Hemolytic Disorders
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is anasarca?
Severe, generalized edema
What are transudates?
Low protein fluid (<3 g/dL), specific gravity <1.012, due to pressure imbalance
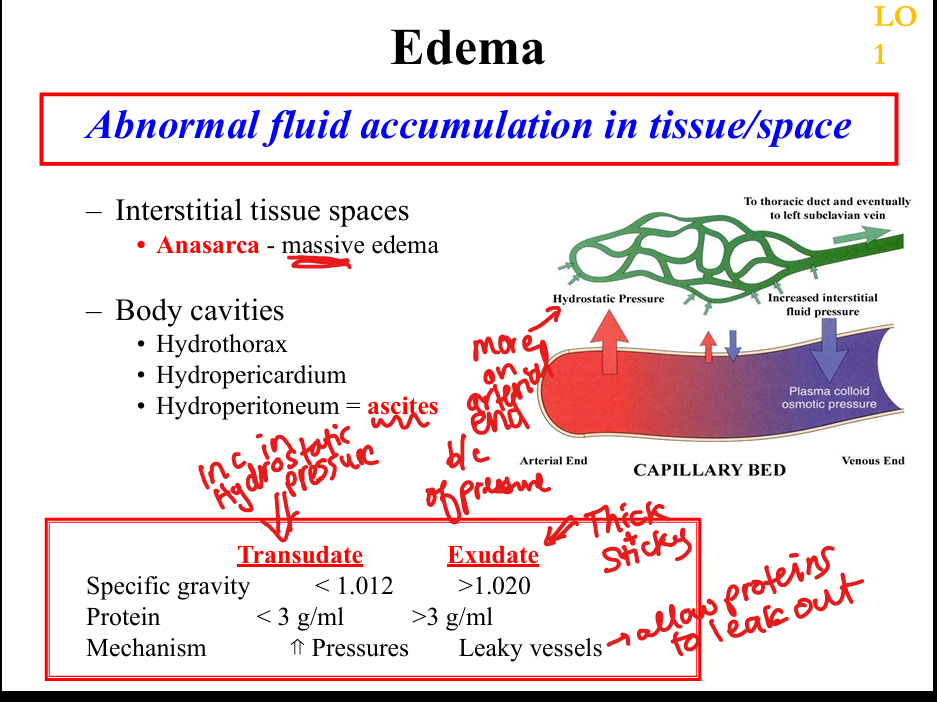
What are exudates?
High protein fluid (>3 g/dL), specific gravity >1.020, due to leaky vessels
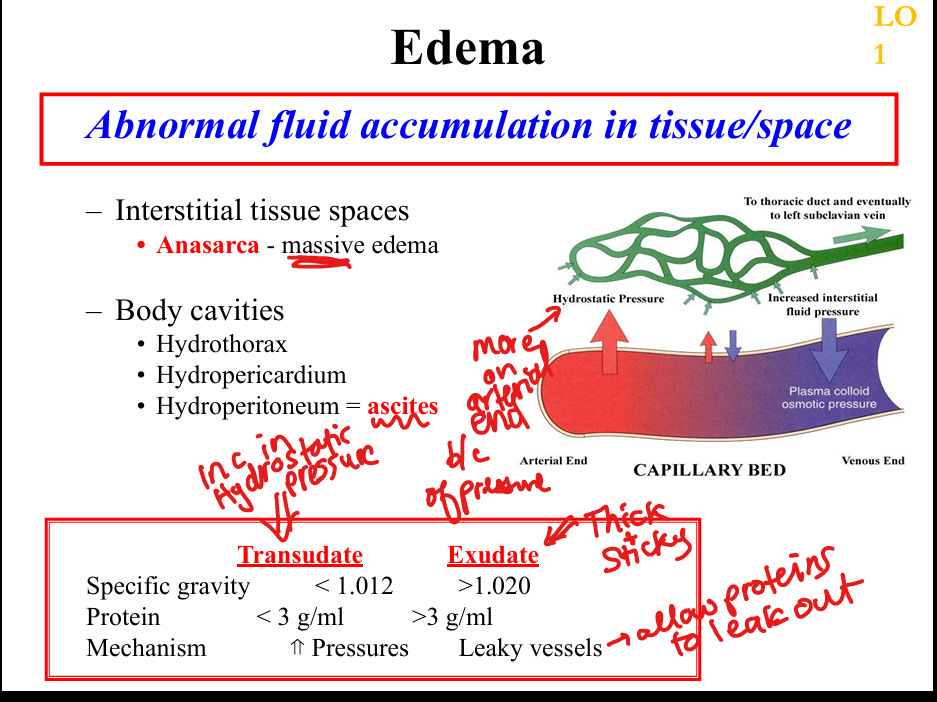
What causes increased hydrostatic pressure?
Congestive heart failure, venous obstruction, portal hypertension
What causes decreased plasma oncotic pressure?
Cirrhosis, nephrotic syndrome, protein malnutrition
What causes lymphatic obstruction?
Inflammation, neoplasia, filariasis, post-surgical damage
What causes chronic pulmonary congestion?
Left heart failure → blood backs up into lungs
What causes chronic hepatic congestion?
Right heart failure → blood backs up into liver ("nutmeg liver")
What is petechiae?
Tiny (1–2 mm) hemorrhages due to platelet defects or capillary fragility ; smallest
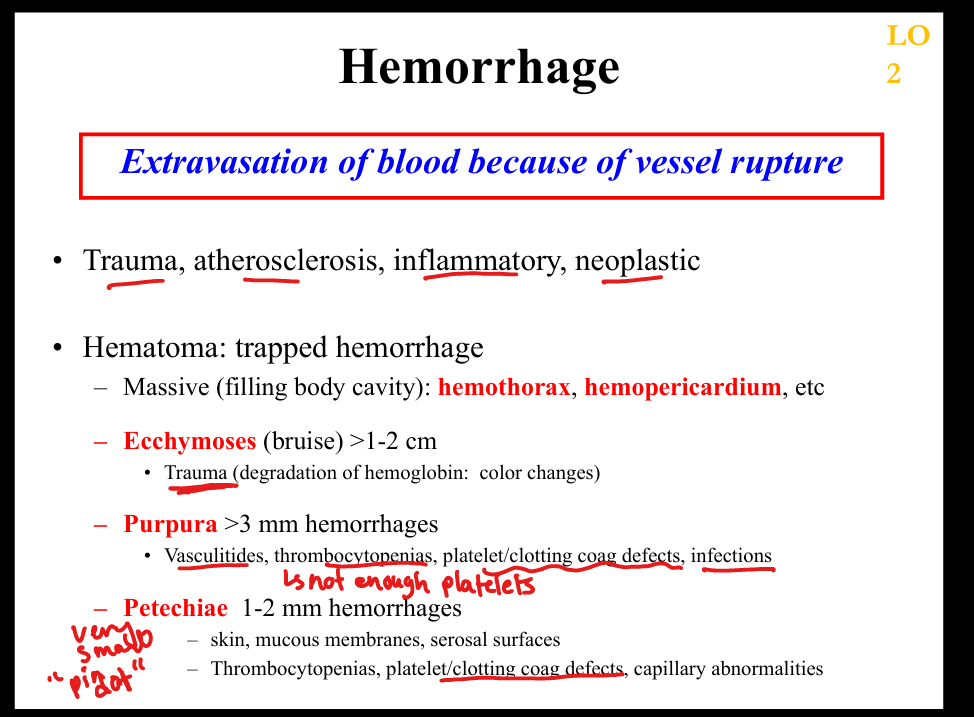
What is purpura?
3–10 mm hemorrhages due to vasculitis or thrombocytopenia
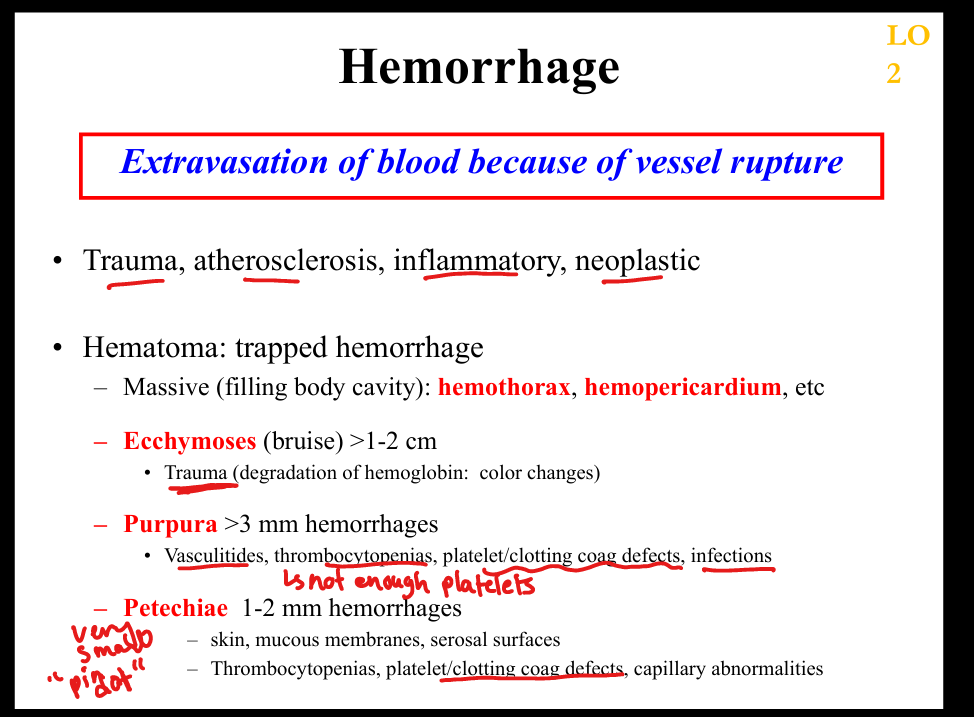
What is ecchymosis?
1–2 cm bruise due to trauma; largest
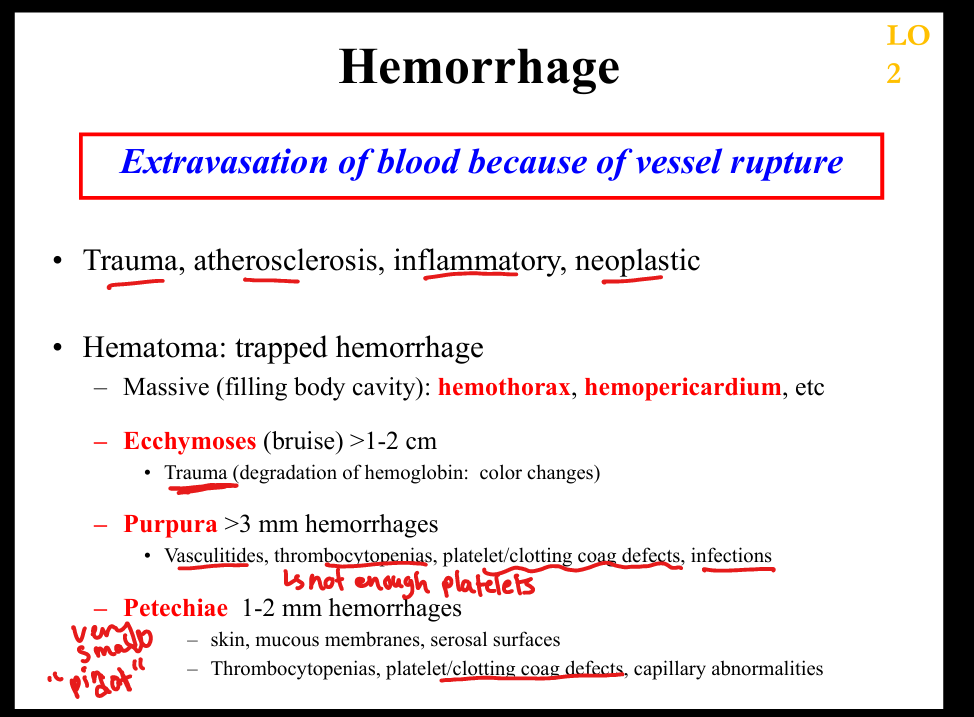
What are the stages of bruise color change?
Hemoglobin → bilirubin → hemosiderin (purple → green → brown)
What initiates platelet adhesion?
vWF binding to GpIb receptor
What causes platelet aggregation?
Fibrinogen binding to GpIIb/IIIa receptor
What activates the extrinsic pathway?
Tissue factor(III) to (Factor VII)
What activates the intrinsic pathway?
Contact activation (Factor XII)
What does antithrombin III inhibit?
Thrombin, Factor Xa, IXa, XIa, XIIa
What activates protein C + S?
Thrombomodulin + thrombin
What does plasmin do?
Breaks down fibrin clots into FDPs
What activates plasmin?
tPA, uPA, streptokinase
What is Virchow’s triad?
Endothelial injury, abnormal blood flow, hypercoagulability
What are Lines of Zahn?
Alternating layers of platelets and RBCs in thrombi (seen in arterial thrombi)
What are red infarcts?
Venous occlusion, dual blood supply organs (lung, intestine), reperfusion
What are white infarcts?
Arterial occlusion in solid organs (heart, kidney, spleen)