Greek Architecture
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Greek (800-300 B.C.)
▪ Delicacy of outline, perfected proportions and refined treatment.
▪ Based the different proportions of their construction systems on mathematical ratios.
▪ The first manifestation was a wooden structure of upright posts supporting beams and sloping rafters.
▪ Completed with sophisticated optical corrections for perspective.
▪ Major public buildings were built with limestone and marble. Blocks of stone were held in place by bronze or iron pins set into molten lead.
AEGEAN PERIOD
▪ Structures were generally rough and massive.
▪ The capital is ornamented with a square abacus, and a circular bulbous echinus.
▪ Cyclopean walls: large stones without mortar, on clay bedding.
▪ Use of corbelled arch.
▪ Megaron: single-storey dwelling with a central room and porticoed entrance; columns support roof; thalamus (bedroom)
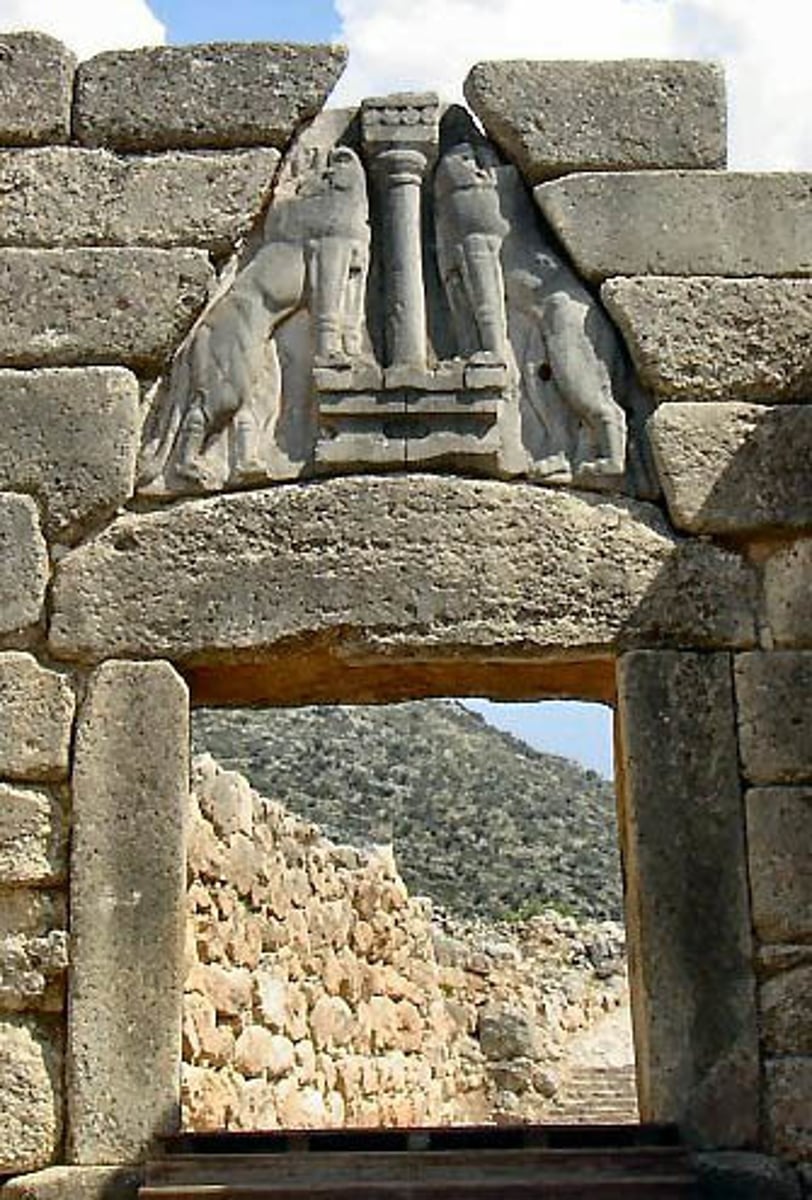
The Lion's Gate
Mycenae, Greece.
Mycenae, Greece.
Part of the citadel palace of Agamemnon; Cyclopean walls of boulders weighing 5-6 tons were eased into alignment with pebbles

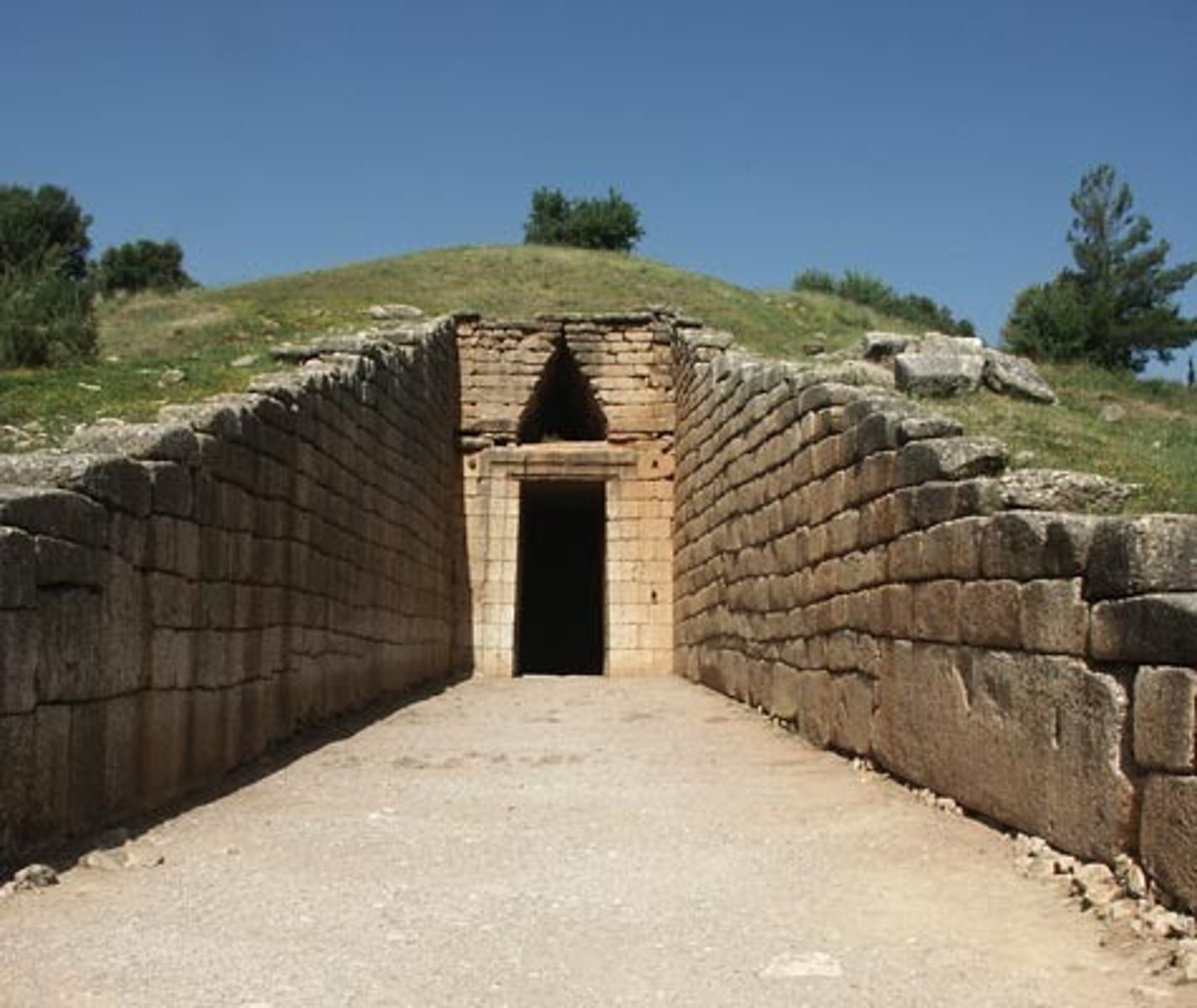
Treasury of Atreus
Beginning in the late Bronze Age, the kings were buried outside the city in great beehive—or tholos—tombs, monumental symbols of wealth and power.

HELLENIC PERIOD
▪ Of or pertaining to ancient Greek history, culture and art.
▪ The temple became the chief building type.
▪ Columnar and trabeated; Carpentry in marble
▪ Materials used were timber, stone, and terra cotta.
▪ Refinements to correct optical illusion (entasis, swelling of columns)
▪ Structures were ornamented with sculptures, colors, and mural paintings.
HELLENISTIC PERIOD
▪ Greek culture was modified by foreign elements.
▪ A diversion from religious building types; civic structures were also built; later will be an inspiration for Roman architecture.
▪ The design and layout of buildings are symmetrical and orderly.
▪ Moldings were used for decorations.
▪ Temple entrances faced east.
Greek Temples
The chief building type of the Hellenic Period.
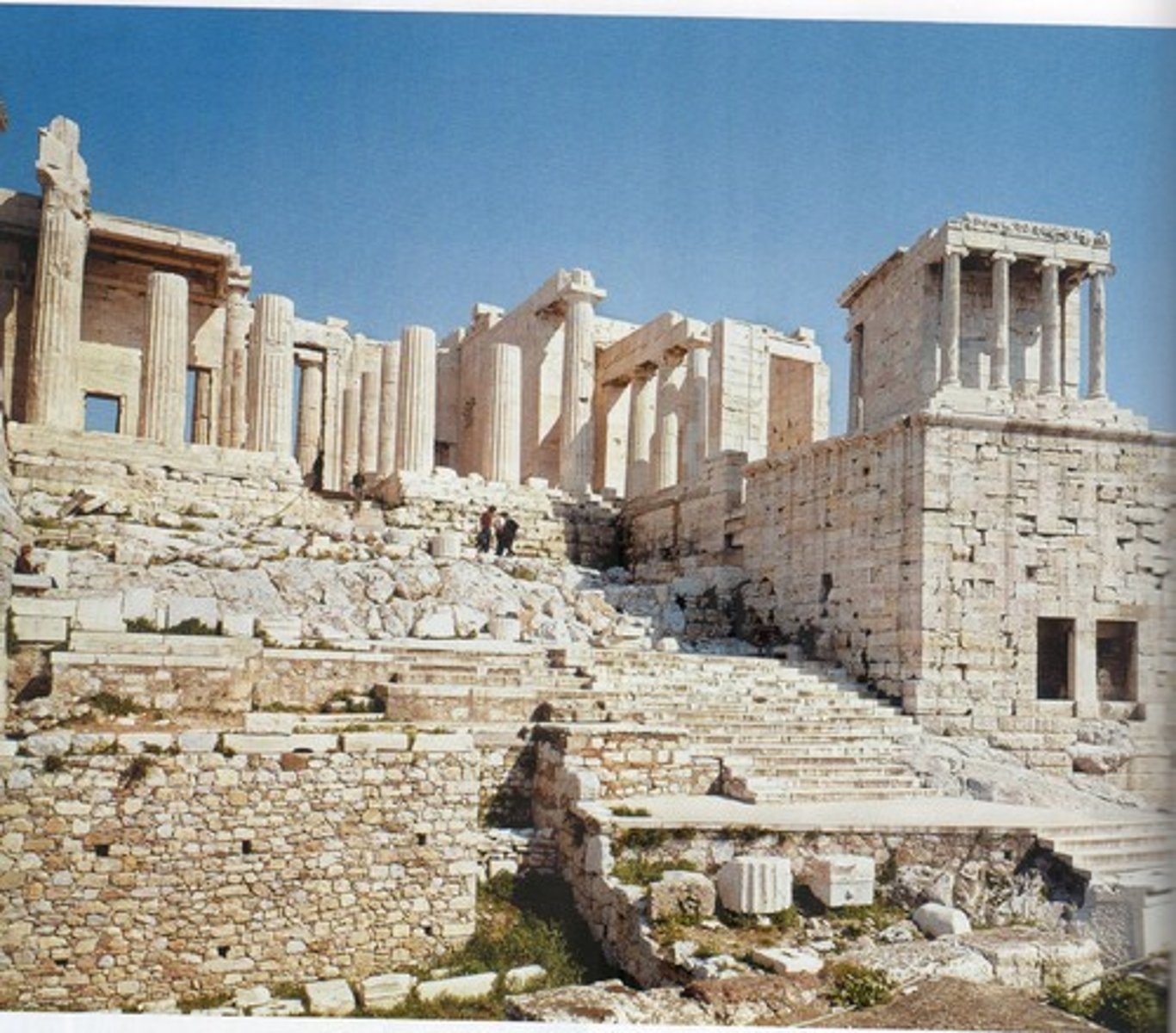
Acropolis
"City on the height." In classical Greek architecture, a city stronghold or fortress constructed on higher ground than surrounding urban fabric.
Temenos
The sacred area or enclosure surrounding a classical Greek temple
Propylaea
A monumental gateway to a sacred enclosure, fortification, town or square

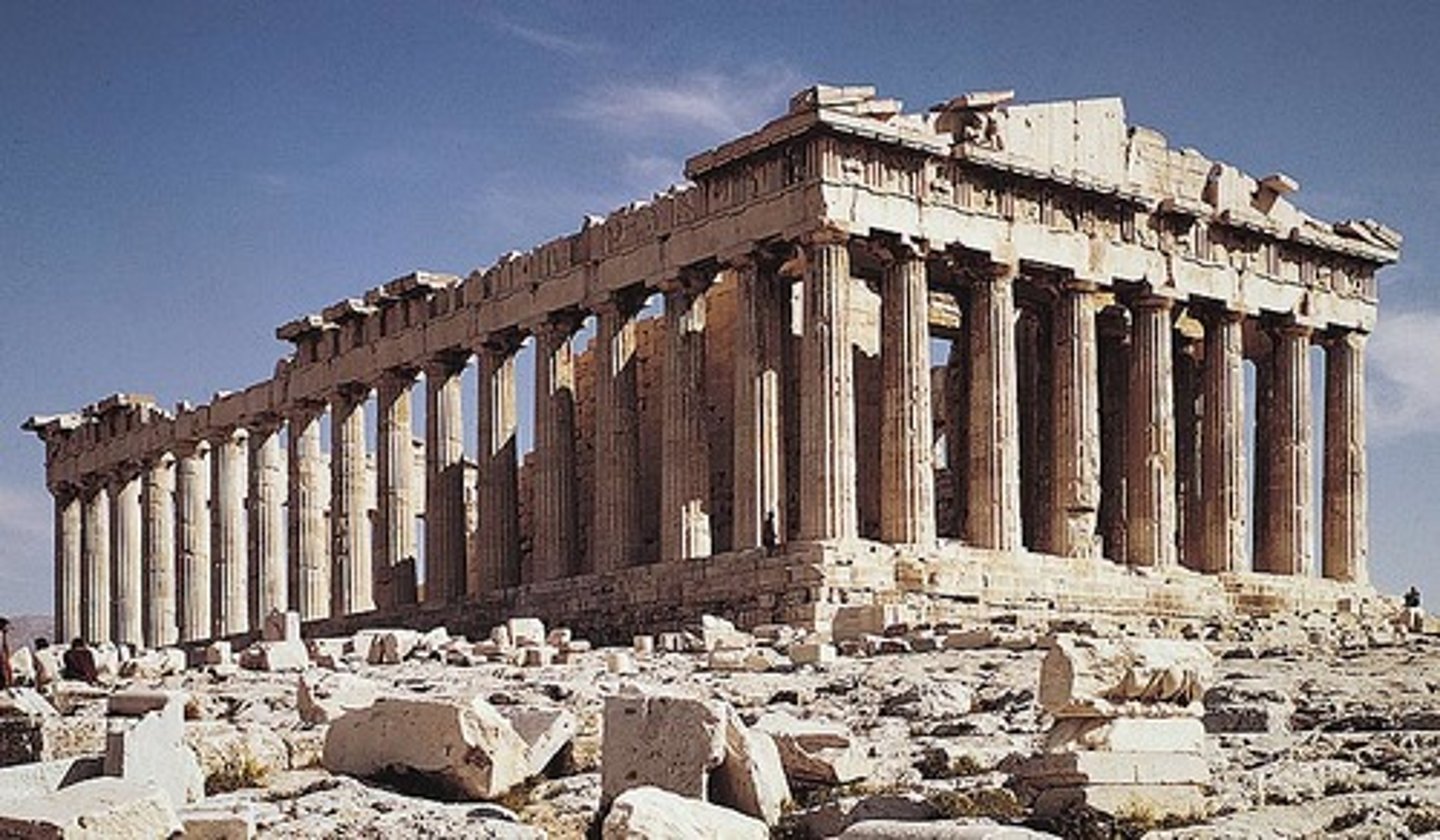
Parthenon
the temple honoring the goddess Athena, built on the acropolis above Athens,Greece. Ictinus and Callicrates.
Built from 447-438 B.C. in honor of Athena, the city's patron goddess. Used the proportion 2n+1 in determining the number of columns on the sides of a temple (n=number of columns at front)

Naos or cella
, principal chamber; enclosed part of the temple where the cult image was kept.
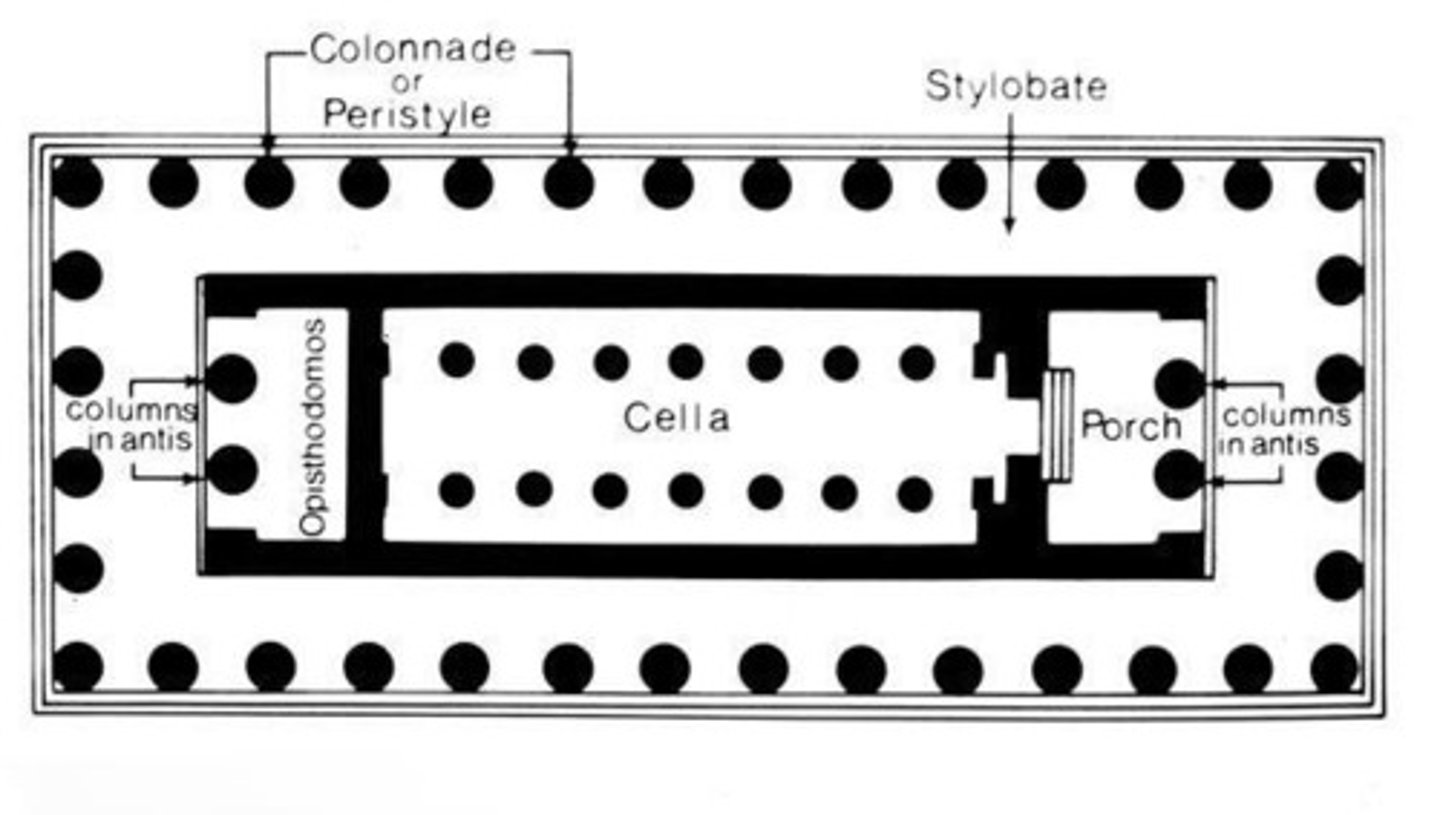
Pronaos or anticum
, an open vestibule before the cella.
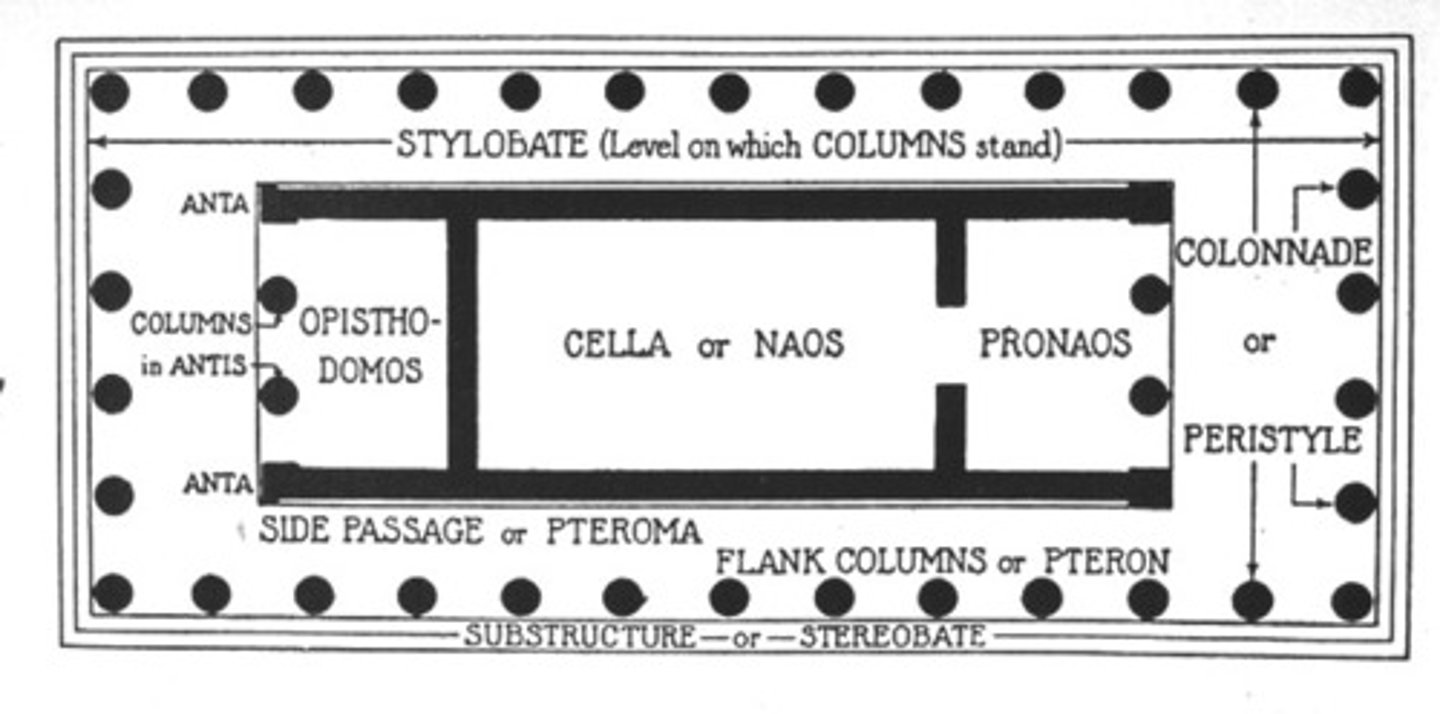
Epinaos or posticum
, rear vestibule.
Opisthodomos
, a small room in the cella as for a treasury
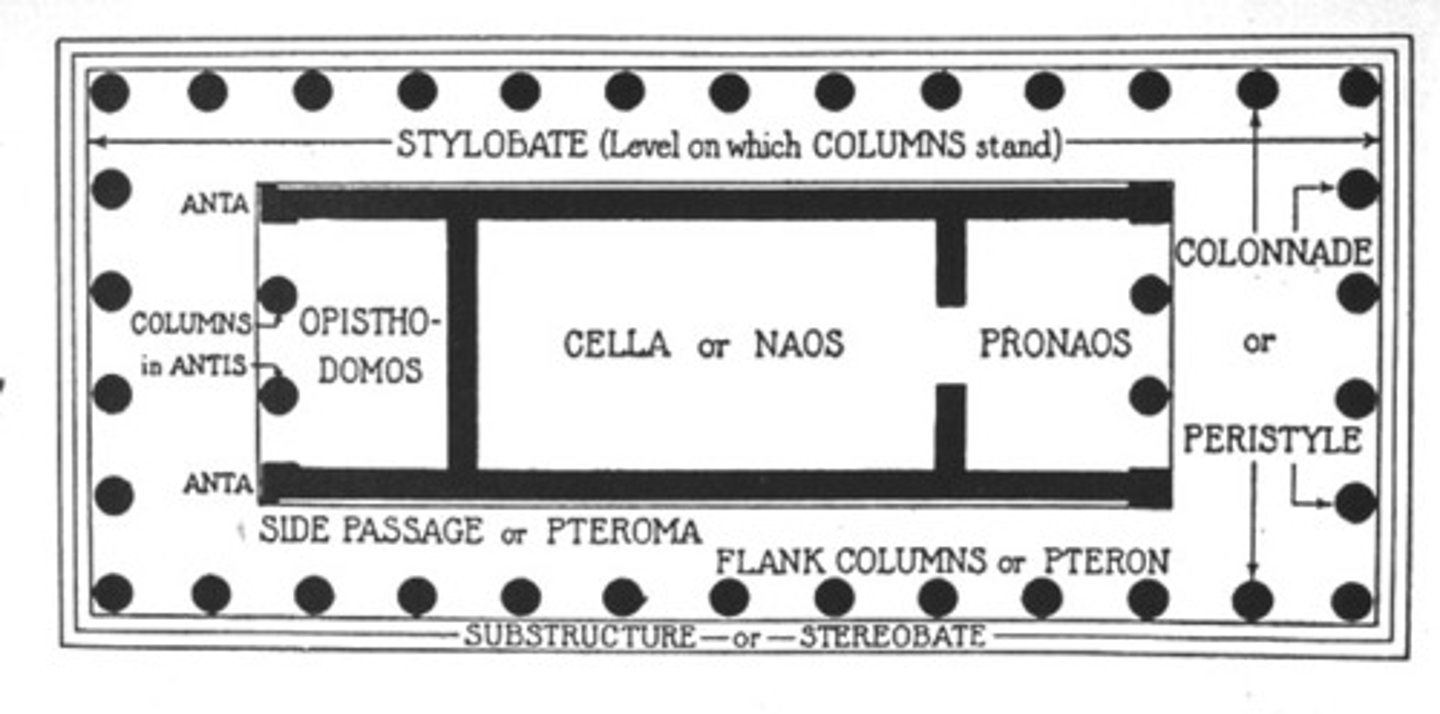
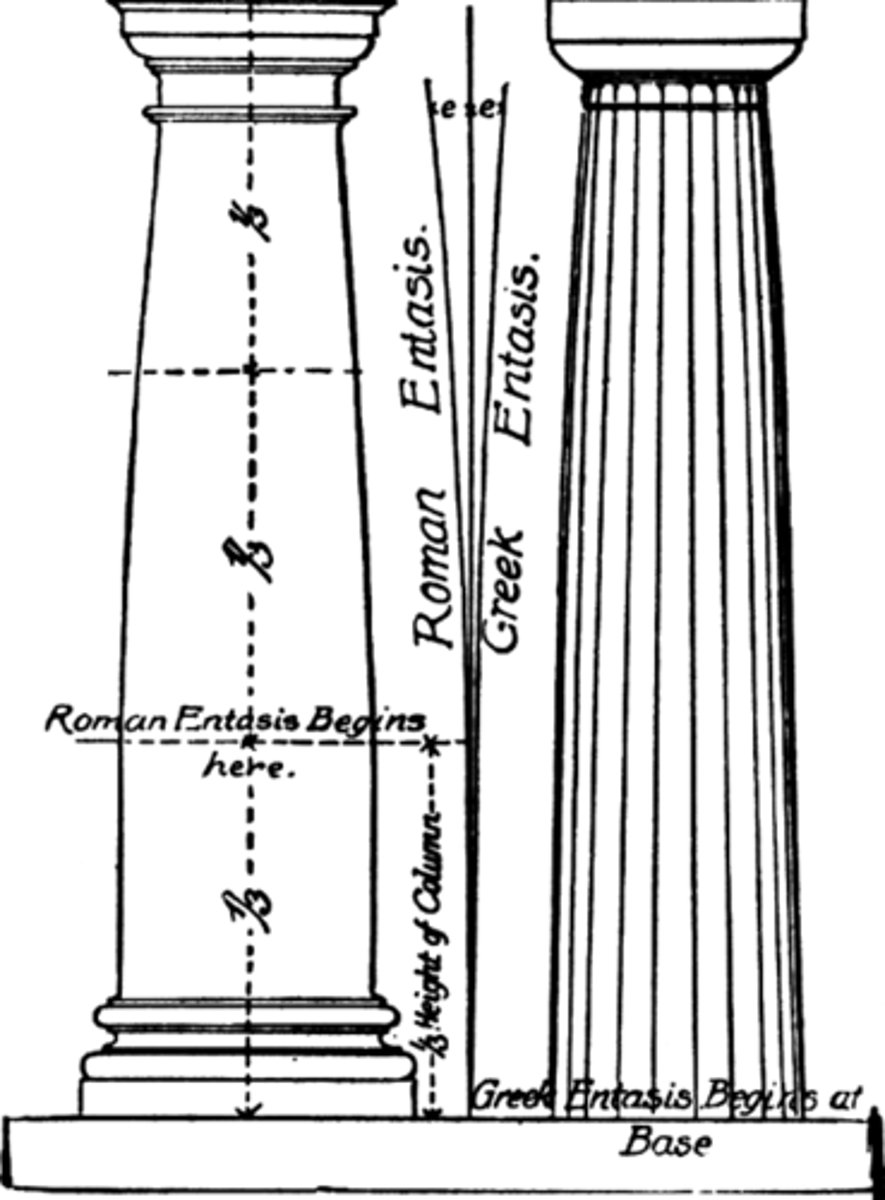
Entasis
, a slight convex curve in the shaft of a column;
▪ the stylobate curves upward;
▪ the columns taper toward the top;
▪ the columns at the corners angle inwards and are thicker than the others;
▪ and the column flutes deepen toward the top
▪ 1.50D Pycnostyle
▪ 2.00D Systyle
▪ 2.25D Eustyle
▪ 3.00D Diastyle
▪ 4.00D Araeostyle
The systematic spacing of columns expressed as multiples of column diameters
DORIC
Oldest, simplest and most massive of the three Greek orders.
▪ Developed in Greece in the 7th century B.C
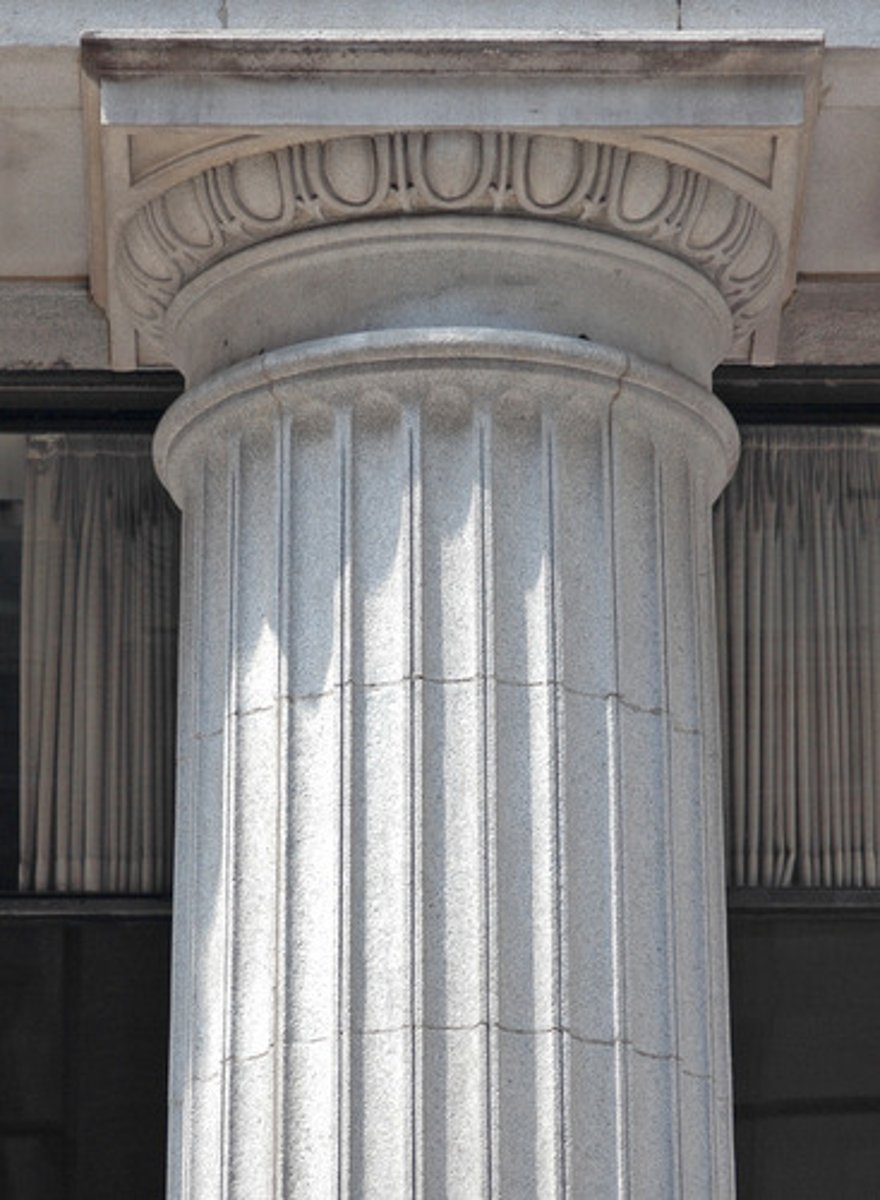

IONIC
Developed in the ___________Islands (now western Turkey) in the 6th century B.C. ▪ Used for smaller buildings and interiors.
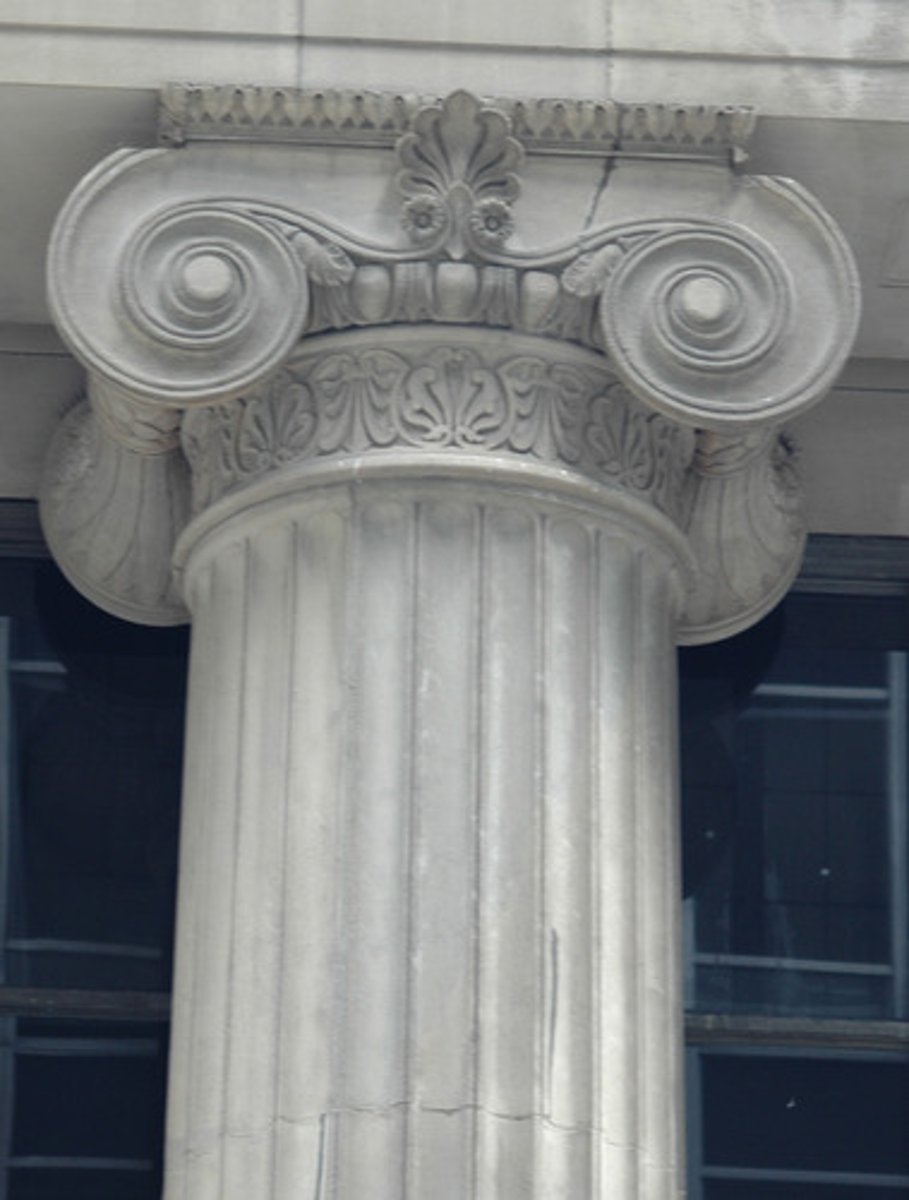

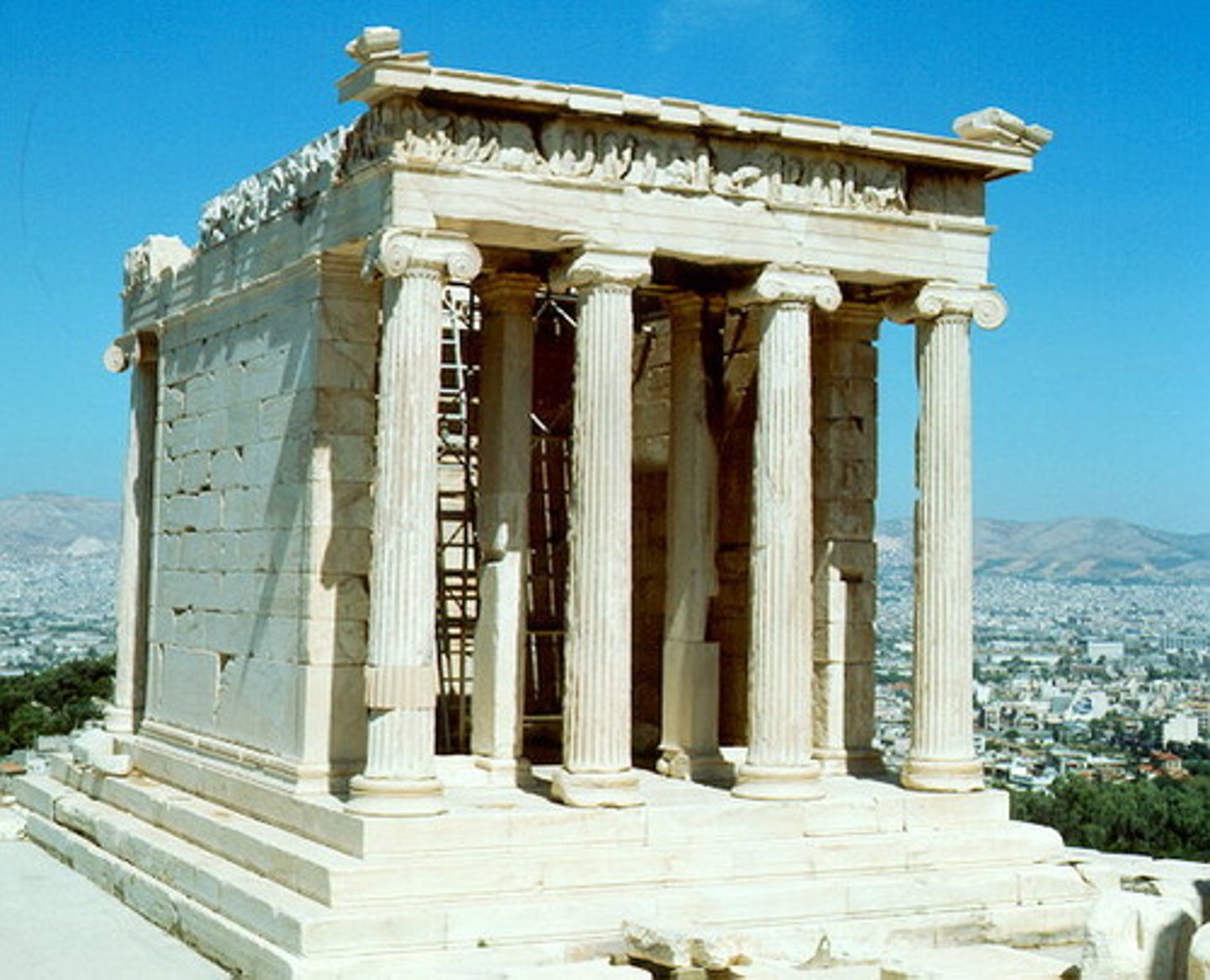
Temple of Athena Nike
Athens, Greece. Callicrates.
Ionic temple that Greets visitors to the sanctuary. Celebrates Athena as bringer of victory against the Persians at marathon. The young ____Image is repeated dozens of times. 427-424 BCE

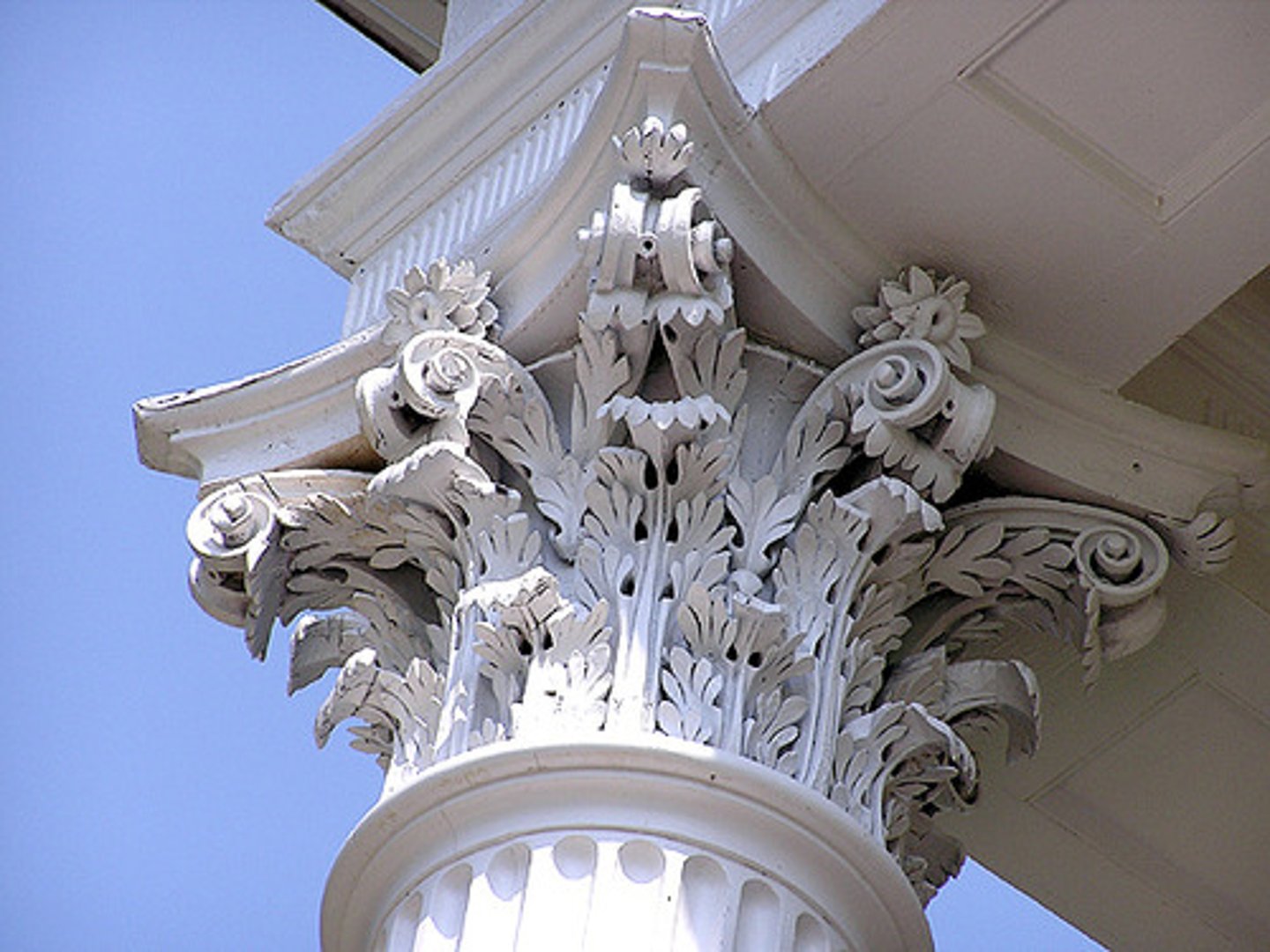
CORINTHIAN
Named after the city of _____________, where sculptor Callimachus supposedly invented it after he spotted boblet surrounded by leaves.
▪ Similar to the Ionic order in its base, column, and entablature, but its capital is more ornate, carved with two tiers of curly acanthus leaves

Temple of Apollo Epicurius
The Corinthian order used for the first time; Built of fine-grained, brittle grey limestone; details in marble, roof of thin marble slabs.
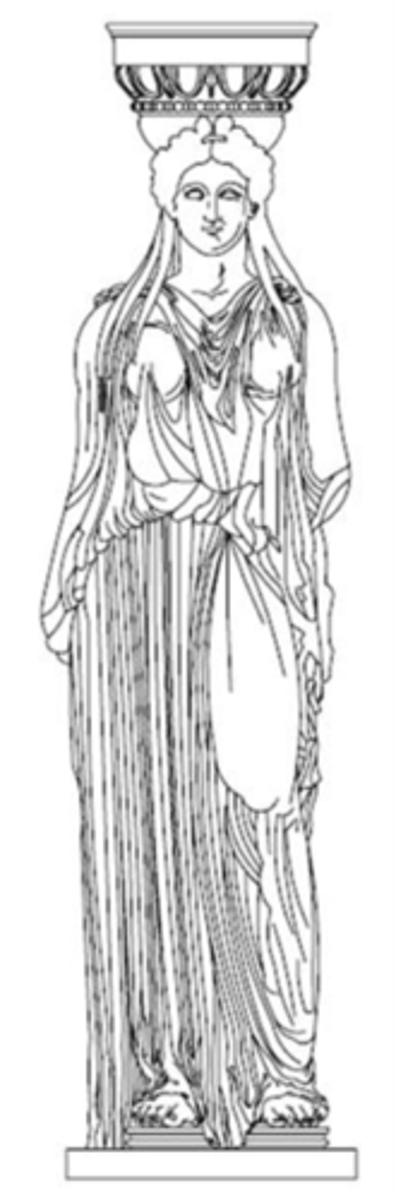
Caryatid
a female figure that functions as a supporting column
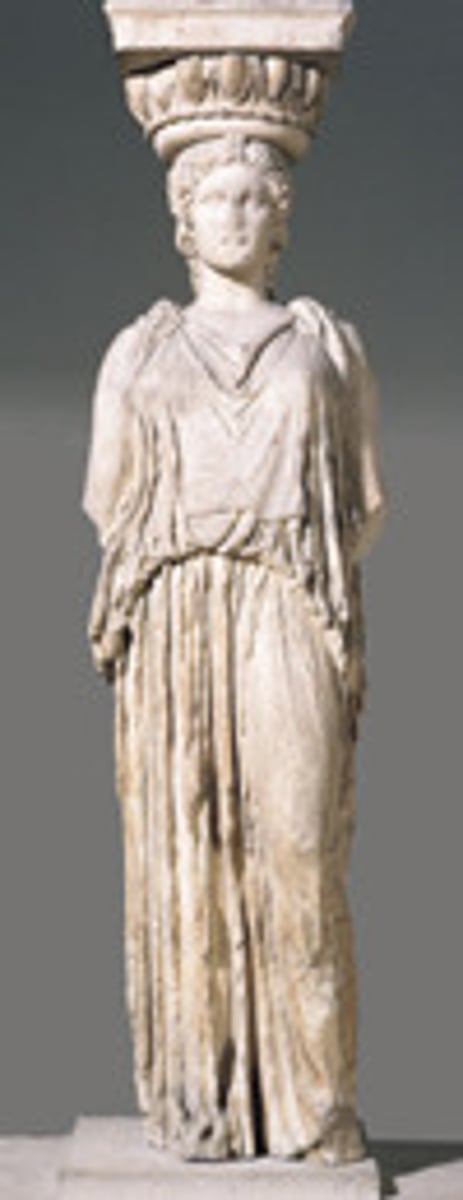

Canephora
Female statues with baskets serving as columns.
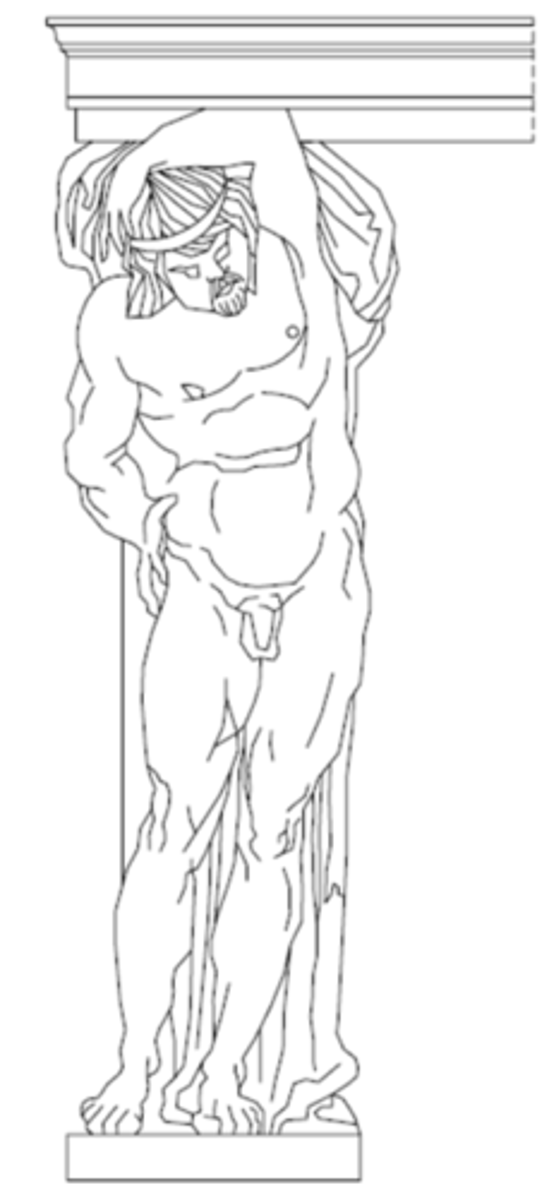
Atlas, telamon
A sculptured figure of a man used as a column.
Herm, herma
a squared tapered column capped with the carve head, bust or torso of a figure, usually Hermes; originally used by the Greeks as a boundary marker, later as decoration
Erechtheion
Mnesikles. Caryatid - Porch of Maidens. A temple to Athena and Poseidon. The layout was very odd because it was built around a saltwater spring and an olive tree that were already there. It is Ionic. This is said to be where Athena and Posiden had their great battle over being the patron god of the Acropolis.
AGORA
a marketplace in ancient Greece, commonly used as a meeting place
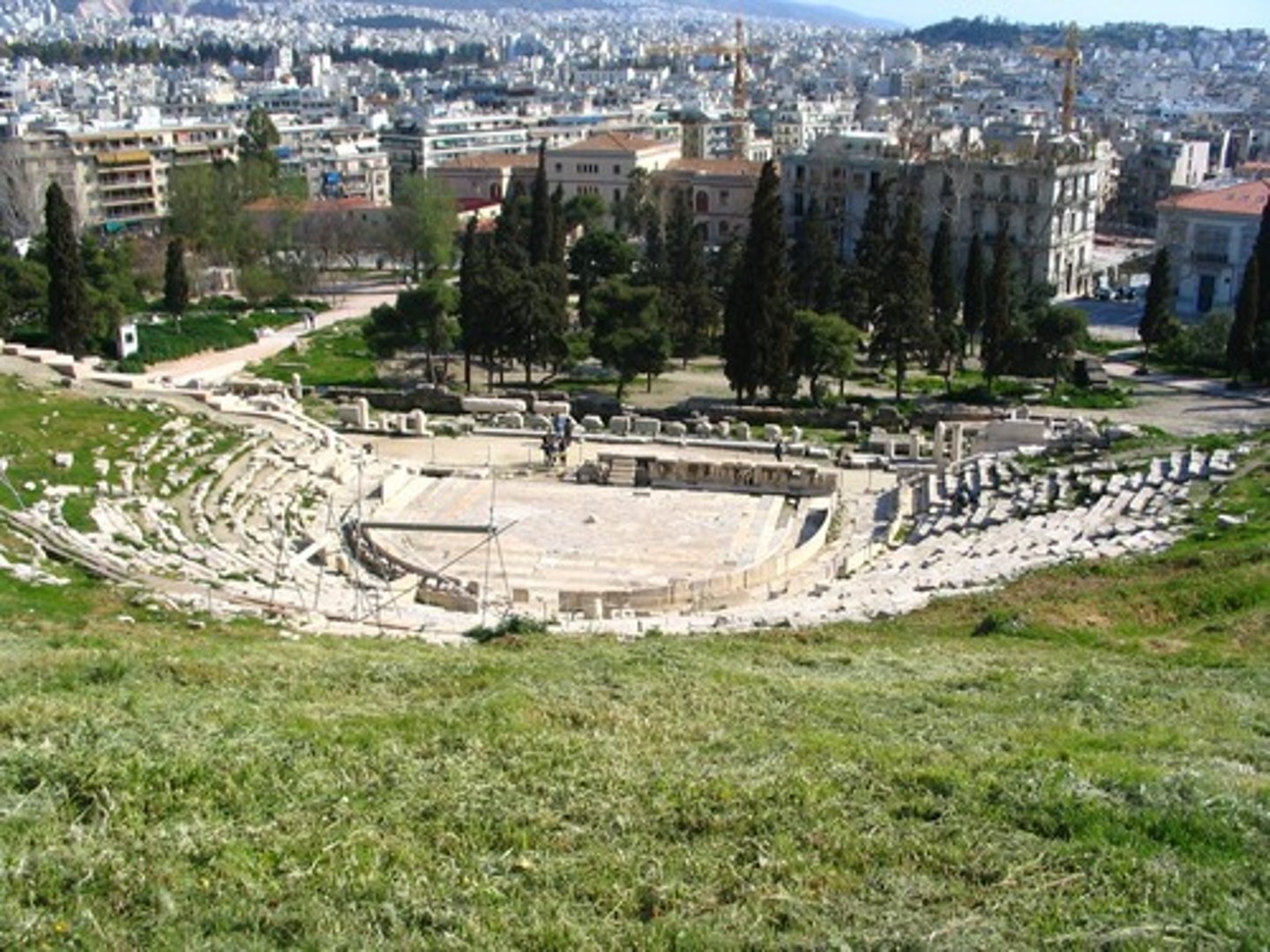
THEATRON
Open-air,
Designed for the presentation of plays in which choral songs and dances were prominent features
"Seeing place" where the audience sat

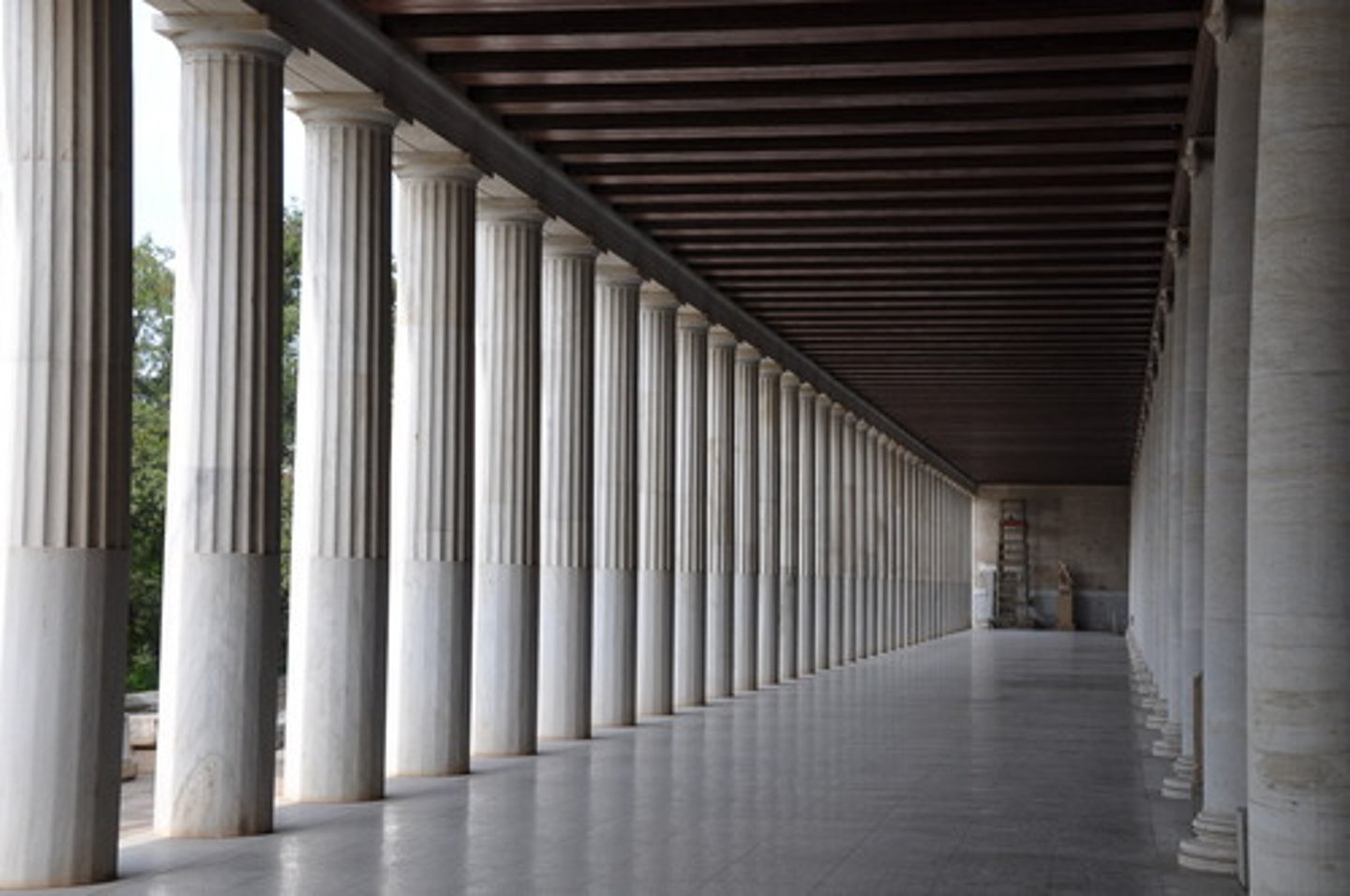
STOA
An ancient Greek portico, usually detached and of considerable length, used as a promenade or meeting place around public places

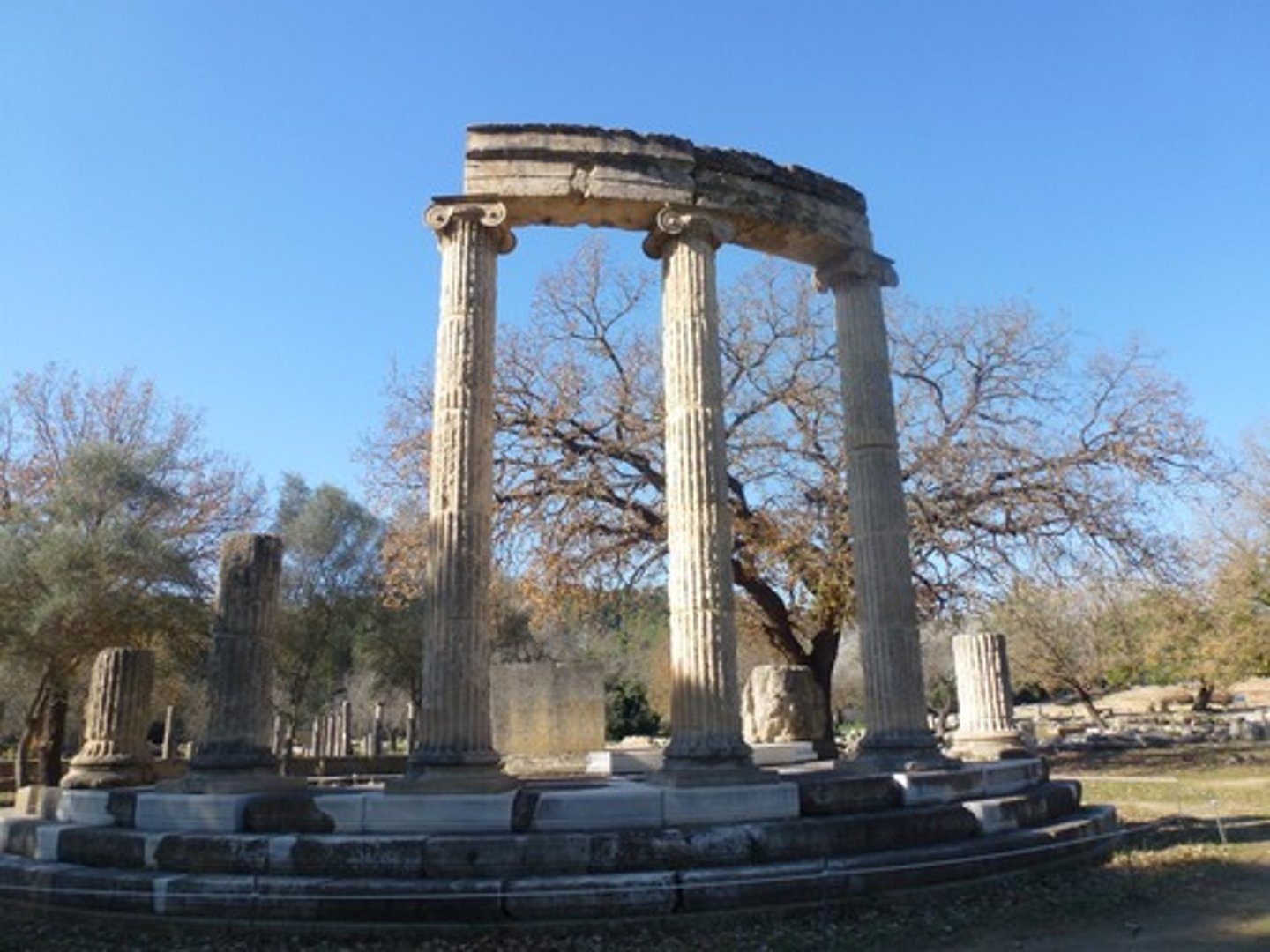
PRYTANEION
__of Panticapaeum. Ukraine.
Senate house; A public town hall for the citizens of ancient Greece, containing state banquet halls and hospitality suites.

BOULEUTERION
. Priene.
Council chamber with rows of stepped benches surrounding a central platform
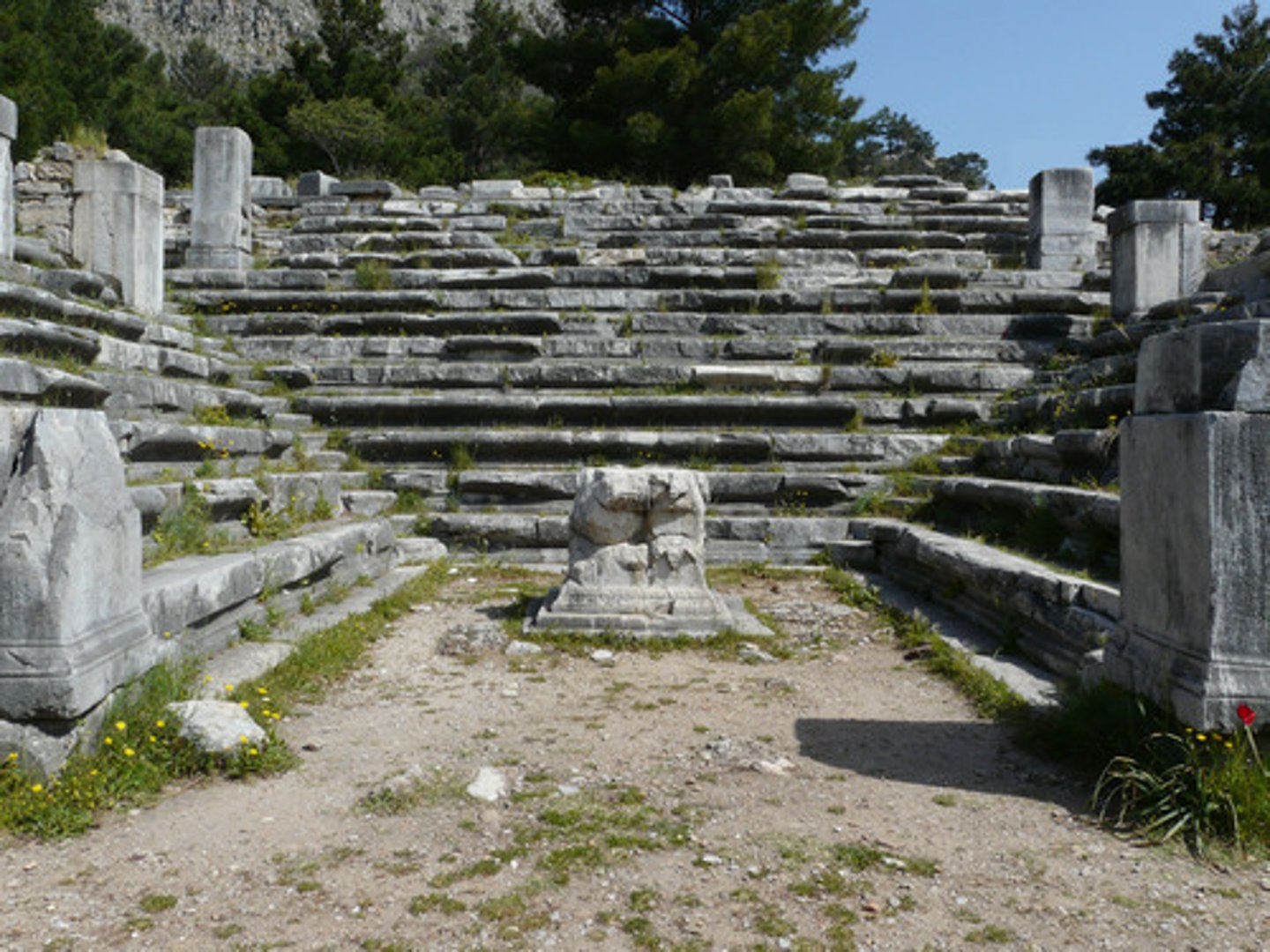

ODEION
Ephesus _______. Turkey. A roofed theatre building in antiquity, especially one for the performance of vocal and instrumental music

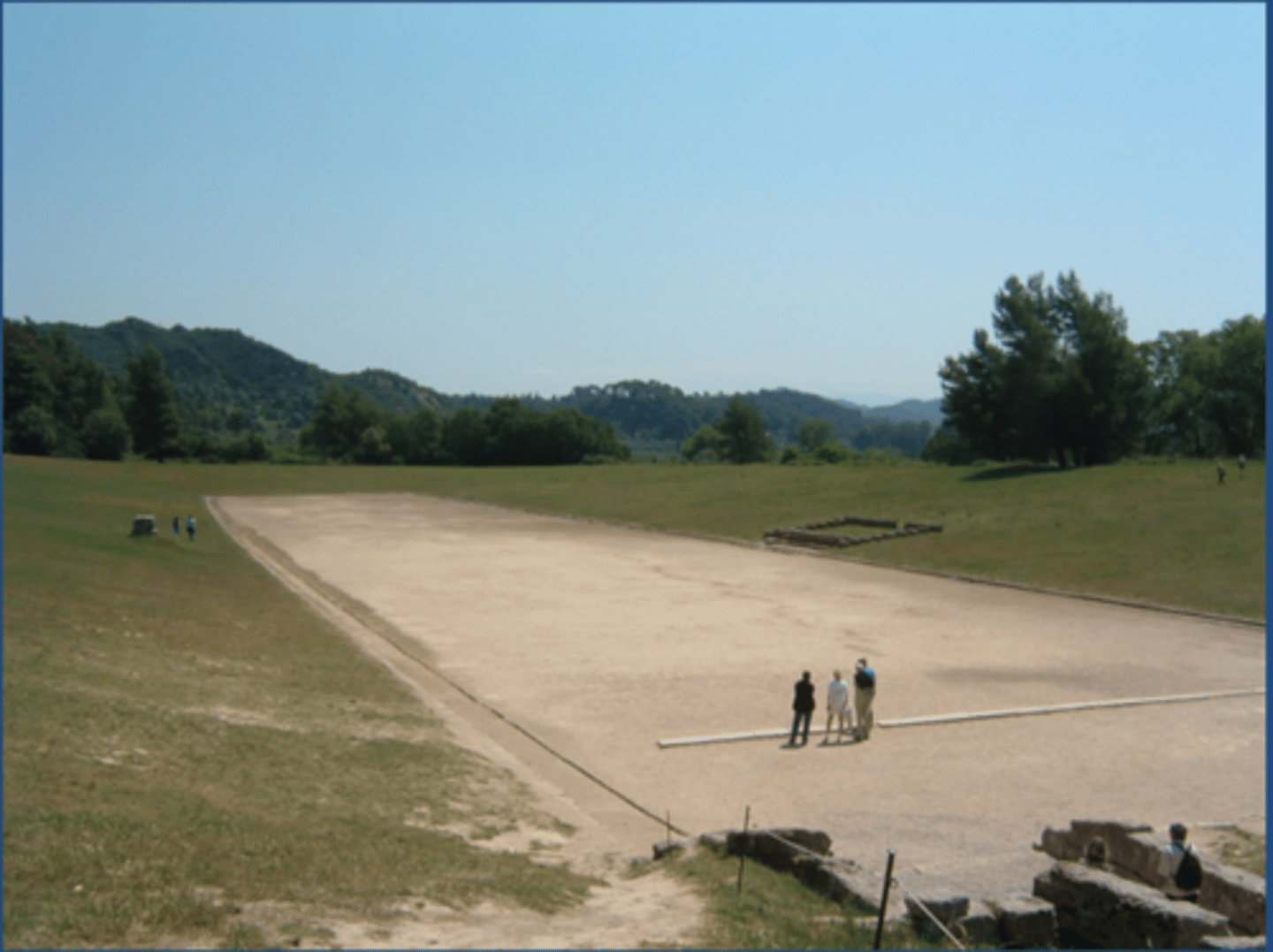
STADION
An ancient Greek elongated sports venue with rounded ends, surrounded on all sides by banked spectator stands; venue for foot racing

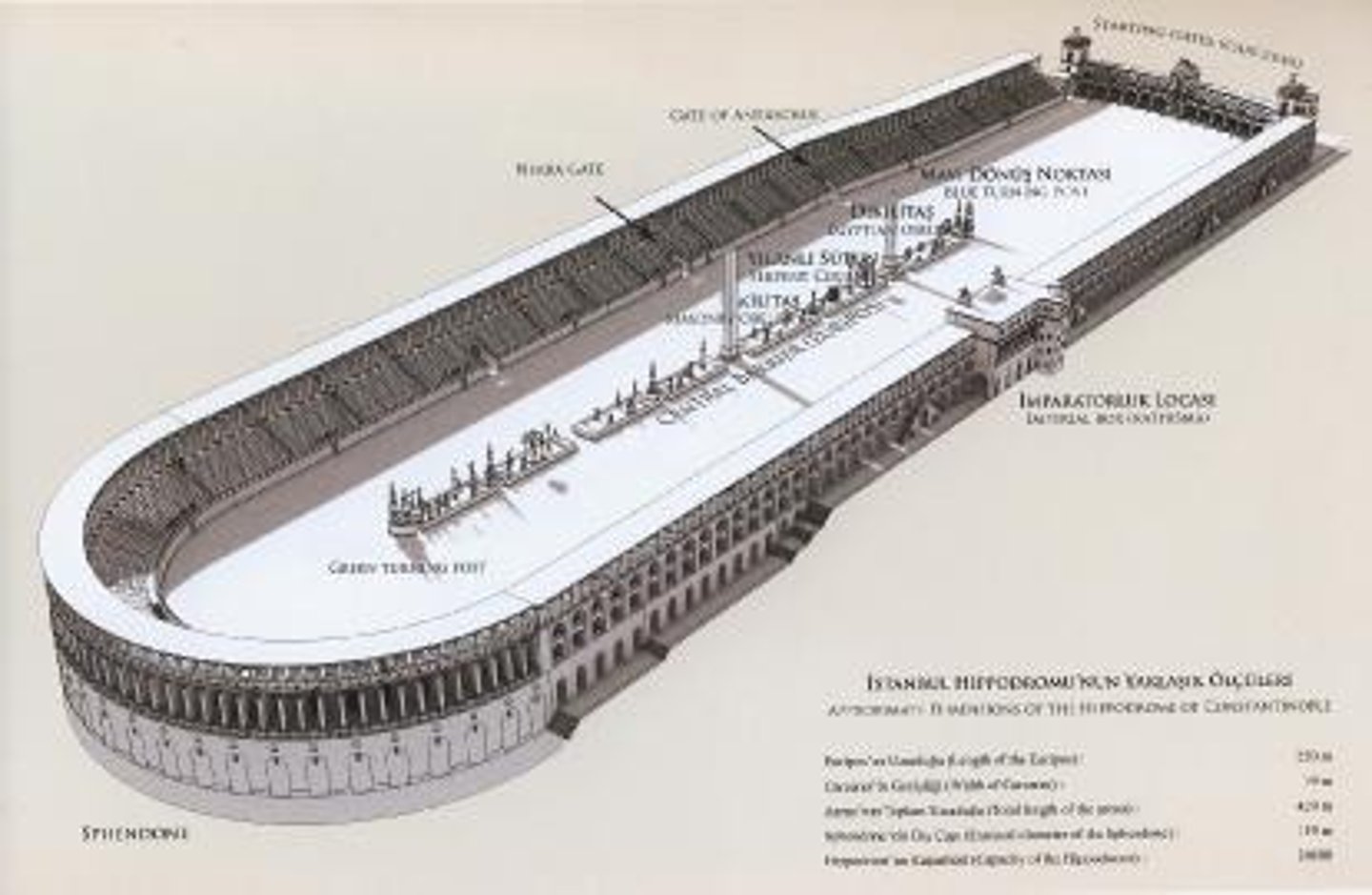
HIPPODROME
An open or roofed track or arena for chariot and horse racing in ancient Greece.
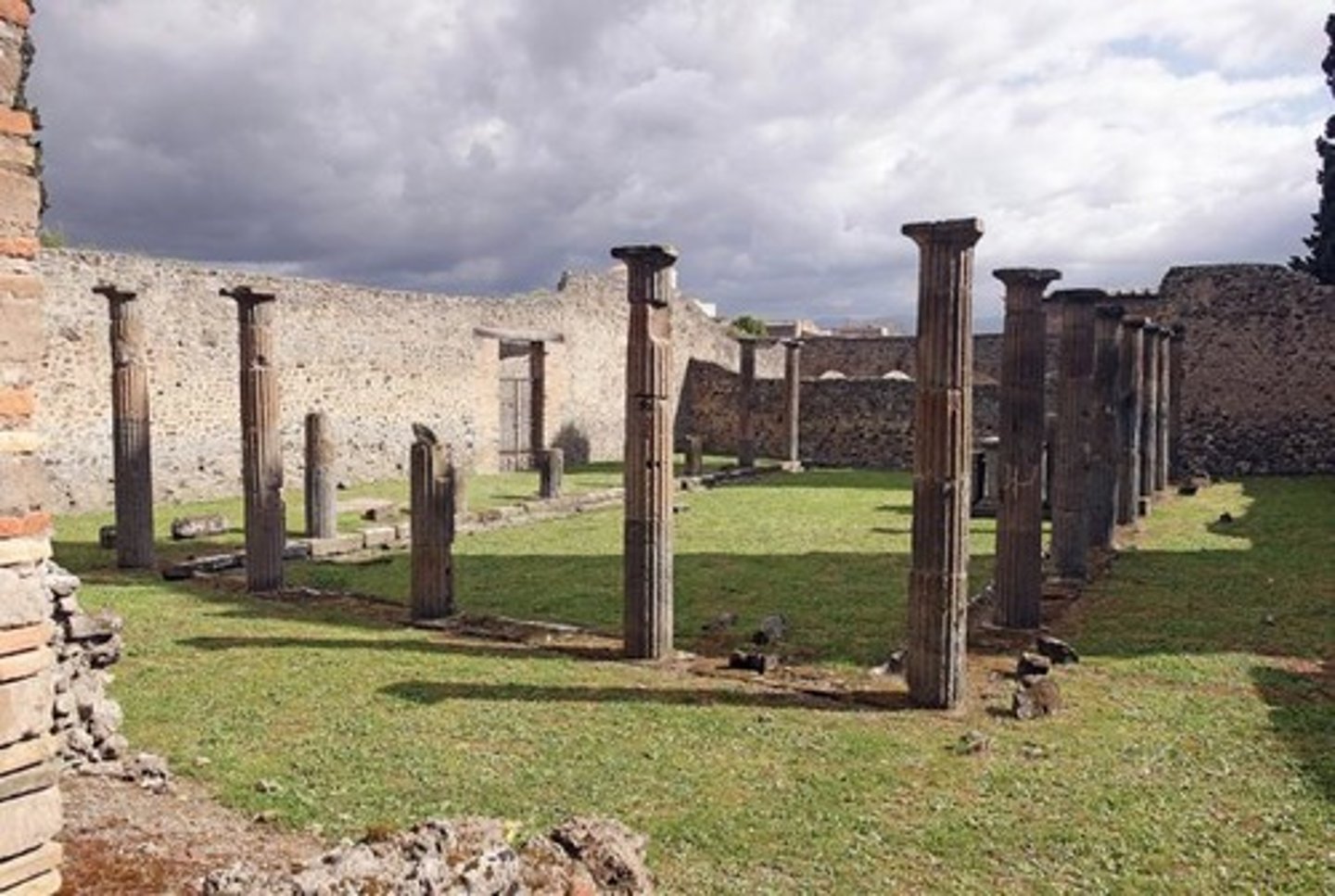
PALAESTRA
Wrestling house; A place used for the instruction and practice of wrestling and athletics

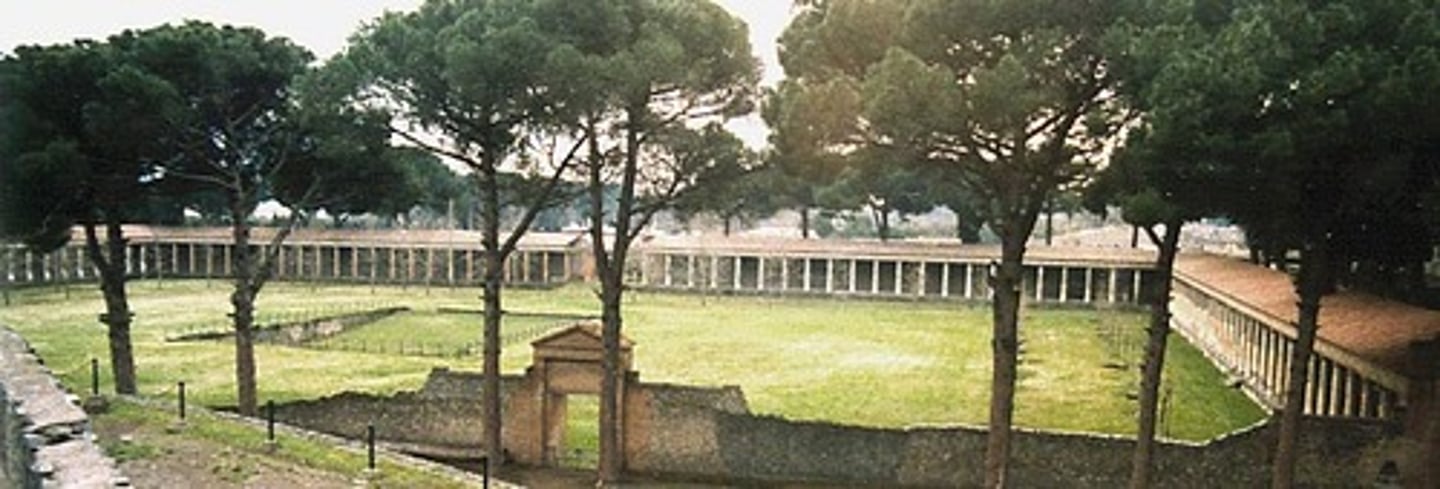
GYMNASION
An ancient Greek centre for sports, with buildings, playing areas and baths

Megaron
The large reception hall and throne room in a Mycenaean palace, fronted by an open, two-columned porch.
Parts consists of an open porch, a vestibule, and a large hall with a central hearth and a throne
Prostas
a greek dwelling type entered from the street via a passage to an open courtyard around which all spaces are arranged; the principal rooms are accessed via a niche-like anteroom.
Pastas
A dwelling-type from the classical period of northern Greece, 423-348 BC, with a courtyard in the centre of the south side and deep columned veranda or affording access to rooms
Peristyle
A Greek dwelling-type whose open courtyard is surrounded by colonnades on all sides, often more luxurious than a prostas or pastas house
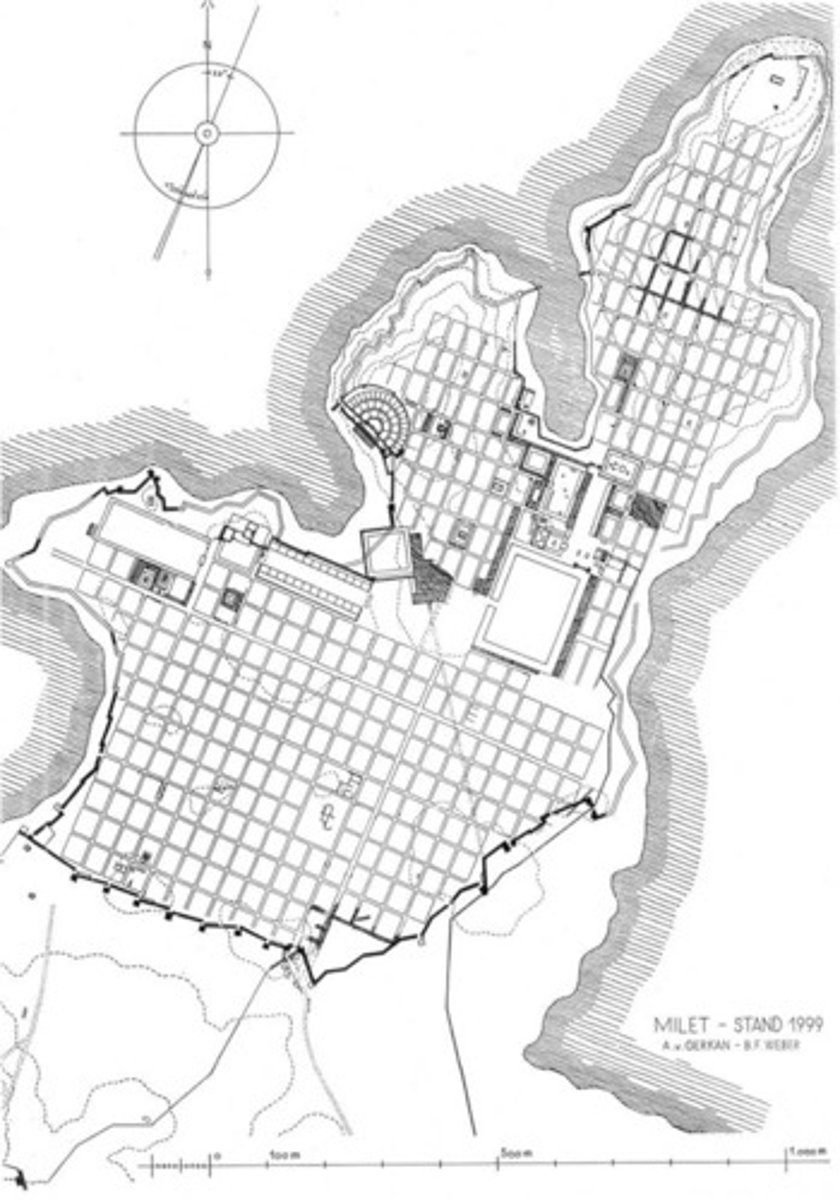
Hippodamian Grid System
A rectilinear town layout in which blocks of dwellings are divided up by narrow side streets linked together by wider main roads, developed by the Ionian Hippodamus of Miletus in the 5th century BC.