A-Level Chemistry CIE
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Define the enthalpy change of atomisation, ΔHat
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of gaseous atoms are formed from its element under standard condition.
Define lattice energy, ΔHlatt (the change from gas phase ions to solid lattice)
The energy change when anions and cations in the gaseous state condense to form 1 mole of an ionic solid.
Define the first electron affinity, EA
The enthalpy change when one mole of electrons are added to one mole of gaseous atoms to form one mole of gaseous ions under standard conditions.
What is enthalpy change ΔH?
The heat energy absorbed or released during a reaction at constant pressure.
Define the enthalpy change of hydration, ΔHhyd
The enthalpy change when 1 mole of a gaseous ion dissolves in water completely.
Define the enthalpy change of solution, ΔHsol
The amount of energy released when 1 mole of the ionic lattice dissolves in water to form a very dilute solution.
Define entropy, S
The number of possible arrangements of the particles and their energy in a given system.
State the Gibbs equation
ΔG⦵ = ΔH⦵ – TΔS⦵
ΔG is Gibbs free energy change (kJ)
ΔH is enthalpy change (kJ/mol)
T is temperature (K)
ΔS is entropy change (kJK/mol)
Following the sign of ΔG⦵ , when is a reaction or process feasible?
When the sign is negative.
Relationship between Faraday constant, Avogadro constant and the charge on an electron.
F = Le
Define standard electrode (reduction) potential
The potential difference of a half cell measured under standard conditions (1 M, 1 atm, 25°C) with a standard hydrogen electrode as the other half cell.
Define standard cell potential.
The potential difference measured across two half cells under standard conditions.
Define conjugate acid-base pairs.
Pairs of reactants and products linked together by the transfer of a proton.
Define mathematically pH
pH = -log[H+]
Define mathematically Ka
Ka = [H+] [A-] / [HA]
HA is the weak acid
H+ is the hydrogen ions
A- is the conjugate base
Define mathematically pKa
pKa = -log Ka
Define mathematically Kw
Kw = [H+] [OH-]
Define a buffer solution
A mixture that resists a change in pH when a small amount of acid or alkali is added.
Define the partition coefficient, Kpc
The ratio of the concentrations of a solute in two different immiscible solvents in contact with each other when an equilibrium has been established.
Define a transition element
A d-block element which forms one or more stable ions with incomplete d orbitals.
Shape of the 3dxy orbital

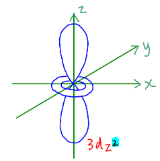
Shape of the 3dz2 orbital
Define ligand
A species that contains a lone pair of electrons that forms a dative covalent bond to a central metal atom/ion.
Define a complex
A molecule or ion formed by a central metal atom/ion surrounded by one or more ligands.
Define coordination number
Number of dative bonds between ligands and transition ion of a complex.
Define degenerate d-orbitals
When the orbitals of a subshell are all equal in energy.
Define non-degenerate d-orbitals
When d-orbitals experience an external force, they no longer remain at the same energy level.
Define the stability constant, Kstab, of a complex
The equilibrium constant for the formation of the complex ion in a solvent from its constituent ions or molecules.
Reactions by which halogenoarenes are produced
Substitution of an arene with Cl2 or Br2 in the presence of catalyst, AlCl3 or AlBr3 respectively.
Examples: benzene forms chlorobenzene
methyl benzene forms 2-chloromethylbenxene and 4-chloromethylbenzene
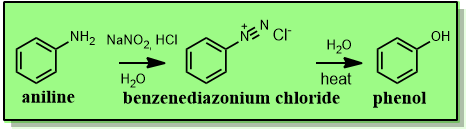
Reaction (reagents and conditions) by which phenol can be produced
phenylamine + HNO2 or NaNO2 and dilute acid
temperature below 10℃
produces diazonium salt
further warming of diazonium salt with H2O
gives phenol
Underlined are reagents
Italics are conditions
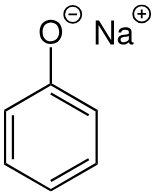
Chemistry of phenol with bases
will produce a salt
e.g. with NaOH(aq) to produce sodium phenoxide
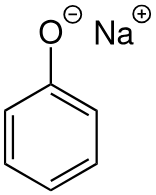
Chemistry of phenol with Na(s)
produces sodium phenoxide and H2(g)
Chemistry of phenol in NaOH(aq) with diazonium salts
Gives azo compounds

Chemistry of the nitration of phenol’s aromatic ring with dilute HNO3(aq) at room temperature
gives a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol
Bromination of phenol with Br2(aq)
forms 2,4,6-tribromophenol
Where does the hydroxy group of a phenol direct incoming electrophiles to?
The 2-, 4-, 6- (ortho and para) positions
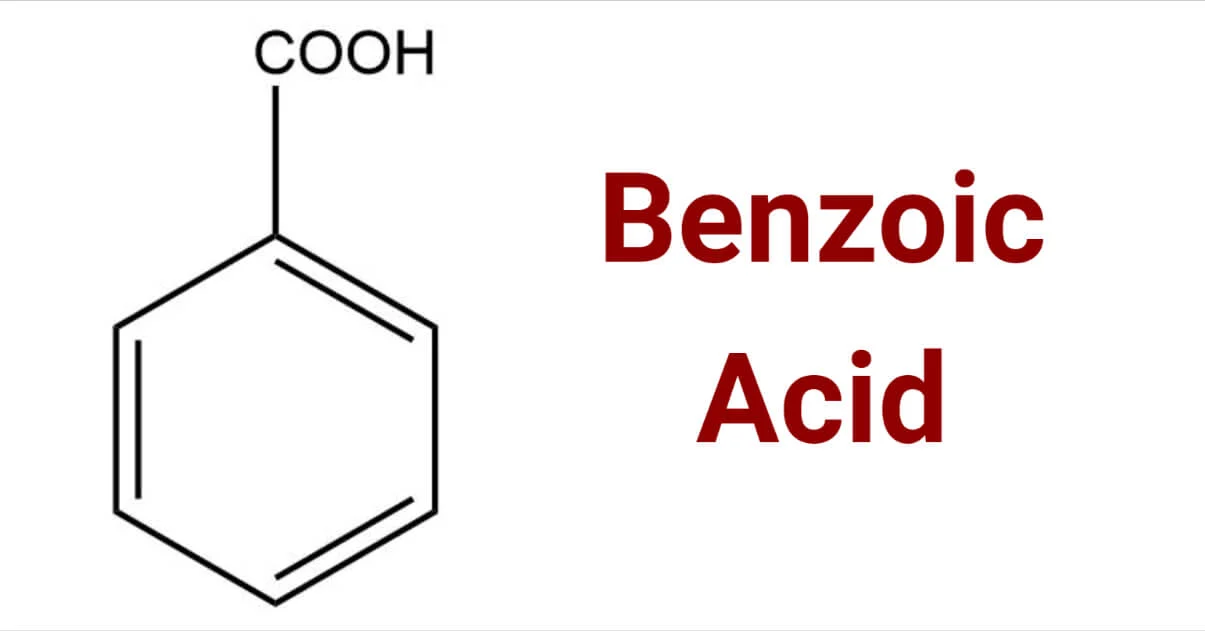
How is benzoic acid produced?
alkylbenzene + hot alkaline KMnO4 + then dilute acid
example: methylbenzene to benzoic acid
How are esters produced?
alcohols + acyl chlorides
examples: formation of ethyl ethanoate and phenyl benzoate
What is the reaction (reagents and conditions) by which acyl chlorides can be produced?
carboxylic acids + PCl3 and heat or PCl5 or SOCl2
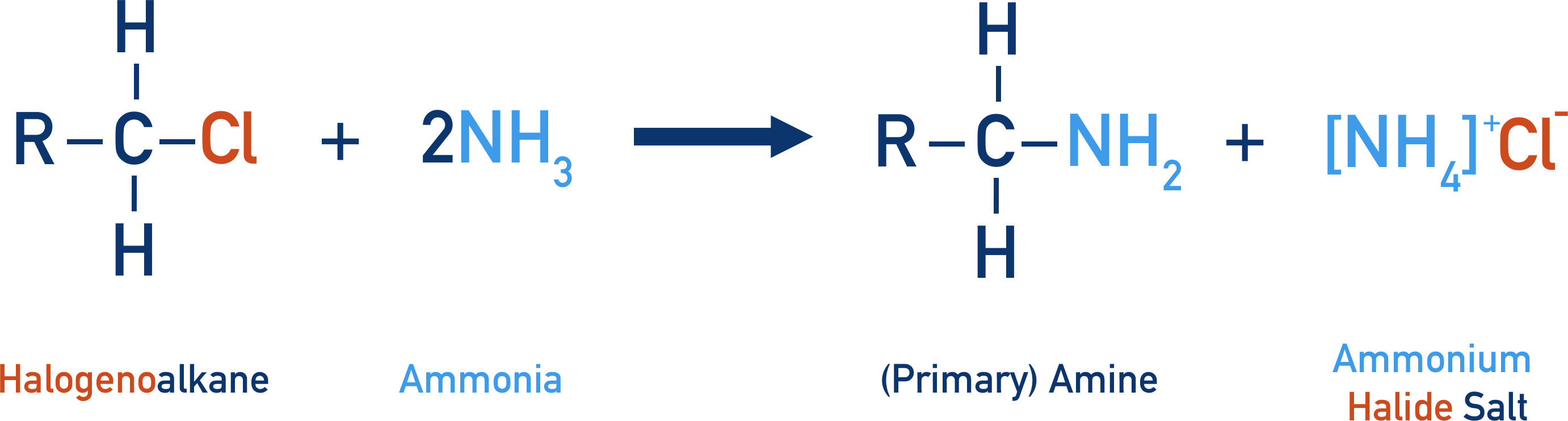
What are the reagents and conditions to form primary and secondary amines from halogenoalkanes?
halogenoalkane + NH3
in ethanol (as a solvent)
heated under pressure
Reagents and conditions to form secondary amines?
halogenoalkanes + primary amines in ethanol
heated in a sealed tube/under pressure
How are azo compounds used?
as dyes
Reagents in coupling reaction to form azo compound.
benzenediazonium chloride + phenol in NaOH (aq)
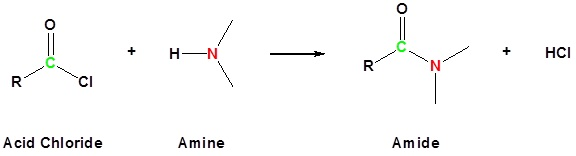
How are amides produced?
ammonia or primary amine
+ an acyl chloride
at room temperature
Which are weaker bases, amines or amides?
amides
The need for deuterated solvents when obtaining a proton NMR spectrum.
Contain deuterium not hydrogen, so no interference with the NMR.
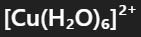
What is the color and state of the complex:
pale blue solution

What is the color and state of the complex:
brown solution
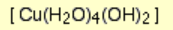
What is the color and state of the complex:
blue ppt.
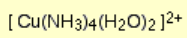
What is the color and state of the complex:
deep blue solution
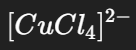
What is the color and state of the complex:
yellow-green solution
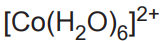
What is the color and state of the complex:
pink solution
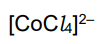
What is the color and state of the complex:
blue solution
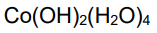
What is the color and state of the complex:
blue ppt. slightly pinkish on browning