UNITS 7,8,9 AP WORLD MATCHING TEST FULL QUIZLET-MNHS
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:03 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
1
New cards
Photosynthesis
Algeria
Algeria
\

2
New cards
Brazil

3
New cards
China

4
New cards
Congo/Zaire

5
New cards
Cuba

6
New cards
Egypt

7
New cards
France

8
New cards
Germany

9
New cards
Ghana

10
New cards
India

11
New cards
Indonesia

12
New cards
Iran

13
New cards
Israel

14
New cards
Japan

15
New cards
Kenya

16
New cards
Koreas

17
New cards
Mexico

18
New cards
Nigeria

19
New cards
Pakistan

20
New cards
Philippines

21
New cards
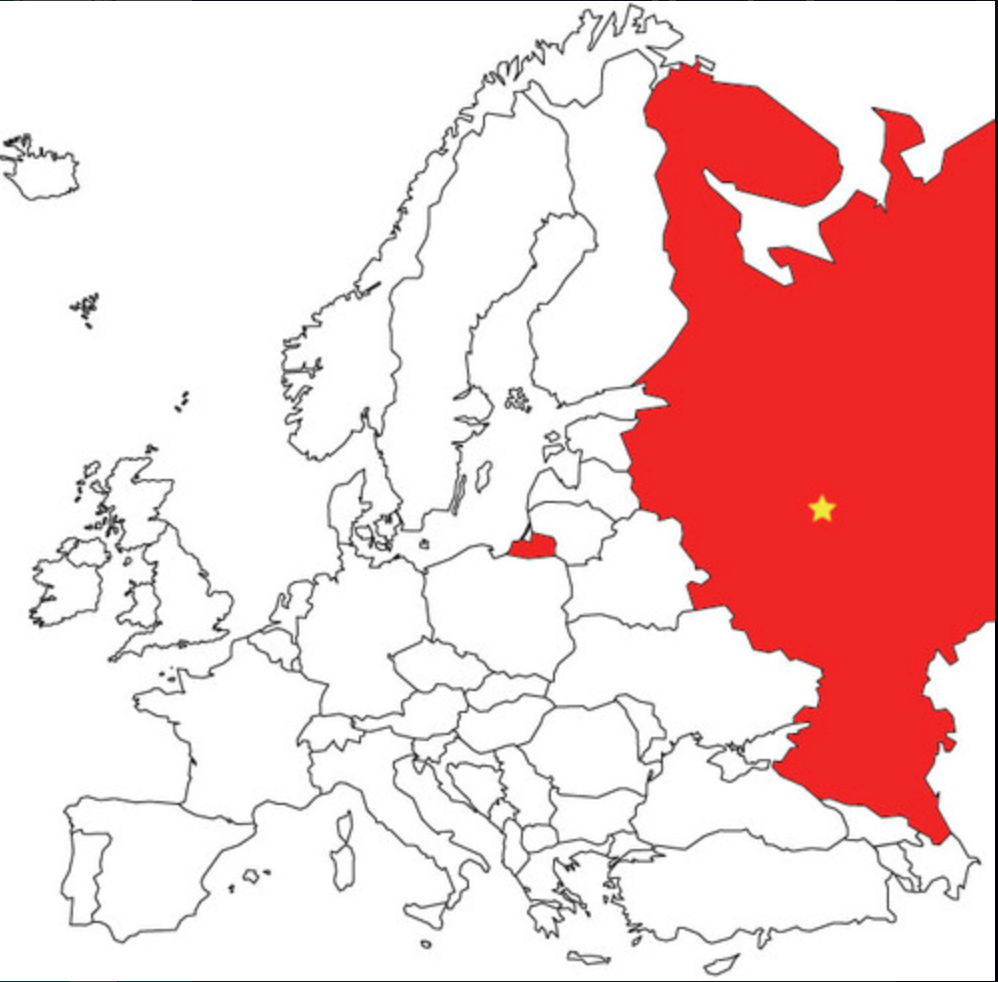
Russia

22
New cards
Rwanda

23
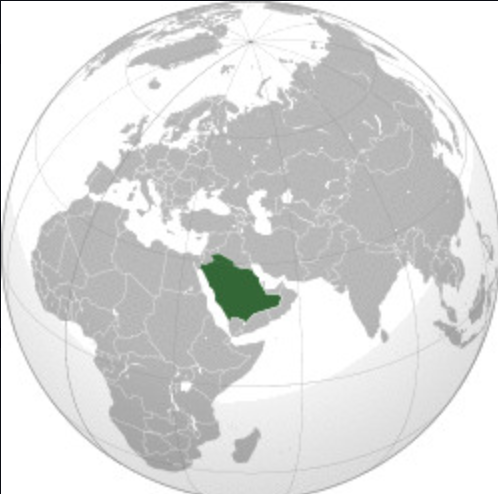
New cards
Saudi Arabia
24
New cards
Senegal

25
New cards
Singapore

26
New cards
South Africa

27
New cards
Sudan

28
New cards
Taiwan

29
New cards
Turkey

30
New cards
United Kingdom

31
New cards
United States

32
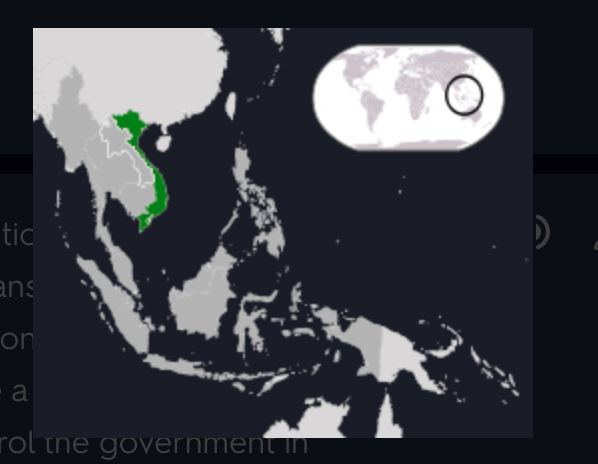
New cards
Vietnam
33
New cards
African National Congress
South African political party established in 1912 by elite Africans who sought to win full acceptance in colonial society; it only gradually became a popular movement that came to control the government in 1994
34
New cards
blitzkrieg
German term meaning "lightning war," used to describe Germany's novel military tactics in World War II, which
35
New cards
involved the rapid movement of infantry, tanks, and airpower over large areas.
36
New cards
Bolsheviks
Russian revolutionary party led by Vladimir Lenin and later renamed the Communist Party
37
New cards
Castro, Fidel
Revolutionary leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008 who gradually turned to Soviet communism and engendered some of the worst crises of the cold war
38
New cards
Chinese Revolution
Long revolutionary process in the period 1912-1949 that began with the overthrow of the Chinese imperial
39
New cards
system and ended with the triumph of the Communist Party under the leadership of Mao Zedong.
40
New cards
collectivization
Process of rural reform undertaken by the communist leadership of both the USSR and China in which private
41
New cards
property rights were abolished and peasants were forced onto larger and more industrialized farms to work and share the proceeds as a community rather than as individuals.
42
New cards
Cultural Revolution
Massive campaign launched by Mao Zedong in the
43
New cards
mid-1960s to combat the capitalist tendencies that he believed reached into even the highest ranks of the Communist Party; the campaign threw China into chaos
44
New cards
Deng Xiaoping
Leader of China from 1976 to 1997 whose reforms essentially dismantled the communist elements of the Chinese economy
45
New cards
fascism
Political ideology marked by its intense nationalism and authoritarianism; its name is derived from the fasces that were the symbol of magistrates in ancient Rome.
46
New cards
Franz Ferdinand, Archduke
Heir to the Austrian throne whose assassination by a Serbian nationalist on June 28, 1914, was the spark that ignited World War I.
47
New cards
Gandhi, Mohandas K.
Political leader and the undoubted spiritual leader of the Indian drive for independence from Great Britain.
48
New cards
Glasnost
Mikhail Gorbachev's policy of "openness," which allowed greater cultural and intellectual freedom and ended most censorship of the media; the result was a burst of awareness of the problems and corruption of the Soviet system
49
New cards
Gorbachev, Mikhail
Leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to 1991 whose efforts to reform the USSR led to its collapse
50
New cards
Great Leap Forward
Major Chinese initiative (1958-1960) led by Mao Zedong that was intended to promote small-scale industrialization and increase knowledge of technology; in reality, it caused a major crisis and exacerbated the impact of a devastating famine
51
New cards
Great Purges
Also called the Terror; massive attempt to cleanse the Soviet Union of supposed "enemies of the people"; nearly a million people were executed between 1936 and 1941, and 4 million or 5 million more were sentenced to forced labor in the gulag
52
New cards
Guomindang
The Chinese Nationalist Party led by Chiang Kai-shek from 1928 until its overthrow by the communists in 1949
53
New cards
Indian National Congress
Organization established in 1885 by Western-educated elite Indians in an effort to win a voice in the governance of India; over time, it became a major popular movement that won India's independence from Britain
54
New cards
Jinnah, Muhammad Ali
Leader of India's All-India Muslim League and first president of the breakaway state of Pakistan (1876-1948)
55
New cards
Khomeini, Ayatollah Ruholla
Important Shia ayattolah (advanced scholar of Islamic law and religion) who became the leader of Iran's Islamic revolution and ruled Iran from 1979 until his death in 1989
56
New cards
Khrushchev, Nikita
Leader of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964
57
New cards
Kristallnacht
Literally, "crystal night"; name given to the night of November 9, 1938, when Nazi-led gangs smashed and looted Jewish shops throughout Germany
58
New cards
Lenin
Adopted name of Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov (1870-1924), the main leader of Russia's communist revolution and head of the Soviet state from 1917 until his death
59
New cards
Mandela, Nelson
South African nationalist (b. 1918) and leader of the African National Congress who was imprisoned for twenty-seven years on charges of treason, sabotage, and conspiracy to overthrow the apartheid government of South Africa; he was elected president of South Africa in 1994, four years after he was finally released from prison.
60
New cards
Mao Zedong
Chairman of China's Communist Party and de facto ruler of China from 1949 until his death in 1976
61
New cards
Marshall Plan
Huge U.S. government initiative to aid in the post-World War II restoration of Europe that was masterminded by U.S. secretary of state George Marshall and put into effect in 1947
62
New cards
McCarthyism
Wave of anticommunist fear and persecution that took place in the United States in the 1950s
63
New cards
Mussolini, Benito
Charismatic leader of the Italian fascist party (1883-1945) who came to power in 1922
64
New cards
Nanjing, Rape of
The Japanese army's systematic killing, mutilation, and rape of the Chinese civilian population in 1938
65
New cards
Nehru, Jawaharlal
The first prime minister of independent India (1889-1964)
66
New cards
New Deal
A series of reforms enacted by the Franklin Roosevelt administration between 1933 and 1942 with the goal of ending the Great Depression
67
New cards
North/South gap
Growing disparity between the Global North and the Global South that appears to be exacerbated by current world trade practices
68
New cards
Nuremberg Laws
Series of laws passed by the Nazi-dominated German parliament in 1935 that forbade sexual relations between Jews and other Germans and mandated that Jews identify themselves in public by wearing the Star of David
69
New cards
Perestroika
Bold economic program launched in 1987 by Mikhail Gorbachev with the intention of freeing up Soviet industry and businesses
70
New cards
Satyagraha
Literally, "truth force"; Mahatma Gandhi's political philosophy, which advocated confrontational but nonviolent political action
71
New cards
second-wave feminism
Women's rights movement that revived in the 1960s with a different agenda than earlier women's suffrage movements; members demanded equal rights for women in employment and education, women's right to control their own bodies, and the end of patriarchal domination
72
New cards
Stalin
Name assumed by Joseph Vissarionovich Jugashvili (1878-1953), leader of the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death; means "made of steel"
73
New cards
Treaty of Versailles
1919 treaty that officially ended World War I; the immense penalties it placed on Germany are regarded as one of the causes of World War II
74
New cards
Triple Alliance
An alliance consisting of Germany, Austria, and Italy that was one of the two rival European alliances on the eve of World War I
75
New cards
Triple Entente
An alliance consisting of Russia, France, and Britain that was one of the two rival European alliances on the eve of World War I
76
New cards
United Nations
International peacekeeping organization and forum for international opinion, established in 1945
77
New cards
Warsaw Pact
Military alliance of the USSR and the communist states of Eastern Europe during the cold war
78
New cards
Wilson, Woodrow
President of the United States from 1913 to 1921 who was especially noted for his idealistic approach to the end of World War I, which included advocacy of his Fourteen Points intended to regulate future international dealings and a League of Nations to enforce a new international order
79
New cards
zaibatsu
The huge industrial enterprises that dominated the Japanese economy in the period leading up to World War II
80
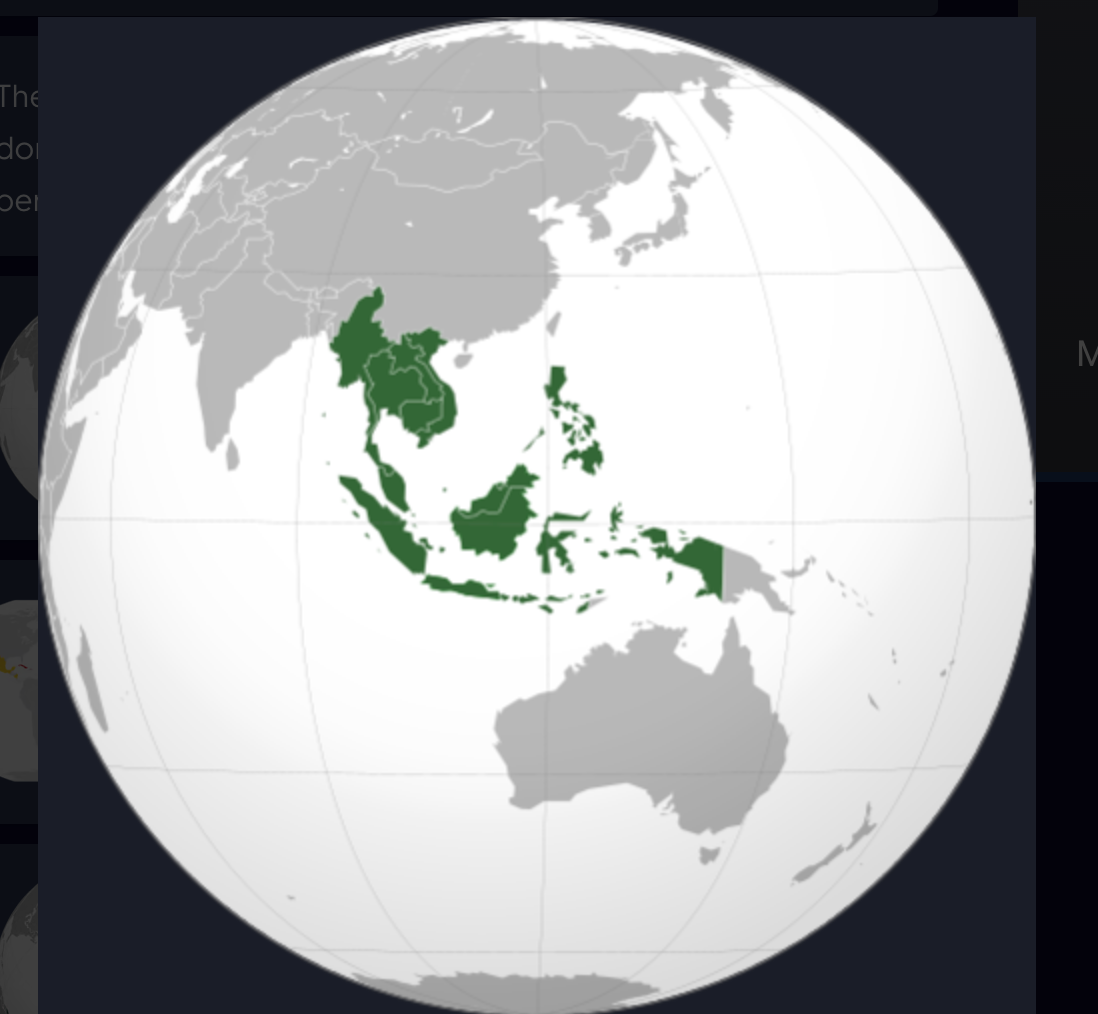
New cards
ASEAN
\
81
New cards
COMECON

82
New cards
European Union

83
New cards
Mercosur

84
New cards
NAFTA

85
New cards
OPEC
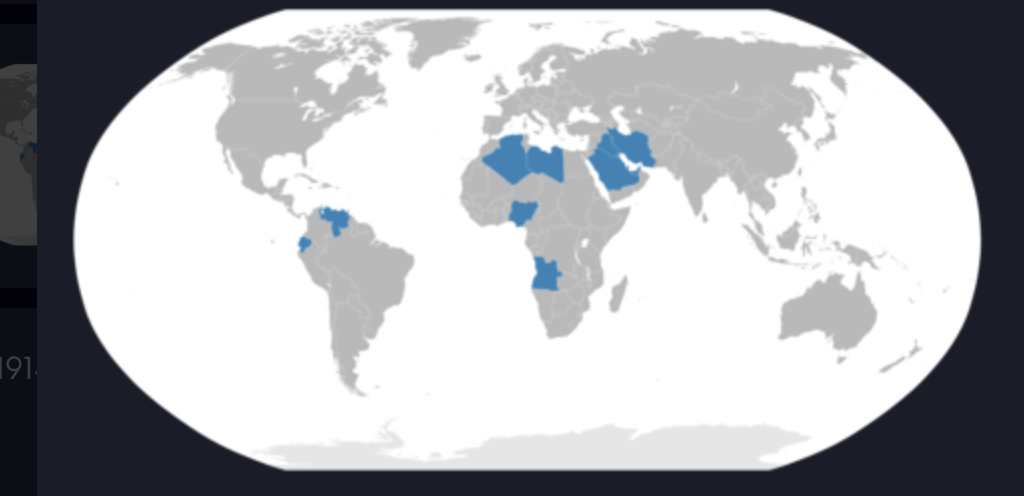
86
New cards
World War I
1914-1918
87
New cards
Russian Revolution
1917
88
New cards
World War II
1939-1945
89
New cards
The collapse of Soviet Union
1991
90
New cards
Cold War
1946-1991
91
New cards
End of Apartheid
1994
92
New cards
Cairo
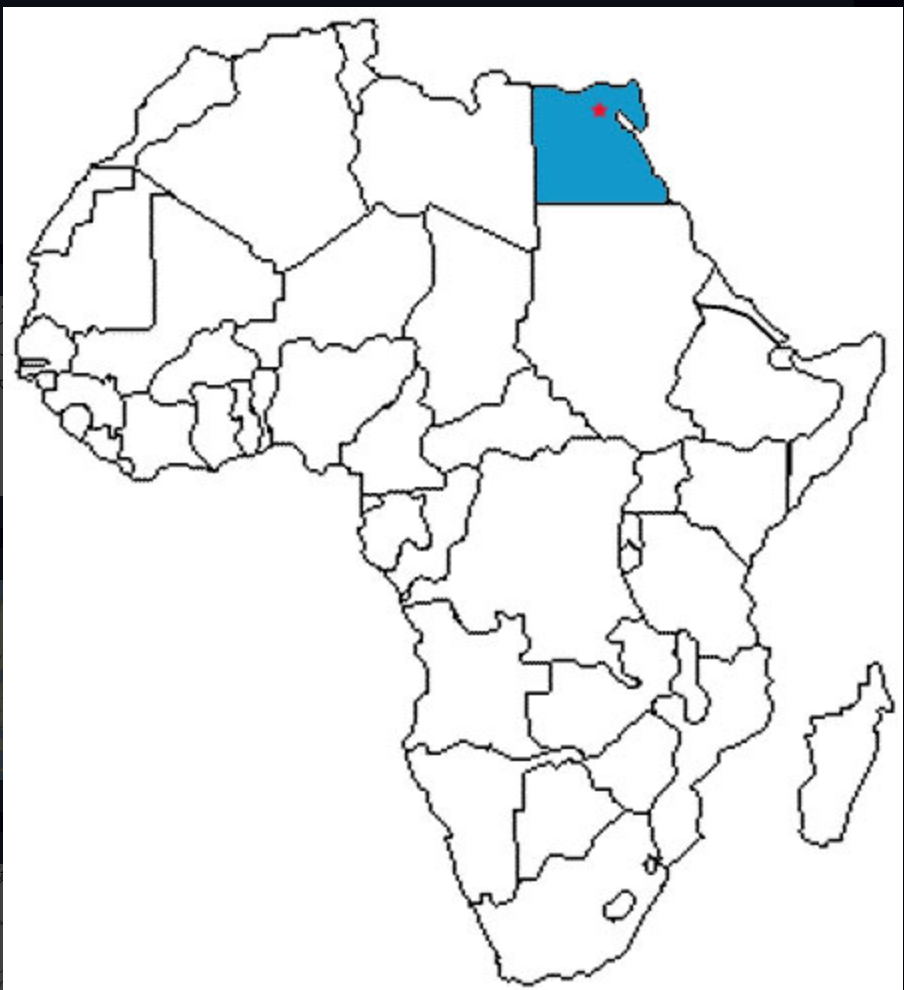
93
New cards
Copenhagen
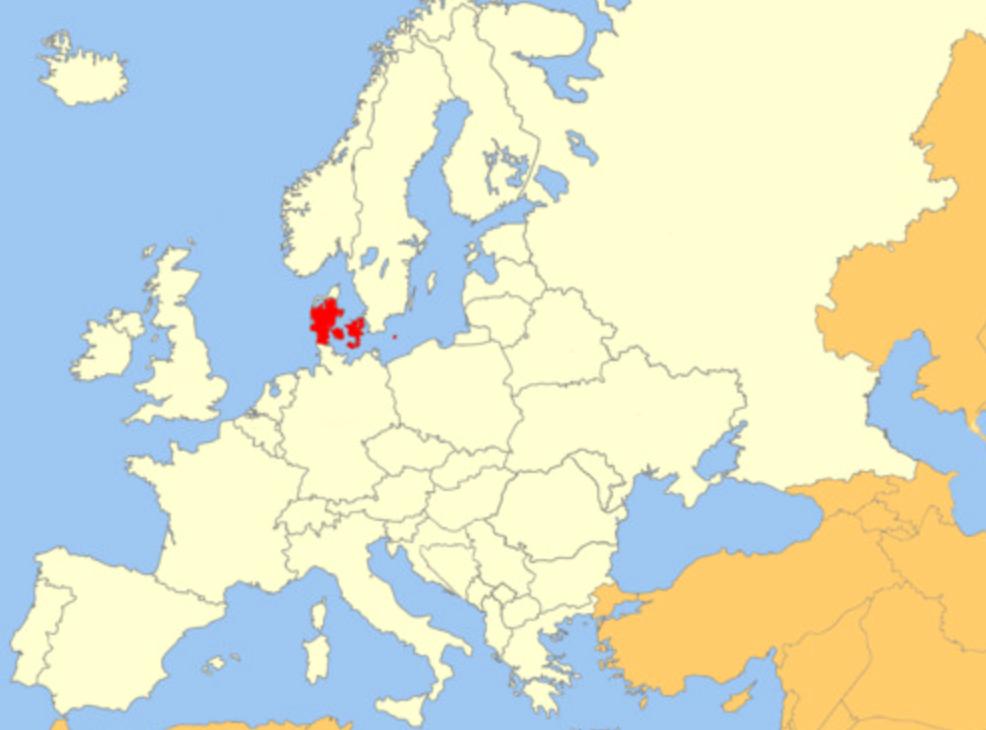
94
New cards
Djakarta
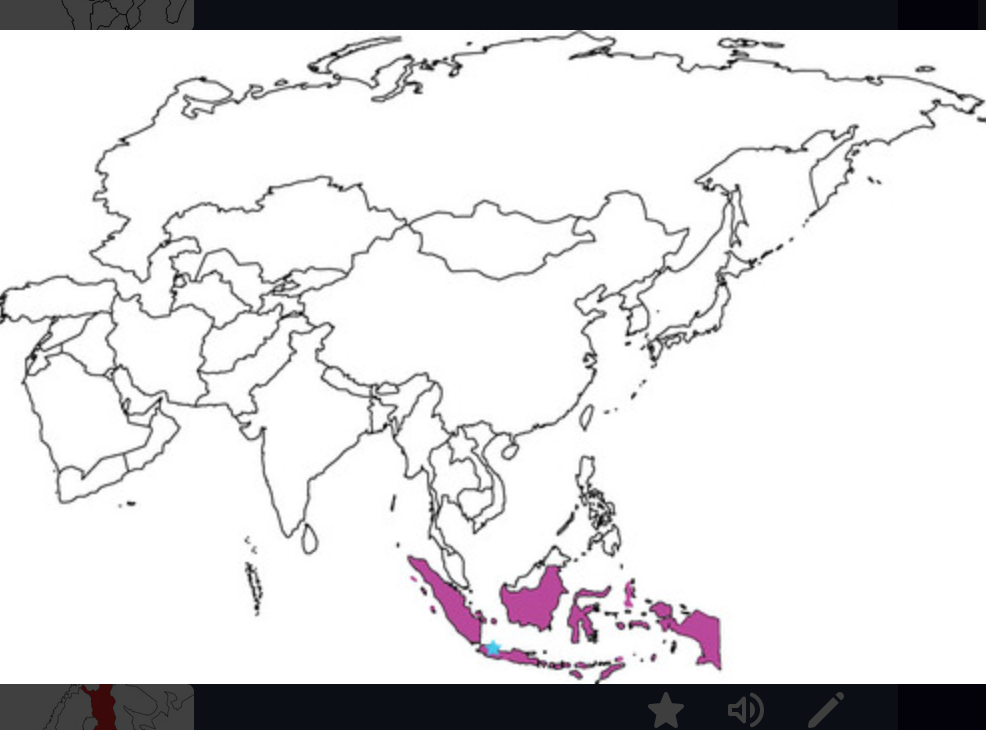
95
New cards
Helsinki
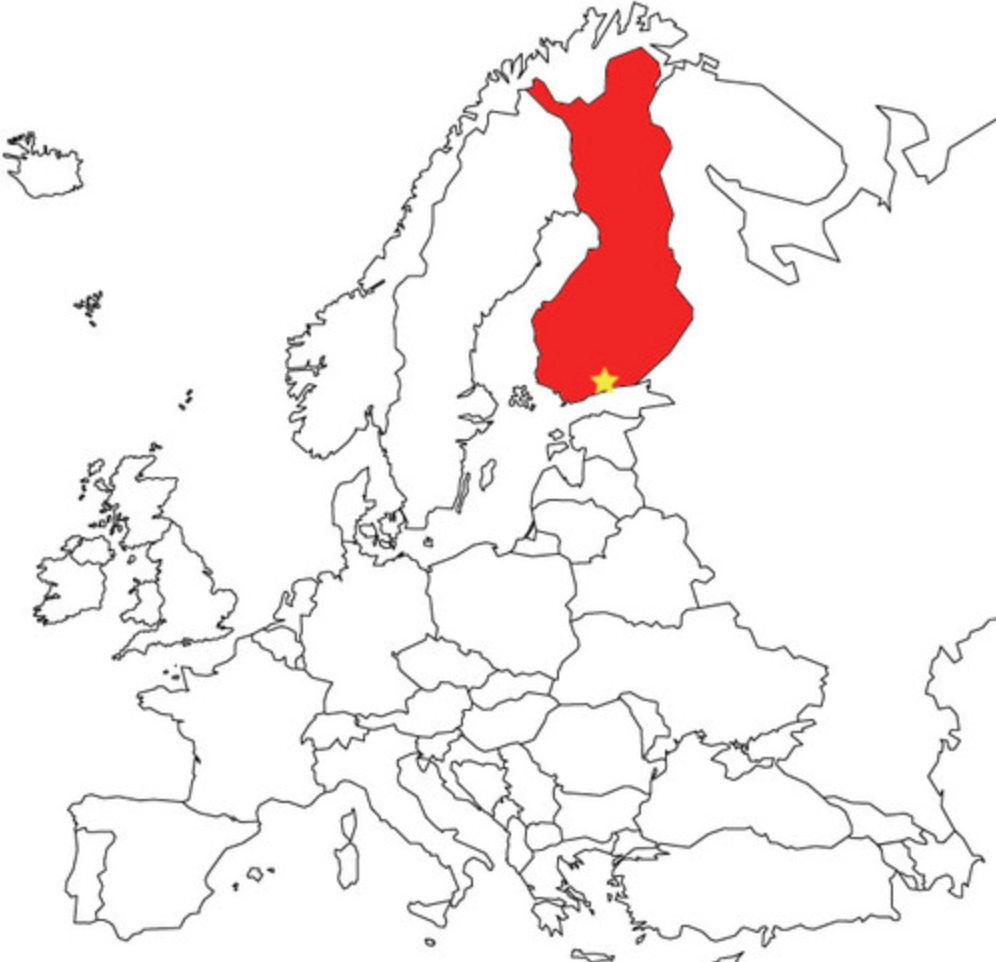
96
New cards
Hong Kong
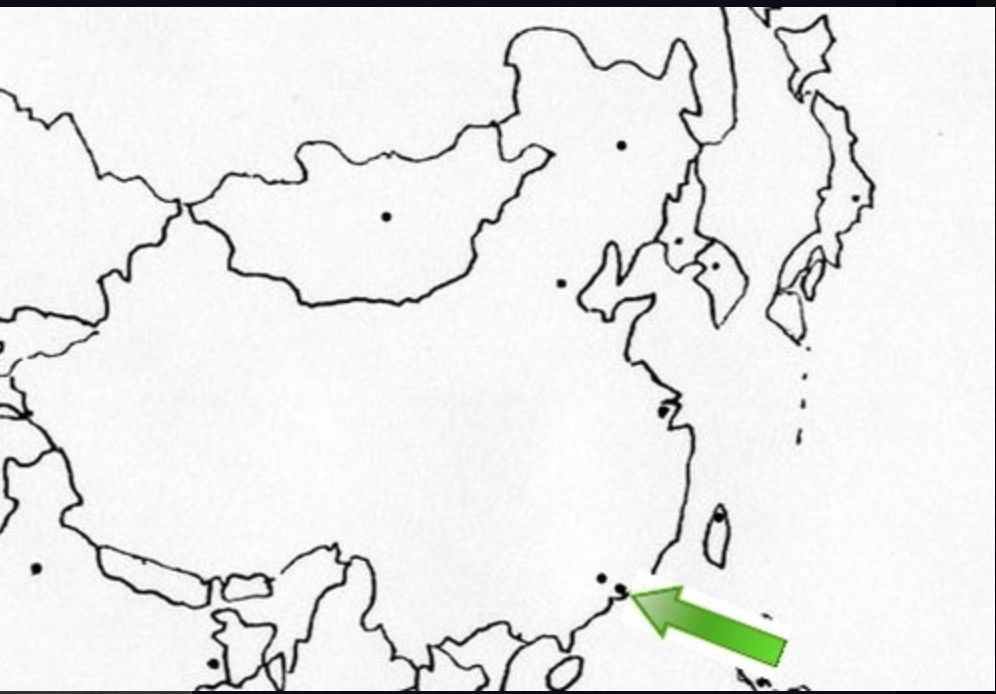
97
New cards
Lagos
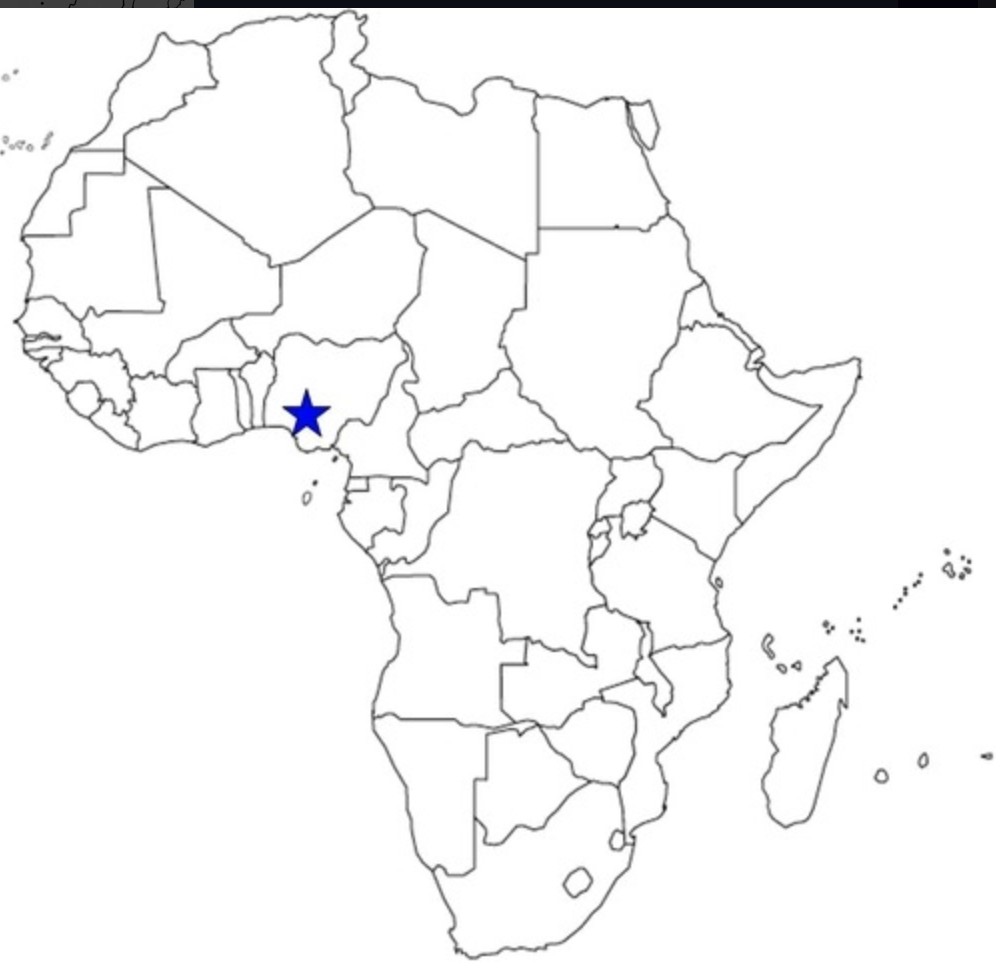
98
New cards
Los Angeles
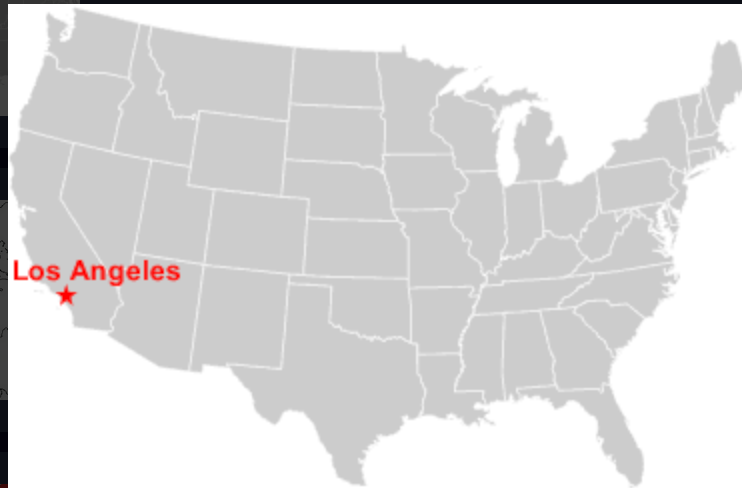
99
New cards
Mexico City
100
New cards
Moscow