SDS-PAGE
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
SDS-PAGE stands for:
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Amino acid subunits
carboxyl group
amino group
unique R-group
alpha-carbon
Amino acids are connected via? How are these bonds made?
Peptide bonds
Dehydration condensation reaction wherein there is a loss of water molecule
Amide or amido group is composed of?
peptide bond and amino group of the other amino acid
Describe a notable characteristic of an amide and what this means
It has a partial double bond character involving a lone pair of electrons/nitrogen that is localized (which means that they can jump around)
Makes them not as rotatable as single bonds nor rigid as double bonds
Hierarchy of protein structure
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
Quaternary
Describe primary structure
linear sequence of a chain of amino acids
Describe secondary structure
local folding of the polypeptide chains into helices or sheets
Simplest motif of the protein
Secondary structure
Describe tertiary structure
3D folding/aggregation of secondary structures due to side-chain interactions
Describe quaternary structure
Oligomerization state of the proteins wherein monomers are converted to polymers through polymerization
Hemoglobin is described as?
Tetrameric made up of 2 ɑ/alpha chains and 2 β/beta chains
What is the driving force between the assembly of tertiary structures into quaternary?
Noncovalent interactions such as hydrophobic or Van der Waals
What bonds keep quaternary structures intact
Disulfide linkages
The higher the band of the gel ⇒ the ___ the molecular size
larger
The ___ the band of the gel ⇒ the smaller the molecular size
lower
Molecular biology technique that characterizes proteins based on their MW or molecular size
SDS-PAGE
The main information you can derive from SDS-PAGE
number of individual/distinct proteins and their corresponding molecular size/weight
Two types of gel electrophoresis
Vertical system
Horizontal system
Basic parts of gel electrophoresis
Power supply
Chamber
Gel Wells
Buffer
Two electrodes (anode and cathode)
Positive anode? Negative anode? Position in SDS-PAGE?
Positive → anode → bottom; negative → cathode → top
Innate nature of protein charges?
They do not have a uniform charge
It's much ___ for proteins to pass through the pores because of its ___
harder, complex structure
Two factors in SDS-PAGE with proteins
Multiple subunits (in a quaternary structure, for example) can have different charges
In terms of structure, proteins are complex aggregates and folds into different conformations
How to achieve SDS-PAGE with proteins?
subject proteins to a chemical treatment before loading them onto polyacrylamide gel
Two chemicals applied to proteins prior to SDS-PAGE
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)
2-mercaptoethanol/β-mercaptoethanol
What does SDS do?
Detergent that will denature proteins, making them linear/cylindrical
SDS monomers are naturally negatively charged and wrap around the proteins
What does 2-mercaptoethanol do?
Disulfide linkages will be cut/cleaved to keep it linear
What does migration distance tell us?
How far the proteins migrated from their initial position (well of the gel) towards the anode
What happens with heavier/bigger proteins? (migration distance and migration rate)
harder for proteins to pass through the pores = shorter migration distance = slower migration rate
What is the migration rate?
how fast the molecules travel to the anode
How do we estimate the size of the protein?
Look at the protein marker/ladder
What is the measure of molecular weight/mass
Dalton
Dalton is equivalent to?
The mass of 1 hydrogen atom in g/mol
How do you contrast a protein marker from a DNA marker?
Bands of DNA markers do not have identities, just known sizes
What are the types of SDS-PAGE? Describe.
Continuous → one type of gel
Discontinuous → stacking gel on top, resolving/running gel below
12 components of SDS-PAGE
Buffer tank/chamber
Electrode assembly
Tank lid with power cables
Power supply
Casting stand
Casting frame
Gasket
Gel releasers
Sample loading guide
Spacer plates
Glass plates
Comb
“The Electric Lamp Provides Stable, Fixed Glow, Releasing Gentle, Soft, Golden Colors”
Ideal stacking gel concentration
4%
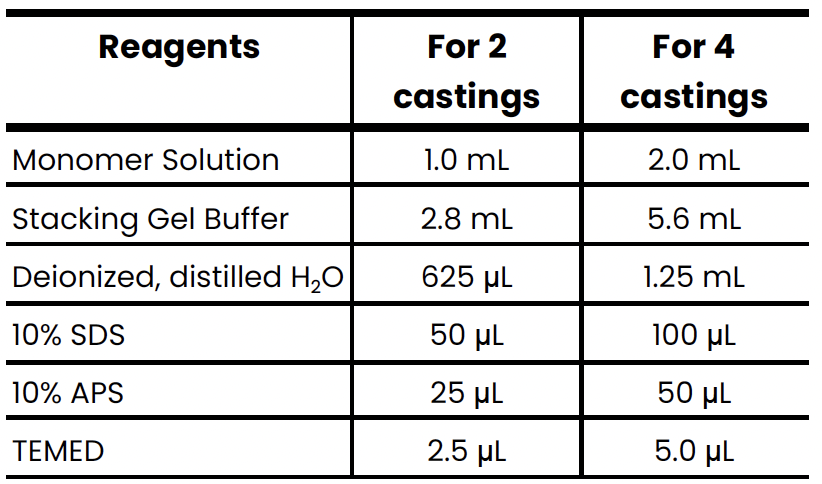
6 components of the stacking gel
Monomer solution
Stacking gel buffer
Deionized, distilled water
10% SDS
10% APS
TEMED
“Most Gel Buffers Drop 10% Smoothly Amid Turbulence”
What does the stacking gel do?
It’s the upper portion of a discontinuous polyacrylamide gel that concentrates or stacks the components of the sample to create a very thin starting zone or band
What is the ideal concentration of the resolving gel?
5-15%
Which of the two gels has a higher concentration/smaller pores?
Resolving/running gel has smaller pores and higher gel concentration
Monomer solution has two components:
Acrylamide
Bis-acrylamide
What is the percentage and ratio of the components of the monomer solution
30% acrylamide/bis-acrylamide solution, 29:1
What is acrylamide for?
a monomer used with a cross-linker to form the matrix used for separating proteins
What is bis-acrylamide for?
a common cross-linker used with acrylamide to form a support matrix
What is the concentration of the running gel buffer and what is it for?
(1.5 M Tris-HCI, pH 8.8)
provide an environment near physiological and maintain pH
What is the concentration of the stacking gel buffer and what is it for?
(0.5 M Tris-HCI, pH 6.8)
It is ideal to stack proteins by having a lesser concentration of this
What is constant weight ratio that SDS binds to polypeptides in?
1:4 (SDS:polypeptide)
What does APS stand for?
ammonium persulfate
What does TEMED stand for?
Tetramethylethylenediamine
Function of APS and TEMED
Radical initiators to catalyze the polymerization through cross-linking of acrylamide and bis-acrylamide in making a polyacrylamide gel
5 components of the sample/reducing treatment buffer
Deionized H2O
Tris-HCl pH (6.8–7.0)
10% SDS
β-mercaptoethanol
1% bromophenol blue
“Daring Tigers Stand Boldly and Bravely“
Function of deionized H2O
Primary vehicle/solvent
Function of Tric-HCl with pH 6.8—7.0
Maintaints optimum pH of the solution and prevents protein degradation
Function of SDS in sample buffer
Makes the net charge of the protein negative
Function of 2-mercaptoethanol in sample buffer
A reducing agent that cleaves disulfide bonds to achieve complete protein unfolding and to maintain proteins in a fully reduced state
Function of 1% bromophenol blue
To track the movement of proteins towards the positive electrode
Function of glycerol
Denser than water to keep samples from floating out of the well
Function of running (Tris/HCl/glycine/SDS) or tank buffer
Provides the ions for the electrical current in an electrophoresis runs
Function of Tris-HCl, glycine, SDS in running/tank buffer
SDS → denaturing agent
Glycine → provides the trailing ions so glycine in the stacking gel can stack or compress the proteins with the chloride ion
Tris-HCl → maintain optimum conditions
3 components of R-250 CBB
Methanol, Glacial Acetic Acid, and H2O
What is destaining the polyacrylamide gel for?
Removes excess stain for a higher resolution of the polyacrylamide image
What are the stacking gel components and their quantities?
___ the polyacrylamide gel removes excess stain for a higher resolution of the polyacrylamide image
De-staining
3 components in G-250 variant?
Methanol
Glacial Acetic Acid
H2O