Lecture 8a: Plate Tectonics, Geologic Principles & Geologic Time
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from Lecture 8a.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Plate tectonics
Theory that Earth's lithosphere is divided into rigid plates that move on the asthenosphere due to mantle convection; explains earthquakes, volcanoes, mountain building, and sea-floor spreading.
Continental drift
Wegener’s hypothesis that continents move relative to one another; evidence includes coastlines fit, fossil matches, and mountain belts; mechanism was not identified at the time.
Mid-ocean ridges
Undersea mountain ranges where new oceanic crust forms as magma rises and cools, fueling sea-floor spreading.
Sea-floor spreading
Process by which new oceanic crust forms at mid-ocean ridges and pushes older crust outward, driving plate motion.
Magnetic polarity reversals
Periodic flips in Earth’s magnetic field direction recorded in rocks, used to track plate movements and sea-floor spreading.
Paleomagnetism
Study of the ancient magnetic properties of rocks to infer past pole positions and plate motions.
Magnetic inclination
Angle between a rock’s magnetization and the horizontal, reflecting the latitude of formation and preserving the field orientation.
Geomagnetics
Science dealing with Earth’s magnetic field and its history, including reversals and rock magnetization.
Magnetite
Iron-oxide mineral that records the Earth's magnetic field as rocks cool and lock in magnetization.
Index fossils
Widely distributed, short‑lived fossils used to identify and correlate the ages of rock layers.
Mesosaurus
Permian reptile whose fossils are found in Africa and South America, supporting continental connection.
Glossopteris
Fossil fern found across southern continents, evidence for a former supercontinent (Gondwana).
Pangaea
Hypothetical supercontinent that included most or all of Earth's landmasses before their breakup.
Tethys Sea
Ancient ocean between Gondwana and Laurasia, later closed by plate tectonics.
Uniformitarianism
Principle that present processes shape the past; natural laws operate today as they did in the past.
Relative dating
Ordering of events or rocks by age relative to each other (not in exact years).
Original horizontality
Sedimentary layers are deposited horizontally; tilting or folding indicates later deformation.
Lateral continuity
Sedimentary layers extend laterally until they thin or terminate; gaps reflect erosion or nondeposition.
Law of superposition
In a sequence of undisturbed sedimentary rocks, oldest layers are at the bottom, youngest at the top.
Cross-cutting relationships
A rock feature that cuts across another is younger than the feature it cuts.
Inclusions
Fragments of older rocks included within a newer rock; inclusions are older than the host rock.
Faunal succession
Successive rock layers are characterized by their fossil content, allowing age correlations.
Unconformities
Surfaces that represent gaps in the geological record due to erosion or non-deposition.
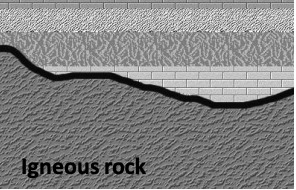
Non-conformity
Sedimentary rocks overlie eroded igneous or metamorphic rocks, indicating a major erosion/deposition gap.
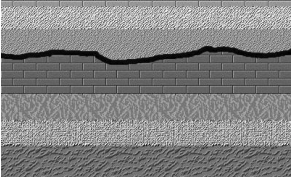
Disconformity
Unconformity where the contact between sedimentary layers is parallel, indicating a time gap in deposition.