module 8 - costs
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
total revenue
the amount a firm receives for sale of its output
total cost
the market value of all inputs a firm uses in production
profit
total revenue - total cost (goal is to max this)
opportunity costs
the cost of something is what you get up to get it.
firm’s cost of production includes all the opporunity costs of making its output of goods and services
explicit costs
input costs that require an outlay of money by the firm
implicit costs
do not require an outlay of money by the firm (ignored by accountants)
economic profit
total revenue - total cost (explicit and implicit costs)
smaller than accounting profit
accounting profit
total revenue - total explicit cost
production function
relationship between the quantity of inputs used o make a good and the quantity of output of that food
typically gets flatter as production rises
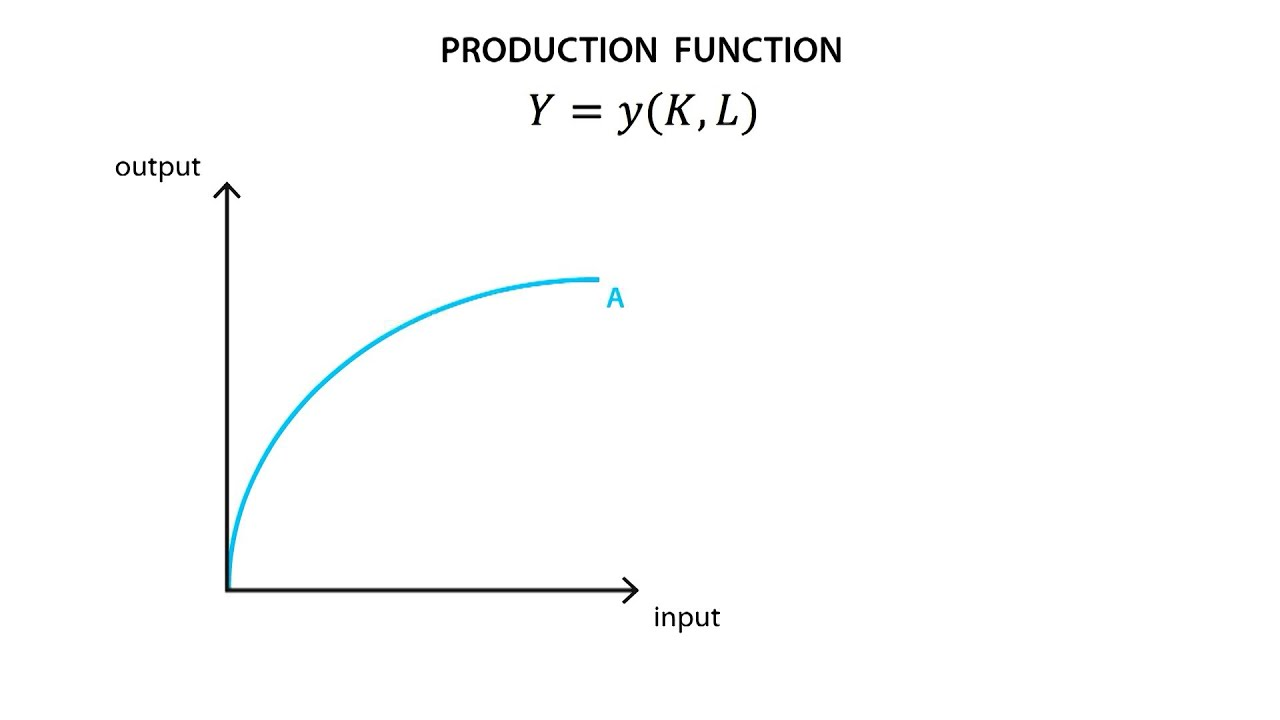
marginal product
the increase in output that arises from an additional unit of input
slope of production function
diminishing marginal product
property whereby the marginal product of an input declines as the quantity of the input increases
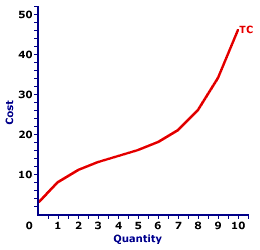
total cost curve
relationship between the quantity produced and the total costs
gets deeper as the amount produced rises due to diminishing marginal product
fixed costs (fc)
do not vary with the quantity of output produced
in short run
variable costs (vc)
vary with the quantity of output produced
applicable in the long run
average fixed cost
fixed cost/quantity of output
fc/quantity always declines as output rises
average variable cost
variable cost/quantity of output
typically increases as output increases
average total cost
total cost/quantity of output
also equals avc + afc
curve is typically U shaped
marginal cost
the increase in total cost arising from an extra unit of production
change in total cost/change in quantity
efficient scale
the quantity of output that minimizes average total cost (atc)
relationship between mc and atc
mc < atc, average total cost is falling
mc > atc, average total cost is rising
marginal cost crosses average total cost curve at minimum
long-run cost curves
differ from short run cost curves, because firms have greater flexibility in the long run (all costs are variable)
much flatter than short run cot curves and lie on or above the short-run cost curves

economies of scale
occur when long run average total cost falls as the quantity of output increases, often due to increasing specialization among workers
constant returns to scale
occur when long run average total cost stays the same as the quantity of output changes
diseconomies of scale
occur when long run average total cost rises as quantity of output increases, often due to increasing coordination problems