HC Ch 9: RCM: billing, coding, and collections
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what are the cash management fundamentals?
accounts receivable, accounts payable, collections, and patient billing
what are accounts receivable?
money owed to the organization for services provided
what are collections?
systematic approach to secure payments for services rendered
what are accounts payable?
financial obligations the organization owes to others
what is patient billing?
key process for ensuring timely service reimbursement
what is the billing and coding process?
patient care → documentation → coding → claim submission
what do each of the processes entail?
patient care: initial medical encounter and service delivery
documentation: recording diagnoses and procedures performed
coding: translating services into standardized codes
claim submission: sending billable information to payers
what is the patient care phase?
patient encounter: the medical office visit is the foundation of the billing process
information gathering: provider collects vital medical information from the patient
service delivery: medical care, treatments, and procedures are performed
care conclusion: medications, prescriptions, and referrals are provided as needed
what is medical records management?
EMR
EHR
what is the difference between EMR & EHR?
EMR: digital version of paper charts in a single practice, contains patients medical history, limited to one practice location, facilitates accurate coding
EHR: comprehensive patient records across providers, broader than EMR systems, accessible by multiple providers
What is the ICD-10 coding system?
it contains about 70,000 diagnosis codes, significantly more detailed than previous version
international classification of diseases: standardized coding system for diagnoses and medical conditions
diagnostic purpose: identifies the patients diagnosis or reason for medical consultation
evolving system: updates regularly as healthcare industry identifies new conditions
CPT coding system
maintained by the American medical association - CPT codes are essential for proper reimbursement
current procedural terminology: standard codes for medical services, procedures, and treatments
treatment identification: specifies procedures performed for diagnosed conditions
code matching: CPT and ICD codes must align in terms of medical necessity
HCPCS Coding system
Healthcare common procedure coding system: codes for supplies, equipment, and non physician services
transportation services: includes ambulance and medical transportation coding
medical supplies: covers durable medical equipment like wheelchairs and crutches
situational usage: not required for all patient visits or encounters
What are the billing code relationships?
ICD-10 - diagnosis
CPT - procedure
HCPCS - supplies
DRG - inpatient stay

what are DRGs?
diagnosis related groups - used by medicare and others to calculate inpatient reimbursement, patients are categorized into groups with similar resource utilization
resource calculation: assigns balue to providers inpatient resources
severity-based: higher acuity requires more resources
applied post discharge: finalized after hospital stay completion
what is the claims preparation process?
thorough preparation minimizes claim denials and accelerates payment
charge master reference: consult organizations established service list with prices
claims scrubbing: internal review to verify claim accuracy
clean claim creation: error-free claims ready for submission
claims submission process
capture all charges: record all medical visit activities and associated costs
final review: verify all medical billing codes for accuracy
submit to payer: send claim to insurance provider in required format
await response: monitor for acknowledgment of claim receipt
What is the EOB and Superbill?
explanation of benefits: insurance company’s response to a claim
summarizes diagnosis and treatment
lists charges for services
shows amounts covered by insurance
indicates patient responsibility
superbill: detailed service record for direct patient billing
lists of diagnoses and treatments
includes provider charges
details supplies and related costs
used when patients bill insurers directly
what does the accounts receivable management entail?
submit claims: initiate billing process for services rendered
monitor payments: track incoming revenues from all payers
manage denials: address rejected claims promptly
resubmit claims: correct and reprocess denied claims
what is claims adjudication?
the process by which insurers evaluate and make final payment decisions on claims - this process ensures claims meet payer requirements before payment
submission methods: electronically or manually
decision outcome: claims may be approved, partially approved, pending additional information, or denied
what is the adjudication process flow?
claims submission: provider sends complete claim to insurer
claims review: insurer evaluate claim against policy guidelines
determination: decision made on payment amount
payment processing: approved claims proceed to payment
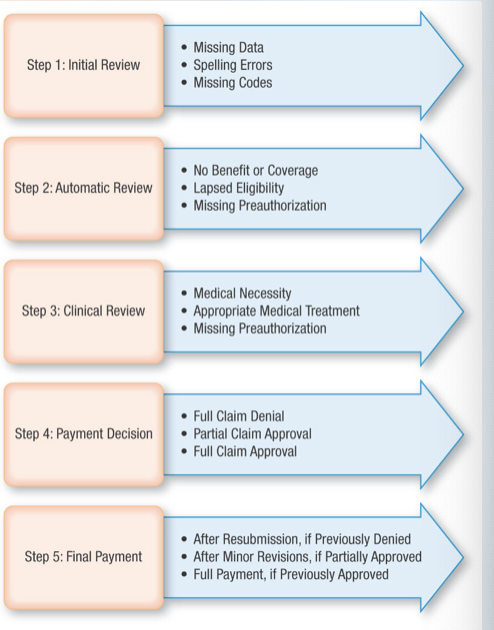
What are the adjudication review stages? (3)
initial review: check for data errors in patient, providers, diagnosis or treatment information
automatic review: verify patient policy coverage for claimed medical services
clinical review: examine medical necessity and preauthorization requirements
what are the adjudication outcomes?
full approval: claim meets all requirements and proceeds to payment
partial approval: some services approved while others denied
denial: payment refused after documentation review
pending: additional information needed before decision
how do you improve claims processing?
performance analysis: track key metrics for continuous improvement
denials management: document and streamline appeals processpatient access: improve registration and eligibility verification
technology upgrades: implement advanced billing and coding systems
what are the collections processing fundamentals?
documented collections process: establish clear procedures for payment collection and follow up
collections aging schedule: track accounts receivable by time intervals since billing
patient accounts receivable: measure average collection time for outstanding reimbursement
performance monitoring: regularly assess collection efficiency and identify improvement areas
what are the receivables management impact?
revenue support: patient services revenue directly funds organizational projects and initiatives
payer mix analysis: breakdown of payer types reveal revenue stream diversity
payer performance: historical data shows claim acceptance rates and payment timeliness