CSF, Meninges and Ventricular System
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Cerebrospinal fluid
The fluid that surround the brain and spinal cord
Provides cushioning and protection
Transports nutrients due to having many blood vessels
CSF is continually secreted, circulated and absorbed
Mainly produced in the lateral ventricle and choroid plexus
Choroid plexus
Production site of CSF
A network of vessels in each ventricle in the brain
Produces CSF via ependymal cells that line the ventricles of the brain
Layers (membrane) that cover the brain
Meninges - dura mater, arachnoid mater and pia mater
Collective function of structural and mechanical protection also cellular protection (blood brain barrier)
Support blood vessels and have a high metabolic demand
Dura mater
Outer layer
Loose and not always connected to the skull
Has two layers
Tough
Arachnoid mater
Middle later
Spider like in appearance
Many blood vessels and branches
Under subdura space
Pia mater
Innermost layer
Close to the brain and tightly connected to it
Location of the ventricles of the brain
Lateral ventricle, third ventricle, fourth ventricle and cerebral aqueduct
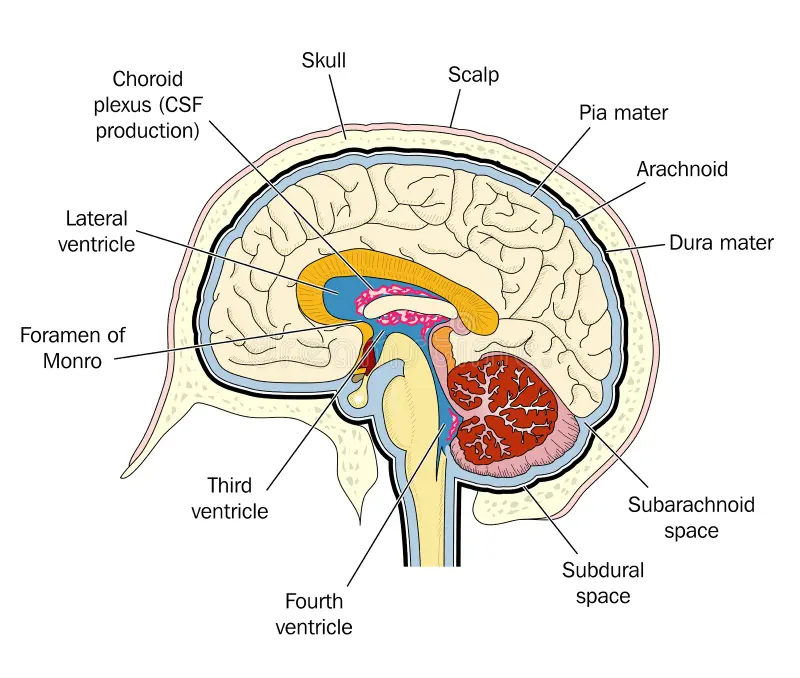
Lateral ventricle
Largest ventricle located in the cerebrum
One in each hemisphere - within each cerebral hemisphere
Third ventricle
Narrow midline space between the right and left thalamus in the diencephalon
Connected to the lateral ventricle by the foramen of Monro
Fourth ventricle
In the brainstem between the pons and medulla oblongata
Cerebral aqueduct
Connects the third and fourth ventricle
Hydrocephalus
Build up of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain
Excess fluid in the ventricular system which exerts a pressure on the brain which can cause the brain to move down
Due to over production of CSF or it not be drained enough/properly
Could also be caused by bleeding
Hydrocephalus symptoms
Headaches, blurred vision, balance loss, nausea, vomiting, poor coordination
Hydrocephalus treatment
Drainage of fluid either a extra ventricular drain or a VP shunt (internal drain)
Where CSF is absorbed
Through the venous sinus and arachnoid villi