse
* the post-synaptic cell responds to that nerve impulse
* **rapid response but transient effects**
* neurotransmitter releases the impulse into the synapse
* the post-synaptic cell responds to that nerve impulse
* **rapid response but transient effects**
2
New cards
Endocrine System
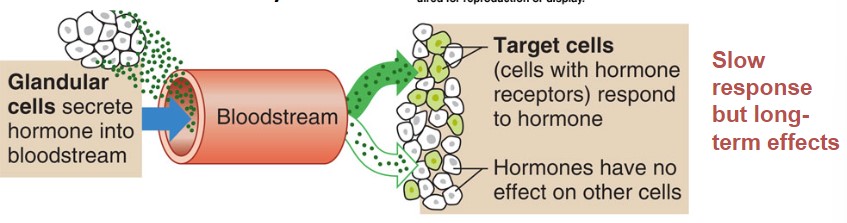
* Glandular cells secrete hormone into the bloodstream
* through the bloodstream, throughout the whole body maybe before they find their receptors. **target cells have to have receptors for hormones to find them**
* Target cells respond to the hormone, **hormones have no effect on other cells of the body**
* **slow response but long-term effects**
* through the bloodstream, throughout the whole body maybe before they find their receptors. **target cells have to have receptors for hormones to find them**
* Target cells respond to the hormone, **hormones have no effect on other cells of the body**
* **slow response but long-term effects**
3
New cards
Endocrine grands
ductless, secrete hormones into blood (or CSF)
4
New cards
Hormones
* act on target cells (require specific receptors to have effects)
* slow onset (minutes-hours), long-term effects (days-weeks)
* slow onset (minutes-hours), long-term effects (days-weeks)
5
New cards
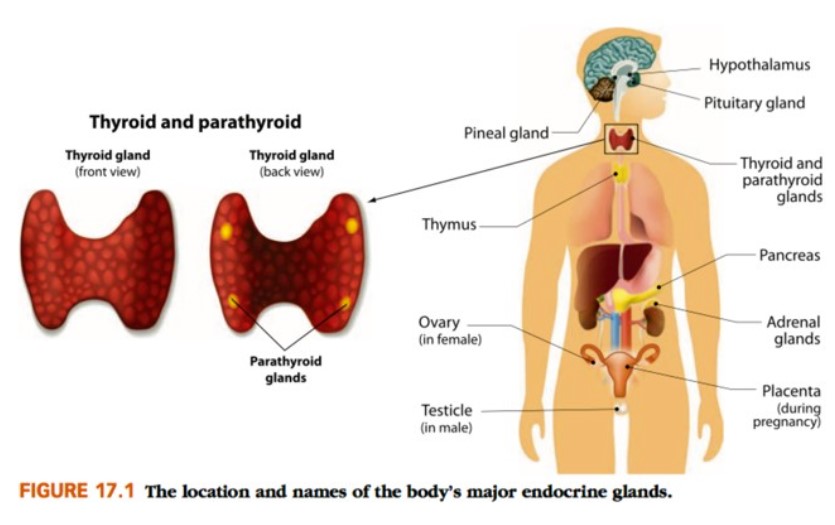
Endocrine Organs
6
New cards
Hormone Action
Chemistry
* hormones can be __water-soluble__ or **lipid soluble**
* hydrophilic
* Amine, peptide, protein, glycoprotein (all amino acid-based)
* Hydrophobic (lipophilic)
* steroid (cholesterol) or prostaglandin (fatty acid-based)
* hormones can be __water-soluble__ or **lipid soluble**
* hydrophilic
* Amine, peptide, protein, glycoprotein (all amino acid-based)
* Hydrophobic (lipophilic)
* steroid (cholesterol) or prostaglandin (fatty acid-based)
7
New cards
Synthesis and Packaging of Hydrophilic hormones
1. Proteins are packaged in secretory vesicles for exocytosis
2. vesicle becomes lysosome
3. Vesicle inserted into the plasma membrane
if we want to secrete a hormone, it needs to be stimulated, proteins can be generated and stored in vesicles so that the hormones are ready to be released when needed
8
New cards
Hormone Action
* hormone chem plays role in location of receptors on target cells
* hormones act in small quantity, but have big effect
* hormones act in minuet quantities, because they are amplified
* only the “free” (unbound) fraction of hormone in plasma is regulated
* plasma concentration is determined by:
* secretion rate, production rate, clearance rate, metabolism rate
* hormones act in small quantity, but have big effect
* hormones act in minuet quantities, because they are amplified
* only the “free” (unbound) fraction of hormone in plasma is regulated
* plasma concentration is determined by:
* secretion rate, production rate, clearance rate, metabolism rate
9
New cards
* Endocrine disorders arise when:
* hormone production is too low (hyposecretion)
* hormone production is too high (hypersecretion)
* hormone receptors are absent (insensitivity)
* hormone production is too high (hypersecretion)
* hormone receptors are absent (insensitivity)
10
New cards
Control Mechanisms: most hormones…
are regulating via negative feedback mechanisms
* ex: high blood glucose stimulates insulin secretion, which results in cell uptake and storage of glucose (lowering blood glucose concentration)
* ex: high blood glucose stimulates insulin secretion, which results in cell uptake and storage of glucose (lowering blood glucose concentration)
11
New cards
Control Mechanisms: some hormones…
are part of positive feedback mechanisms
* ex: cervical stretch receptors signal the brain to release oxytocin, which results in uterine contraction (effectively causing more stretch as the baby’s head is forced against the cervix)
* ex: cervical stretch receptors signal the brain to release oxytocin, which results in uterine contraction (effectively causing more stretch as the baby’s head is forced against the cervix)
12
New cards
Hypothalamus
integration center
* body temp
* thirst and urine output
* appetite
* Anterior pituitary hormones (produces 6 hormones)
* posterior pituitary hormones (**produces oxytocin and ADH**)
stimulus from the hypothalamus that influences the posterior pituitary
* body temp
* thirst and urine output
* appetite
* Anterior pituitary hormones (produces 6 hormones)
* posterior pituitary hormones (**produces oxytocin and ADH**)
stimulus from the hypothalamus that influences the posterior pituitary
13
New cards
Anterior pituitary hormones
Bridge to endocrine system
* Stimulates or inhibits A.P. hormone secretion via “releasing -” and “inhibiting hormones”
* Synthesizes P.P. hormones
* Stimulates or inhibits A.P. hormone secretion via “releasing -” and “inhibiting hormones”
* Synthesizes P.P. hormones
14
New cards
circadian rhythm: **biological clocks**
approximate 24 hour cycles for body functions
* ex: temperature, gene expression, behavior, hormone secretion
* pineal gland secretes melatonin to synchronize
* ex: temperature, gene expression, behavior, hormone secretion
* pineal gland secretes melatonin to synchronize
15
New cards
circadian rhythm: **Melatonin**
Secreted during periods of darkness
* Light/dark cycle entrains biological rhythms
Proposed roles
* Can induce natural sleep
* Inhibits sex hormones
* Puberty initiated by drop in melatonin levels
* In other species → seasonal breeding, hibernation, migration cycles
* Birth control
* High levels shut down ovulation
* Antoxidant
* Slows aging process
* Enhance immunity
* Also slows regression of thymus
* Light/dark cycle entrains biological rhythms
Proposed roles
* Can induce natural sleep
* Inhibits sex hormones
* Puberty initiated by drop in melatonin levels
* In other species → seasonal breeding, hibernation, migration cycles
* Birth control
* High levels shut down ovulation
* Antoxidant
* Slows aging process
* Enhance immunity
* Also slows regression of thymus
16
New cards
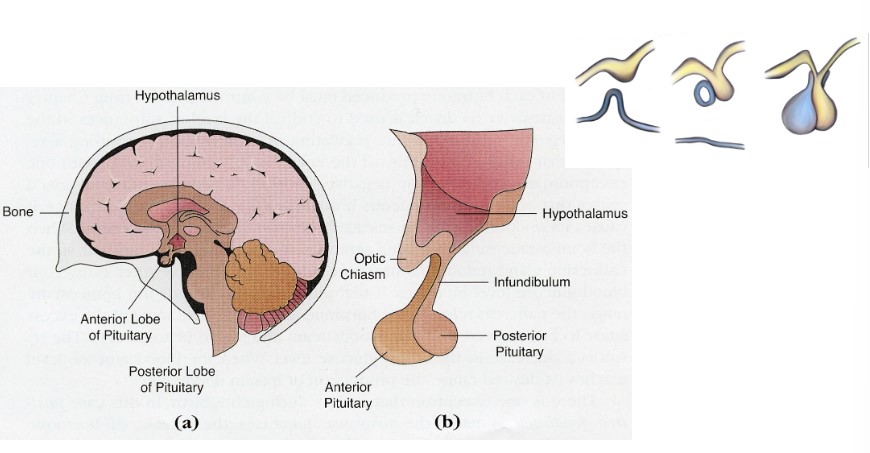
Pituitary Gland
consists of two separate tissues
* anterior pituitary is gland tissue (true gland tissue)
* posterior pituitary is neural tissue (extension of NS)
* anterior pituitary is gland tissue (true gland tissue)
* posterior pituitary is neural tissue (extension of NS)
17
New cards
Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis) secrets two hormones: **Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) (Vasopressin)**
* targets kidney → stimulates water reabsorption
* targets blood vessels → stimulates vasoconstriction
__Helps with regulation of blood pressure via negative feedback__
\*This hormone acts w/ many other mechanisms during hypovolemia and/or hypotension
* targets blood vessels → stimulates vasoconstriction
__Helps with regulation of blood pressure via negative feedback__
\*This hormone acts w/ many other mechanisms during hypovolemia and/or hypotension
18
New cards
Posterior Pituitary (Neuro**hypophysis(means pituitary)**) secrets two hormones: **Oxytocin**
* targets uterine smooth muscle (myometrium)
* targets myoepithelial cells lining milk ducts
__participates in parturition and milk ejection via positive feedback__
* targets myoepithelial cells lining milk ducts
__participates in parturition and milk ejection via positive feedback__
19
New cards
Anterior pituitary (Adenohypophysis): six secreted hormones (all negative feedback mechanisms) involved in growth, metabolism, or reproduction
Prolactin (PRL)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Growth Hormone (GH)
Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
20
New cards
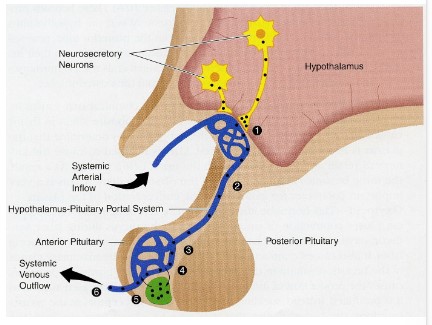
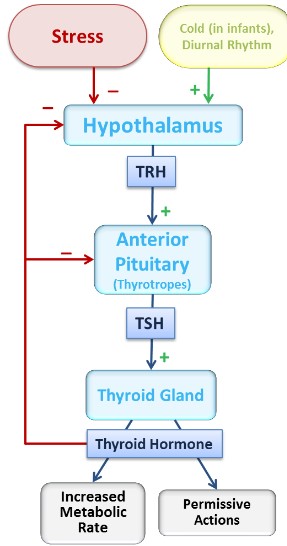
Hypothalamic-Anterior Pituitary Axis
\
21
New cards
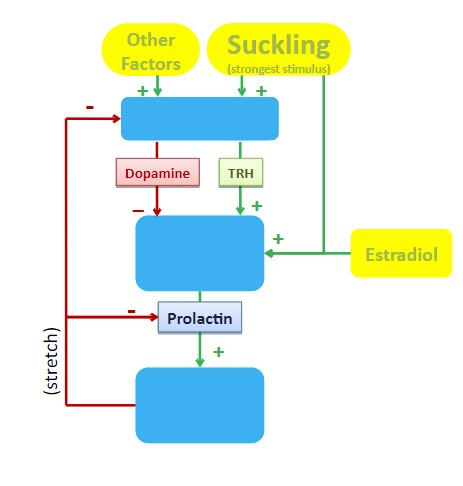
Prolactin
* promotes milk production (secretion) from mammary glands
* also inhibits ovulation
* ‘nature’s contraceptive
* **feedback loop*\*
* also inhibits ovulation
* ‘nature’s contraceptive
* **feedback loop*\*
22
New cards
Growth Hormone
* metabolic hormone
* promotes growth of tissues (indirectly)
* bone and muscle, and most soft tissues
* If hyposecretion:
* in kids = dwarfism
* in adults = muscle weakness, metabolic issues
* If hypersecretion:
* in children = gigantism
* in adults = acromegaly
* **feedback loop*\*
* promotes growth of tissues (indirectly)
* bone and muscle, and most soft tissues
* If hyposecretion:
* in kids = dwarfism
* in adults = muscle weakness, metabolic issues
* If hypersecretion:
* in children = gigantism
* in adults = acromegaly
* **feedback loop*\*
23
New cards
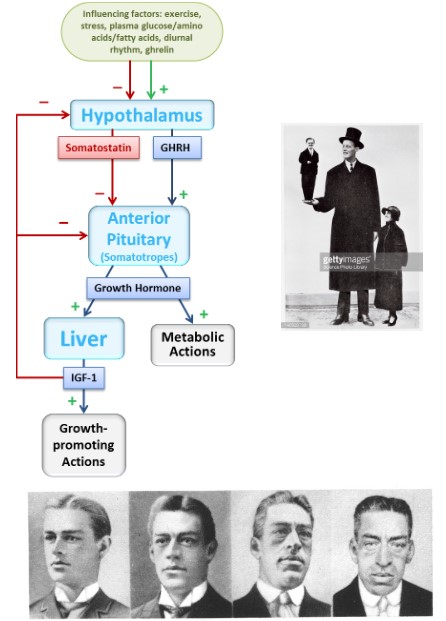
Growth Hormone (Important Points)
**ON EXAM*\*
Pathway of control of growth and development
* GHRH stimulates GH secretion
* GH stimulates IGF-1 (negative feedback control)
* GH acts __directly__ on tissues to stimulate __metabolism__
* GH acts __indirectly__ to promote __growth-related actions__
* via IGF-1
Pathway of control of growth and development
* GHRH stimulates GH secretion
* GH stimulates IGF-1 (negative feedback control)
* GH acts __directly__ on tissues to stimulate __metabolism__
* GH acts __indirectly__ to promote __growth-related actions__
* via IGF-1
24
New cards
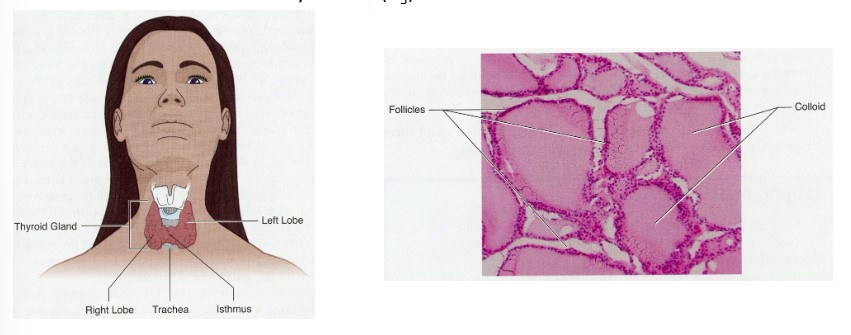
Thyroid Gland
Major histological structure = follicle
* cells forming follicle are called follicular cells
* help produce __thyroid hormone__ in the colloid
* thyroxine (tetraiodothyronine, T4)
* Triiodothyronine (T3)
* Iodine
* sequestered in thyroid gland
* required for T3/T4 synthesis
* cells forming follicle are called follicular cells
* help produce __thyroid hormone__ in the colloid
* thyroxine (tetraiodothyronine, T4)
* Triiodothyronine (T3)
* Iodine
* sequestered in thyroid gland
* required for T3/T4 synthesis
25
New cards
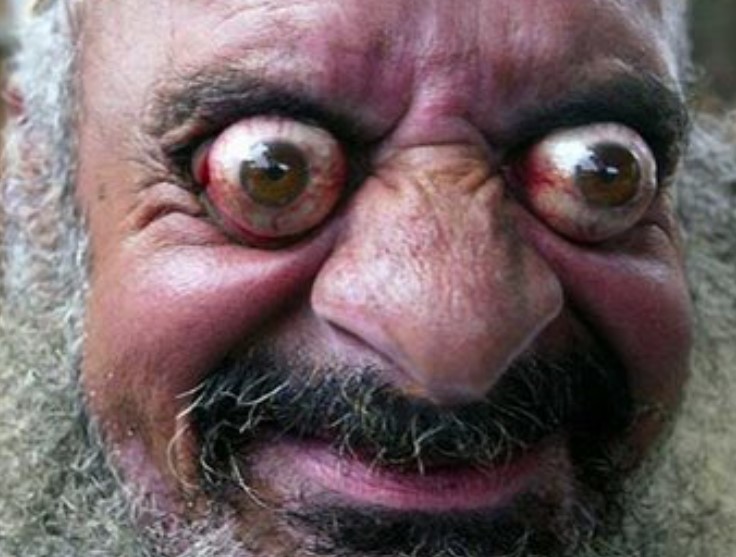
Hyperthyroidism
too much TSH
or, thyroid tumor
or, TSI
* thyroid tumor (primary hyperthyroidism)
* excessive tropic hormones (secondary)
* or, most common
* symptoms:
* elevated metabolic rate
* heat tolerance
* weight loss (but increase food intake)
* increased heart rate
* excess mental alertness
* exophthalmos
or, thyroid tumor
or, TSI
* thyroid tumor (primary hyperthyroidism)
* excessive tropic hormones (secondary)
* or, most common
* symptoms:
* elevated metabolic rate
* heat tolerance
* weight loss (but increase food intake)
* increased heart rate
* excess mental alertness
* exophthalmos

26
New cards
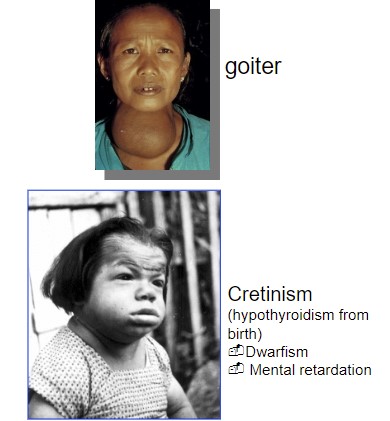
Hypothyroidism
too little TSH
or, other thyroid dysfunction
* thyroid gland failure (primary hypothyroidism)
* deficiency of tropic hormones (secondary)
* Symptoms:
* Reduced metabolic rate
* cold intolerance
* weight gain
* reduced cardiac output
* lethargy (fatigue)
* Edema
or, other thyroid dysfunction
* thyroid gland failure (primary hypothyroidism)
* deficiency of tropic hormones (secondary)
* Symptoms:
* Reduced metabolic rate
* cold intolerance
* weight gain
* reduced cardiac output
* lethargy (fatigue)
* Edema
27
New cards
Thyroid Gland Metabolism
ATP production and utilization
Thermogenesis O2 consumption
Growth: muscle, bone, nervous
Thermogenesis O2 consumption
Growth: muscle, bone, nervous
28
New cards
Password
IGF1
29
New cards
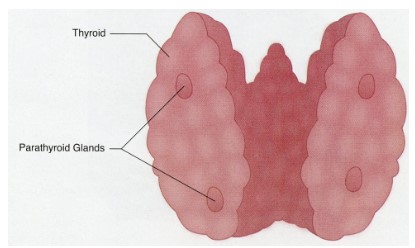
Parathyroid Gland
produces __parathyroid hormone__
* reverses low blood calcium levels
* stimulates osteoclasts to remove calcium from bone
* stimulates kidney to reabsorb calcium
* stimulates kidney to increase Vit. D activation
* promotes intestinal uptake of calcium
* reverses low blood calcium levels
* stimulates osteoclasts to remove calcium from bone
* stimulates kidney to reabsorb calcium
* stimulates kidney to increase Vit. D activation
* promotes intestinal uptake of calcium
30
New cards
PTH Hypersecretion
Hyperparathyroidism
* hypersecreting tumor
* symptoms may vary w/ magnitude of problem
* **hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia**
* decrease muscle and nervous tissue excitability
* muscle weakness
* neurological disorders
* decrease alertness, poor memory, depression
* cardiac arrhythmias
* **Thinning of bone**
* deformities
* factures
* **incidence of Ca2+: containing kidney stones**
* decrease renal function
* pain
* **peptic ulcers, nausea, and constipation**
* hypersecreting tumor
* symptoms may vary w/ magnitude of problem
* **hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia**
* decrease muscle and nervous tissue excitability
* muscle weakness
* neurological disorders
* decrease alertness, poor memory, depression
* cardiac arrhythmias
* **Thinning of bone**
* deformities
* factures
* **incidence of Ca2+: containing kidney stones**
* decrease renal function
* pain
* **peptic ulcers, nausea, and constipation**

31
New cards
PTH Hyposecretion
Hypoparathyroidism
* surgical removal → most common cause
* autoimmune destruction
**-Hypocalcemia and Hyperphosphatemia**
* increase muscle and neuron excitability
* Muscle cramps and twitches
* Tingling and pins-and-needles sensation
* Irritability and paranoia
* death (in absence of PTH)
* surgical removal → most common cause
* autoimmune destruction
**-Hypocalcemia and Hyperphosphatemia**
* increase muscle and neuron excitability
* Muscle cramps and twitches
* Tingling and pins-and-needles sensation
* Irritability and paranoia
* death (in absence of PTH)
32
New cards
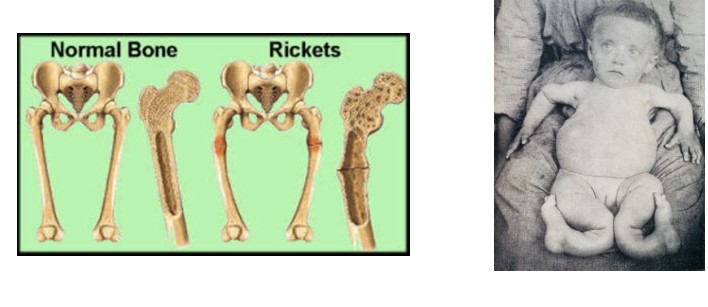
Vitamin D deficiency
impaired Ca2+ absorption
* PTH maintains plasma Ca2+ at expense of bones
* Softened bones deform
* Rickets (in children)
* Osteomalacia (in adults)
* PTH maintains plasma Ca2+ at expense of bones
* Softened bones deform
* Rickets (in children)
* Osteomalacia (in adults)
33
New cards
Endocrine Pancreas
Glucose-sensing cells called pancreatic islets (islets of Langerhans) form the endocrine pancreas
* alpha islets are sensitive to low blood glucose
* secrete __glucagon__
* Beta islets are sensitive to high blood glucose
* secrete __insulin__
* alpha islets are sensitive to low blood glucose
* secrete __glucagon__
* Beta islets are sensitive to high blood glucose
* secrete __insulin__
34
New cards
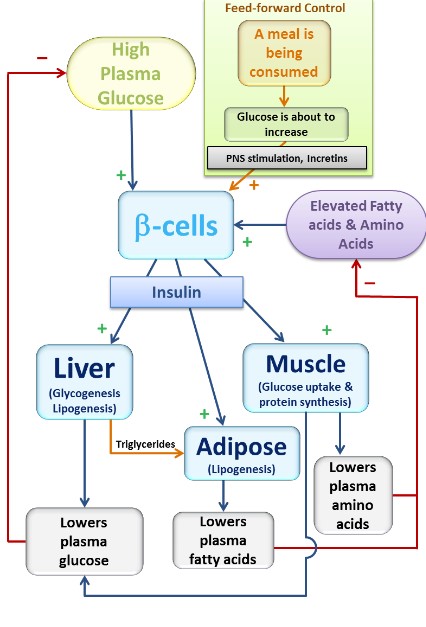
Insulin actions
targets the liver, adipose, and muscle to promote the storage of glucose
* glucose transporters are stimulated
* glucose is phosphorylated to keep it in the cell
* glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) is linked together to form __glycogen__
* glucose transporters are stimulated
* glucose is phosphorylated to keep it in the cell
* glucose-6-phosphate (G6P) is linked together to form __glycogen__
35
New cards
Feedback loop
36
New cards
Glucose Transport
1. **Passive facilitated diffusion into cell (through GLUT)**
2. glucose → glucose-6-phosphate
1. phosphorylation
1. traps glucose inside cell
2. keeps intracellular glucose concentration low
Insulin triggers glucose transporter (GLUT-4) recruitment in body celss
37
New cards
Glucose transporters
GLUT-1
* Blood-brain barrier
GLUT-2
* __B-islets,__ kidney, liver and intestinal cells
GLUT-3
* Neurons
GLUT-4
* most cells of body
* __**only transporter that is sensitive to insulin**__
* Blood-brain barrier
GLUT-2
* __B-islets,__ kidney, liver and intestinal cells
GLUT-3
* Neurons
GLUT-4
* most cells of body
* __**only transporter that is sensitive to insulin**__
38
New cards
GLUT-1
transports to blood-brain barrier
39
New cards
GLUT-2
transport to __B-islets,__ kidney, liver and intestinal cells
40
New cards
GLUT-3
transport to neurons
41
New cards
GLUT-4
Most cells of body
__**Only transporter that is**__
__**sensitive to insulin**__
__**Only transporter that is**__
__**sensitive to insulin**__
42
New cards
transporter recruitment
* pool of internal vesicles containing GLUT-4
* Insulin binds to receptor
* signaling cascade induces vesicles to fuse w/ plasma membrane
* 10-30 fold increase glucose uptake
* decrease insulin → endocytosis of GLUT-4 and return to intracellur pool
* Insulin binds to receptor
* signaling cascade induces vesicles to fuse w/ plasma membrane
* 10-30 fold increase glucose uptake
* decrease insulin → endocytosis of GLUT-4 and return to intracellur pool
43
New cards
Tissues not dependent on insulin:
* Brain
* Skeletal muscle cells
* liver
* Skeletal muscle cells
* liver
44
New cards
Tissues not dependent on insulin: brain
freely permeable to glucose
* GLUT-1 and GLUT-3
* GLUT-1 and GLUT-3
45
New cards
Tissues not dependent on insulin: Skeletal cells
__Not dependent__ __**on insulin**__ during exercise
* __***____muscle contraction triggers insertion of GLUT-4__ (in absence of insulin)\*
dependent on insulin at rest
* __***____muscle contraction triggers insertion of GLUT-4__ (in absence of insulin)\*
dependent on insulin at rest
46
New cards
Tissues not dependent on insulin: liver
does not use GLUT-4
**But** insulin does enhance carbohydrate metabolism
* stimulates glucose phosphorylation
**But** insulin does enhance carbohydrate metabolism
* stimulates glucose phosphorylation
47
New cards
Glucagon action
essentially the opposite of insulin
glucagon does not affect muscle tissue
primary target is the liver
* promotes cleavage of glycogen into G6P
* G6P is dephosphorylated
* Free glucose molecules diffuse out of hepatocytes
glucagon does not affect muscle tissue
primary target is the liver
* promotes cleavage of glycogen into G6P
* G6P is dephosphorylated
* Free glucose molecules diffuse out of hepatocytes
48
New cards
Insulin deficiency: Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1
* insulin dependent
* pancreas does not produce enough insulin
* develops rapidly
* usually diagnosed in childhood
* pancreas does not produce enough insulin
* develops rapidly
* usually diagnosed in childhood
49
New cards
Insulin deficiency: Diabetes Mellitus: Type 2
* adult onset diabetes
* insulin receptors not responsive to insulin, or pancreas not secreting enough to meet needs
* develops slowly
* obesity is factor
* can be controlled w/ diet
* insulin receptors not responsive to insulin, or pancreas not secreting enough to meet needs
* develops slowly
* obesity is factor
* can be controlled w/ diet
50
New cards
Insulin deficiency: gestational diabetes
* develops in women who are pregnant
* correlates w/ type 2 development later in life
* baby could develop diabetes later in life
* correlates w/ type 2 development later in life
* baby could develop diabetes later in life
51
New cards
acute complications
osmotic diuresis, electrolyte imbalance, ketoacidosis, circulatory failure, cell shrinking, nervous malfunction → Diabetic coma
52
New cards
Chronic complications
* manifest after 15-20years
* degeneration of vascular tissues
* blood vessel legions
* kidney failure
* blindness
* gangrenous
* heart disease
* strokes
* degeneration in nervous system
* nerve lesions result in neuropathies
* brain dysfunction
* spinal cord dysfunction
* peripheral nerve dysfunction
* pain, numbness, tingling in extremities
* renal failure
* dialisis → 2 year life expectency
* degeneration of vascular tissues
* blood vessel legions
* kidney failure
* blindness
* gangrenous
* heart disease
* strokes
* degeneration in nervous system
* nerve lesions result in neuropathies
* brain dysfunction
* spinal cord dysfunction
* peripheral nerve dysfunction
* pain, numbness, tingling in extremities
* renal failure
* dialisis → 2 year life expectency
53
New cards
Insulin excess
characterized by hypoglycemia arising two ways
* diabetic patient injects too much insulin
* insulin shock
* Hypersecretion of insulin
* beta cell tumor
* beta cell over-responsive to glucose
* reactive hypoglycemia
* diabetic patient injects too much insulin
* insulin shock
* Hypersecretion of insulin
* beta cell tumor
* beta cell over-responsive to glucose
* reactive hypoglycemia
54
New cards
Insulin excess: consequences
primarily effects brain
* decrease glucose → brain starves
* tremor, fatigue, sleepiness, inability to concentrate
* unconsciousness
* death
* Treatment
* limit glucose intake
* decrease glucose → brain starves
* tremor, fatigue, sleepiness, inability to concentrate
* unconsciousness
* death
* Treatment
* limit glucose intake
55
New cards
Adrenal Gland
Consists of two endocrine glands
* adrenal cortex
* Adrenal medulla
* adrenal cortex
* Adrenal medulla
56
New cards
Adrenal gland: adrenal cortex
* regulated via hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
* secretes cortical hormones (steroids)
* Mineralocorticoid
* aldosterone
* Glucocorticoid
* cortisol
* Gonadocorticoid
* DHEA
* Androgen
* secretes cortical hormones (steroids)
* Mineralocorticoid
* aldosterone
* Glucocorticoid
* cortisol
* Gonadocorticoid
* DHEA
* Androgen
57
New cards
Adrenal gland: Adrenal medulla
* part of sympathetic NS
* secrets catecholamines
* epinephrine (adrenaline)(80%)
* Norepinephrine (20%)
* secrets catecholamines
* epinephrine (adrenaline)(80%)
* Norepinephrine (20%)
58
New cards
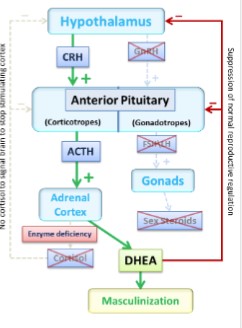
Cortical hormones: Gonadocorticoid (sex hormones)
* primarily the androgen __**dehydroepiandrosterone**__ (__**DHEA**__), but also some estrogen
* Not important as a major source of androgen in males (they have testosterone; 1000X more potent)
* **In women, DHEA is important** for sex drive and pubic/axillary hair growth
* stimulated via ACTH
* Not important as a major source of androgen in males (they have testosterone; 1000X more potent)
* **In women, DHEA is important** for sex drive and pubic/axillary hair growth
* stimulated via ACTH
59
New cards
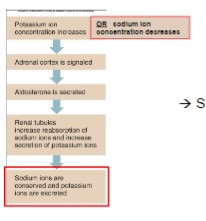
Cortical Hormones: Mineralocorticoids = __**Aldosterone**__
* targets kidney, resulting in sodium reabsorption
* stimulated via low blood pressure/volume regulation
* if salt is recovered from urine, water follows follows passively
* also stimulates potassium excretion, to maintain ionic equilibrium
* stimulated via low blood pressure/volume regulation
* if salt is recovered from urine, water follows follows passively
* also stimulates potassium excretion, to maintain ionic equilibrium
60
New cards
Cortical Hormones: glucocorticoids = __**cortisol**__
Chronic stress hormone, targets glucose metabolism in many tissues
* Liver: stimulates conversion of proteins/lipids into glucose (**gluconeogenesis)**
* muscle: promotes utilization of fatty acids as an energy source
Control: CRH → ACTH → Cortisol
* Liver: stimulates conversion of proteins/lipids into glucose (**gluconeogenesis)**
* muscle: promotes utilization of fatty acids as an energy source
Control: CRH → ACTH → Cortisol
61
New cards
Aldosterone
Mineralocorticoids
* **from: Zona glomerulosa**
* aldosterone
* conservation of sodium
* water retention by osmosis
* **from: Zona glomerulosa**
* aldosterone
* conservation of sodium
* water retention by osmosis
62
New cards
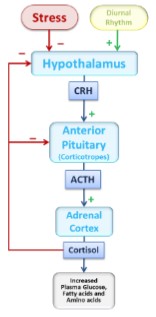
Cortisol
Cortisol is critical for survival during prolonged fasts
* increase blood glucose concentrations, at expense of protein and fat stores
* **increase gluconeogenesis**
* **increase amino acids**
* **increase blood fatty acids**
* permissive to other hormones
* Ex: catecholamine induced vasoconstriction
* →if unavailable during stressful condition → shock
* **PROTECTS AGAINST STRESS**
* mechanism largely unknown
* helpful in surgery patients (demand to have surgery in morning)
* Pharmacological actions
* decrease inflammation and immune response
* increase blood glucose concentrations, at expense of protein and fat stores
* **increase gluconeogenesis**
* **increase amino acids**
* **increase blood fatty acids**
* permissive to other hormones
* Ex: catecholamine induced vasoconstriction
* →if unavailable during stressful condition → shock
* **PROTECTS AGAINST STRESS**
* mechanism largely unknown
* helpful in surgery patients (demand to have surgery in morning)
* Pharmacological actions
* decrease inflammation and immune response
63
New cards
Adrenocortical Dysfunction: Hypersecretion: Aldosterone
* Adrenal tumor of aldosterone-secreting cells (**Conn’s syndrome)**
* primary hyperaldosteronism
* High activity of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
* secondary hyperaldosteronism
→ __**Exaggerated effects**__: **Na+ retention, K+ depletion, increase BP**
* primary hyperaldosteronism
* High activity of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
* secondary hyperaldosteronism
→ __**Exaggerated effects**__: **Na+ retention, K+ depletion, increase BP**
64
New cards
Adrenocortical Dysfunction: Hypersecretion: Cortisol
* overstimulation by CRH and/or ACTH
* Adrenal tumor of cortisol-secreting cells
* ACTH-secreting tumors located outside pituitary
→ __**Exaggerated effects of cortisol:**__
* **excessive gluconeogenesis**
**→ excess glucose and protein shortage: Hyperglycemia and glucosuria**
→ **some of excess glucose deposited as body fat → “buffalo hump” and “moon face”: Cushing’s Syndrome**
* Muscle weakness, fatigue, skin streaks, bruising, poor wound healing, bone fracture
* Adrenal tumor of cortisol-secreting cells
* ACTH-secreting tumors located outside pituitary
→ __**Exaggerated effects of cortisol:**__
* **excessive gluconeogenesis**
**→ excess glucose and protein shortage: Hyperglycemia and glucosuria**
→ **some of excess glucose deposited as body fat → “buffalo hump” and “moon face”: Cushing’s Syndrome**
* Muscle weakness, fatigue, skin streaks, bruising, poor wound healing, bone fracture
65
New cards
Adrenocortical insufficiency: Primary insufficiency
Addison’s disease
* __All sones exhibit reduced secretion__
* Likely autoimmune destruction
* Aldosterone deficiency is most life-threatening
* hyperkalemia (K+ retention)
* abnormal ECG
* Hyponatremia (Na+ loss)
* hypotension
* __All sones exhibit reduced secretion__
* Likely autoimmune destruction
* Aldosterone deficiency is most life-threatening
* hyperkalemia (K+ retention)
* abnormal ECG
* Hyponatremia (Na+ loss)
* hypotension
66
New cards
Adrenocortical insufficiency: Secondary insufficiency
* Pituitary or hypothalamic abnormalities → decrease ACTH secretion
* cortisol is deficient
* poor response to stress
* hypoglycemia (decrease gluconeogenesis)
* loss of permissiveness
* hyperpigmentation (excessive ACTH → binds alpha MSH → skin darkening)
* cortisol is deficient
* poor response to stress
* hypoglycemia (decrease gluconeogenesis)
* loss of permissiveness
* hyperpigmentation (excessive ACTH → binds alpha MSH → skin darkening)
67
New cards
Adrenal Medulla (refer back to nervous system section)
Considered part of the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system
* Innervated by sympathetic neurons
* “fight-or-fight”
* Major hormone for short-duration stress responses
* Promotes long-lasting effects than nervous input to tissues, alone.
* Aimed at promoting an increase in blood glucose and fatty acids
* Glucose available for brain use
* Fatty acids for liver (gluconeogenesis) and muscles (energy)
* Innervated by sympathetic neurons
* “fight-or-fight”
* Major hormone for short-duration stress responses
* Promotes long-lasting effects than nervous input to tissues, alone.
* Aimed at promoting an increase in blood glucose and fatty acids
* Glucose available for brain use
* Fatty acids for liver (gluconeogenesis) and muscles (energy)
68
New cards
Integrated Stress Response
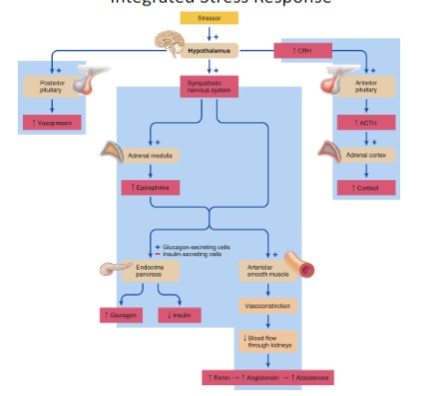
69
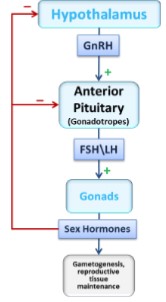
New cards
Testes
* produce testosterone from Leydig cells
* control: GnRH → LH → Testosterone
* control: GnRH → LH → Testosterone
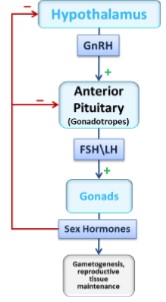
70
New cards
Ovaries
* Produce estrogen and progesterone
* Control: GnRH → FSH → Estrogen and GnRH → LH → Progesterone
* Estrogen and progesterone both have effects on the uterus, promoting a healthy environment for gestation
* Control: GnRH → FSH → Estrogen and GnRH → LH → Progesterone
* Estrogen and progesterone both have effects on the uterus, promoting a healthy environment for gestation
71
New cards
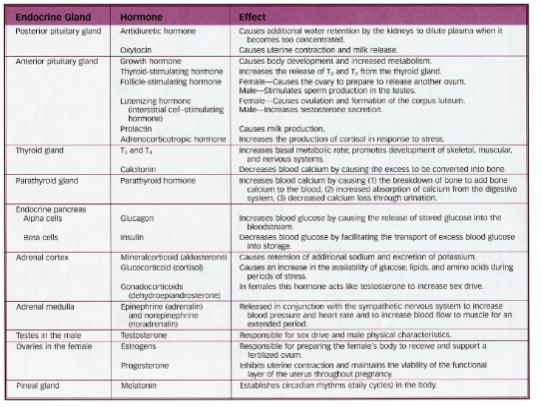
72
New cards
Functions of the Reproduction system: For both males and females
* produce gametes
* Oocytes and spermatocytes
* requires hormone production, also
* deliver gametes to the site of fertilization
* ampulla of the fallopian tube
* Oocytes and spermatocytes
* requires hormone production, also
* deliver gametes to the site of fertilization
* ampulla of the fallopian tube
73
New cards
Functions of the Reproduction system: female specific
* prepare uterus for implantation
* requires hormones
* protection of fetus
* allow fetal growth and development (gestation)
* parturition (give birth)
* lactation
* requires hormones
* protection of fetus
* allow fetal growth and development (gestation)
* parturition (give birth)
* lactation
74
New cards
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System: Male reproductive structures
External Genitalia
* Penis
* Corpus cavernosum
* corpus spongiosum
* urethra
* Scrotum
* Testes
* Seminiferous Tubules
* Epididymis
Internal Genitalia
* ductus deferens (vas deferens)
* ejaculatory duct
* urethra
* accessory sex glands
* seminal vesicles
* prostate gland
* bulbourethral glands
* Penis
* Corpus cavernosum
* corpus spongiosum
* urethra
* Scrotum
* Testes
* Seminiferous Tubules
* Epididymis
Internal Genitalia
* ductus deferens (vas deferens)
* ejaculatory duct
* urethra
* accessory sex glands
* seminal vesicles
* prostate gland
* bulbourethral glands
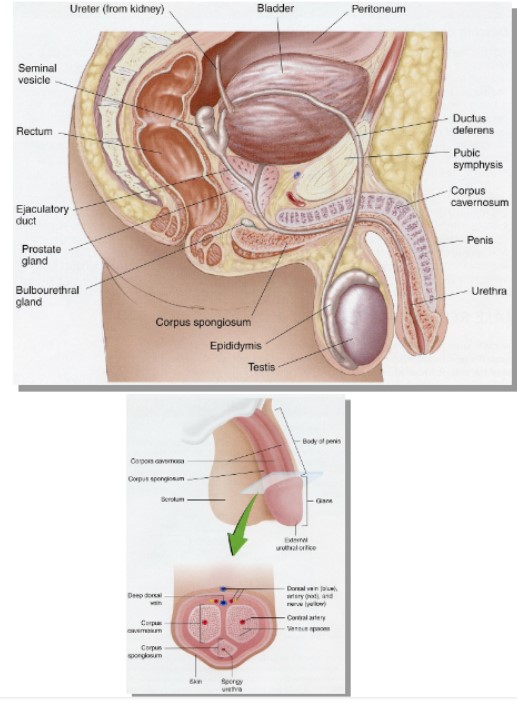
75
New cards
Testes
contain seminiferous tubules
* site of **spermatogenesis**
* requires two cell types for production
* **interstitial cells of Leydig**
* Testosterone
* **Sertoli cells**
* Nurture the process
* Temperature sensitive
* site of **spermatogenesis**
* requires two cell types for production
* **interstitial cells of Leydig**
* Testosterone
* **Sertoli cells**
* Nurture the process
* Temperature sensitive
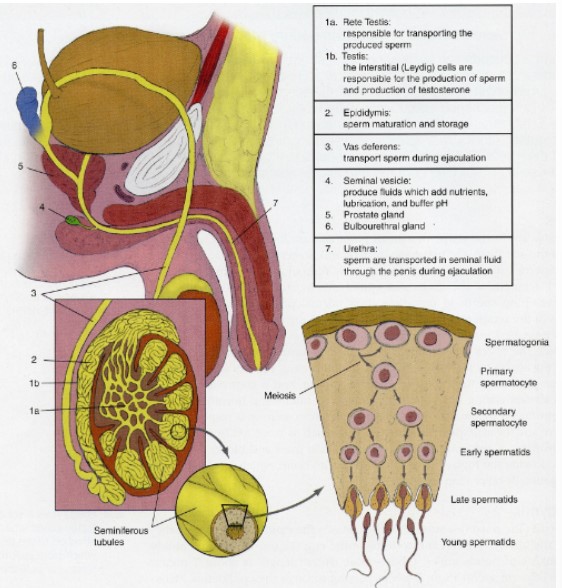
76
New cards
Spermatogensis
cremaster is in the groin
* begins at puberty
* continues throughout life
* **one** primary spermatocyte produces **four** sperm cells
* 2-month development period
* Several hundred million produced per day
* begins at puberty
* continues throughout life
* **one** primary spermatocyte produces **four** sperm cells
* 2-month development period
* Several hundred million produced per day
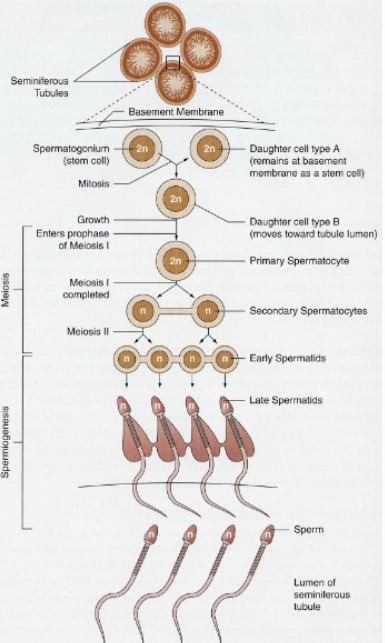
77
New cards
Sperm
structure of sperm fits its function of delivering male genetic material
* a mobile, trimmed-down cell
* a mobile, trimmed-down cell
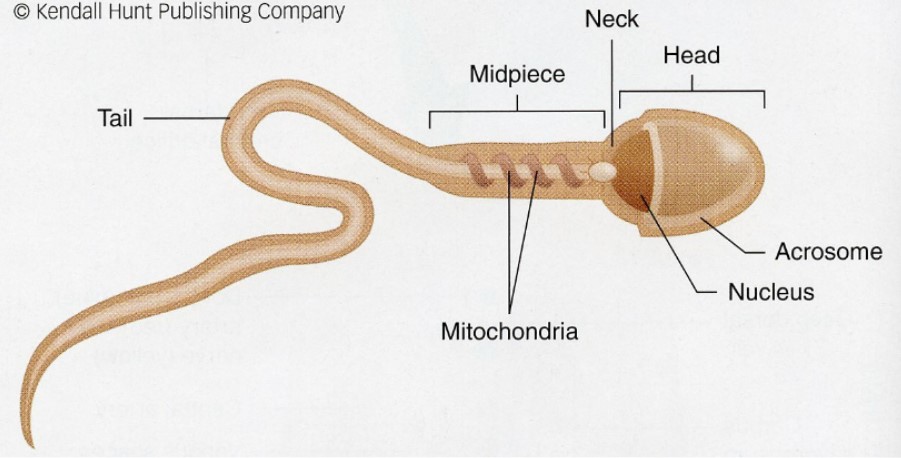
78
New cards
Accessory Sex Glands
* Seminal Vesicles
* Provide majority (60%) of semen fluid volume
* Helps dilute thick mass of sperm cells
* Fructose, prostaglandins, fibrinogen
* Prostate Gland
* Alkaline fluid, clotting enzymes, prostate-specific antigen
* Bulbourethral Glands
* Mucus-Like secretion
Semen consists of: Sperm, Seminal fluid, Prostate Fluid, Bulbourethral fluid
* 2-6mL total/ejaculation
* \~66 million sperm/mL
* Total range: 120-400 million sperm
* Provide majority (60%) of semen fluid volume
* Helps dilute thick mass of sperm cells
* Fructose, prostaglandins, fibrinogen
* Prostate Gland
* Alkaline fluid, clotting enzymes, prostate-specific antigen
* Bulbourethral Glands
* Mucus-Like secretion
Semen consists of: Sperm, Seminal fluid, Prostate Fluid, Bulbourethral fluid
* 2-6mL total/ejaculation
* \~66 million sperm/mL
* Total range: 120-400 million sperm
79
New cards
male repro loop
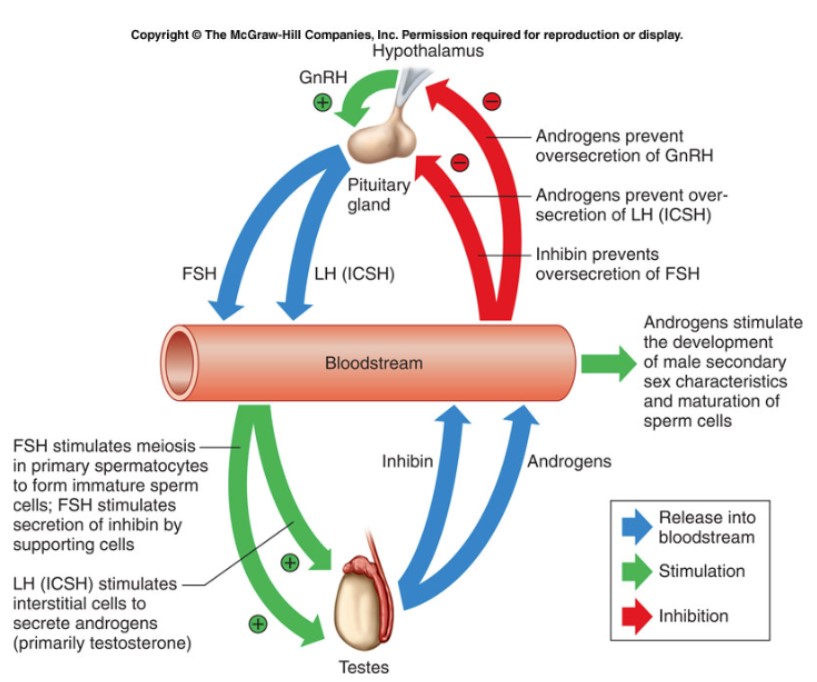
80
New cards
Anatomy of the female Reproductive System: External Genitalia (Vulva)
* Opening of the vagina = vestibule
* Urethral opening
* Labia minora and majora
* Clitoris
* Mons pubis
* Urethral opening
* Labia minora and majora
* Clitoris
* Mons pubis
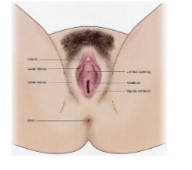
81
New cards
Anatomy of the female Reproductive System: Internal Genitalia
* Vagina
* Uterus
* Cervix
* Fallopian tubes
* Ovary
* Site of oogenesis
* Uterus
* Cervix
* Fallopian tubes
* Ovary
* Site of oogenesis
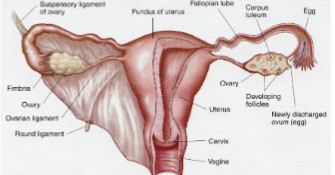
82
New cards
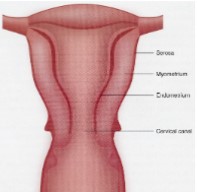
Uterus
* Body is pear-shaped
* Cervix is cylindrical
* Walls consist of myometrium and endometrium
* Cervical canal
* Entrance for sperm
* Exit for fetus
* Cervix is cylindrical
* Walls consist of myometrium and endometrium
* Cervical canal
* Entrance for sperm
* Exit for fetus
83
New cards
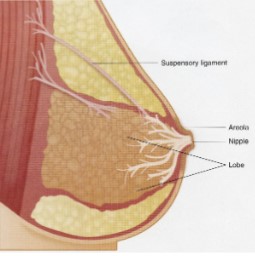
Accessory Glands
Mammary glands
* lactation
* lactation
84
New cards
Ovaries
* Site of oogenesis- production of oocyte
* Suspended from pelvic cavity wall and attached to uterus
* Fallopian tube held close, with fimbria hovering over ovary
* Oocytes are released in process of ovulaton
* Suspended from pelvic cavity wall and attached to uterus
* Fallopian tube held close, with fimbria hovering over ovary
* Oocytes are released in process of ovulaton
85
New cards
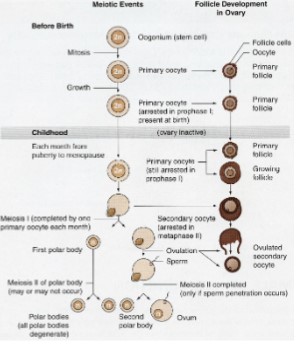
Oogenesis
Begins during development of female fetus
* produces primary oocytes
Process arrests by birth (during meiotic division)
* process resumes at puberty
* one viable oocyte per 28 days
* process is lost by menopause
* produces primary oocytes
Process arrests by birth (during meiotic division)
* process resumes at puberty
* one viable oocyte per 28 days
* process is lost by menopause
86
New cards
The Ovarian Cycle
Repeating cycle divided into two parts, separated by ovulation
* Follicular phase
* Luteal phase
* Follicular phase
* Luteal phase
87
New cards
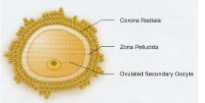
The Ovarian Cycle: Follicular phase
* Growth of follicle
* Resumption of meiotic divisions
* One of several develops to ovulation
* Characterized by rising levels of estrogen
* High estrogen triggers LH surge, resulting in ovulation
* Resumption of meiotic divisions
* One of several develops to ovulation
* Characterized by rising levels of estrogen
* High estrogen triggers LH surge, resulting in ovulation
88
New cards
The Ovarian Cycle: Luteal phase
* high LH concentration triggers luteinization of follicular remnants
* characterized by progesterone secretion
* characterized by progesterone secretion
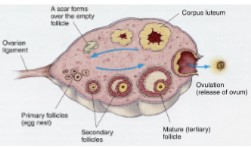
89
New cards
The Uterine Cycle
* Correlates w/ the Ovarian Cycle
* Hormones produced by ovary drive uterine changes
* **Estrogen** promotes endometrial lining thickening and development of glandular tissues and vessels (proliferation)
* **Progesterone** promotes glandular secretion (secretory) and maintenance of the endometrial lining and vessels. Also, inhibits myometrial contractions
* Withdrawal of E and P triggers **menses** (the shedding of the thick endometrial lining)
* Prostaglandin production promotes vasoconstriction
* Hormones produced by ovary drive uterine changes
* **Estrogen** promotes endometrial lining thickening and development of glandular tissues and vessels (proliferation)
* **Progesterone** promotes glandular secretion (secretory) and maintenance of the endometrial lining and vessels. Also, inhibits myometrial contractions
* Withdrawal of E and P triggers **menses** (the shedding of the thick endometrial lining)
* Prostaglandin production promotes vasoconstriction
90
New cards
Correlation between Ovarian and Uterine Cycles
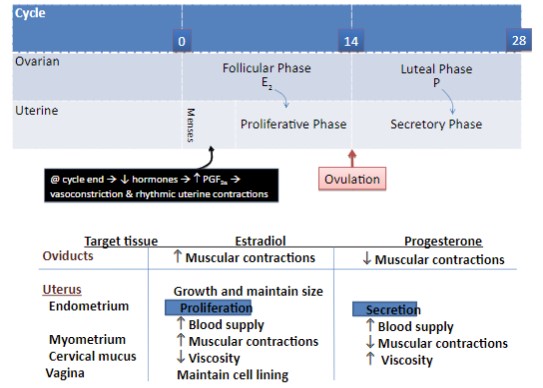
91
New cards
The Human Response Cycle
* Excitement/ Arousal phase
* Plateau Phase
* Orgasmic Phase
* Resolution Phase
* Plateau Phase
* Orgasmic Phase
* Resolution Phase
92
New cards
Male Sex Act
Sexual Response cycle
* Excitement phase
* Excretion and increase sexual awareness
* Plateau phase
* increase HR, increase BP, increase Resp. Rate, increase muscle tension
* Orgasmic phase
* Ejaculation
* emission
* delivery of prostatic, sperm, and sem. ves. fluids into urethra
* Expulsion
* Semen in urethra → sk. muscle contraction in base of penis
* increase sexual excitement → collective experience of intense physical pleasure
* Resolution
* refractory period
* return to pre-arousal state
* Excitement phase
* Excretion and increase sexual awareness
* Plateau phase
* increase HR, increase BP, increase Resp. Rate, increase muscle tension
* Orgasmic phase
* Ejaculation
* emission
* delivery of prostatic, sperm, and sem. ves. fluids into urethra
* Expulsion
* Semen in urethra → sk. muscle contraction in base of penis
* increase sexual excitement → collective experience of intense physical pleasure
* Resolution
* refractory period
* return to pre-arousal state
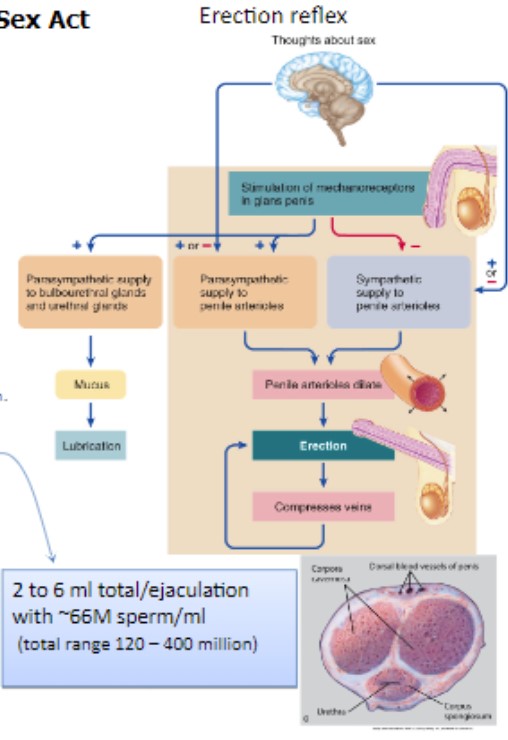
93
New cards
Female Sex Act
Sexual response cycle
* excitement phase
* plateau phase
* Orgasmic phase
* Resolution
* excitement phase
* plateau phase
* Orgasmic phase
* Resolution
94
New cards
Female Sex Act: Sexual Response cycle: Excitement phase
* Erection and ↑ sexual awareness
* Nipples erect, breasts enlarge
* “sex flsh” → ↑ blood flow through skin
* Nipples erect, breasts enlarge
* “sex flsh” → ↑ blood flow through skin
95
New cards
Female Sex Act: Sexual Response cycle: Plateau phase
* ↑ HR, ↑ BP, ↑ Resp. Rate, ↑ muscle tension, vasocongeston in vagina → ↓ vaginal capacity
* Tenting effect
* Uterus raises, lifting cervix
* Tenting effect
* Uterus raises, lifting cervix
96
New cards
Female Sex Act: Sexual Response cycle: Orgasmic phase
* Rhythmic contractions of pelvic musculature
* 0.8 second intervals
* ↑ sexual excitement → collective experience of intense physical pleasure
* 0.8 second intervals
* ↑ sexual excitement → collective experience of intense physical pleasure
97
New cards
Female Sex Act: Sexual Response cycle: Resolution
* No refractory period → repeated orgasms
* up to 12 successive organisms
* Return to pre-arousal state
* up to 12 successive organisms
* Return to pre-arousal state
98
New cards
Lubrication
* Vasocongeston → forces fluid into vaginal lumen
* Mucus secretion from vestibular glands (outer vagina)
* Mucus from male
* Mucus secretion from vestibular glands (outer vagina)
* Mucus from male
99
New cards
Fertilization: Primary site = ampulla
Oviduct cups around ovary
* Fimbriae “sweep” ovulated oocyte into lumen
* Cilia contribute
* Peristaltic contractions and ciliary action move oocyte toward ampulla
* Fimbriae “sweep” ovulated oocyte into lumen
* Cilia contribute
* Peristaltic contractions and ciliary action move oocyte toward ampulla
100
New cards
Fertilization: Sperm transport
* Cervical mucus thins (↑ E2)
* For 2-3 days
* Dispersal via uterine contractions
* Retrograde peristalsis
* Possible chemotaxis
* For 2-3 days
* Dispersal via uterine contractions
* Retrograde peristalsis
* Possible chemotaxis